Last Updated on November 4, 2025 by mcelik
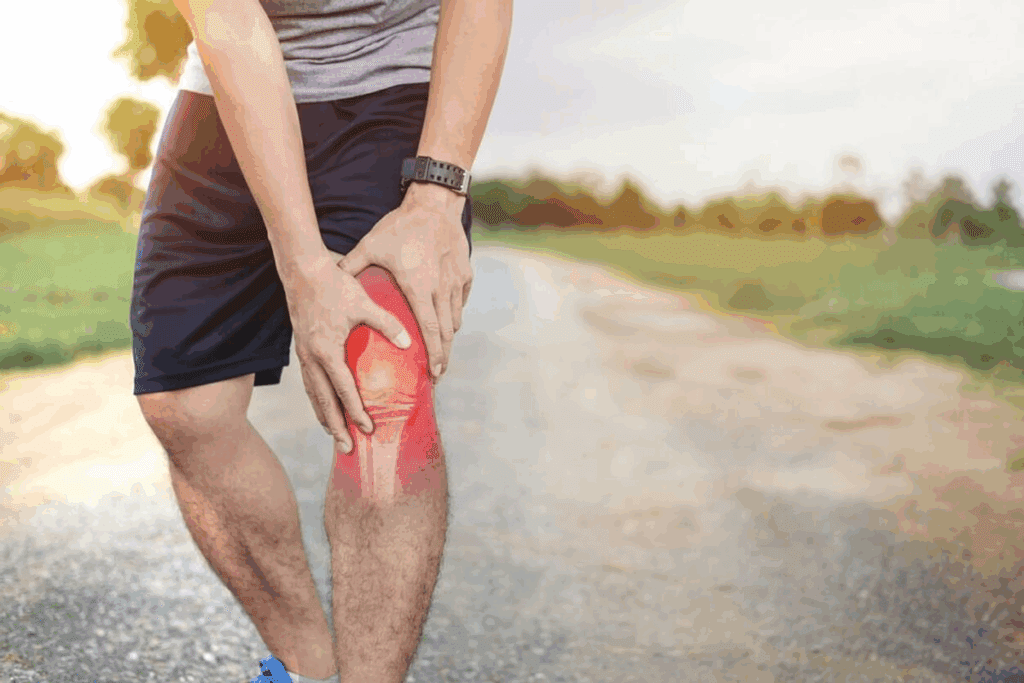

Did you know hip bursitis can make simple tasks hard? Hip bursitis is when the bursae, fluid-filled sacs, get inflamed. These sacs cushion joints and reduce friction.
When the bursae in the hip get inflamed, it hurts, mainly when walking. Treatment of bursitis of hip is important because hip bursitis can really limit your movement and quality of life.
Knowing what causes hip bursitis and the treatment options is key. We’ll look into hip bursitis and its treatment to help you deal with it.
For those who feel pain while walking or doing physical activities, knowing about bursitis is key. Bursitis is when bursae, fluid-filled sacs, get inflamed. These sacs cushion bones, tendons, and muscles near joints. When they swell, it causes pain and discomfort, mainly when moving.
Bursitis happens when bursae get irritated or inflamed. This can be from doing the same thing over and over, getting hit directly, or getting an infection. Repetitive motion is a big reason, like for runners who hit their joints a lot.
Swelling of the bursae leads to pain and discomfort, significantly restricting movement. Knowing why it happens helps in treating it better.
Bursitis can happen in many places, like the hip, knee, elbow, and shoulder. The hip is often affected, leading to trochanteric bursitis. Other common spots are the knee and foot.
Several things can make you more likely to get bursitis. Age, job, and some health conditions are risk factors. Older people get it more because their joints wear out. Jobs that make you do the same thing over and over also increase the risk.
Athletes, like runners, are at high risk because of the constant stress on their joints. Some health issues, like rheumatoid arthritis, also raise the risk.
| Risk Factor | Description |
| Age | Older individuals are more susceptible due to wear and tear on joints. |
| Occupation | Jobs involving repetitive tasks or heavy lifting increase the risk. |
| Athletic Activities | Runners and athletes in high-impact sports are prone to bursitis. |
| Medical Conditions | Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis increase the risk of developing bursitis. |
Knowing how walking impacts bursitis is key to managing it well. Walking can make bursitis pain worse, mainly if it’s in the hip or knee. The constant motion and pressure on the bursae can cause or increase pain.
Walking can make bursitis pain worse because of the constant rubbing and irritation of the inflamed bursae. When you walk, the bursae around your hip or other affected areas face stress and rubbing. This can make inflammation and pain worse.
