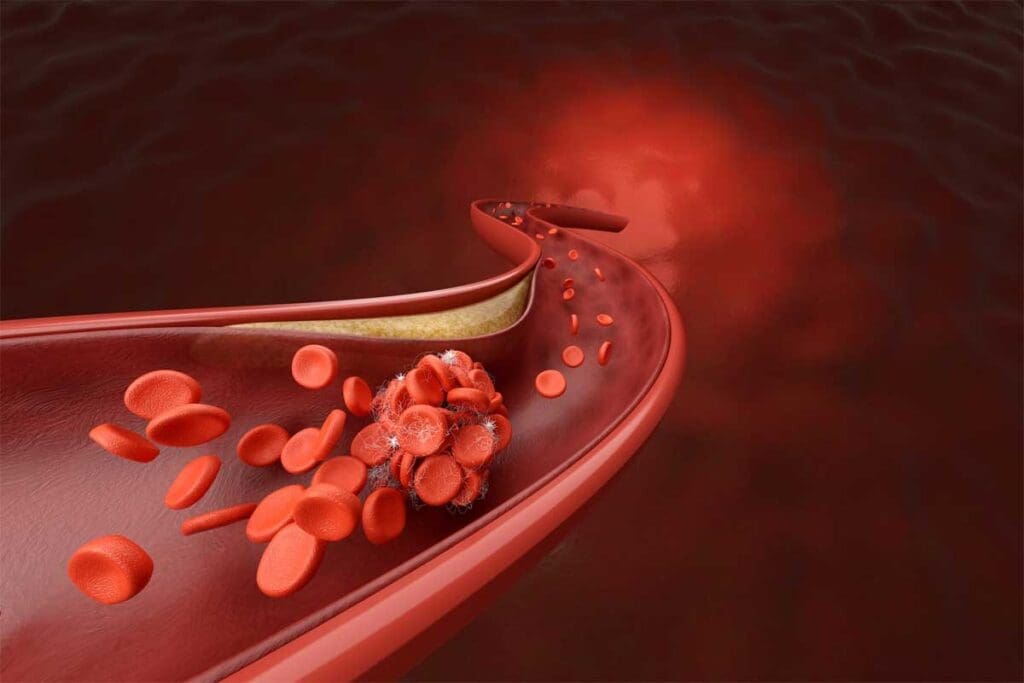
At LivHospital, we know how vital clear info about serious health issues is. Thrombosis is a serious condition where a blood clot blocks blood flow in a vessel. This can be very dangerous. Discover the thrombosis meaning , its causes, and the main symptoms that indicate a blood clot.
Terms like tromboza and thrombose definition mean the same as thrombosis. Knowing these terms is important for patients and their families.
We take thrombosis very seriously because it can cause strokes and heart attacks. Our goal is to help those looking for medical info and treatment.
Key Takeaways
- Thrombosis is a serious medical condition involving the formation of a blood clot within a blood vessel.
- It can lead to life-threatening events such as strokes and heart attacks.
- Understanding thrombosis and related terms is important for patients and their families.
- LivHospital is committed to providing clear information and medical support.
- Early recognition of symptoms is key to effective treatment.
Thrombosis Meaning: Understanding Blood Clot Formation
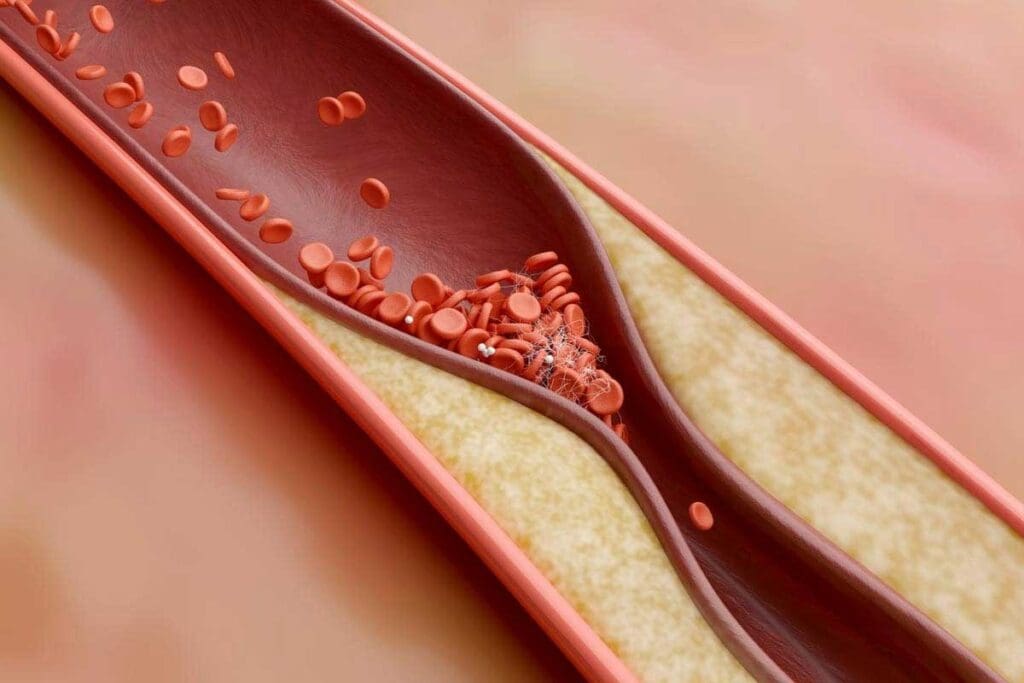
Thrombosis happens when a blood clot forms inside a blood vessel. This can block blood flow. It’s a complex process that affects our health.
