Last Updated on November 4, 2025 by mcelik

Treatment challenges for bursitis are common for people dealing with joint pain and inflammation.
Bursitis is a condition where the fluid-filled sacs (bursae) around joints get inflamed, affecting millions worldwide. Almost 1 in 10 people experience bursitis at some point, and many struggle to find effective relief.
Living with bursitis can be challenging due to persistent pain and discomfort. It makes everyday tasks difficult and can also affect your mental health — making it important to tackle these treatment challenges head-on.
Key Takeaways
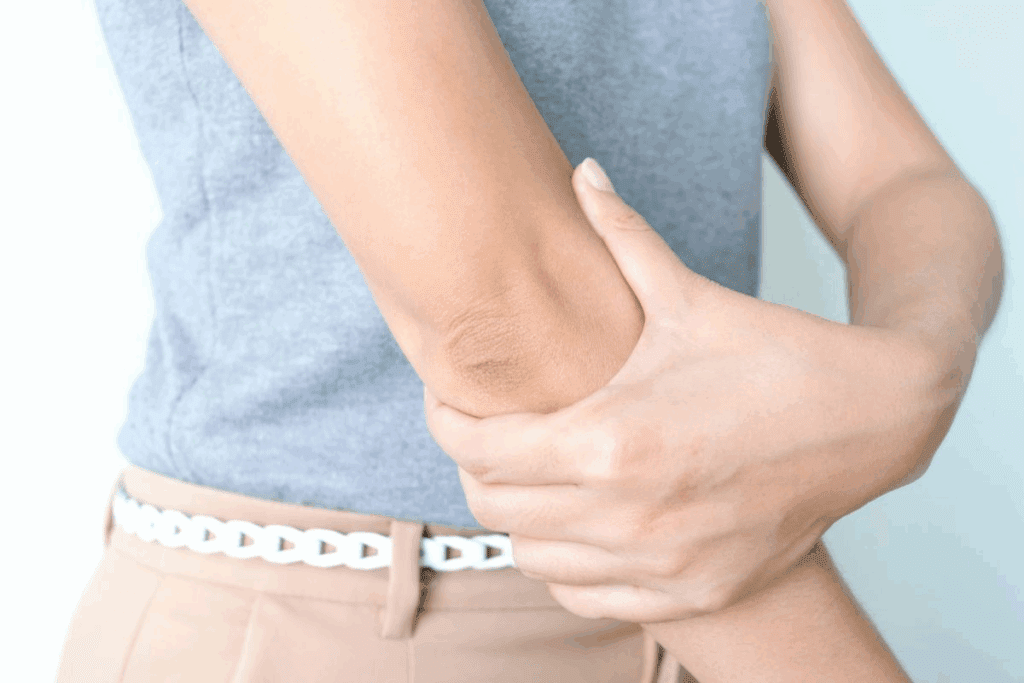
To tackle bursitis effectively, it’s essential to first comprehend what bursae are and how they function. Bursitis is a condition that involves the inflammation of bursae. These are fluid-filled sacs that cushion bones, tendons, and muscles near joints.
Understanding the nature of bursitis is key to addressing its complexities and finding the right treatments. We will explore the function of bursae, how inflammation occurs, and where bursitis commonly occurs.
Bursae are small, fluid-filled sacs that play a significant role in reducing friction between bones, tendons, and muscles. They act as cushions, allowing for smooth movement of joints. Normally, bursae are not noticeable, but when they become inflamed, they can cause significant pain and discomfort.
The primary function of bursae is to facilitate the smooth operation of joints by reducing friction and absorbing shock. This is important in areas like the shoulder, hip, and knee, where movement is frequent and varied.
Inflammation in bursae, or bursitis, can develop due to repetitive motion, direct injury, or infection. When a bursa is subjected to repetitive stress or trauma, it can become inflamed. This leads to pain, swelling, and limited mobility.
The inflammation process involves the increased production of fluid within the bursa, leading to swelling. This swelling can irritate surrounding tissues, causing pain and discomfort. In some cases, the inflammation can become chronic, making it challenging to treat.
