Last Updated on November 20, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir
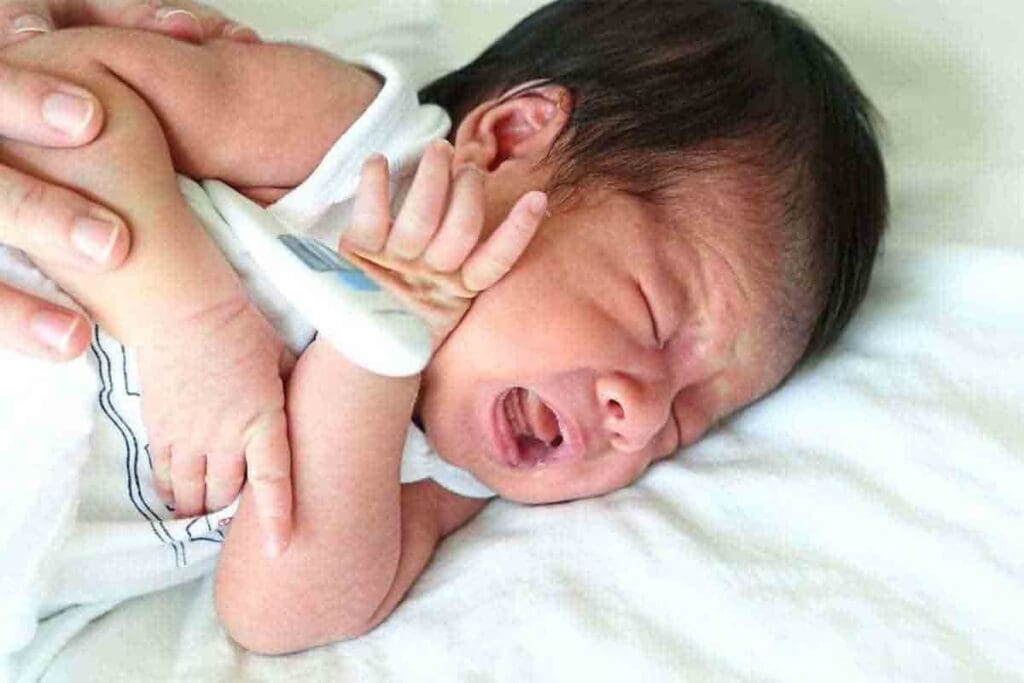
Infantile leukemia is a rare but aggressive blood cancer that affects newborns and babies. Early detection is key for effective treatment and saving lives. We know how important it is to spot symptoms early to get medical help fast.
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is the most common childhood cancer. Its symptoms can be subtle. They include persistent fever, fatigue, and unusual bruising or bleeding. At Liv Hospital, we help parents know these signs so they can get medical care quickly.
It’s vital to understand the key symptoms of leukemia in newborns and infants. We’re dedicated to giving families the care and support they need during this tough time.
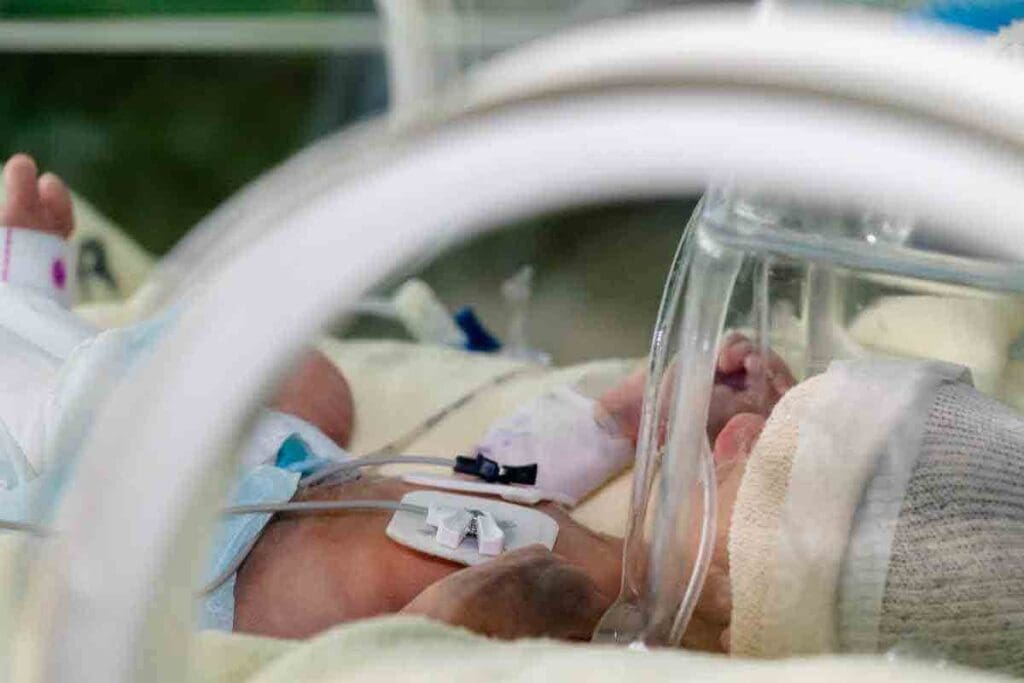
Infantile leukemia is a rare and serious condition that affects newborns and infants. It needs immediate medical attention. This cancer starts in the blood-forming cells of the bone marrow.
