Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
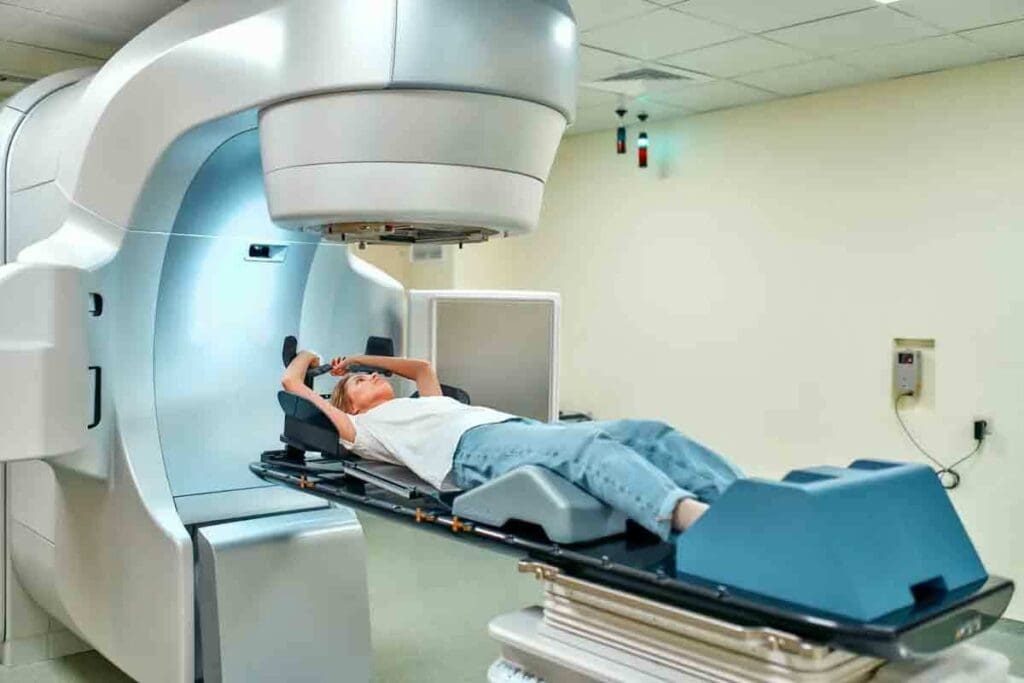
Radiation therapy is a key part of cancer treatment. It uses targeted methods to fight tumors while protecting nearby healthy tissue. At Liv Hospital, we offer several types of radioNuclear Medicinetherapy to provide the best possible outcomes for our patients.
Our specialists use advanced technology to deliver high-energy rays that destroy cancer cells effectively. The different types of radiotherapy we use are carefully selected based on each patient’s condition, ensuring maximum benefit and safety.
Overall, radiation therapy for cancer treatment has improved significantly over the years, thanks to advancements in equipment and techniques. Understanding the types of radiotherapy available helps patients make informed decisions about their care.
Key Takeaways
- Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to destroy cancer cells.
- Various types of radiotherapy are designed to target tumors precisely.
- Leading institutions trust radiation therapy for its effectiveness.
- Cancer treatment radiation methods are continually evolving.
- Radiotherapy cancer treatment aims to minimize damage to healthy tissues.
