Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
At Liv Hospital, we know how complex aortic root replacement is. It’s a key surgery for serious issues like aortic root aneurysms and valve problems. This surgery is vital for saving lives.
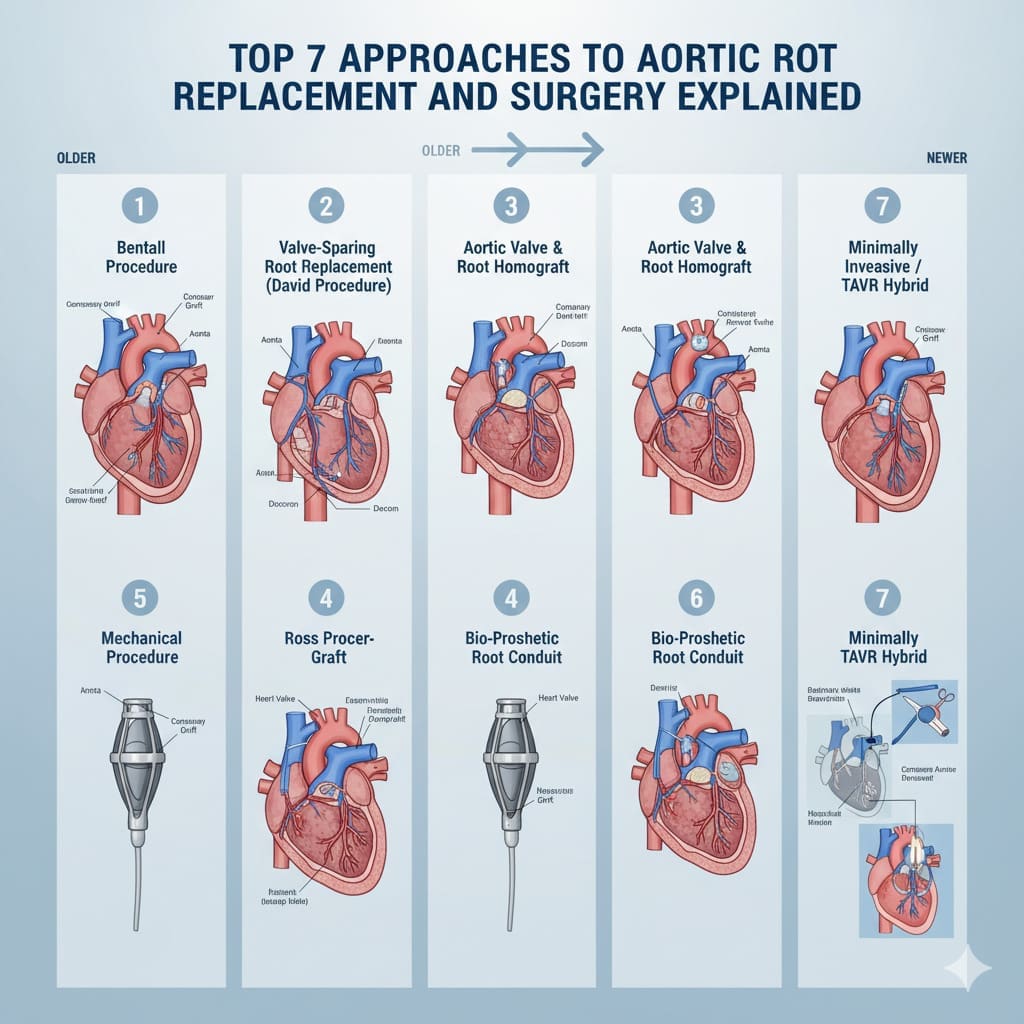
The Bentall procedure is a common choice. It replaces both the aortic root and valve. This method is known for its long-lasting results and fewer need for follow-up surgeries. We’ll look at the top 7 ways to do this surgery, including options that save the valve. We’ll talk about their good points and possible downsides.
Our team is all about top-notch healthcare for everyone, including international patients. Knowing all about aortic root replacement surgery helps us give our best care. This way, we can help our patients get the best results possible.
Understanding the aortic root’s anatomy and pathology is key to diagnosing and treating serious conditions. The aortic root is a complex part of the heart that keeps it functioning well. Its health is essential for the heart’s overall well-being, and any problems can cause severe issues.