Bursitis can occur in various parts of the body, but it is most commonly found in the shoulder, hip, elbow, and knee. The specific location of bursitis can influence the symptoms and the approach to treatment.
| Location | Common Activities Causing Bursitis | Symptoms |
| Shoulder | Lifting, throwing, or repetitive overhead movements | Pain when moving the shoulder, specially overhead |
| Hip | Running, cycling, or direct trauma to the hip | Pain on the outer hip or groin area |
| Elbow | Repetitive bending or direct pressure on the elbow | Pain and swelling on the back of the elbow |
| Knee | Kneeling, jumping, or direct trauma to the knee | Pain below the kneecap or on the sides of the knee |
Understanding these aspects of bursitis is key for developing effective treatment plans. These plans should address both the symptoms and the underlying causes.

Understanding bursitis pain is key to finding good treatments. Bursitis pain is more than just inflammation. It involves complex body processes that can cause long-lasting pain.
Bursitis pain comes from inflamed bursae. These are fluid-filled sacs that protect joints and reduce friction. When they get inflamed, the nearby tissues get irritated, causing pain.
The pain from bursitis can be sharp and intense, mainly when moving. This is because the inflamed bursa gets compressed or stretched. Managing bursitis pain well means tackling both the inflammation and the mechanical stress.
Pain sensitization plays a big role in bursitis pain lasting long. When a bursa is inflamed, it sends out chemicals that make pain receptors more sensitive. This makes even small movements or pressures hurt.
“Pain is not just a passive response to injury; it’s an active process that involves changes in the nervous system.”
This process, called central sensitization, can lead to chronic pain. Even after the initial inflammation goes away, the pain can stay. It’s important to understand this to find effective treatments for chronic bursitis pain.
Bursitis can also cause pain in other places, not just where the bursa is inflamed. This happens because of how nerves are connected in joints and tissues. Pain signals from the inflamed bursa can be sent to other areas through these nerves.
| Location of Bursitis | Common Referred Pain Areas |
| Shoulder (Subacromial Bursitis) | Upper arm, side of the shoulder |
| Elbow (Olecranon Bursitis) | Back of the elbow, forearm |
| Hip (Trochanteric Bursitis) | Outer thigh, groin area |
Knowing about these pain patterns is key for accurate diagnosis and treatment. By understanding the complex nature of bursitis pain, doctors can create better treatment plans. These plans address both the local inflammation and the broader pain mechanisms.
Understanding why bursitis heals slowly is key to treating it. Bursitis, which is inflammation of the bursae, makes recovery tough. This is because of its unique anatomy.
Bursae have a limited blood supply. This is a big reason why bursitis heals slowly. They get fewer nutrients and less oxygen, which are vital for healing. This is because bursae are not as vascular as other tissues.
Bursae, near joints, face mechanical stress. This stress comes from movement, friction, or pressure. It can make the bursae more inflamed, slowing down healing.
Bursae are closely tied to tendons, ligaments, and muscles. Problems in these areas can affect the bursae, slowing healing. For example, tight or inflamed tendons can put more pressure on the bursae, making recovery harder.
| Anatomical Factor | Impact on Healing |
| Limited Blood Supply | Reduced nutrient and oxygen delivery |
| Mechanical Stress | Increased irritation and inflammation |
| Relationship with Surrounding Structures | Interconnected issues complicating recovery |
Knowing the different types of bursitis is key to treating and recovering well. Bursitis is when the bursae, which cushion joints, get inflamed. Each type has its own recovery hurdles.
Bursitis can be either acute or chronic. Acute bursitis is short-term and usually caused by sudden injury or too much use. It’s known for sharp pain and swelling. On the other hand, chronic bursitis lasts longer, often from repeated motion or constant irritation.
Recovery times vary a lot. Acute bursitis might heal in a few weeks with the right treatment. But chronic bursitis can take months or even years to manage well.
The spot where bursitis happens affects how long it takes to heal. Bursitis in places with poor blood flow, like the heel or elbow, heals slower. This is because these areas don’t get as much blood.
It’s important to understand these location-specific challenges. This helps create treatment plans that meet each patient’s unique needs.
As we dive deeper into bursitis, it’s clear that a detailed approach is needed. This approach should consider both the type and location of bursitis. This is key to better recovery outcomes.