Factors that contribute to bursitis pain during walking include:
The pain from walking with bursitis can differ. Some feel sharp, stabbing pain, while others have a dull ache or stiffness. The pain might stay in the affected area or spread to other parts of the leg or hip.
| Pain Type | Description |
| Sharp/Stabbing | Severe, intense pain that occurs with specific movements |
| Dull Ache | Persistent, mild pain that is present during activity |
| Stiffness | Reduced mobility and stiffness in the affected joint |
Changes in how you walk can be a way to avoid discomfort from bursitis. People with hip bursitis might change their walk to avoid stressing the inflamed bursae. This can lead to an unusual gait.
Common gait changes include:
By understanding these changes and their link to bursitis, people can manage their condition better. This can improve their quality of life.
It’s important to know the symptoms and how to diagnose hip bursitis. This condition can cause a lot of pain and make daily life hard.
Hip bursitis symptoms can vary. They often include pain on the outer hip, tenderness, and swelling. Pain gets worse with activities like walking or climbing stairs. Some people might hear a snapping or clicking sound in their hip.
To diagnose hip bursitis, doctors use physical exams, medical history, and sometimes imaging. A doctor will check for pain and tenderness. Tests like X-rays or MRI scans might be needed to confirm the diagnosis.
It’s key to tell hip bursitis apart from other hip issues. Conditions like tendinitis or osteoarthritis can have similar symptoms. A doctor’s thorough diagnosis is needed to find the cause of hip pain. This might include physical exams, imaging tests, and injections.
Treating bursitis of the hip involves many steps. We use different medical methods to help symptoms and aid in recovery. Let’s look at the various treatments for hip bursitis, their effectiveness, and benefits.
Medicine is key in managing hip bursitis symptoms. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are often used to lessen pain and swelling. We might also suggest other pain medicines based on how severe the condition is.
For some, we might add muscle relaxants to help with muscle spasms.
Corticosteroid injections are very effective in reducing inflammation in hip bursitis. By injecting corticosteroids into the affected bursa, we can greatly reduce swelling and pain. This method is great when oral medicines aren’t enough or when a more precise approach is needed.
In severe cases of hip bursitis, surgery might be needed if other treatments don’t work. Surgery can include removing the inflamed bursa or fixing any underlying problems, like tendon repairs.
We only consider surgery when other treatments have failed and the condition greatly affects the patient’s life.
For those with hip bursitis, knowing how walking affects their condition is key. Walking can impact hip bursitis in different ways.
Walking gently can help in recovering from hip bursitis. It helps move the muscles around the hip, reducing swelling and improving movement. It also boosts blood flow, which aids in healing.
A study in the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy found walking helps. Start with short walks and slowly increase them as you feel better.
“A well-structured walking program can be an effective adjunct to other treatments for hip bursitis, promoting recovery and reducing symptoms.”
Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy
Walking can also make hip bursitis worse if done too much or wrong. Too much strain on the hip can lead to more swelling and pain. Pay attention to your body and adjust your walks as needed.
| Factors That May Worsen Hip Bursitis | Impact on Hip Bursitis |
| Excessive walking or overuse | Increased inflammation and pain |
| Poor walking posture or gait | Additional strain on the hip joint |
| Inadequate footwear | Increased stress on the hip and surrounding tissues |
To walk safely with hip bursitis, follow these tips:
By following these guidelines, people with hip bursitis can enjoy walking safely. This helps them manage their condition without making it worse.
The time hip bursitis lasts can vary a lot. It depends on how bad the condition is and how well treatment works. Knowing how long it takes to get better is key. This helps everyone understand the healing process better.
Acute hip bursitis usually comes from sudden injury or too much strain. With the right treatment, most people get better in 6 to 12 weeks. During this time, pain and swelling go down as the bursa heals.
Many things can affect how long it takes to heal from hip bursitis. These include:
Chronic hip bursitis means ongoing pain and swelling that doesn’t go away. It needs a long-term plan for treatment. This might include ongoing physical therapy, changes in lifestyle, and sometimes injections.
People with chronic hip bursitis need to work with their doctors to make a treatment plan. The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons says, “Managing chronic bursitis is about easing symptoms and improving function, not curing it.”
Physical therapy is key in treating hip bursitis. It offers various treatments to ease pain and boost mobility. Each patient gets a treatment plan that fits their needs.
Stretching is a big part of physical therapy for hip bursitis. It makes muscles more flexible and less stiff. Here are some stretches that work well:
It’s important to strengthen the muscles around the hip. This helps in recovery and prevents future problems. Here are some exercises to do:
Manual therapy is a hands-on method used by physical therapists. It aims to reduce pain and swelling. Here are some techniques used:
| Therapy Technique | Purpose | Benefits |
| Piriformis Stretch | Improve flexibility | Reduces stiffness, alleviates pain |
| Clamshell Exercise | Strengthen hip muscles | Supports recovery, prevents flare-ups |
| Soft Tissue Mobilization | Reduce muscle tension | Relaxes muscles, reduces pain |
Using these physical therapy methods in a treatment plan can greatly help those with hip bursitis. They can manage pain better and move more easily.