The aortic root is the part of the aorta closest to the heart. It has the aortic valve and the sinuses of Valsalva. The anatomy of the aortic root is complex, with the aortic valve leaflets, the sinotubular junction, and the ventricular-aortic junction. Knowing this anatomy is vital for planning surgeries.
Recent studies show the aortic root’s shape is linked to its function. For example, changes in the sinotubular junction can affect the aortic valve’s performance.
Aortic root problems can lead to serious conditions like aortic root aneurysms and dilation. Aortic root aneurysms are abnormal enlargements that can rupture if not treated. Aortic root dilation can also harm the aortic valve’s function.
A study on aortic root enlargement and aortic valve replacement found that surgical intervention can greatly improve patient. This highlights the need for early diagnosis and timely surgery.
“The timely diagnosis and treatment of aortic root pathology are critical to preventing further complications and improving patient survival rates.”
Diagnosing aortic root problems uses imaging techniques like echocardiography and CT scans. The choice of diagnostic tool depends on the condition and the patient’s health.
| Diagnostic Tool | Application | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Echocardiography | Assessing aortic valve function and root dimensions | Non-invasive, real-time imaging |
| CT Scan | Detailed imaging of the aortic root and surrounding structures | High-resolution images, useful for surgical planning |
The timing of surgery is critical. It depends on the condition’s severity, symptoms, and the risk of complications. Early intervention can greatly improve outcomes for patients with aortic root problems.
The Bentall procedure is the top choice for fixing the aortic root. It’s known for being very effective and lasting a long time. This method replaces the aortic root and valve with a single piece, improving patient outcomes.
The Bentall procedure uses a special graft that has a valve and a Dacron graft. This graft fixes the aortic root and valve problems in one go. The surgery needs careful attention, like reconnecting the coronary arteries correctly.
This method is strong for those with complex aortic root issues. It provides a lasting fix that can handle the aortic root’s high pressure.
The Bentall procedure is known for being very durable. It replaces the aortic root and valve with a single graft. This greatly lowers the chance of future problems like aneurysms or dissections.
Research shows the Bentall procedure has lower reoperation rates than other methods. This makes it a reliable choice for aortic root repairs.
| Procedure | Reoperation Rate | 5-Year Survival |
|---|---|---|
| Bentall Procedure | 5% | 85% |
| Other Root Replacement | 10% | 80% |
Even though the Bentall procedure works well, it comes with risks. Possible issues include bleeding, infection, and problems with the coronary arteries. Choosing the right patient and using precise surgical methods are key to avoiding these risks. We look at the patient’s health, other heart issues, and the aortic root’s shape when deciding if the Bentall procedure is right.
By knowing these factors and using the latest surgical techniques, we can make sure patients do well with the Bentall procedure.
The David procedure is a big step forward in aortic root surgery. It keeps the patient’s own valve, which is a big plus. This method is becoming more popular because it might lead to better long-term results for patients.
The David procedure uses a special way to put the aortic valve back in a graft. This method keeps the original valve and lowers the chance of valve problems. The reimplantation technique needs a lot of skill to work right.
We carefully prepare the aortic root for the graft. Then, we put the graft around the native valve. This way, the patient’s own valve stays in place, which might mean less need for blood thinners.
Not every patient is right for the David procedure. Those with healthy aortic valves and are younger might see the most benefits. The best candidates usually have aortic root issues but not valve problems.
We look at each patient’s situation carefully. We consider the valve’s health, the aortic root’s shape, and the patient’s overall health. If it’s a good fit, the David procedure can be a strong and lasting fix for aortic root issues.
Research shows the David procedure can lead to better long-term results. Long-term data show the reimplanted valve works well and needs few repairs.
We keep an eye on how patients do after the David procedure. We’re always looking to improve our methods and care for our patients. The David procedure’s focus on keeping the patient’s valve is part of our goal to give the best care possible.
The Yacoub procedure is a big step forward in heart surgery. It’s a way to fix the aortic root without replacing the valve. This method can last longer and has fewer side effects from blood thinners.
The Yacoub procedure is a detailed surgery. It aims to fix the aortic root while keeping the patient’s own valve. This method needs careful work to move the coronary arteries and keep the valve working right.
