Last Updated on November 25, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir

Seeing blood clots in your urine can be scary and makes you worry about your health. These clots can look different, like strings or red pieces, based on why they’re there and how much blood is involved small blood clots in urine.
At Liv Hospital, we know how important it is to get help fast if you see clots or blood in your urine. We focus on you, using top medical standards and care to help right away.
If you notice peeing clumps of blood or other odd symptoms, it’s key to know when to go to the ER. Some issues might fix themselves, but others need quick doctor help to avoid bigger problems.
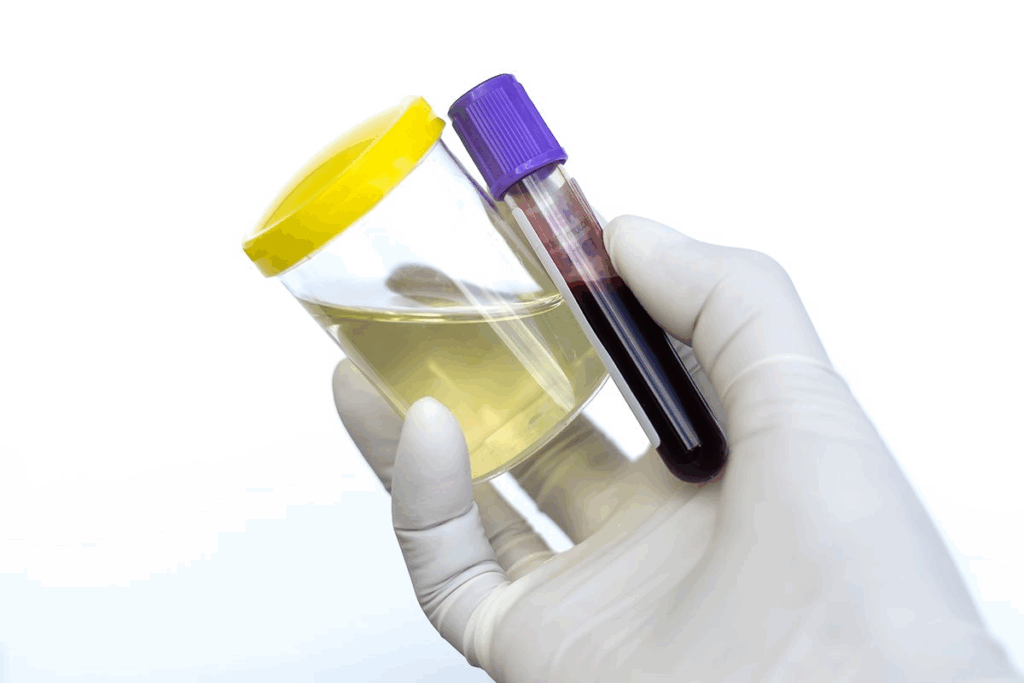
Hematuria, or blood in urine, is common among adults. About 30 percent of adults will experience it at some point. We’ll look into what it is, how common it is, and its types.
Hematuria means there’s blood in your urine. It’s a sign of something else going on that needs a doctor’s check-up. It’s quite common, with 30% of adults dealing with it at some time. It’s divided based on how you can see the blood.
Hematuria comes in two forms: microscopic and gross. Microscopic hematuria means you can only see the blood with a microscope. On the other hand, gross hematuria makes the urine look pink, red, or brown. Knowing the difference helps figure out the cause and how to treat it.
| Type of Hematuria | Description | Visibility |
| Microscopic Hematuria | Blood detected under a microscope | Not visible to the naked eye |
| Gross Hematuria | Urine appears pink, red, or brown | Visible to the naked eye |
It’s important to remember that blood in urine can mean many things. It could be a sign of an infection or something more serious. If you see blood in your urine, see a doctor right away.

Blood clots in urine can look different, and knowing what they look like is key. They can show up in many ways, and figuring out why they’re there is important.