The Process of Thrombus Development
Creating a thrombus involves many steps. Platelets, fibrin, and clotting factors play key roles. When a blood vessel gets hurt, the body tries to stop bleeding by forming a clot.
- Platelets start to gather at the injury site.
- The coagulation cascade kicks in, leading to fibrin formation.
- Fibrin strands weave together, trapping blood cells and forming a clot.
This clotting is vital to stop too much bleeding. But, it can also happen without injury, causing a blockage in blood vessels.
How Blood Clots Obstruct Vessels
A thrombus can block blood flow in different ways:
- Partial Obstruction: The clot might only partially block the vessel, reducing blood flow to tissues.
- Total Occlusion: Sometimes, the clot can fully block the vessel, causing tissue damage or death.
- Embolism: A piece of the clot can break off and travel through the blood until it gets stuck in a smaller vessel, causing an embolism.
Knowing how thrombosis works is key to treating it. Doctors can spot the signs early and act fast to prevent serious problems.
Types of Thrombosis and Their Characteristics
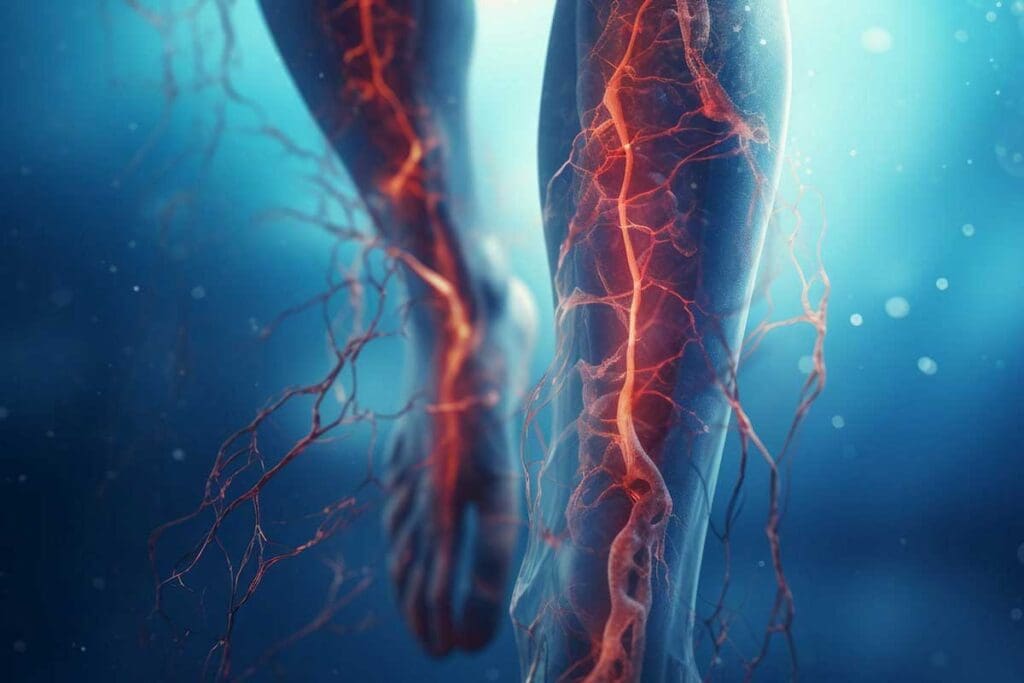
Thrombosis can be divided into several types based on where and how the blood clot forms. Knowing these differences is key to managing and treating it effectively.