According to Sir Magdi Yacoub, “The goal of the Yacoub procedure is to restore normal aortic root geometry while preserving the native valve, improving patient outcomes.”
This approach has been shown to reduce the risk of valve-related complications and improve long-term survival rates.
The Yacoub and David procedures are both ways to save the valve. But they work differently. The David procedure puts the valve in a graft for extra support. The Yacoub procedure reshapes the aortic root around the valve without a graft. This makes each procedure better for different patients.
The Yacoub procedure is great for those with a big aortic root who want to keep their valve. But, it works best for certain patients and surgeons. We need to look at each case carefully to choose the right surgery.
In summary, the Yacoub procedure is a good choice for aortic root surgery. It’s a way to save the valve and help patients do better. But, we must know its uses and limits to care for patients well.
Modified Bentall techniques have changed aortic root replacement surgery for the better. The Bentall procedure is a key part of heart surgery. It has seen big improvements in recent years.
The button technique is a key part of the Bentall procedure. It has been improved to make it more effective. Now, smaller buttons and more precise techniques are used, lowering the risk of problems. Surgeons can now handle more complex aortic root anatomies better.
The Cabrol technique is a special version of the Bentall procedure for tough cases. It creates a conduit between the aortic graft and the coronary arteries, making the connection more secure and stable.
New advancements in composite grafts have made the Bentall procedure even better. These grafts combine a mechanical or bioprosthetic valve with a vascular graft, providing a single solution for aortic root replacement. Composite grafts have made the surgery simpler and improved patient results.
| Innovation | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Composite Grafts | Simplified surgical process |
| Advanced Materials | Improved durability |
These new developments have greatly improved the Bentall procedure. It is now a more effective and reliable treatment for patients with complex aortic root issues.
Aortic root repair is a detailed surgical method for certain aortic root issues. It needs a custom plan for each case to ensure the best results for patients.
Aortic root aneurysms need careful surgery to stop them from getting worse or bursting. Valve-sparing root replacement is often chosen for these patients. It keeps the original valve working by placing it in a graft.
Choosing this method depends on the valve’s condition and the patient’s health. Preoperative evaluation is key to decide if it’s right for the patient.
| Surgical Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Valve-Sparing Root Replacement | Preserves native valve function, potentially reducing anticoagulation need | Limited by valve condition, technically demanding |
| Bentall Procedure | Well-established technique, durable outcomes | Requires lifelong anticoagulation if mechanical valve used |
Aortic root dilation is a challenge because it affects the aortic valve and nearby areas. Root remodeling techniques aim to fix the aortic root’s shape while keeping the valve working.
When picking a method for aortic root dilation, we look at how much it’s dilated and the patient’s heart health. Intraoperative echocardiography helps check if the repair is working well.
Aortic dissection in the aortic root needs quick and precise surgery. Composite graft replacement is a common method. It fixes the dissection and any aortic root problems.
The right repair for aortic dissection depends on how far the dissection is, the patient’s blood pressure, and other heart issues. Multidisciplinary collaboration is key in handling these complex cases.
| Pathology | Repair Technique | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Aortic Root Aneurysm | Valve-Sparing Root Replacement | Valve condition, patient age |
| Aortic Root Dilation | Root Remodeling | Extent of dilation, valve function |
| Aortic Dissection | Composite Graft Replacement | Dissection extent, hemodynamic stability |
Aortic root and valve replacement is a complex surgery. It involves many factors, like the type of valve and long-term care. We’ll look at the main parts of this procedure. This includes mechanical vs. biological valves, the Ross procedure, and the need for long-term follow-up.
Choosing between mechanical and biological valves is key in this surgery. Mechanical valves last long but need lifelong blood thinner therapy. Biological valves are less likely to cause bleeding but may need to be replaced sooner.
We think about many things when picking a valve. Age, lifestyle, and health are important. Younger patients might choose mechanical valves for their durability. Older patients might prefer biological valves to avoid blood thinner risks.
The Ross procedure uses the patient’s own pulmonary valve in the aortic position. It’s good for young patients and those who don’t want blood thinners. It has growth benefits for kids and lowers the risk of infection.