Blood clots might look like stringy or worm-like formations in your urine. These shapes suggest the bleeding is coming from higher up, like the kidneys or ureters. This is because the clot forms in a tube, like the ureter, before it gets into your urine.
Sometimes, blood clots show up as red or dark chunks in your urine. These pieces can be different sizes and shapes. The color can be bright red or dark brown, depending on how old the blood is. Fresh blood looks red, while older blood turns brown because of oxidation.
The color of your urine can change a lot when blood clots are present. It might look pink, red, brown, or cola-colored, based on the blood amount and cause. Even a little blood can change the color, but seeing actual clots means there’s more bleeding. A doctor says, “Seeing blood clots in urine means there’s a lot of bleeding and you need to see a doctor.”
Knowing how blood clots look and what colors they can turn your urine can help you talk about your symptoms with doctors. This can lead to better diagnoses and treatments.
Understanding blood clot formation in the urinary tract helps us understand hematuria. Blood clots in urine mean there’s bleeding in the urinary system. This could be due to infections, stones, or injuries.
Blood clotting is a natural response to injury. When the urinary tract’s blood vessels get damaged, the body starts the coagulation process. This involves platelets and fibrin.
Platelets gather at the injury site. Fibrin strands form a mesh that traps more platelets and blood cells. This creates a clot.
Blood clots in urine are often long and stringy. This is because they form in narrow passages like the ureters and urethra. As they move, they take on elongated shapes.
The shape and size of the clot can hint at where the bleeding is happening.
Fresh blood clots are red or pink and gelatinous. Older clots are darker, sometimes brown or cola-colored. This change in appearance can tell us about the timing and source of the bleeding.
| Characteristics | Fresh Blood Clots | Older Blood Clots |
| Color | Red, Pink | Brown, Cola-colored |
| Texture | Gelatinous | More solid, possibly fragmented |
| Shape | Often elongated or stringy | Can be irregular, sometimes more compact |
By looking at blood clot characteristics, doctors can learn a lot. This helps them figure out the cause of hematuria. It’s key for choosing the right tests and treatments.
Several factors can cause blood clots in urine. These include infections and kidney stones. Knowing these causes helps find the right medical care.
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) often lead to blood clots in urine. Bacteria in the urinary tract cause inflammation and irritation. This can lead to bleeding. The presence of blood clots may indicate a more severe infection that needs quick treatment.
UTIs are usually treated with antibiotics. Sometimes, more steps are needed to manage symptoms and prevent problems.
Kidney and bladder stones can also cause blood clots in urine. These stones irritate and damage the urinary tract lining, leading to bleeding. The movement of stones through the urinary tract can also cause trauma, resulting in blood clots.
Treatment for stones depends on their size and location. It may include medication, lifestyle changes, or surgery.
Certain medications can increase the risk of blood clots in urine. Blood thinners and aspirin are examples. They can affect blood clotting, leading to urinary tract bleeding.
It’s important for patients to talk to their healthcare provider about their medications. This is if they have blood clots in their urine. Adjustments to their medication may be needed to reduce this risk.
In conclusion, blood clots in urine can come from many sources. These include urinary tract infections, kidney and bladder stones, and medication side effects. Finding the cause is key to the right treatment and preventing complications.
Many people know about common reasons for blood in urine. But, there are also less common causes that can be just as serious. These should not be ignored.
Trauma or injuries to the groin can cause bleeding in the urinary tract. This leads to blood clots in the urine. Such injuries can happen from accidents, sports, or other physical traumas. It’s important to see a doctor if you have blood in your urine after a groin injury.
A study showed that injuries to the abdomen or pelvis can hurt the urinary tract. This can cause bleeding and clot formation. The injury’s severity matters, but getting medical help is key.
Kidney infections can cause inflammation and damage to the kidney. This can lead to bleeding and blood clots. Kidney diseases like polycystic kidney disease (PKD) also raise the risk of blood in urine.