Arterial Thrombosis
Arterial thrombosis happens when a blood clot blocks an artery. This stops blood from reaching important organs. It’s often linked to cardiovascular events like heart attacks and strokes.
- Typically occurs in arteries supplying the heart or brain
- Often results from atherosclerosis or plaque rupture
- Can lead to acute limb ischemia or organ damage
Venous Thrombosis
Venous thrombosis is when a blood clot forms in a vein. It usually happens in the deep veins of the legs. This is also known as deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
- More common in individuals with limited mobility
- Risk factors include genetic predispositions, surgery, and cancer
- Can lead to complications like pulmonary embolism if left untreated
Pulmonary Thrombosis
Pulmonary thrombosis, or pulmonary embolism, happens when a blood clot reaches the lungs. It can block blood flow and is a serious condition that needs immediate care.
The severity of pulmonary thrombosis can vary. But it’s always a medical emergency. Knowing the risk factors and symptoms is vital for quick diagnosis and treatment.
Thrombosis Terminology Across Languages and Cultures
Thrombosis terms differ a lot in various languages and cultures. As healthcare connects more globally, knowing these differences is key. It helps doctors talk clearly with each other and with patients.
Thrombosis in English Medical Literature
In English, thrombosis means a blood clot in a blood vessel. It’s a big topic in medical studies and practice. Doctors use a common set of words to talk about it.
A top medical journal says knowing what thrombosis is is vital. It’s key for diagnosing and treating it.
International Variations: Thrombis, Trombos, Tromboza
In other countries, the words change. For example, thrombis, trombos, and tromboza are used in some places. These differences can cause confusion, mainly in international health settings or when traveling for medical care.
- Thrombis is used in some Eastern European languages.
- Trombos is found in certain Romance languages.
- Tromboza is commonly used in Slavic languages.
Understanding Terms: Trbosis, Trombosus, and Thrombose in English
Some English medical texts use trbosis, trombosus, and thrombose. These words come from translations or old usage. Doctors in diverse settings need to know these terms.
“The diversity in thrombosis terminology highlights the need for clear communication and education in global healthcare.”
Knowing these differences helps us better care for patients. It also makes international medical work more effective.
Risk Factors Contributing to Thrombosis Development
Knowing the risk factors for thrombosis is key to managing it. Thrombosis is when blood clots form inside vessels. It can be caused by genetics, lifestyle, and medical conditions.
Genetic Predispositions
Genetics play a big role in thrombosis. People with a family history of blood clots are at higher risk. Certain genetic mutations, like Factor V Leiden, can also increase clotting tendency.
While we can’t change our genes, knowing them helps. It lets us take preventive steps. For example, those at risk can get regular check-ups and talk to their doctor about their risk.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Lifestyle and environment also play a big part. Sedentary behavior and long-distance travel can raise the risk of blood clots. Other factors like smoking, obesity, and high blood pressure also increase the risk.
- Smoking
- Obesity
- High blood pressure
Changing these factors can lower the risk of thrombosis. It can also help prevent heart disease.
Medical Conditions That Increase Risk
Some medical conditions raise the risk of thrombosis. Cancer, heart disease, and autoimmune disorders are examples. Managing these conditions is key to preventing blood clots.
Surgery and hospital stays also increase the risk due to being immobile for long periods. To prevent this, doctors often use anticoagulant medications and mechanical devices.
In summary, knowing the risk factors for thrombosis is vital. By addressing genetics, lifestyle, and medical conditions, we can lower the risk of blood clots. This improves patient outcomes.
Recognizing Symptoms of Different Thrombotic Conditions
Knowing the signs of thrombotic conditions is key to better treatment. Blood clots can form in various parts of the body. This leads to different symptoms based on where and what type of clot it is.
Common Warning Signs
Symptoms of thrombosis vary. For example, a clot in a limb can cause pain, swelling, redness, and warmth. People often feel a heavy or aching sensation in the limb, which can be confused with other issues.
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) symptoms include swelling, pain, or tenderness in one leg. This is usually in the calf or thigh. The skin may turn red or discolored and feel warm. Yet, some people with DVT may not show any symptoms.