Knowing which exercises to skip is key to managing hip bursitis. It’s important to change your workout routine to avoid making the condition worse. This lets it heal properly.
High-impact activities can make hip bursitis symptoms worse. These activities put a lot of stress and impact on the hip. This can irritate the bursae and slow down healing.
It’s important to stay away from these activities when you’re first recovering from hip bursitis.
Some movements can make hip bursitis worse by adding stress to the bursae. Knowing these movements helps you change your daily activities.
| Movement | Why It Aggravates Hip Bursitis |
| Lying on the affected side | Puts direct pressure on the inflamed bursa |
| Repetitive hip flexion | Causes friction and irritation to the bursa |
| Standing on one leg | Increases stress on the hip joint and surrounding bursae |
Changing your workout routine is important when recovering from hip bursitis. You should replace high-impact activities with low-impact ones. Also, be careful about the movements you make.
Low-impact alternatives:
By avoiding high-impact activities and certain movements, people with hip bursitis can improve their recovery.
Bursitis can be quite debilitating, but there are several home remedies and self-care strategies that can provide relief. Managing bursitis symptoms effectively requires a multi-faceted approach that includes rest, therapy, and lifestyle adjustments.
Rest is key in the early stages of bursitis treatment. Avoiding activities that make the condition worse can greatly reduce pain and swelling. Modifying daily activities to lessen stress on the affected joint is vital. For hip bursitis, this might mean avoiding direct pressure on the hip or taking regular breaks to rest.
An orthopedic specialist, notes, “Resting the affected area and modifying activities can significantly improve symptoms in patients with bursitis.”
Both ice and heat therapy can be effective in managing bursitis symptoms. Ice packs are typically used in the acute phase to reduce inflammation, while heat therapy can help relax muscles and improve blood flow in the later stages.
| Therapy Type | Application | Benefits |
| Ice Therapy | Apply ice pack for 15-20 minutes, 3-4 times a day | Reduces inflammation and pain |
| Heat Therapy | Apply warm compress or heating pad for 15-20 minutes, 3-4 times a day | Relaxes muscles, improves blood flow |
Incorporating natural anti-inflammatory agents into your diet can help manage bursitis symptoms. Omega-3 fatty acids, turmeric, and ginger are known for their anti-inflammatory properties.
“Dietary changes can play a significant role in managing inflammation. Including foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, and anti-inflammatory spices like turmeric can be beneficial.” –
Nutritionist, Sarah Johnson
By combining these home remedies and self-care strategies, individuals with bursitis can effectively manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Bursitis isn’t just a hip problem; it can also hit the knee, foot, and shoulder. It happens when the bursae, small sacs filled with fluid, get inflamed. Knowing how it affects different joints is key for the right treatment.
Walking can be tough on the knee when you have bursitis. Is walking good for knee bursitis? It depends on how bad the condition is and your health. Gentle walks can help keep the joint moving and build muscle, which might help you get better. But, too much walking can make things worse.
“Moderation is key when it comes to walking with knee bursitis,” as it allows for some movement without putting too much strain on the affected bursa. We recommend starting with short, gentle walks and gradually increasing the distance and intensity based on comfort and pain levels.
Bursitis in the foot can really hurt because the foot bears weight all the time. You might feel pain and swelling, mostly on the top or bottom. To manage it, rest, ice, and the right shoes are important. Also, exercises to strengthen the foot muscles and improve flexibility can help.
How long it takes to recover from bursitis varies a lot. It depends on the joint, how bad the condition is, and the treatment. Knee or foot bursitis might take longer to heal than hip or shoulder bursitis. Knowing these differences helps set realistic goals and plan the best treatment.
| Joint Affected | Typical Recovery Time | Factors Influencing Recovery |
| Knee | 2-6 weeks | Severity of inflammation, effectiveness of treatment |
| Foot | 3-8 weeks | Weight-bearing activities, footwear |
| Shoulder | 2-4 weeks | Range of motion exercises, physical therapy |
Understanding the unique challenges and recovery times for bursitis in different joints helps us manage it better. This way, we can improve outcomes for those affected.
Running can lead to bursitis because of the constant impact on joints. Runners often face this issue due to the repetitive stress and friction.
Bursitis in runners often comes from overuse or repetitive motion. This causes inflammation in the bursae, which are fluid-filled sacs that cushion joints. Poor running techniques, inadequate footwear, and sudden changes in training intensity or frequency can all contribute to bursitis.