Kidney infections often come from bacteria moving up from the lower urinary tract. Untreated, these infections can cause serious damage. They can also increase the risk of blood clots.
| Kidney Condition | Risk of Hematuria | Common Symptoms |
| Pyelonephritis | High | Fever, flank pain, hematuria |
| Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) | Moderate | Cysts on kidneys, hypertension, hematuria |
| Kidney Stones | High | Severe pain, hematuria, nausea |
Bleeding disorders like hemophilia or von Willebrand disease can lead to bleeding in the urinary tract. This can cause blood clots. These conditions make it hard for the body to stop bleeding.
Even small injuries in the urinary tract can cause a lot of bleeding in people with bleeding disorders. It’s important to manage these conditions well to avoid complications.
Knowing about these less common causes of urinary blood clots is key. If you notice unusual symptoms, get medical help right away. Early treatment can greatly improve outcomes for these conditions.
Blood clots in urine can signal serious health issues that need quick attention. These clots can point to severe diseases affecting the urinary tract.
Urinary tract cancer is a major concern with blood clots in urine. Visible blood in urine, known as gross hematuria, raises cancer risk more than microscopic hematuria. Urinary tract cancers can hit the bladder, kidneys, or ureters, making early detection key for treatment.
While not all hematuria leads to cancer, blood clots in urine need a detailed medical check. This is to rule out cancer.
Kidney failure is another serious issue linked to blood clots in urine. It happens when kidneys can’t filter waste from blood well. Blood clots may show kidney damage or disease, which could lead to kidney failure if not treated.
Kidney failure can stem from diabetes, high blood pressure, or certain kidney diseases. Blood clots in urine might signal kidney problems that need attention.
In men, blood clots in urine can hint at prostate issues like prostatitis, BPH, or prostate cancer. Prostate problems can cause urinary tract bleeding, leading to blood clots.
Prostate conditions are common in older men. While many are not cancerous, they can cause discomfort and health problems. Blood clots in urine should prompt a medical check to find the cause.
In summary, blood clots in urine can signal serious health issues like urinary tract cancers, kidney failure, and prostate problems in men. It’s vital to see a doctor if you notice blood clots in your urine for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Blood clots in urine mean different things for men and women. Some causes are the same for both, but others are unique. This is because of differences in body parts, hormones, and health issues specific to each gender.
Women might see blood clots in their urine because of endometriosis. This is when tissue like the uterine lining grows outside the uterus. It can affect the bladder or ureters, causing bleeding, often during their period.
Other reasons for women include:
A study found that endometriosis can really hurt a woman’s quality of life. It’s important to not ignore its effects on the urinary tract.
Men are more likely to have blood clots in their urine because of prostate enlargement or cancer. Problems with the prostate can cause bleeding into the urinary tract, leading to blood clots.
Other causes specific to men include:
A medical expert says, “Prostate health is key for men. Symptoms like hematuria need a detailed check-up.”
Blood clots in urine often come with other signs. These signs can tell us a lot about what’s going on. Knowing these symptoms helps us understand how serious the issue is and what might be causing it.
Pain or discomfort while urinating is common. This pain can feel like a mild burn or be very uncomfortable. Back pain or lower abdominal pain can also happen, depending on where the bleeding is.
Changes in how you urinate can be a big clue. You might find yourself needing to go more often, feeling urgent, or having trouble starting or stopping. In some cases, you might not be able to urinate at all, which is a serious emergency.
Systemic symptoms can show up if the blood clots are caused by an infection or another serious problem. These symptoms include fever, nausea, and vomiting. In severe cases, these signs can mean a life-threatening issue that needs quick medical help.
If you have blood clots in urine and any of these symptoms, you should see a doctor right away. Knowing these symptoms helps doctors figure out what’s wrong and how to treat it.
It’s important to know when to get help for blood clots in urine. These clots can be a sign of serious health issues. Some problems need quick medical help.
If you have these symptoms, go to the emergency room right away:
These signs can mean serious issues like kidney stones, infections, or cancer. Getting medical help fast is key to avoid serious problems.
