Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
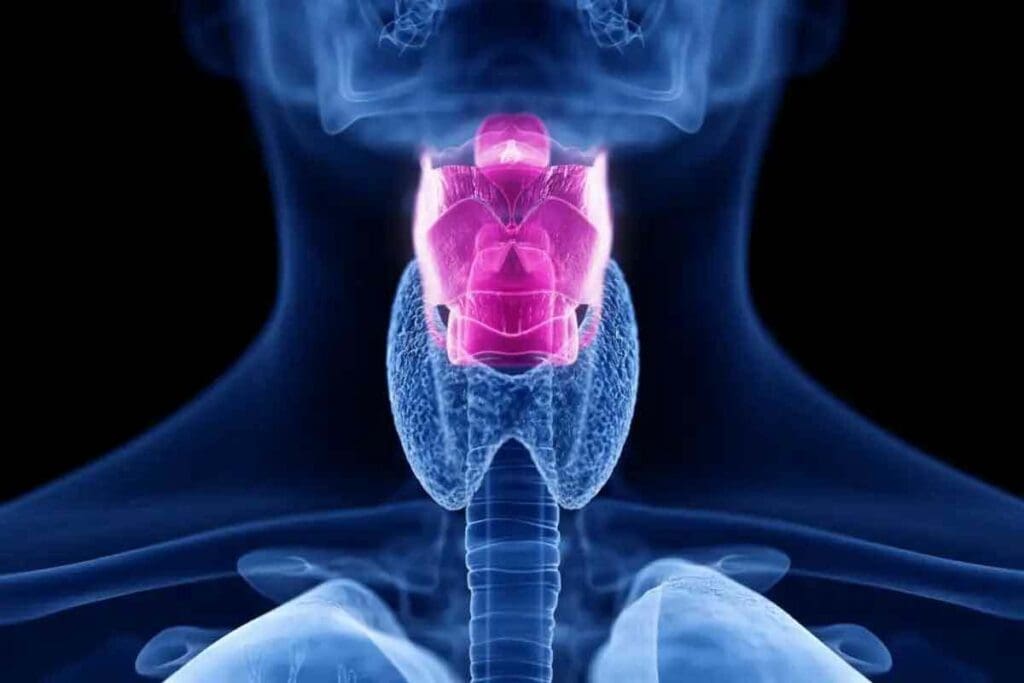
A thyroid CT with contrast is a detailed imaging test that uses iodinated contrast agents to provide clear images of the thyroid gland. This scan is essential for detecting thyroid problems such as nodules, cysts, goiters, and cancers.
Understanding what to expect during a thyroid CT with contrast can help reduce anxiety and prepare you for the procedure. In this guide, we cover seven important facts about thyroid CT scans—from preparation to interpreting results—drawing on the expertise of Liv Hospital to ensure accurate and safe testing.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the role of contrast agents in thyroid CT scans
- Preparation steps for a thyroid CT scan
- What to expect during the scanning process
- Potential risks and side effects associated with thyroid CT scans
- How thyroid CT scans aid in diagnosing thyroid conditions
- The significance of accurate imaging for treatment planning
- Insights into interpreting thyroid CT scan results
Understanding Thyroid CT Scans
Thyroid CT scans use X-rays to show detailed images of the neck, including the thyroid gland. This tool is key for doctors to see the thyroid’s shape and spot problems.
What Is a Thyroid CT Scan?
A thyroid CT scan is a non-invasive test that uses X-rays to show the thyroid gland and nearby areas. It helps doctors understand the gland’s size, shape, and any issues.
When you get a thyroid CT scan, you lie on a table that moves into a CT scanner. The scanner moves around you, taking pictures from different angles. These pictures are then put together to show the thyroid gland in detail.
How CT Imaging Differs from Other Thyroid Tests
CT imaging is different from other thyroid tests, like ultrasound or nuclear medicine. Ultrasound is great for looking at the thyroid gland and finding nodules. But CT scans show more, including the neck’s surrounding tissues.
According to radiology.ucsf.edu, CT scans are best for seeing how far thyroid disease has spread or if lymph nodes are involved. They are also good in emergencies or when a detailed look is needed.