Leukemia in infants is different from the kind in older kids and adults. It has its own challenges. We will look into what it is, its types, and specifics to understand it better.
Infantile leukemia is leukemia found in babies under one year old. It starts in the bone marrow and spreads quickly to the blood and other parts. The main types are Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) and Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML).
“Leukemia is a complex disease that requires a multifaceted approach to diagnosis and treatment.”
Pediatric Oncologist
Most infant leukemia is ALL, making up about three out of four cases. AML is less common but serious, mainly in newborns.
AML in newborns is rare but aggressive. It often comes with genetic problems and has a unique presentation.
Infantile leukemia is rare, with ALL being more common than AML. Thanks to better treatments, survival rates have gone up.
| Type of Leukemia | Prevalence | 5-Year Survival Rate |
| ALL | 75-80% | 85-90% |
| AML | 15-20% | 60-70% |
Knowing these stats helps parents and caregivers understand how serious infantile leukemia is. It shows why early detection and treatment are key.
The exact causes of infant leukemia are not fully understood. But, research has found several possible factors. Knowing these factors helps in finding better ways to prevent and treat the disease.
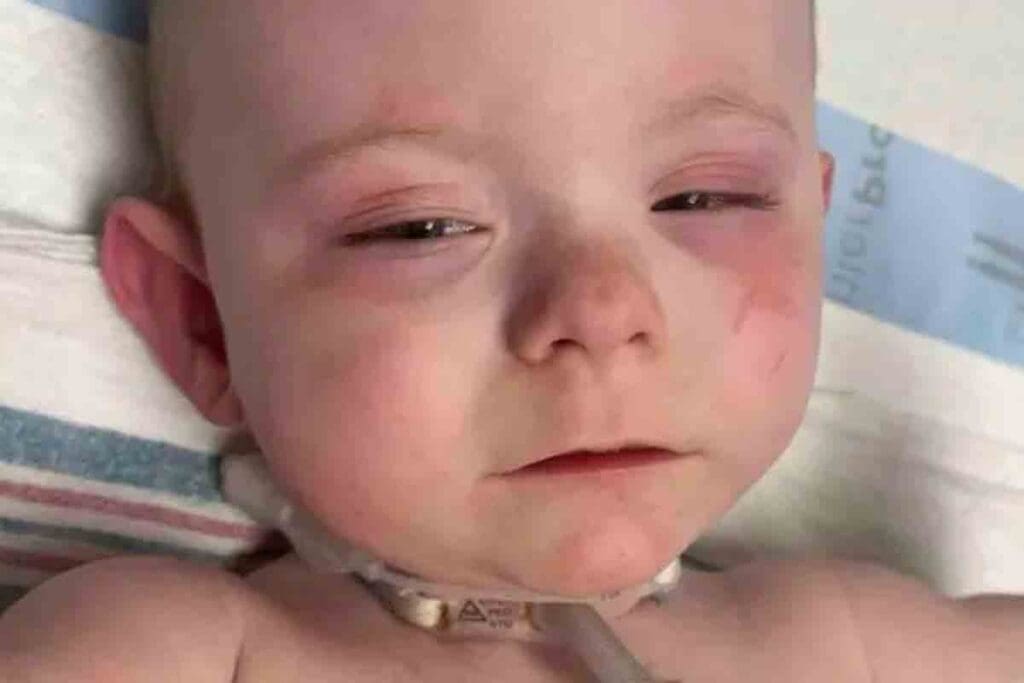
Genetics are a big part of why some infants get leukemia. Chromosomal problems, like MLL gene translocations, are common in these cases. These genetic changes can cause cancer cells to grow out of control. For more on this, check out studies on reputable medical databases.
