Last Updated on November 25, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir
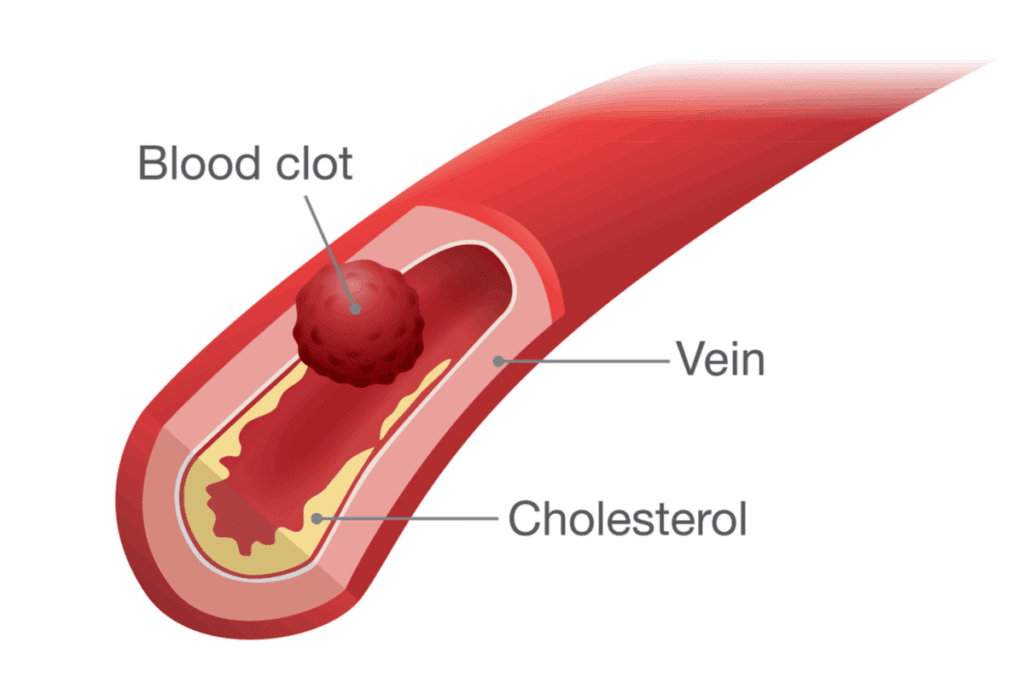
Blood Disease That Causes Blood Clots: Amazing 7 FactsSeeing blood clots in urine can be scary. But knowing why it happens is the first step to getting better. At Liv Hospital, we offer trusted care and focus on you. We help figure out if you need quick help or just a check-up.Is the link between UTI and blood clots serious? Learn what causes blood clots in your urine during a urinary tract infection and when to worry.
Blood clots in urine, also known as hematuria, happen when there’s enough bleeding in the urinary tract. This lets clots form and pass when you pee. It can mean different things, like infections, kidney stones, or serious diseases.
We’ll look at the causes of blood clots in urine. This includes infections, stones, and cancer. Knowing when to see a doctor is key. It helps get the right treatment.
Blood clots in urine, known as hematuria, can be scary and needs checking. It affects up to 30% of adults at some time. It can show as tiny blood in urine or big clots you can see.
Hematuria means blood in the urine. It’s split into two types. Microscopic hematuria is found in tests, while gross hematuria makes urine look pink, red, or brown. Seeing blood in urine can mean many urinary problems.
Blood clots in urine come from platelets and fibrin. When the urinary system bleeds, the body tries to stop it by clotting. Platelets gather, and fibrin forms, creating a clot. These clots can be small or big and may come out in the urine.
Urinary blood clots can look red, brown, stringy, or jelly-like. Their look can hint at what’s causing the bleeding. Big clots might mean serious bleeding. Knowing what these clots look like helps figure out why there’s blood in the urine.
We’ll look at why clots in urine happen next. We’ll cover the main reasons and what they mean for your health.
It’s important to know why blood clots might show up in your urine. These clots can be a sign of many things, from simple infections to serious diseases like cancer.
Several things can lead to blood clots in the urine. These include:
These issues can cause bleeding in the urinary tract, which leads to clot formation. Finding out the cause is key to treating it right.
Some people are more likely to get conditions that cause urinary blood clots. These include:
Demographic differences affect who gets urinary blood clots. For example:
| Condition | Demographic Most Affected | Common Age Range |
| Urinary Tract Infections | Women | 20-50 years |
| Kidney Stones | Men | 30-60 years |
| Bladder Cancer | Older Adults | 60+ years |
Knowing these differences helps us spot who’s at higher risk. It’s a step towards early detection and treatment.
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) play a big role in blood clots in urine. UTIs happen when bacteria get into the urinary tract. This can cause infections and lead to bleeding in the urine.
UTIs can make the urinary tract bleed. The infection irritates the bladder or urethra, causing damage. This damage can lead to blood clots in the urine.
The signs of UTI-related bleeding can vary. They often include:
These symptoms can be uncomfortable and mean you need to see a doctor.
To treat UTI-induced bleeding, you need to get rid of the infection. Antibiotics are usually given to fight the bacteria. Patients are also told to:
At times, more treatments might be needed to manage symptoms or complications. It’s important to follow your doctor’s treatment plan. This helps clear the infection and prevents it from coming back.
Urinary stones are common and can cause a lot of pain and bleeding. They form when minerals in the urine crystallize. This can lead to discomfort, worse when they move or get stuck in the urinary tract.