The Role of Contrast in Thyroid CT With Contrast
Contrast-enhanced CT scans of the thyroid gland give a clearer view of the thyroid’s anatomy and any issues. This clear view is key to making accurate diagnoses and planning treatments.
What Is Iodinated Contrast?
Iodinated contrast agents are used in CT scans to make internal structures more visible. These agents contain iodine, which absorbs x-rays and shows up bright on CT images. This makes it easier to see the differences between different tissues.
Iodinated contrast is very helpful in thyroid imaging because it makes the thyroid gland and nearby structures stand out. It’s a common practice in many CT scan procedures, including those for the thyroid.
How Contrast Enhances Thyroid Visualization
When contrast is given during a thyroid CT scan, it makes the thyroid gland much clearer. Contrast agents highlight the differences between tissues. This helps spot issues like nodules, cysts, or tumors.
Enhanced visualization lets radiologists better see the size, shape, and density of the thyroid gland. This is important for diagnosing thyroid problems and figuring out the best treatment.
Benefits of Using Contrast for Thyroid Imaging
Using contrast in thyroid CT scans has many benefits. It improves how well doctors can diagnose and see the thyroid’s anatomy. Contrast agents help spot problems and plan treatments more effectively.
- Improved diagnostic accuracy
- Enhanced visualization of thyroid anatomy
- Better detection of abnormalities
- More effective treatment planning
In conclusion, contrast plays a big role in thyroid CT scans. It makes CT scans more accurate and helps in better patient care.
When Is a Thyroid CT Scan Necessary?
A thyroid CT scan is needed in many medical situations. It’s used when serious thyroid conditions are suspected. Other imaging methods, like ultrasound, are often used first. But CT scans offer more detailed information in complex cases.
Common Medical Indications
A thyroid CT scan is often needed when symptoms or signs suggest thyroid problems. Some common reasons include:
- Suspicion of thyroid nodules or goiter
- Assessment of thyroid gland size and position
- Evaluation of thyroid cancer or metastasis
- Investigation of thyroiditis or other inflammatory conditions
Table 1: Common Indications for Thyroid CT Scan
When CT Is Preferred Over Ultrasound
Ultrasound is usually the first choice for thyroid imaging. But there are times when a CT scan is better. This is true for substernal thyroid glands or when cancer might have spread beyond the gland. CT scans give a clearer view of the gland and nearby areas.
Complex Cases Requiring Advanced Imaging
In complex cases, like large goiters or suspected cancer, a CT scan is key. It helps doctors plan surgeries better. The detailed images from CT scans guide them in making the right decisions.
Knowing when to use a thyroid CT scan helps doctors better diagnose and treat thyroid issues. This leads to better health outcomes for patients.
| Indication | Description |
| Suspicion of Thyroid Nodules | Evaluation of nodule size, number, and characteristics |
| Thyroid Cancer Assessment | Staging and evaluating the extent of thyroid cancer |
| Thyroiditis Investigation | Assessing inflammation and thyroid gland damage |
Normal Thyroid CT Scan Appearance
Knowing what a normal thyroid gland looks like on CT scans is key to correct diagnosis and treatment. The thyroid gland is shaped like a butterfly and sits in the neck, around the trachea. On CT scans, it shows up as soft tissue with a specific density and how it looks after contrast.
Typical Thyroid Anatomy on CT
The thyroid gland has two lobes joined by an isthmus. On CT scans, it looks symmetrical with smooth, even lobes. It’s usually in front of the trachea and next to the laryngeal cartilages.
Normal Density and Enhancement Patterns
Without contrast, the thyroid gland looks denser than muscles because of its iodine. After contrast, it enhances a lot, making it easier to see its shape and any issues. The enhancement is usually even, but sometimes it can look a bit different.
Common Anatomical Variations
There are common variations in thyroid anatomy that doctors need to know about. These include different gland sizes, a pyramidal lobe, and sometimes uneven lobes. Knowing these variations helps doctors not mistake them for diseases.
In summary, knowing the normal thyroid gland on CT scans is vital for accurate diagnosis. By understanding its typical look, density, and how it changes with contrast, doctors can spot problems and help patients better.
Abnormal Thyroid CT Scan Findings
Abnormal thyroid CT scans can show different thyroid issues, like benign nodules or cancer. Radiologists look for signs that might mean thyroid problems.