Understanding Radiation Tumor Treatment
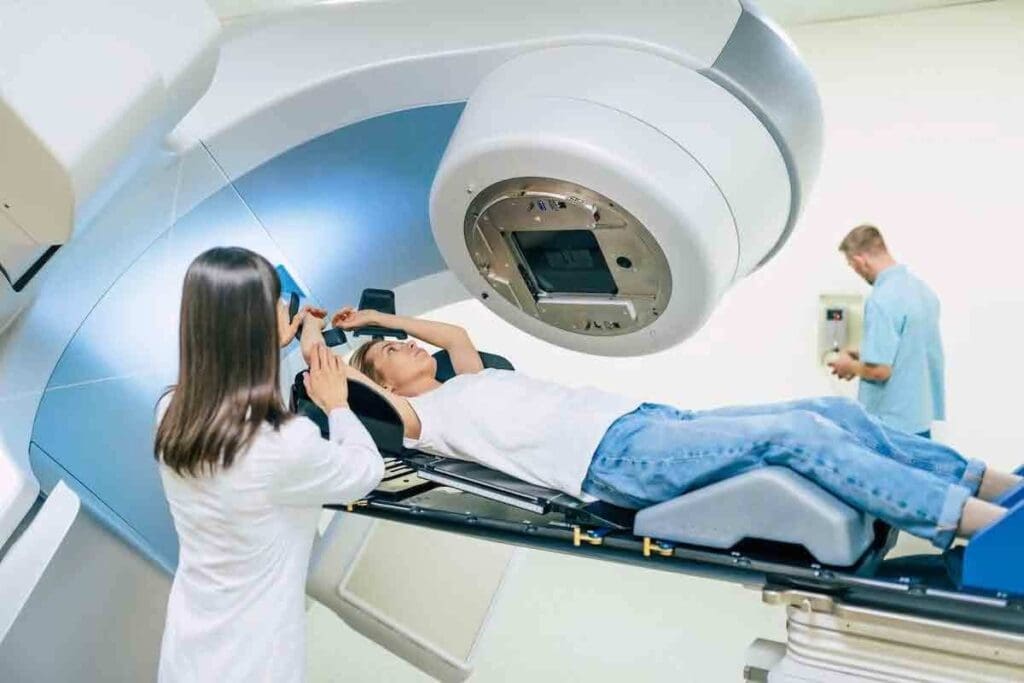
It’s key for patients to understand radiation tumor treatment for effective cancer care. This treatment uses high-energy particles or waves to destroy cancer cells. These include X-rays, gamma rays, electron beams, or protons.
The Science Behind Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy damages cancer cells’ DNA, stopping them from growing. At high doses, it can kill these cells. The aim is to target the tumor without harming healthy tissues.
How Radiation Destroys Cancer Cells
Cancer cells are more vulnerable to radiation than normal cells. This is because they divide quickly. Radiation damages their DNA, preventing them from dividing and leading to cell death.
Goals of Radiation Treatment in Cancer Care
The main goals of radiation treatment are to cure cancer, prevent its return, or stop its growth. It can also ease symptoms in advanced cancer by shrinking tumors.
| Goals of Radiation Therapy | Description |
| Curative | Aim to cure cancer by eliminating the tumor. |
| Palliative | Relieve symptoms and improve quality of life. |
| Adjuvant | Used after surgery to eliminate any remaining cancer cells. |
The 7 Major Types of Radiotherapy
Knowing the different types of radiotherapy is key to managing cancer well. Radiotherapy, or radiation therapy, is a main part of cancer treatment. It comes in various forms, each suited to a patient’s needs. We’ll look at the seven main types, their special features, and how they’re used.
Overview of Treatment Categories
Radiation therapy for cancer falls into three main groups: external beam radiation therapy, brachytherapy, and systemic radiotherapy. These groups have more specific techniques within them.
- External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT): This is the most common type, where radiation is delivered from outside the body.
- Brachytherapy: Involves placing radioactive material directly inside or near the tumor.
- Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT): A type of EBRT that allows for precise targeting of tumors.
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT): Techniques that deliver high doses of radiation to small, well-defined tumors.
- Proton Therapy: Uses protons instead of X-rays to kill cancer cells.
- Image-Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT): Uses imaging technologies to guide radiation delivery.
- Systemic Radiotherapy: Involves the use of radioactive substances that travel through the body to target cancer cells.
Evolution of Radiation Therapy Techniques
Radiation therapy has changed a lot over time. New techniques allow for better tumor targeting and fewer side effects. The introduction of IMRT and IGRT has been a big step forward.
Today, we focus on personalized and precise radiation therapy. Advances in imaging and delivery systems have made this possible. Ongoing research is pushing the field further, with new technologies like proton therapy and stereotactic radiosurgery.
Matching Treatment Types to Cancer Needs
Finding the right radiotherapy for a cancer patient is very important. The type and stage of cancer, and the patient’s health, are all considered.
- Type and Stage of Cancer: Different cancers respond better to different types of radiation therapy.
- Tumor Location: Tumors in sensitive areas may require more precise forms of radiation therapy, like proton therapy.
- Patient’s Overall Health: The patient’s health status can influence the choice between different radiotherapy options.
Understanding these factors and the various types of radiotherapy helps healthcare providers create targeted plans. These plans aim to give patients the best possible outcomes.