Exposure to certain things before birth can raise the risk of leukemia in infants. This includes radiation, chemicals, and infections from the mother. But, we need more research to know how big of a role these play.
Yes, babies can be born with cancer, including leukemia. This rare condition is called congenital leukemia. It’s thought that genetic changes during pregnancy are to blame.
| Potential Causes | Description |
| Genetic Factors | Chromosomal abnormalities, such as MLL gene translocations |
| Prenatal Exposures | Maternal exposure to radiation, chemicals, and infections |
| Congenital Factors | Genetic mutations during fetal development |
Understanding why infants get leukemia is key to finding better treatments. Even though we don’t know all the causes, research keeps finding out more about genetics, environment, and birth factors.
Early detection of infant leukemia is key to effective treatment. This rare but serious condition needs quick diagnosis and treatment.
Rapid diagnosis is vital for infant leukemia. The disease can spread fast, causing serious problems. Early detection leads to better treatment outcomes.
By spotting the signs early, doctors can start treatment right away.
Finding leukemia symptoms in babies is hard. Symptoms like fever, tiredness, and bruises can look like other things. Babies can’t tell us how they feel.
Infantile leukemia can grow fast, sometimes in just days or weeks. Its aggressive nature in infants makes early detection and treatment critical. Knowing the signs helps parents get medical help quickly.
| Signs of Infantile Leukemia | Common Symptoms | Importance of Early Detection |
| Persistent fever | Frequent infections | Allows for timely treatment |
| Unexplained bruising | Fatigue and paleness | Improves survival rates |
| Swollen lymph nodes | Loss of appetite | Enhances treatment effectiveness |
Knowing the importance of early detection helps parents and doctors. Together, they can spot infantile leukemia early and start the right treatment.
It’s important to spot the early signs of infantile leukemia to get medical help fast. This rare but serious disease needs quick action. We’ll list the main signs parents and caregivers should look out for to help their baby get the right care.
Infantile leukemia shows symptoms that can look like common baby health problems. But, there are specific signs that point more to leukemia. Look out for ongoing fever, tiredness, swollen lymph nodes, trouble gaining weight, belly swelling, and odd bruising or bleeding.
Telling normal baby health issues from leukemia symptoms can be tricky. For example, while babies often get fevers from infections, a fever that keeps coming back might mean leukemia. Also, while bruising and bleeding in babies usually come from accidents or vitamin K issues, sudden bruising or bleeding gums could hint at leukemia.
Keep a close eye on your baby’s health. If you see any odd or ongoing symptoms, talk to a doctor right away.
If your baby shows any of these signs, get medical help fast:
Spotting and treating infantile leukemia early can greatly improve survival chances and lower risks of serious problems. If you’re worried about your baby’s health, reach out to a healthcare expert without delay.
Infants with leukemia often have persistent fever and fatigue. These symptoms show how the disease affects their young bodies. They are key signs of leukemia.
A persistent fever in infants might mean an infection. But in babies with leukemia, it shows their immune system is weak. Leukemia affects the body’s ability to make normal blood cells, including white blood cells needed to fight infections.
Fevers in these infants can keep coming back. Their immune systems are not strong. So, it’s important for parents to watch their baby’s temperature closely. They should get medical help if the fever doesn’t go away.
Fatigue in infants can be hard to spot. It might look like irritability or not wanting to eat. But unusual tiredness or sluggishness can mean leukemia. Also, paleness or pallor can show anemia, common in leukemia patients.
Parents should watch for changes in their baby’s behavior. Look for being more tired than usual or signs of anemia. These can be important signs of leukemia.
Infants with leukemia get infections easily because their immune systems are weak. The disease stops the bone marrow from making healthy white blood cells. Frequent infections or recurrent fevers mean the immune system is not working right.
Parents need to know that babies with leukemia are at higher risk for infections. If they see signs of infection, like fever, cough, or trouble breathing, they should get medical help fast.
Unusual bruising and bleeding can be signs of infantile leukemia. This rare condition affects newborns and infants. It’s important for parents and caregivers to know the subtle signs that may point to a serious health issue.
Infants with leukemia may show unusual bruising patterns. These can be unexplained marks or bruises on the skin. It’s key to watch the frequency, size, and location of these bruises.