Hypodense Thyroid Nodules
Hypodense thyroid nodules are darker than the thyroid tissue on CT scans. They might be harmless or cancerous. Finding hypodense thyroid nodules on a CT scan usually means more tests are needed.
Signs of Malignancy on CT
Some CT scan features suggest cancer. These include irregular shapes, tiny calcium spots, and growth into nearby areas. Signs of malignancy on CT scans help spot cancerous nodules.
Thyroid Cysts and Goiters
Thyroid cysts are fluid-filled areas in the thyroid gland on CT scans. Goiters are when the thyroid gland gets bigger. Both can be seen on thyroid CT scans, with goiters showing a bigger thyroid.
Metastatic Disease Appearance
CT scans can spot thyroid cancer spread. This looks like bigger lymph nodes or growths in the neck. The appearance of metastatic disease on a thyroid CT scan is key for cancer staging and treatment planning.
It’s important to understand these abnormal findings on thyroid CT scans for diagnosing and treating thyroid issues. Radiologists and doctors work together to read these scans and decide what to do next.
Preparing for Your Thyroid CT With Contrast
To get the most out of your thyroid CT scan with contrast, following specific pre-scan instructions is key. Proper preparation is vital for accurate diagnostic results.
Pre-Scan Instructions
Before the scan, patients may need to remove jewelry or metal objects. They should wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing. Also, arriving early to complete paperwork is important.
Medication Considerations
Certain medications might need to be adjusted or stopped before the scan. Inform your healthcare provider about all medications, including diabetes meds and thyroid meds. This includes any that could interact with the contrast agent.
Fasting Requirements
Fasting for 4-6 hours before the scan is common. But the exact time may vary based on your healthcare provider’s instructions.
The Thyroid CT Scan Procedure: Step by Step
Learning about the thyroid CT scan process can help ease anxiety for those getting this test. A thyroid CT scan with contrast uses advanced imaging to show detailed pictures of the thyroid gland. This helps doctors diagnose and track thyroid issues.
Before the Scan
Before a thyroid CT scan, patients get certain instructions. These include:
- Removing any jewelry or metal objects that could interfere with the scan
- Informing the doctor about any allergies, especially to iodine or contrast dye
- Disclosing any medical conditions, such as kidney disease or diabetes
- Informing the doctor about any medications being taken
During the CT Scan
During the CT scan thyroid gland process, the patient lies on a table that slides into the CT scanner. The scanner takes X-ray images from multiple angles. These images are then made into detailed pictures of the thyroid gland.
| Step | Description |
| 1 | The patient is positioned on the CT table, usually on their back. |
| 2 | The table slides into the CT scanner, a large, doughnut-shaped machine. |
| 3 | The CT scanner rotates around the patient, taking X-ray images. |
| 4 | The patient may be asked to hold their breath for a few seconds during the scan. |
Contrast Administration Process
The thyroid CT scan with contrast uses a contrast dye to make the thyroid gland and nearby structures more visible. The dye is injected into a vein in the arm.
Duration and Positioning
The whole CT thyroid scan takes about 10 to 30 minutes. The patient must stay very quiet during the scan to get clear images. The table might move a bit as the scanner takes pictures from different angles.
By knowing these steps, patients can prepare better for the thyroid CT scan. This can help reduce anxiety and make the experience smoother.
Potential Risks and Side Effects of Thyroid CT With Contrast
Thyroid CT scans with contrast are usually safe. But theree are risks and side effects to know about. It’s important to understand these to make informed choices.
Common Contrast Reactions
Contrast agents in CT scans can cause reactions. These can be mild or severe.
- Mild reactions may include nausea, vomiting, and itching.
- Moderate reactions can involve hives, rash, and facial swelling.
- Severe reactions, though rare, can be life-threatening. They include symptoms like difficulty breathing and a sudden drop in blood pressure.
Thyroid-Specific Concerns
Iodinated contrast in thyroid CT scans can affect thyroid function. This is a concern for those with pre-existing thyroid conditions.
Some patients may see changes in thyroid hormone levels after iodinated contrast. This is more common in those with thyroid disease.