External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT)
External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT) is a key cancer treatment. It uses high-energy rays to hit tumors from outside the body. This method has changed a lot, getting better at hitting the right spots and being more effective.
A machine called a linear accelerator sends X-rays or particles to the tumor. This way, we can hit cancer cells without harming healthy tissues too much. Our goal is to kill cancer cells while keeping other parts of the body safe.
3D Conformal Radiation Therapy
3D Conformal Radiation Therapy uses new tech to make a 3D picture of the tumor. This helps us aim better at the tumor, cutting down on damage to healthy areas. We can give more radiation to the tumor, making it more effective.
Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT)
Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) is even more precise than 3D Conformal. It changes the strength of the radiation beams. This lets us tailor the treatment to fit the tumor’s shape and location. IMRT is great for tumors near important areas or with tricky shapes.
Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT)
Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT) sends radiation in a circle around the patient. This makes treatment faster and more accurate. VMAT can make treatments shorter, making patients more comfortable and reducing the chance of the tumor moving during treatment.
These new methods in External Beam Radiation Therapy are big steps forward in fighting cancer. They help patients get better results with fewer side effects. We keep working to make our treatments even better for those fighting cancer.
Internal Radiotherapy: Brachytherapy
Brachytherapy is a treatment for some cancers that sends radiation right to the tumor. It uses radioactive materials placed inside or near the tumor. This method gives a strong dose of radiation to the tumor while protecting the surrounding tissues.
Temporary vs. Permanent Implants
Brachytherapy can be temporary or permanent. Temporary implants are in the tumor for a few days before being taken out. Permanent implants stay in the body and lose radioactivity over time.
We use temporary implants for tumors needing a quick, high dose of radiation. Permanent implants are for slower-growing tumors.
High-Dose vs. Low-Dose Rate Approaches
Brachytherapy can also be high-dose rate (HDR) or low-dose rate (LDR). HDR gives a high dose of radiation in a short time, usually in a few fractions. LDR gives a low dose of radiation over a longer time.
The choice between HDR and LDR depends on the cancer type, tumor size, and location. HDR is often used for aggressive tumors needing quick radiation. LDR is for tumors sensitive to longer radiation exposure.
Ideal Candidates for Brachytherapy
Brachytherapy works well for prostate, cervical, and breast cancers. It’s best for patients with tumors that can be reached for radioactive material placement.
We check each patient to see if brachytherapy is right for them. We look at tumor size, location, and overall health. The goal is to treat effectively while keeping side effects low and improving quality of life.
Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Radiotherapy
Stereotactic radiosurgery and radiotherapy are key in fighting cancer. They use high doses of radiation with great precision. This is important for tumors in hard-to-reach places.
Single-Session vs. Fractionated Treatment
These treatments can be given in different ways. Single-session treatment is for smaller tumors. It gives a big dose of radiation at once.
Fractionated treatment spreads the dose over several sessions. This is for bigger tumors or sensitive areas.
Choosing between these treatments depends on the tumor and the patient’s health. Our team picks the best plan for each case.
Gamma Knife and CyberKnife Technologies
New technologies have made these treatments better. Gamma Knife targets tumors in the brain with gamma radiation. CyberKnife is a robot that treats tumors all over the body with great accuracy.
Both Gamma Knife and CyberKnife are non-invasive. They reduce the need for surgery and help patients recover faster.
Applications for Brain, Spine, and Body Tumors
These treatments work for many types of tumors. In the brain, they treat both benign and malignant tumors. They also help with certain vascular malformations.
For spine tumors, they target lesions carefully. Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) treats tumors in the lungs, liver, and prostate, too.
These treatments are great for patients who can’t have traditional surgery. They accurately target tumors in different parts of the body.
Proton Therapy and Particle Radiation
Proton therapy is a big step forward in cancer treatment. It uses protons instead of X-rays to hit tumors. This method is precise, aiming directly at tumors and protecting healthy tissues.
The Physics of Proton Beam Therapy
Proton beam therapy works by speeding up protons to hit cancer cells accurately. Unlike X-rays, protons stop at the tumor, not passing through the body. This is because protons have mass and charge, making them easy to control.