Understanding chronic inflammation is key to solving bursitis pain. It’s a complex process with many factors and pathways.
Acute inflammation is the body’s first response to injury or infection. Bursitis often starts with irritation or trauma to the bursae. Normally, this inflammation goes away once the cause is fixed, and healing starts.
But sometimes, the inflammation doesn’t stop. It turns chronic due to ongoing stress, not fully resolving the initial inflammation, or underlying conditions.
Chronic inflammation in bursitis involves inflammatory mediators like cytokines and chemokines. These molecules fuel inflammation and harm tissues.
These mediators create a cycle. Inflammation damages tissues, which in turn keeps the inflammation going.
| Inflammatory Mediator | Role in Bursitis | Effect on Tissue |
| Cytokines (e.g., TNF-alpha, IL-1) | Promote inflammation and pain | Tissue damage and degradation |
| Chemokines | Recruit inflammatory cells | Perpetuate inflammation |
| Prostaglandins | Mediate pain and inflammation | Contribute to pain sensitization |
Stopping chronic inflammation in bursitis is hard because of the many factors involved. Just treating symptoms with anti-inflammatory drugs isn’t enough. We need to tackle the causes of inflammation.
Adding to the challenge are mechanical stress, lifestyle factors, and underlying conditions. A detailed approach that includes these factors and targeted treatments is needed to break the cycle.
Healthcare providers can develop better treatments by understanding chronic inflammation and its role in bursitis. This way, they can not only ease symptoms but also tackle the condition’s root causes.
Bursitis is hard to treat because of its complexities. Standard treatments often don’t work well. We’ll look at why rest, anti-inflammatory meds, and physical therapy can face obstacles.
Doctors often tell people with bursitis to rest and change their activities. But, these steps have big limits. Complete rest is often impractical for those with busy lives or jobs that need physical effort. Also, just cutting down on activity might not fix the real problem of bursitis.
A study in the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy showed that rest and activity changes can help a bit. But, they don’t stop bursitis from coming back without other treatments.
“Rest is essential for the initial management of bursitis, but it is not a standalone solution. Addressing the underlying causes and modifying risk factors are critical for long-term recovery.”
Anti-inflammatory meds are key in treating bursitis. But, they come with their own set of problems. Long-term use of NSAIDs can lead to gastrointestinal complications. Some people don’t get enough relief or get used to these meds.
| Medication Type | Common Side Effects | Limitations in Bursitis Treatment |
| NSAIDs | Gastrointestinal issues, renal impairment | May not provide complete pain relief; risk of dependency |
| Corticosteroids | Osteoporosis, weight gain, mood changes | Short-term relief; possible rebound inflammation |
Physical therapy is key in treating bursitis. It helps get movement back and strengthens muscles. But, it can hit roadblocks, like if the real problem isn’t fixed or if it hurts too much.
A good plan includes manual therapy, exercises, and teaching how to move right. Using things like ultrasound or laser therapy can also help heal tissues and lessen pain.
In summary, while common treatments for bursitis have their good points, they face many challenges. Knowing these challenges helps us find better ways to treat bursitis and help people recover for good.
Understanding biomechanical factors is key to beating bursitis recovery time. These issues can make healing hard, leading to ongoing pain and swelling.
Poor movement patterns are a big problem for bursitis. They add stress to the bursae, causing more inflammation and pain. For example, hip bursitis can be caused by an abnormal gait. Fixing these patterns is vital for easing bursa stress and helping recovery.
Physical therapy is essential for fixing these issues. It teaches patients to move in ways that don’t strain their bursae. This helps in recovery and stops bursitis from coming back.
Muscle imbalances are another big factor in bursitis. When some muscles work too much and others too little, it causes bad movement and stress on the bursae. For example, shoulder bursitis can be caused by muscle imbalances in the rotator cuff.
Fixing these imbalances with exercises can help restore normal movement. This is a key part of treating bursitis.
Posture also affects bursitis. Bad posture puts extra stress on the bursae, like in the neck, shoulder, and lower back. Sitting too much can lead to forward head posture, causing shoulder or upper back bursitis.
Adding postural correction to treatment can help. This includes ergonomic changes, exercises, and tips for good posture. By fixing posture, patients can avoid long recovery times and better their musculoskeletal health.
