Last Updated on November 25, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir

Chronic stress can deeply affect our health, mainly our heart.stress and the heartClogged Heart Stent: Causes and What to Know When we’re stressed, our body goes into “fight or flight” mode. This releases hormones like adrenaline and cortisol.
These hormones make our heart rate and blood pressure go up. This can strain our heart and blood vessels.
At Liv Hospital, we know how vital it is to keep your heart healthy. We offer top-notch, patient-focused care to safeguard your heart. In this article, we’ll dive into how stress affects your heart and the body’s response to it.

It’s important to know how stress affects the heart. This knowledge helps keep our heart healthy and prevents heart problems. Stress and heart health are linked in a complex way, with stress hormones affecting our heart over time.
Stress makes our body release hormones like adrenaline and cortisol. These hormones get us ready to either fight or run away. They make our heart beat faster and our blood pressure go up.
This response is meant to be short-lived. But, if we’re stressed all the time, it can harm our heart. Stress hormones can cause chest pain and make it hard to breathe. Stress also makes us less likely to eat well or exercise, which can hurt our heart even more.
The heart is very sensitive to long-term stress. Stress can cause inflammation, damage blood vessels, and increase heart disease risk. Here’s a table showing how stress affects the heart.
| Effect of Chronic Stress | Description | Potential Outcome |
| Increased Heart Rate | Stress hormones cause the heart to beat faster | Potential for heart palpitations and arrhythmias |
| Elevated Blood Pressure | Constant strain on blood vessels due to stress | Increased risk of hypertension and cardiovascular disease |
| Inflammation and Arterial Damage | Chronic stress leads to inflammatory responses | Risk of arterial plaque formation and coronary artery disease |
Knowing how stress affects the heart and why it’s vulnerable helps us protect our heart. We can take steps to reduce stress and keep our heart healthy.
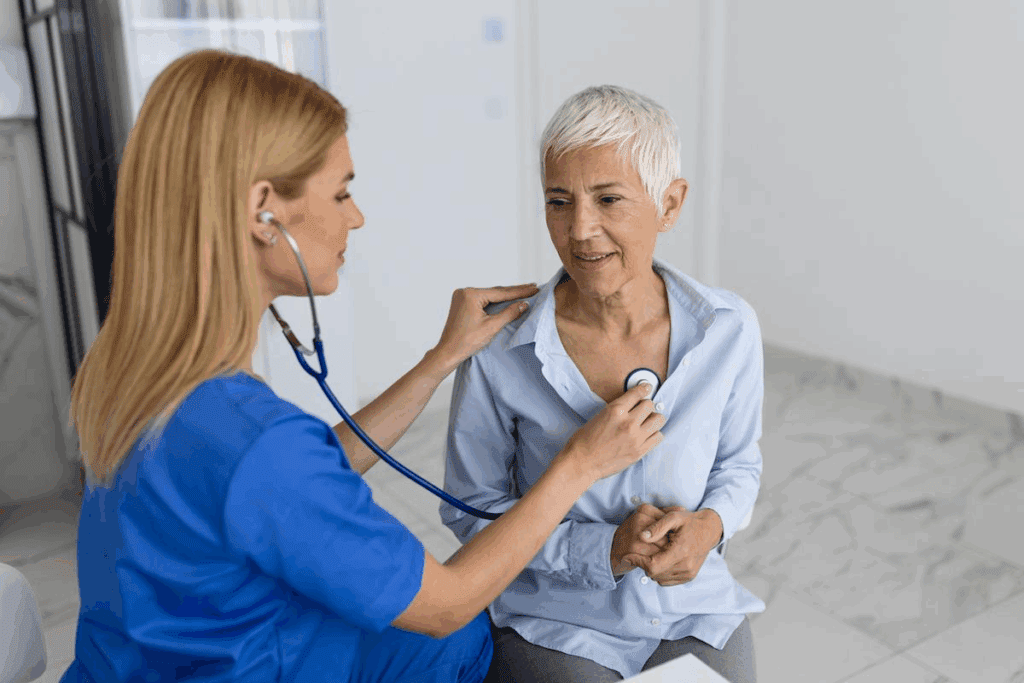
Stress can deeply affect our heart and blood vessels. It’s a natural response to danger, but too much stress can harm our heart over time.