When to Seek Emergency Medical Attention
It’s important to know when to get help for thrombosis symptoms. If you have chest pain, shortness of breath, or severe headache, go to the emergency room. These could be signs of a pulmonary embolism or stroke, both serious.
If you have a history of thrombosis or are at risk, watch for warning signs. Being alert to unusual or severe symptoms is important. Don’t hesitate to get medical help.
In short, knowing the symptoms of thrombosis and when to get help can save lives. We urge everyone, but those at risk, to learn about these critical signs.
Define Thrombotic Complications and Their Impact
It’s important to know about thrombosis complications for good patient care. Thrombosis is when blood clots form in vessels. If not treated, it can be very dangerous.
When a clot breaks loose, it can travel and block another vessel. This can harm many organs and cause serious health problems.
Pulmonary Embolism: When Clots Travel to the Lungs
A pulmonary embolism happens when a clot reaches the lungs. It can block a lung artery. This is a serious condition that needs quick medical help.
Symptoms include sudden breath trouble, chest pain, and coughing up blood. If you see these signs, get emergency help right away.
Stroke: Thrombosis Affecting the Brain
A stroke happens when the brain doesn’t get enough blood. Thrombosis is a main cause, often from a brain-supplying vessel clot.
Knowing stroke signs is key. Look for sudden weakness, trouble speaking, and vision changes.
“Time is brain” when it comes to stroke treatment, stressing the need for fast action to reduce brain damage.
Myocardial Infarction: Heart-Related Complications
A myocardial infarction, or heart attack, is when heart blood flow is blocked. Thrombosis is a main cause, often from a coronary artery clot.
Symptoms include chest pain, breath trouble, and arm or stomach pain.
| Condition | Common Symptoms | Impact |
| Pulmonary Embolism | Sudden shortness of breath, chest pain | Life-threatening, requires immediate care |
| Stroke | Sudden weakness, difficulty speaking | Can cause permanent brain damage |
| Myocardial Infarction | Chest pain, shortness of breath | Can lead to heart damage or death |
We need to understand these complications to care for patients at risk. Early treatment is vital for better outcomes.
Diagnostic Approaches for Identifying Thrombosis
Diagnosing thrombosis requires a mix of clinical checks and advanced tests. We examine patients physically, review their medical history, and use imaging and lab tests. This helps us pinpoint thrombosis accurately.
Physical Examination and Medical History
Checking a patient’s physical state and medical background is key. We look for swelling, redness, and warmth in limbs. We also check for pain or tenderness. Knowing a patient’s medical history helps us spot risk factors like recent surgery or family history of thrombosis.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging is vital for confirming thrombosis. We employ:
- Ultrasound: This non-invasive method uses sound waves to see blood flow and find clots in veins.
- Computed Tomography (CT) scans: CT scans give detailed images of the body’s inside, helping spot clots in places like the lungs.
- Venography: Though less used, venography involves injecting a contrast agent into veins to see clots.
Laboratory Tests and Biomarkers
Labs play a big role in diagnosing thrombosis and checking for complications. We run:
- D-dimer test: This blood test checks D-dimer levels, a sign of clot dissolution. High levels suggest thrombosis, but can also mean other conditions.
- Blood tests for clotting factors: We test clotting factor levels to understand a patient’s coagulation status.
By using these methods together, we can accurately diagnose thrombosis. Then, we create a treatment plan that fits each patient’s needs.
Treatment Options and Management Strategies
Managing thrombosis well means knowing about medicines, surgery, and lifestyle changes. It’s key to understand the different ways to treat it. This helps us tackle thrombotic complications effectively.
Anticoagulant Medications
Anticoagulants are vital in treating thrombosis. They stop new clots from forming and prevent existing ones from growing. Common ones include warfarin, apixaban, rivaroxaban, and dabigatran. The right medicine depends on the patient’s health and the clot’s location.
- Warfarin: Needs regular blood tests to get the dose right.
- Apixaban and Rivaroxaban: Don’t need blood tests as often, making them easier for some.
- Dabigatran: Works fast and is often used to prevent strokes in people with atrial fibrillation.
A leading medical journal says new oral anticoagulants have changed how we treat thrombosis. They offer better and more reliable treatment options.
“The use of anticoagulants has become more streamlined with the advent of newer agents that have a more predictable pharmacokinetic profile.”
Surgical and Interventional Approaches
Sometimes, just medicine isn’t enough. Surgery or interventional procedures might be needed. These include removing the clot, angioplasty, and stenting to keep arteries open.