Bursitis coming back is a big worry for both patients and doctors. Knowing why it happens is key to finding better ways to treat it.
When bursitis doesn’t heal fully, it’s more likely to come back. Not treating it well or going back to activity too soon makes it worse. This leads to a cycle of more inflammation.
It’s vital to give the bursa enough time to heal. Using the right rehab plans helps lower the chance of it happening again.
Staying inflamed because of constant pressure is another big reason for bursitis to return. Bad movement, not adjusting workspaces well, or not changing activities enough can cause this.
Fixing these issues with physical therapy, better workspaces, and changing how we do things is key to stopping bursitis from coming back.
Not fixing the real reasons for bursitis is a big mistake. Bursitis often shows up because of muscle problems, bad posture, or how our body moves. If we don’t fix these, the bursa keeps getting inflamed.
We need to take a full approach. This means finding and treating the real causes of bursitis. This way, we can stop it from coming back and help it heal for good.
Systemic conditions can greatly impact how well the body heals from bursitis. A complete treatment plan is needed. Systemic health is a key factor in bursitis recovery.
Autoimmune diseases make it hard for the body to heal from bursitis. Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis can make symptoms worse. Managing autoimmune conditions well is important for bursitis treatment.
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis might have more severe bursitis. It’s important to treat both the bursitis and the autoimmune disease together.
Metabolic disorders, like diabetes, can slow down bursitis healing. These conditions can cause poor circulation and slow healing. Diabetes can lead to long-lasting inflammation and slow healing. Keeping blood sugar levels under control is part of the treatment.
Age also affects bursitis healing. As we get older, our bodies change in ways that can slow recovery. Older adults need more personalized care to address these changes.
“The aging process affects not just the musculoskeletal system but also the body’s overall ability to heal and recover from injuries and conditions like bursitis.”
Knowing how systemic factors affect bursitis healing helps us create better treatment plans. By focusing on both local and systemic factors, we can improve outcomes and lower the chance of complications or future problems.
Septic bursitis adds a new challenge to treating bursitis. It happens when a bursa gets infected, usually with bacteria. This makes treatment harder and recovery longer.
Septic bursitis makes treatment harder because it needs antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. The infection makes inflammation worse and recovery slower. Getting septic bursitis treated right away is key, often with antibiotics.
To diagnose septic bursitis, doctors do a clinical check-up and might take bursal fluid for culture. Knowing the bacteria is important for the right antibiotic.
Dealing with septic bursitis gets harder because of antibiotic resistance. As bacteria resist antibiotics, treatment gets tougher. Doctors need to keep up with new resistance patterns to help patients.
To fight antibiotic resistance, doctors use broad-spectrum antibiotics when they don’t know the bacteria. They also follow antibiotic stewardship programs to use antibiotics wisely.
Septic bursitis can lead to long-term problems if not treated well. These include chronic pain, infections that keep coming back, and less mobility in the joint. Quick and effective treatment is key to avoid these issues.
Knowing the long-term effects shows why early diagnosis and treatment are so important. We must think about how septic bursitis affects a patient’s life and manage it fully.
| Complication | Description | Management Strategy |
| Antibiotic Resistance | Increasing bacterial resistance to antibiotics complicates treatment. | Use of broad-spectrum antibiotics and antibiotic stewardship programs. |
| Chronic Pain | Long-term pain following septic bursitis. | Pain management strategies, including medication and physical therapy. |
| Recurrent Infections | Repeated infections in the same bursa. | Prophylactic antibiotics and monitoring for early signs of infection. |
Advanced treatments offer hope for those with stubborn bursitis. When usual treatments don’t work, it’s time to try new methods. These can help with relief and healing.
Corticosteroid injections are a common treatment for bursitis. They reduce swelling and pain, giving temporary relief. But, they can weaken tendons and may not work as well over time.
Key considerations for corticosteroid injections include:
Ultrasound-guided aspiration is a precise way to drain fluid from the bursa. It reduces pressure and inflammation right away. It also helps diagnose by analyzing the fluid.