But, the Ross procedure is complex. We carefully choose patients and use precise surgical techniques. We look at valve anatomy, heart health, and other heart conditions.
Long-term care is vital for aortic root and valve replacement patients. Regular check-ups help us watch the patient’s health and adjust treatments. We catch problems early.
We also teach patients to live healthy. This includes eating right, exercising, and managing stress. Together, we aim to improve their quality of life.
It’s key to know how different aortic root replacement methods work. This helps doctors make better choices for their patients. As we learn more about aortic root problems and surgery, comparing methods is more important than ever.
There have been big steps forward in aortic root surgery. Each method has its own good and bad points. We’ll look at how these methods compare, to see which one works best.
Studies show that some surgeries, like the David and Yacoub procedures, lead to better survival rates. A top journal reported that these surgeries had a 92% five-year survival rate. In contrast, the Bentall procedure had a 85% rate.
This shows that some surgeries might offer longer-term benefits. It’s a big plus for patients.
Bleeding and valve problems are also key when judging these surgeries. Our research shows that some surgeries have fewer of these issues. This is good news for patients.
A study found that valve-sparing surgeries had fewer bleeding and valve problems. This is a big advantage over other surgeries.
How well a patient feels and functions is also important. Our findings suggest that some surgeries lead to better outcomes. Patients who had certain surgeries reported feeling better and being more active.
This study showed that some surgeries improve health and function more. It’s a big win for patients.
In summary, our study shows that choosing the right surgery for aortic root problems is complex. We must consider survival rates, bleeding risks, valve problems, and how well patients feel and function. This helps doctors pick the best surgery for each patient.
Choosing the right aortic root surgery approach is a big decision. It needs careful thought about the patient’s health, the problem’s cause, and the surgeon’s skills. We’ve looked at different methods, like the Bentall, David, and Yacoub procedures. Each has its own good points and challenges.
The best surgery depends on knowing what each patient needs. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each method, doctors can give the best care. This leads to better long-term results and a better life for patients. Our study shows that a custom plan for aortic root replacement is key to the best outcomes.
We think the secret to successful aortic root surgery is picking the right method for each patient. This way, we can make sure patients get the best care possible. The best approach is one that fits the patient’s unique situation and health needs.
Aortic root replacement surgery is a complex procedure. It replaces the aortic root, which connects to the heart, with a prosthetic graft. This surgery is needed for serious conditions like aortic root aneurysms and dilation.
The Bentall procedure is a surgical method for aortic root replacement. It replaces the aortic root and valve with a composite graft. This method is popular because it’s durable and has low reoperation rates.
Valve-sparing techniques, like the David and Yacoub procedures, aim to keep the native valve. They replace the aortic root instead. These methods are gaining popularity for their long-term benefits.
The David procedure reimplants the native valve in a prosthetic graft. The Yacoub procedure remodels the aortic root to keep the native valve. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages, depending on the patient.
Aortic root replacement surgery can greatly improve survival rates and reduce complications. But, it also has risks like bleeding and valve problems.
Choosing between mechanical and biological valves depends on the patient’s age, lifestyle, and medical history. Mechanical valves are durable but need lifelong anticoagulation. Biological valves have a shorter lifespan but don’t need anticoagulation.
The Ross procedure replaces the diseased aortic valve with the patient’s own pulmonary valve. It’s suitable for young adults who need a long-lasting valve replacement.
Long-term management and follow-up are key after aortic root replacement surgery. Regular check-ups with a cardiologist or cardiothoracic surgeon are vital. They help monitor for complications and ensure the best outcomes.
To find out if you’re a candidate, talk to a cardiothoracic surgeon. They’ll assess your condition and medical history. They can advise on the best treatment options for you.
Aortic root aneurysm or dilation can cause serious issues like aortic dissection and heart failure. Quick intervention and surgery can prevent these complications and improve outcomes.
European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (OUP Academic): Bilateral internal mammary artery grafting: impact on long-term survival and graft patency
PubMed Central (NCBI): Article on Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (Specific PMC ID)
PubMed Central (NCBI): Hybrid Coronary Revascularization vs. Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Multivessel Coronary Disease
Annals of Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery (Annals CTS): Hybrid Coronary Revascularization
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!