Stress makes our body release important hormones: adrenaline and cortisol. Adrenaline gets us ready to ‘fight or flight’ by speeding up our heart and raising blood pressure. Cortisol, known as the “stress hormone,” keeps our body responding to stress for longer.
“The body’s stress response is complex, involving many hormonal pathways,” says Dr. Jane Smith, a top cardiologist. “Knowing this is key to handling stress-related heart issues.”
The sympathetic nervous system is vital for heart function under stress. It turns on the ‘fight or flight’ response, making our heart beat faster and pump harder. This is meant to be short-lived, but constant stress can damage our heart.
The main effects of the sympathetic nervous system on the heart are:
By grasping how stress impacts our heart through hormones and the nervous system, we see why managing stress is vital for our heart’s health.
Chronic stress can lead to high blood pressure, a major heart disease risk. Stress triggers our “fight or flight” response. This prepares us to face threats or run away.
Stress hormones like adrenaline and cortisol increase our heart rate and blood pressure. This is meant to be short-term. But, long-term stress keeps these hormones active, causing blood pressure to stay high.
Stress-induced hypertension involves the nervous, endocrine, and cardiovascular systems. When we feel stressed, our hypothalamus starts the sympathetic nervous system. This releases adrenaline and cortisol.
These hormones make blood vessels narrow, heart rate go up, and cardiac output increase. All these factors raise blood pressure. Chronic stress also changes how our body responds, making blood vessels more resistant and affecting baroreflex sensitivity.
“The continuous activation of the body’s stress response can lead to long-term changes in the cardiovascular system, increasing the risk of developing hypertension and cardiovascular disease.”
Chronic stress and high blood pressure can severely harm heart health. High blood pressure damages blood vessels. This makes them more likely to block or burst.
| Condition | Description | Risk |
| Hypertension | High blood pressure | Heart disease, stroke |
| Cardiovascular Disease | Disease of the heart and blood vessels | Heart attack, stroke |
| Kidney Disease | Damage to the kidneys due to high blood pressure | Kidney failure |
Managing chronic stress is key to keeping blood pressure and heart health in check. Mindfulness, meditation, and deep breathing can help lower stress.
By understanding how stress affects blood pressure and heart health, we can take steps to manage stress. This reduces the risk of hypertension and its heart-related complications.
Stress can make your heart beat faster and cause palpitations. When we’re stressed, our body goes into “fight or flight” mode. This releases hormones like adrenaline into our system.
Adrenaline is released when we’re stressed. It gets our body ready to face or run from danger. This hormone makes our heart beat quicker, sending more blood to our muscles.
This quick heart rate is due to our sympathetic nervous system. It’s what gets us ready to act fast. But, long-term stress can mess with our heart rhythm. Our heart rate can change for many reasons, like our physical shape, age, and health.
Most of the time, a faster heart rate from stress isn’t a big deal. But, if you have persistent or severe palpitations, see a doctor. They can figure out if it’s stress or something more serious.
To understand how stress affects our heart rate, let’s look at some important facts:
| Condition | Normal Heart Rate | Stressed Heart Rate |
| Average Adult | 60-100 bpm | 100-140 bpm |
| Athletes | 40-60 bpm | 80-120 bpm |
Knowing how stress affects our heart is key to keeping it healthy. By spotting signs of stress on our heart, we can take steps to manage stress and protect our heart.
Stress can cause inflammation in our heart. This inflammation is a big problem for heart health.
Stress makes our body release stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones help us react quickly, but too much of them can harm our blood vessels.
Key mechanisms include:
This inflammation is a natural defense. But, it can harm our heart health if it lasts too long.
Chronic stress can cause plaque to form in our arteries. This is called atherosclerosis. The plaque narrows our arteries, making it hard for blood to reach our heart.
The process involves several steps:
This can lead to coronary artery disease. It raises the risk of heart attacks and other heart problems.
A leading cardiologist says, “Chronic stress is a big risk for heart disease. It’s important to manage stress for heart health.”
“The relationship between stress and cardiovascular disease is complex and bidirectional. Stress can contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease, and having cardiovascular disease can also be a source of stress.”
— Dr. Jane Smith, Cardiologist
It’s key to understand how stress, inflammation, and heart health are connected. This helps us find better ways to prevent and treat heart problems.