The Bragg Peak: A big plus of proton therapy is the Bragg peak. As protons slow down, they release most of their energy at the tumor’s location. This means less damage to tissues around the tumor.
Bragg Peak Targeting Advantage
The Bragg peak is a big help when treating tumors near important areas. It delivers radiation right to the tumor, protecting nearby vital organs. This is very important for kids, where avoiding long-term side effects is key.
Pediatric Applications and Sensitive Locations
In kids, proton therapy is very useful because it reduces radiation to developing tissues. It’s safe for tumors in sensitive spots like the brain or spine. This precision helps treat tumors effectively without harming nearby areas.
| Tumor Location | Proton Therapy Benefits | Conventional Radiation Limitations |
| Brain Tumors | Precise targeting, sparing surrounding brain tissue | Risk of damage to surrounding brain structures |
| Pediatric Tumors | Minimizes long-term side effects on development | Potential for significant long-term side effects |
| Tumors near critical structures | Highly localized dose distribution | Higher risk of damage to adjacent critical structures |
Proton therapy is a top choice in radiation therapy because of its precision. It targets tumors well, causing less harm to nearby tissues. This makes it a great option for many cancer patients.
Image-Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT)
Image-Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT) is a big step forward in fighting cancer. It lets us target tumors more accurately. This means we can damage less of the healthy tissue around them.
IGRT uses top-notch imaging to guide the radiation therapy. It lets us watch and adjust the treatment beam in real-time. This makes sure it hits the tumor right where it is and how it’s shaped.
Real-Time Tumor Tracking Technologies
IGRT is great at tracking tumors as they move. Tools like cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) and fluoroscopy show us the tumor and its surroundings right before and during treatment.
These tools help us tweak the radiation beam. This way, the tumor gets the right dose, and nearby important areas stay safe.
Adaptive Radiation Therapy Approaches
IGRT also makes adaptive radiation therapy possible. It watches how the tumor and its surroundings change during treatment. Then, we can adjust the plan to get the best results.
This is really helpful when the tumor changes a lot in size or position during treatment.
Managing Organ Movement During Treatment
One big problem in radiation therapy is that organs and tumors move during treatment. IGRT solves this by giving us live updates on where everything is.
With methods like respiratory gating and tumor tracking, we can time the radiation with the tumor’s movement. This ensures we hit the tumor right every time.
Thanks to these advanced tools and methods, we can give radiation therapy with unmatched precision. This leads to better results and fewer side effects.
Systemic Radiotherapy: Intravenous Radiation
Systemic radiotherapy is a new way to fight cancer. It uses intravenous radiation to reach cancer cells all over the body. This method sends radioactive substances through the blood, treating cancer that has spread or might spread.
Understanding systemic radiotherapy is key. It’s a targeted treatment for many cancers. “Systemic therapy is a critical component in the management of various cancers, providing a targeted approach to treating both localized and disseminated disease,” say oncologists worldwide.
Radioactive Iodine for Thyroid Cancer
Radioactive iodine is a well-known treatment for thyroid cancer. It uses the thyroid gland’s natural iodine uptake. This allows it to destroy thyroid tissue, including cancer cells.
Getting radioactive iodine is simple. Patients take a capsule or liquid orally. It then targets thyroid cancer cells, treating them even though it’s given systemically.
Targeted Radiopharmaceuticals
Targeted radiopharmaceuticals are another part of systemic radiotherapy. These drugs find specific cancer cells and deliver radiation right to them. This reduces harm to healthy tissues nearby.
For example, radium-223 dichloride helps with prostate cancer. Lutetium-177 dotatate is used for certain neuroendocrine tumors. These treatments have shown great promise in trials, improving patients’ lives.
Treatment for Metastatic Disease
Systemic radiotherapy is great for treating cancer that has spread. It sends radiation through the blood to hit many tumors at once. This offers a broad treatment plan.
This is very helpful for those with advanced cancer. It’s a strong option when other treatments don’t work. As research goes on, we expect systemic radiotherapy to get even better.
In summary, systemic radiotherapy is a big step forward in cancer treatment. It offers targeted care for many cancers, including thyroid cancer and metastatic disease.
Effectiveness and Applications of Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is a key tool in fighting cancer. It’s used in many ways, based on the cancer type, stage, and the patient’s health.