The benefits of ultrasound-guided aspiration include:
Regenerative medicine, like PRP and stem cell therapy, is a new way to treat bursitis. It uses the body’s own cells to heal.
Regenerative medicine offers several benefits:
Exploring these advanced treatments helps healthcare providers create better plans for stubborn bursitis.
Living with bursitis can be challenging due to persistent pain and discomfort.
A bursectomy, or removing a bursa, is considered when other treatments don’t help. Doctors decide on surgery after checking with imaging and evaluating the bursa’s health.
The reasons for bursectomy include:
Modern surgery for bursitis is less invasive. These methods cause less damage, heal faster, and hurt less after surgery.
Benefits of these surgeries include:
| Benefit | Description |
| Smaller Incisions | Less damage to tissues |
| Reduced Recovery Time | Patients can get back to normal sooner |
| Less Post-Operative Pain | Less pain after surgery |
Recovering after surgery for bursitis has its own hurdles. Knowing these challenges helps improve outcomes.
Common recovery challenges include:
Understanding when to use surgery, the benefits of new surgical methods, and recovery challenges helps doctors. They can then plan better treatments and manage patient hopes.
Managing bursitis isn’t just about medical treatment. It also involves making lifestyle changes. These changes can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Dietary changes can help manage bursitis. Anti-inflammatory nutrition focuses on foods that reduce inflammation. Eating fatty fish, nuts, and leafy greens is beneficial. Avoid processed foods and sugars.
Eating colorful vegetables and fruits is good for antioxidants. Drinking plenty of water is also key for healthy joints.
Good sleep is vital for healing, including managing bursitis. Poor sleep can make inflammation worse. A consistent sleep schedule and a restful environment can improve sleep.
Avoid caffeine and electronic devices before bed. Create a relaxing bedtime routine to signal sleep time.
Chronic stress can worsen bursitis symptoms. Using stress management techniques like meditation or yoga can help. Deep breathing exercises are also beneficial.
Regular, tailored physical activity can manage stress and improve well-being. Finding the right balance between activity and rest is important.
Recovering from bursitis needs a mix of steps to tackle the root causes of inflammation and aid in healing. We’ve looked into the details of bursitis, including its nature and the reasons behind slow healing. We’ve also talked about the challenges of treatment and the key role of lifestyle changes.
It’s key to tackle treatment challenges to get better from bursitis. This means understanding the condition, spotting factors that keep it going, and using good management strategies. This way, people can stop the cycle of ongoing inflammation and reduce pain.
Good bursitis management includes many steps, like getting the right diagnosis, using targeted treatments, and making lifestyle changes. Adding anti-inflammatory foods, getting better sleep, and managing stress help the body heal naturally. We stress the need for a full approach to manage bursitis, helping people take charge of their recovery and get the best results.
Bursitis is when the bursae, fluid-filled sacs, get inflamed. These sacs cushion joints and reduce friction. It happens when these sacs get irritated or injured, often from repetitive motion or direct trauma.
Bursitis hurts because the inflammation irritates nerves and tissues. This leads to pain. The pain gets worse because of how our bodies react to it.
Bursitis can last from a few weeks to months or years. It depends on the type, location, and how severe it is.
Bursitis often comes back because it doesn’t fully heal. It can also come back if the cause isn’t fixed. Knowing and fixing these causes is key to avoiding it.
Treating bursitis is hard because of limited blood supply and mechanical stress. It’s also hard because of chronic inflammation. Traditional treatments like rest and medication often don’t work well.
Poor movement patterns and muscle imbalances can make recovery harder. They keep putting stress on the bursae. Fixing these issues is important for treatment.
For tough cases, treatments like corticosteroid injections and ultrasound-guided aspiration are used. These can help when usual treatments don’t work.
Surgery might be needed if other treatments don’t work. It’s also needed for septic bursitis to drain or remove the infected bursa.
Changes like eating anti-inflammatory foods and improving sleep can help. Stress management also helps by reducing inflammation and improving overall health.
Yes, conditions like autoimmune diseases and metabolic disorders can slow healing. Age can also affect how well the body heals and responds to treatment.
Septic bursitis is hard because it needs quick antibiotic treatment. There’s also a risk of antibiotic resistance. If not managed well, it can have long-term effects.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!