Radiation Exposure Considerations
CT scans expose you to ionizing radiation. This carries a small risk of cancer. The risk is higher with more scans or in younger patients.
| Radiation Exposure Factors | Considerations |
| Age | Younger patients are at higher risk due to their longer life expectancy. |
| Number of Scans | Multiple CT scans increase cumulative radiation exposure. |
| Scan Protocol | Low-dose protocols can minimize radiation exposure. |
Who Should Avoid Contrast CT
Certain individuals should avoid or take precautions before a contrast-enhanced CT scan.
- Patients with severe kidney disease may need to avoid iodinated contrast due to the risk of contrast-induced nephropathy.
- Those with a history of severe allergic reactions to contrast agents should inform their healthcare provider.
- Pregnant women should discuss the risks and benefits with their doctor, as contrast agents can cross the placenta.
After Your CT Scan of the Thyroid Gland
After a thyroid CT scan, you might wonder what happens next. The journey doesn’t stop with the scan. There are steps like post-scan care and waiting for results.
Immediate Post-Scan Care
Usually, you can go back to your normal routine right after the CT scan of the thyroid gland. But, your doctor might give you some special instructions, like if you got contrast dye.
It’s key to listen to your healthcare team’s advice. Often, they’ll tell you to drink lots of water. This helps get rid of the contrast dye.
Contrast Clearance Timeline
The dye used in a thyroid CT scan goes out through your kidneys and urine. It takes a few days to a week to clear out.
| Time Frame | Contrast Clearance Progress |
| First 24 hours | The majority of contrast is excreted |
| 2-3 days | Contrast levels significantly decrease |
| 1 week | Contrast is usually fully cleared |
When to Expect Results
How long it takes to get your thyroid CT scan results can vary. Usually, your doctor gets the images and report in a few hours to a couple of days.
Your doctor will then talk to you about the results. They’ll explain what they mean for your health and what to do next.
Knowing what happens after a CT thyroid gland scan can ease your worries. It helps you get ready for what’s next.
CT Scan vs. Other Thyroid Imaging Methods
There are many ways to image the thyroid, each with its own benefits and drawbacks. The right choice depends on the situation, the patient, and what information is needed for diagnosis and treatment.
CT vs. Ultrasound for Thyroid Assessment
Ultrasound is often the first choice for thyroid imaging. It’s non-invasive, doesn’t use radiation, and is affordable. But CT scans have their own strengths. They give detailed images that are important for seeing how far thyroid disease has spread or for checking on goiters that go into the chest.
A leading radiologist says, “CT scans are great when we need to see how the thyroid relates to nearby structures. This is true for suspected cancer or big goiters that go into the chest.” This shows how CT scans can help in thyroid imaging.
- CT scans are better for evaluating large or substernal goiters.
- Ultrasound is preferred for routine thyroid nodule assessment.
- CT provides better visualization of lymph node metastases.
CT vs. MRI for Thyroid Evaluation
MRI is good for seeing soft tissues and is great for checking how far thyroid disease has spread. But CT scans have some benefits too. They are faster and better at showing calcifications in thyroid nodules.
| Imaging Modality | Strengths | Limitations |
| CT | Detailed cross-sectional imaging, fast acquisition | Radiation exposure, contrast use |
| MRI | Excellent soft tissue contrast, no radiation | Longer examination times, higher cost |
CT vs. Nuclear Medicine Studies
Nuclear medicine studies, like thyroid scans with radioactive iodine or technetium, show how the thyroid works. CT scans, on the other hand, give detailed pictures of the thyroid’s structure. The choice depends on whether you need to know about the thyroid’s anatomy or function.
In summary, while CT scans have their own limits, they are very useful in some cases. They are an important part of checking thyroid disorders.
Advances in Thyroid CT Imaging Technology
New CT imaging tech has changed how we diagnose and treat thyroid issues. It has made images clearer and cut down on radiation. This makes CT scans safer and more useful for doctors.
Low-Dose CT Protocols
Low-dose CT scans are a big step forward. They use less radiation but keep image quality high. A study on the National Center for Biotechnology Information shows they’re safe and effective.
Benefits of Low-Dose CT:
- Less radiation
- More patient safety
- Images as good as regular CT scans
Dual-Energy CT Applications
Dual-energy CT (DECT) is another big leap. It uses two X-ray levels to give more detailed tissue info.