Curative vs. Palliative Treatment Goals
Radiation therapy can have two main goals. Curative radiation therapy aims to get rid of cancer completely. On the other hand, palliative radiation therapy aims to ease symptoms and improve life quality when a cure is not possible.
Choosing between these goals depends on the cancer type, stage, and the patient’s health. Our oncologists help decide the best treatment plan for each patient.
Neoadjuvant Therapy: Shrinking Tumors Before Surgery
Radiation therapy is also used as neoadjuvant therapy to shrink tumors before surgery. This makes surgery easier and can lead to better outcomes. It helps in preserving more healthy tissue.
In cases of rectal or breast cancer, neoadjuvant radiation therapy is very effective. It makes tumors smaller, making them easier to remove surgically.
Does Radiation Cure Cancer? Success Rates by Type
The success of radiation therapy in curing cancer depends on the type and stage. For some cancers, like early-stage laryngeal or prostate cancer, radiation therapy can be very effective. Buu, its success rate varies across different cancer types and stages.
Our data show that radiation therapy works best for cancers that are localized or diagnosed early. For more advanced cancers, it’s often used with other treatments like chemotherapy or surgery. This combination aims to achieve the best results.
Understanding how radiation therapy works helps patients make better choices. We’re here to support and guide patients through their treatment journey.
Conclusion: Advances in Targeted Radiation Therapy
Targeted radiation therapy has seen big improvements, changing how we treat cancer. Now, treatments are more precise, cutting down on side effects and boosting patients’ quality of life. This is thanks to new techniques that let doctors tailor treatments to each patient.
New tech in radiation therapy has made treatments more accurate and effective. Tools like intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) have improved how radiation is delivered. These advancements have made targeted radiation therapy a key part of cancer care.
As we keep exploring new ways in radiation oncology, even more breakthroughs are on the horizon. The future of cancer treatment looks bright, with targeted radiation therapy leading the way. By using these advances, we can make treatments better and improve the lives of cancer patients.
FAQ
What is radiation therapy, and how does it work?
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. It damages their DNA, stopping them from growing. We use different types of radiotherapy, each suited for specific cancers.
What are the goals of radiation treatment in cancer care?
Radiation treatment aims to cure or stop cancer from growing. It also helps manage symptoms in advanced cases. This improves patients’ quality of life.
What are the different types of radiotherapy?
Radiotherapy includes external beam, brachytherapy, and more. Each type targets cancer differently. We choose the best one for each patient’s needs.
What is external beam radiation therapy?
External beam radiation therapy (EBRT) uses advanced techniques. It targets tumors while protecting healthy tissues. This ensures precise treatment.
What is brachytherapy, and who is it ideal for?
Brachytherapy places a radioactive source inside tumors. It’s best for prostate, cervical, and breast cancers. We use it based on the patient’s cancer type.
What is stereotactic radiosurgery and radiotherapy?
Stereotactic radiosurgery and radiotherapy use advanced technologies. They treat brain, spine, and body tumors. We choose single-session or fractionated treatments based on the tumor.
What is proton therapy, and what are its advantages?
Proton therapy uses proton beams to target tumors. It’s precise, minimizing damage to healthy tissues. We use it for pediatric patients and sensitive areas.
What is image-guided radiation therapy?
Image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) tracks tumors in real-time. It ensures accurate radiation delivery. This improves treatment outcomes.
Can radiation therapy cure cancer?
Yes, radiation therapy can cure or control cancer. Success rates vary by cancer type. We discuss its effectiveness with our patients.
What is neoadjuvant therapy, and how is radiation therapy used?
Neoadjuvant therapy shrinks tumors before surgery. Radiation therapy is used to improve surgery outcomes. It also reduces cancer recurrence risk.
What is systemic radiotherapy?
Systemic radiotherapy treats cancer that has spread. We use radioactive iodine for thyroid cancer and targeted radiopharmaceuticals for metastatic disease.
Does radiation therapy have side effects?
Yes, radiation therapy can have side effects. These depend on the radiation type, dose, and tumor location. We guide patients on managing these effects.
How is radiation therapy tailored to individual patients?
We tailor radiation therapy to each patient’s needs. This includes cancer type, stage, and overall health. Advanced technologies ensure precise treatment.
Reference:
PubMed Central. (2017). An overview on radiotherapy: From its history to its advances.