Chronic stress can mess with the heart’s rhythm, causing arrhythmias and other heart rhythm disorders. When we’re stressed, our body goes into “fight or flight” mode. This releases hormones like adrenaline and cortisol, which can affect the heart’s electrical signals.
Stress can lead to different types of arrhythmias, including:
These arrhythmias can be concerning, as they may happen often or with other symptoms like chest pain or shortness of breath.
It’s important to know the warning signs of serious arrhythmias to get medical help quickly. Look out for symptoms like:
If you have any of these symptoms, seek medical help. We can work together to manage stress and reduce the risk of arrhythmias, promoting overall heart health.
Severe emotional stress can cause Takotsubo cardiomyopathy, or “Broken Heart Syndrome.” It temporarily weakens the heart muscles. This condition looks like a heart attack and is often caused by intense emotional or physical stress.
Takotsubo cardiomyopathy makes the heart muscle suddenly weak. It usually happens because of extreme stress or a traumatic event. The name comes from the Japanese term for “octopus pot,” which describes the heart’s shape during an episode.
Severe emotional stress triggers our body’s “fight or flight” response. This releases stress hormones like adrenaline and cortisol. These hormones can make the heart rate and blood pressure surge, weakening the heart muscles temporarily.
The exact reasons behind Takotsubo cardiomyopathy are not fully known. But it’s thought to be related to how the heart reacts to stress. Research suggests it might be linked to changes in the heart’s blood vessels and how the heart muscle works under stress.
| Symptom | Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy | Heart Attack |
| Chest Pain | Common | Common |
| Shortness of Breath | Common | Common |
| ECG Changes | Often present | Often present |
| Coronary Artery Blockage | Rarely present | Often present |
Recovering from Takotsubo cardiomyopathy means managing stress and reducing the risk of more episodes. This can be done through lifestyle changes, stress management, and medical treatment.
“The key to managing Takotsubo cardiomyopathy is to reduce stress and promote heart health through lifestyle changes and stress management techniques.”
Dr. Jane Smith, Cardiologist
Effective ways to prevent Takotsubo cardiomyopathy include stress-reducing activities like meditation or deep breathing. Regular physical activity and a healthy diet also help. By taking these steps, we can lower our risk of this condition and improve our heart health.
To relax the heart and lower the risk of stress-related heart issues, it’s key to do activities that help relax and reduce stress. This can include yoga, tai chi, or simply taking time to relax and unwind.
When we’re stressed, we might use unhealthy coping behaviors. These can harm our heart health. Stress eating, smoking, and drinking too much alcohol are examples. They can make heart disease risk higher.
Stress eating can lead to weight gain and high blood pressure. It often involves foods high in fats, salt, and sugar. “Comfort foods” during stress are bad for our hearts, studies show.
Stress can make us drink more alcohol and smoke. Both are bad for our hearts. Alcohol can raise blood pressure and cause irregular heartbeats. Smoking damages arteries and increases heart disease risk.
To break the cycle, we need a plan. First, we must recognize the problem. Then, we should find better ways to cope, like exercise or meditation.
Understanding stress, coping behaviors, and heart health is key. We can protect our hearts by making smart choices. It’s about caring for our mental and physical health.
Long-term stress can greatly raise the chance of heart failure. It harms the heart in many ways, leading to long-term damage.
Stress triggers our body’s “fight or flight” response. This releases hormones like adrenaline and cortisol. These hormones help us react to threats but can harm the heart if present for too long.
The heart faces many challenges from stress. This can lead to:
These changes can raise the risk of heart failure. Heart failure means the heart can’t pump enough blood for the body’s needs.
It’s important to know when stress is hurting your heart. Look out for these signs:
| Symptom | Description |
| Persistent Fatigue | Feeling unusually tired or weak, even after resting |
| Shortness of Breath | Experiencing difficulty breathing or feeling winded even when sitting or doing light activities |
| Swelling in Legs, Ankles, or Feet | Noticing swelling due to fluid buildup, a sign that the heart is not pumping efficiently |
If you notice these symptoms, see a doctor. They can check your heart health and help manage stress to lower heart failure risk.
Understanding stress’s impact on heart health is key. By managing stress, we can protect our hearts and lower heart failure risk.