- Thrombectomy: Surgery to remove the clot, used for severe cases.
- Angioplasty and Stenting: Procedures to open blocked arteries and keep them open.
Lifestyle Modifications for Management
Changing your lifestyle is key in managing thrombosis and preventing it from coming back. Patients should:
- Keep a healthy weight to reduce vein pressure.
- Exercise regularly to improve blood flow.
- Avoid sitting or lying down for too long.
- Eat a balanced diet with lots of fruits, veggies, and whole grains.
By using these treatment options and lifestyle changes, people with thrombosis can live better lives. The term trombosus highlights the need for a full approach to managing clotting issues.
Prevention Strategies and Living with Thrombosis Risk
To prevent thrombosis, we need a mix of healthy habits and sometimes medical help. Knowing what causes clots helps us find ways to lower the risk.
Daily Habits to Reduce Risk
Healthy daily habits are key to avoiding thrombosis. Eating well, drinking plenty of water, and exercising regularly are important. Exercise boosts blood flow and helps keep weight in check, lowering thrombosis risk. It’s also wise to avoid sitting for too long, like on long flights or in bed.
“Regular movement is key to preventing blood clots,” says why staying active is so important. Even small steps or stretches can help a lot.
Medical Preventive Measures
For those at higher risk, medical steps might be needed. This could mean taking anticoagulant drugs to stop blood clots. Anticoagulants are vital for managing risk, mainly for those prone to clots or with certain health issues.
Compression stockings might also be suggested to help blood flow and prevent DVT. “The right preventive steps can greatly lower thrombosis risk and its complications,” showing how important medical advice is.
Combining healthy habits with medical care is key to fighting thrombosis. By staying informed and working with doctors, we can manage our risk well.
“Prevention is always better than cure, specially with thrombosis. Healthy habits and medical advice can greatly reduce this serious condition’s risk.”
Conclusion: Advances in Thrombosis Research and Treatment
Understanding thrombosis is key to knowing its causes, symptoms, and types. This includes the serious case of pulmonary thrombosis. Thanks to medical research and technology, we can now diagnose and treat thrombotic conditions better.
Studies and clinical trials keep improving our understanding of thrombosis. This leads to more effective treatments and better results for patients. For example, new medicines and imaging tools have changed how we manage thrombosis.
It’s important to stay informed about thrombosis, its risks, and what it means. By doing this, we can lower the number of thrombotic events. This helps improve the lives of those affected, including those at risk of pulmonary thrombosis, as explained on Wikipedia.
FAQ
What is thrombosis and how does it occur?
Thrombosis is when a blood clot blocks a blood vessel. It happens when platelets and fibrin come together. This can be due to injury, inflammation, or genetics.
What are the different types of thrombosis?
There are several types of thrombosis. These include arterial, venous, and pulmonary thrombosis. Each type affects health differently.
What is the difference between arterial and venous thrombosis?
Arterial thrombosis blocks arteries and can cause heart attacks or strokes. Venous thrombosis blocks veins and often leads to deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
How is thrombosis diagnosed?
Doctors use physical exams, medical history, and imaging like ultrasound and CT scans. They also do lab tests, like D-dimer assays.
What are the risk factors for developing thrombosis?
Risk factors include genetics, lifestyle choices like smoking, and certain medical conditions. These can increase the chance of getting thrombosis.
What are the symptoms of thrombosis?
Symptoms depend on the type and location of the thrombosis. Common signs are pain, swelling, and redness in limbs. Shortness of breath or chest pain can also occur.
How is thrombosis treated?
Treatment includes anticoagulant medications and surgery. Lifestyle changes are also important to prevent more clots. The treatment plan varies based on the type and severity.
What is thrombis, trombos, or tromboza?
Thrombis, trombos, and tromboza are terms for thrombosis in different languages. Knowing these terms helps in international healthcare communication.
How can I reduce my risk of developing thrombosis?
To lower your risk, live a healthy lifestyle. This includes regular exercise, a balanced diet, and not smoking. Managing health conditions and following preventive measures also helps.
What are the complications of thrombosis?
Complications include pulmonary embolism, stroke, and myocardial infarction. These can have serious effects on health and outcomes.
References
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (2022). Venous Thromboembolism. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/venous-thromboembolism


