Runners with biomechanical issues like overpronation or supination are at higher risk. This is because abnormal stress on their joints can lead to bursitis. It’s important for runners to know these risk factors to prevent bursitis.
To prevent bursitis, runners need to focus on proper training, equipment, and technique. Here are some strategies:
Coming back to running after bursitis needs a careful plan. It’s important to let the affected area fully heal before starting to run again.
A gradual return to running is best, starting with low-impact activities like cycling or swimming. Then, move to short, easy runs. Listen to your body and adjust your training plan to avoid bursitis coming back.
Key things to consider include:
Dealing with hip bursitis means knowing what daily habits make it worse. It’s not just the injury or inflammation. It’s also about how our daily choices affect it.
Sitting and standing habits are key in hip bursitis. Sitting for too long tightens hip flexors, making bursitis worse. Standing for long periods also stresses the hip bursae. Adjusting our daily routines to stretch and move can help.
| Habit | Effect on Hip Bursitis | Modification |
| Prolonged Sitting | Tightens hip flexors, exacerbating bursitis | Take regular breaks to stand and stretch |
| Prolonged Standing | Puts continuous stress on hip bursae | Rest and elevate legs periodically |
Our sleep position affects hip bursitis. Sleeping on the side without support can pressure the bursae. Using a pillow between the knees helps keep the hips aligned and reduces pressure.
Some everyday activities can make hip bursitis worse. Activities that move the hip a lot or press on it can hurt more. It’s best to change or skip these activities while recovering.
Understanding and changing these lifestyle factors can help those with hip bursitis recover better. It also reduces the chance of making the condition worse.
It’s important to know the difference between greater trochanteric pain syndrome (GTPS) and hip bursitis. Both affect the hip but need different treatments.
GTPS and hip bursitis share similar symptoms like pain on the outer hip. But, they target different parts. Hip bursitis is about inflammation around the hip joint. GTPS, on the other hand, is about pain on the greater trochanter, linked to gluteal tendinopathy.
| Condition | Primary Symptoms | Treatment Approaches |
| Hip Bursitis | Pain and tenderness over the bursa, limited mobility | Anti-inflammatory medications, corticosteroid injections, physical therapy |
| Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome | Pain and tenderness over the greater trochanter, often associated with gluteal tendinopathy | Exercises for gluteal strengthening, manual therapy, lifestyle modifications |
Walking can be good or bad for GTPS, depending on the person and how they walk. Gentle walking can help keep the joint moving and reduce stiffness. But, bad walking or too much walking can make symptoms worse. It’s important to check how you walk and change it if needed to avoid making GTPS worse.
Seeing a healthcare professional to find the right exercise plan for GTPS is a good idea. This might include walking as part of a full recovery program.
Managing bursitis well means using medical treatment, changing your lifestyle, and taking care of yourself. It’s key to tackle the root causes for better joint health over time. With a full plan, you can handle your bursitis and keep your joints healthy.
Handling bursitis needs a mix of natural treatments and lifestyle changes. This includes doing gentle exercises and avoiding activities that hurt. These steps help ease symptoms and stop future problems, helping your joints stay healthy.
We suggest working with doctors to make a treatment plan that fits you. Being proactive about bursitis care can lower the risk of long-term joint issues. This way, you can keep your joints working well.
Bursitis is when the bursae, fluid-filled sacs, get inflamed. These sacs cushion joints and reduce friction. It happens from repetitive motion, direct blows, or infection, causing pain and limited movement.
Walking can help hip bursitis if done right. It keeps the joint moving and strengthens muscles. But, too much walking can make it worse.
Hip bursitis can last from a few weeks to months or more. It depends on how bad it is and the treatment.
Symptoms include pain on the outer hip, tenderness, and swelling. Activities like walking or climbing stairs can make it worse.
Doctors use a physical exam, medical history, and imaging like X-rays or MRI. They might also do diagnostic injections.
Treatment includes pain meds, corticosteroid injections, and physical therapy. Surgery might be needed for severe cases.
Yes, walking can make hip bursitis worse if not done carefully. Wrong walking can stress the hip more.
Yes, avoid high-impact activities like running. Also, avoid deep squats or lunges. Modify or skip these exercises during recovery.
Walking can help knee bursitis by keeping the joint moving. But, avoid too much and use knee pads if needed.
Rest, ice and heat, and natural anti-inflammatory methods help. Also, avoid activities that make it worse.
Runners get bursitis from repetitive motion and joint impact. Proper training, shoes, and exercises can help prevent it.
Sitting, standing, sleep positions, and daily activities can worsen hip bursitis. Changing these habits can help recovery.
Walking can help if done carefully. It keeps the joint moving. But, address the cause and avoid making it worse.
Start with a training plan, include strength and flexibility exercises, and wear the right shoes. This helps prevent it from coming back.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!