Chronic stress can harm your heart health. But, there are ways to relax your heart and lower this risk. Relaxation techniques help manage stress and improve heart health. Let’s look at some methods to relax your heart and boost your heart health.
Physical activity is a top way to reduce stress and keep your heart healthy. Regular exercise lowers blood pressure, boosts circulation, and strengthens the heart. Try brisk walking, cycling, or swimming for at least 30 minutes, most days.
Exercise also releases endorphins, which make you feel better. This can help fight stress’s negative effects. Plus, it can help you sleep better, which stress often disrupts.
Mindfulness and meditation are great for managing stress and heart health. They help you focus on the present, reducing anxiety and stress. Regular practice can lower blood pressure and heart rate.
Start with guided meditation apps or videos. Even a few minutes a day can help. The key is to be consistent and make it a daily habit.
Deep breathing exercises are simple yet effective in reducing stress and lowering heart rate. Slow, deep breaths calm your nervous system and reduce stress effects. Try diaphragmatic breathing or the 4-7-8 method.
To practice deep breathing, sit comfortably and focus on your breath. Inhale slowly through your nose, hold for a few seconds, and exhale slowly through your mouth. Do this several times.
Social connections and relationships are key to our well-being, including heart health. Strong social support can lessen stress’s effects. Engage in social activities, spend time with loved ones, or join a group to feel supported and less lonely.
| Technique | Description | Benefits |
| Physical Activity | Engage in regular exercise like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming | Lowers blood pressure, improves circulation, strengthens the heart |
| Mindfulness and Meditation | Practice guided meditation or mindfulness exercises daily | Reduces anxiety, lowers blood pressure and heart rate |
| Deep Breathing Exercises | Practice diaphragmatic breathing or the 4-7-8 method | Calms the nervous system, reduces stress |
| Social Connection | Engage in social activities, spend time with loved ones | Provides emotional support, reduces feelings of loneliness |
By adding these techniques to your daily routine, you can greatly improve your heart health and overall well-being. Try these methods and find what works best for you.
It’s important to know how stress affects our heart health. Chronic stress can cause high blood pressure and heart rate issues. It can even lead to serious heart problems like Takotsubo cardiomyopathy and heart failure.
By using stress-reducing methods and living a healthy lifestyle, we can lower our risk of heart disease. Activities like exercise, mindfulness, and deep breathing help a lot. They lessen stress’s impact on our heart.
To keep our heart healthy, we need to manage stress well. We should also stay active and make smart lifestyle choices. By focusing on stress reduction and heart health, we can avoid long-term heart problems caused by stress.
Choosing a healthy lifestyle and using stress-reducing techniques is key. It helps protect us from heart disease and keeps us feeling good overall. This is all about taking care of our heart and managing stress well.
Stress makes the body release hormones like adrenaline and cortisol. These hormones can make the heart beat faster and blood pressure go up. This extra work can strain the heart.
Yes, stress can make your heart rate go up. It does this by activating the body’s “fight or flight” response. This is a natural reaction to stress.
Long-term stress can cause high blood pressure. This happens because the body’s stress response is always on. It makes blood vessels narrow and the heart work harder.
Stress can start inflammation in the heart and blood vessels. This is because it releases chemicals that cause inflammation. This can lead to plaque buildup and heart disease.
Takotsubo cardiomyopathy, or “broken heart syndrome,” is a heart condition. It happens when severe emotional stress weakens the heart muscles. This can make the heart act like it’s having a heart attack.
Yes, long-term stress can harm the heart. It can cause lasting damage and make the heart work less efficiently. This increases the risk of heart failure.
To relax your heart, try physical activity, mindfulness, and meditation. Deep breathing and staying connected with others can also help. These activities can lessen stress’s impact on your heart.
Unhealthy coping behaviors like eating too much, smoking, and drinking too much alcohol can harm your heart. They can lead to obesity, high blood pressure, and heart disease.
Keep an eye on your heart rate and blood pressure. Be aware of symptoms like chest pain or irregular heartbeats. This can help you know when stress is affecting your heart.
Yes, stress can cause irregular heartbeats or rhythm problems. It does this by disrupting the heart’s electrical system. This can lead to arrhythmias.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!