Be careful if you see bruises in places like the face, back, or chest. Also, watch out for bruises without a clear reason.
Bleeding gums and prolonged bleeding are warning signs. Leukemia can affect blood cell production, including platelets. This can lead to prolonged bleeding or oozing from minor cuts or during teething.
If your infant’s gums bleed or they bleed a lot, see a doctor right away.
Petechiae, small spots on the skin, can be a sign of leukemia. These spots are tiny hemorrhages and may mean low platelet count. Other signs include pale skin or a rash.
It’s important to tell the difference between common skin issues and signs of leukemia. If you see petechiae or other unusual skin signs, get medical help.
Parents need to watch for swollen lymph nodes and belly changes in their babies. These signs might mean leukemia. It’s very important to see a doctor right away.
Swollen lymph nodes can mean infection, but in babies, they might show leukemia. Look for big, hard nodes in the neck, armpits, or groin.
Key characteristics include:
Leukemia can make the liver and spleen big, causing belly pain. Watch for a big belly or pain when feeding.
| Signs | Symptoms |
| Enlarged liver or spleen | Abdominal discomfort, loss of appetite |
| Palpable abdominal mass | Vomiting, irritability |
Big belly, yellow skin, and throwing up are serious signs. Yellow skin means the liver isn’t working right.
As one doctor says,
“Finding leukemia early is key to treating it well. Spotting the signs early can really help.”
It’s vital to watch for these signs and get medical help fast if you see them.
Leukemia in infants can show through different symptoms that need quick action. We’ll look at how leukemia impacts growth and brain development in babies. We’ll also talk about key signs parents and caregivers should watch for.
One big sign of leukemia in babies is failure to thrive. This means they don’t gain weight or might even lose it. The disease can make it hard for babies to eat enough, affecting their growth.
Nutritional deficiencies can make things worse, leading to significant weight loss. It’s vital for parents to keep an eye on their baby’s eating and growth. If they see anything odd, they should talk to a doctor.
| Symptom | Description | Potential Complications |
| Failure to Thrive | Lack of weight gain or weight loss | Malnutrition, delayed development |
| Loss of Appetite | Reduced interest in feeding | Nutritional deficiencies, weight loss |
Leukemia can also slow down a baby’s brain growth. This might mean they don’t hit milestones on time or lose skills they had.
It’s important to watch how a baby is developing. If they’re not meeting milestones or seem to be losing skills, it could be a sign of leukemia.
Leukemia can also affect a baby’s nervous system. This can cause a variety of brain-related symptoms.
Babies with leukemia might act differently or seem really upset or tired. These changes could mean their brain is involved and need medical help.
We stress the need to watch for these signs and get medical help if you’re worried about your baby’s health or development.
If your child shows any signs of infantile leukemia, see a doctor right away. Early diagnosis is key to effective treatment and better recovery chances.
Stay alert and act fast if you think your child might have infantile leukemia. Quick diagnosis helps doctors create a treatment plan that fits your child’s needs.
When you visit the doctor, share all details about your child’s symptoms. Tell them when you first noticed them and any changes. This helps doctors make an accurate diagnosis and provide the right care.
Infantile leukemia is a cancer that affects newborns and babies. It happens when white blood cells grow abnormally in the bone marrow.
Yes, newborns can be born with leukemia. It’s often linked to genetic mutations or chromosomal abnormalities.
Symptoms include persistent fever, fatigue, and unusual bruising and bleeding. Other signs are swollen lymph nodes, abdominal changes, and failure to thrive.
It can progress quickly. Early detection and timely treatment are key for effective care.
The exact cause is often unknown. But genetic factors, chromosomal abnormalities, and prenatal exposures may play a role.
Normal issues can cause fever and bruising. But leukemia symptoms are persistent and severe. They often include swollen lymph nodes and abdominal changes.
Yes, it can be treated with chemotherapy and targeted therapy. The prognosis depends on the disease’s type and severity.
Survival rates vary based on the disease’s type and severity. They also depend on treatment effectiveness. Advances in medical care are improving these rates.
Diagnosis involves a physical exam, blood tests, and a bone marrow biopsy. Imaging studies like X-rays and ultrasound are also used.
The rash, known as petechiae, appears as small spots on the skin. It’s often accompanied by bruising or bleeding.
Yes, leukemia can cause developmental delays or regression. This is due to the disease or treatment effects on the developing brain and body.
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) is rare in newborns. But it can occur, and prompt medical attention is necessary for diagnosis.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!