Some situations need a trip to the emergency room. If you see many or big clots in your urine, or can’t urinate, get help fast. Also, if you have kidney or bladder problems and start seeing clots, see a doctor.
| Situation | Action |
| Heavy bleeding with clots | Seek ER immediately |
| Severe pain | Visit ER |
| Difficulty urinating | Go to ER |
When you get to the emergency room, doctors will check you carefully. They will do a physical exam, lab tests, and might use imaging like ultrasound or CT scans. This helps find out why you have blood clots.
Knowing what to expect can make you feel better. The doctors will find out what’s causing your symptoms. They will then treat you to make you stable and fix any problems.
To find out why you have blood clots in your urine, doctors use several steps. They do physical checks, lab tests, and imaging studies. These steps help doctors figure out what’s causing the blood and plan the best treatment.
The first thing doctors do is a physical check-up. They look for signs of health problems that might be causing the blood clots. They check for:
Lab tests are key in finding out why you have blood clots in your urine. These tests include:
These tests give doctors important clues about what might be causing the blood clots.
Imaging studies help doctors see inside the urinary tract to find problems. Common methods include:
By combining the results from physical checks, lab tests, and imaging studies, doctors can accurately diagnose blood clots in urine. They then create a treatment plan to help you.
Treating blood clots in urine depends on the cause. The severity and what the patient needs also matter. These factors help decide the best treatment.
Medicines are often the first choice for treating blood clots in urine. Antibiotics are used for urinary tract infections. Pain relievers help with discomfort from kidney stones or other issues. Sometimes, anticoagulant medications are needed to stop more clots, if there’s a bleeding disorder.
For severe cases or when other treatments don’t work, surgery might be needed. Surgical procedures can be simple or complex.
Changing your lifestyle can help manage and prevent blood clots in urine. Dietary adjustments like drinking more water and eating less salt can prevent kidney stones. Regular exercise and a healthy weight can also lower the risk of urinary tract problems.
Knowing about different treatments helps patients work with their doctors. Together, they can create a plan that meets the patient’s needs and condition.
Blood clots in urine can signal many health issues, from infections to serious diseases like cancer. It’s key to know the causes and signs to get the right medical help.
We’ve looked at blood clots in urine, including what they look like, why they happen, and related health issues. It’s important to notice symptoms like pain and changes in how you pee.
If you see blood in your urine, get medical help right away. Doctors will use tests like physical exams, lab work, and imaging to find out why. Treatment depends on the cause and might include medicine, surgery, or changes in your lifestyle.
In short, don’t ignore blood clots in urine. Knowing the causes and getting medical care can lead to better health outcomes.
Blood clots in urine can look like strings or worms. They can also be red or dark chunks, or even jellylike blobs. The color of the urine can change a lot, from pink to brown, depending on the blood amount and cause.
Yes, if you see blood in your urine, you should see a doctor. Go to the ER if you have a lot of bleeding, pain, or a fever. Also, if you can’t pee, have bad stomach pain, or have had urinary problems before.
Blood clots in urine can be caused by infections, stones in the kidneys or bladder, and some medicines. These problems can irritate or damage the urinary tract, leading to bleeding and clots.
Yes, blood clots in urine can mean serious health issues like cancer, kidney failure, or prostate problems. It’s important to see a doctor to find out why.
Doctors use physical exams, lab tests, and imaging to diagnose blood clots in urine. These steps help find the cause and plan treatment.
Treatment depends on the cause, how bad it is, and what the patient needs. It can include medicines, surgery, or changes in lifestyle.
Yes, there are differences. Women might get blood in urine from endometriosis, while men often get it from prostate problems.
Symptoms can include pain, changes in how you pee, and other signs. These can show what’s causing the problem and how serious it is.
Yes, injuries to the groin can cause bleeding in the urinary tract, leading to blood clots.
At the ER, you’ll get a physical exam, lab tests, and maybe imaging studies. Doctors will check your condition and treat you as needed.
Government Health Resource. (2025). What Do Blood Clots in Urine Look Like. Retrieved from https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/hematuria-blood-urine
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!