Advantages of DECT:
- Better thyroid nodule details
- Clearer differentiation of thyroid issues
- Spotting iodine contrast better
3D Reconstruction Techniques
Three-dimensional (3D) reconstructions are key in thyroid CT scans. They help doctors see the thyroid’s anatomy and problems better.
| Technique | Benefits | Clinical Applications |
| Low-Dose CT | Less radiation | Thyroid imaging |
| Dual-Energy CT | Better tissue info | Thyroid nodule checks |
| 3D Reconstruction | Full view of anatomy | Planning and follow-up for surgery |
These new CT imaging techs have boosted accuracy, safety, and results for patients. As tech keeps improving, we’ll see even better ways to handle thyroid problems.
Conclusion: Making Informed Decisions About Thyroid CT Scans
It’s important to understand the role of thyroid CT with contrast and the can of the thyroid gland. This knowledge helps patients make smart choices about their health.
A thyroid CT scan shows detailed images of the thyroid gland. It helps doctors find and treat problems in the gland.
Knowing the good and bad of CT thyroid scans helps patients. They can then make better choices during their diagnosis and treatment.
Being well-informed lets patients talk better with their doctors. This ensures they get the right care for their thyroid issues.
FAQ
What is a thyroid CT scan with contrast?
A thyroid CT scan with contrast uses X-rays and a special dye to show the thyroid gland in detail. It helps doctors find and diagnose thyroid problems.
How does a thyroid CT scan differ from a thyroid ultrasound?
A thyroid CT scan shows more details of the thyroid gland and nearby areas. On the other hand, a thyroid ultrasound is better for checking thyroid nodules and cysts.
What is the role of contrast in a thyroid CT scan?
The contrast dye makes the thyroid gland and nearby areas clearer. This helps doctors make more accurate diagnoses of thyroid conditions.
What are the benefits of using contrast for thyroid imaging?
Using contrast helps find thyroid nodules, cysts, and other issues more easily. It also helps tell the difference between harmless and harmful growths.
When is a thyroid CT scan necessary?
A thyroid CT scan is needed for complex thyroid cases or when cancer is suspected. It’s also used when other tests don’t give clear results.
What is the normal appearance of the thyroid gland on a CT scan?
The normal thyroid gland looks like a butterfly on a CT scan. It has a uniform shape and density, with a specific enhancement pattern.
What are hypodense thyroid nodules on a CT scan?
Hypodense thyroid nodules are areas in the thyroid gland that are less dense. They could be harmless or cancerous, so they need more checking.
How do I prepare for a thyroid CT scan with contrast?
To get ready for a thyroid CT scan with contrast, follow the instructions given. Tell your doctor about any medications or allergies you have. Also, you’ll need to fast for a certain time.
What are the possible risks and side effects of a thyroid CT scan with contrast?
Risks and side effects include reactions to the contrast dye, thyroid issues, radiation exposure, and allergic reactions.
What should I expect after a thyroid CT scan?
After a thyroid CT scan, you’ll get immediate care. The contrast dye will be cleared from your body. You’ll get the results in a few days or weeks.
How does a thyroid CT scan compare to other thyroid imaging methods?
A thyroid CT scan offers more detail than an ultrasound. But, it might not be as good as an MRI or nuclear medicine study for some thyroid issues.
What are the advances in thyroid CT imaging technology?
New technology in thyroid CT imaging includes low-dose scans, dual-energy CT, and 3D images. These advancements improve image quality and reduce radiation.
What is the significance of a hypodense thyroid nodule on a CT scan?
A hypodense thyroid nodule on a CT scan might mean it’s benign or cancerous. It needs more tests to figure out what it is.
Can I undergo a thyroid CT scan if I have a thyroid condition?
Yes, you can have a thyroid CT scan even with a thyroid condition. Just tell your doctor about your condition and any medications you’re taking.
References:
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2022). Thyroid uptake and scan. StatPearls. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK555978/
- Acıbadem University Medical Ethics Committee. (2025). Comparison of AI-TIRADS and established thyroid nodule classification systems in CT and ultrasound: A diagnostic accuracy study. Diagnostic Imaging Reports, 15(4), 340-352. https://www.dirjournal.org/articles/comparison-of-the-diagnostic-performance-of-the-artificial-intelligence-based-tirads-algorithm-with-established-classification-systems-for-thyroid-nodules/doi/dir.2025.253428