Stones form when minerals in the urine concentrate. This can happen due to dehydration, certain diets, or genetics. These factors help create the perfect environment for stones to form.
Stones can irritate or damage the lining of the kidneys, ureters, or bladder. This irritation can lead to bleeding. Blood clots in the urine often mean a stone is causing a lot of irritation or blockage.
The size of a stone affects how much bleeding it causes. Bigger stones can lead to more pain, blockage, and bleeding. Where the stone is in the urinary tract also affects symptoms.
Treatment for bleeding due to stones depends on the stone’s size, location, and type. It also depends on how bad the symptoms are. Treatment can range from simple hydration and pain relief to more complex procedures like lithotripsy or surgery.
| Stone Size | Treatment Approach | Expected Outcome |
| Small (<5 mm) | Conservative management | Spontaneous passage |
| Medium (5-10 mm) | Medical expulsion therapy | Facilitated passage |
| Large (>10 mm) | Lithotripsy or surgery | Stone fragmentation or removal |
Knowing about urinary stones and their treatment is key to managing symptoms and avoiding complications. If you’re experiencing symptoms, getting medical help is important to find the right treatment.
Blood clots in urine can signal kidney diseases that need quick diagnosis and treatment. We’ll look at kidney diseases that cause blood clots, like inflammatory conditions and infections.
Glomerulonephritis is an inflammatory disease that harms the kidneys’ filtering units, the glomeruli. It can cause hematuria, leading to blood clots in urine. Other conditions, like vasculitis and lupus nephritis, can also cause similar symptoms.
Symptoms of glomerulonephritis include hematuria, proteinuria, and kidney failure in severe cases. Treatment focuses on the underlying cause, reducing inflammation, and managing symptoms.
Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) is a genetic disorder with numerous cysts in the kidneys. These cysts can damage the kidneys and impair function, causing hematuria and blood clots.
PKD can also lead to kidney stones, infections, and kidney failure. Managing PKD involves monitoring kidney function, controlling blood pressure, and addressing complications.
Pyelonephritis is a kidney infection that can cause a lot of discomfort. It happens when bacteria infect the kidneys, causing inflammation and potentially leading to hematuria and blood clots.
Symptoms of pyelonephritis include flank pain, fever, and urinary symptoms. Treatment involves antibiotics to clear the infection and supportive care to manage symptoms.
When blood clots appear in urine, it’s important to watch kidney function to avoid long-term damage. Regular tests and imaging studies are needed to check kidney function and structure.
Managing kidney diseases that cause blood clots in urine requires a thorough approach. This includes regular check-ups with a healthcare provider and following treatment plans.
| Kidney Disease | Characteristics | Symptoms | Treatment Approaches |
| Glomerulonephritis | Inflammatory disease affecting glomeruli | Hematuria, proteinuria, kidney failure | Address underlying cause, reduce inflammation |
| Polycystic Kidney Disease | Genetic disorder with cysts in kidneys | Hematuria, kidney stones, infections, kidney failure | Monitor kidney function, control blood pressure |
| Pyelonephritis | Kidney infection | Fever, flank pain, urinary symptoms | Antibiotics, supportive care |
Hematuria, or blood in the urine, can be a sign of urinary tract cancers. This is why it’s important to see a doctor right away. Cancers in the urinary system can cause blood in the urine, which might clot. Knowing about this link is key for catching cancer early and treating it well.
Bladder cancer often shows up as blood in the urine. This blood might be seen with the eye or found in lab tests. Other signs include painful urination, needing to urinate a lot, and pelvic pain in later stages. Spotting these signs early can help doctors find and treat the cancer quickly.
Key symptoms to watch for include:
Kidney cancer, or renal cell carcinoma, can cause blood in the urine when it bleeds. Hematuria is not always there at first, but it’s more common as the cancer grows. Other signs might be flank pain, a mass that can be felt, and symptoms like weight loss and fever.
It’s essential to note that kidney cancer may not always present with symptoms early on, making regular check-ups for high-risk individuals critical.
In men, prostate cancer can lead to urinary problems, including blood in the urine, if it’s spread or advanced. Symptoms like a weak urine flow or trouble starting to urinate can also happen. Getting screened for prostate cancer early is very important.
Finding cancers early that cause hematuria can greatly improve treatment results. Regular check-ups, knowing your and your family’s health history, and telling your doctor about any unusual symptoms are all key. Catching these cancers early can help avoid serious problems like blood clots in the urine.
We emphasize the importance of:
Many patients face blood clots in their urine due to hidden conditions. Infections, stones, and cancers are common causes. But, other serious health issues can also lead to this symptom.
An enlarged prostate, or Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), is common in older men. It can cause bleeding due to pressure on the urethra. The risk of developing BPH increases with age. It’s key to watch for symptoms and seek help if blood clots appear in the urine.
Trauma to the urinary system can cause bleeding and clotting. This can happen from accidents, sports injuries, or medical procedures. The severity of the trauma determines the extent of the bleeding. Sometimes, surgery is needed to fix the injury.
People with bleeding disorders, like hemophilia, or those on anticoagulant meds, face a higher risk of hematuria. These conditions make it hard for the body to clot blood properly. This increases the risk of bleeding in the urinary tract.
| Bleeding Disorder | Effect on Urinary System |
| Hemophilia | Increased risk of bleeding in the urinary tract |
| Anticoagulant therapy | Higher risk of hematuria due to impaired clotting |
Certain meds can raise the risk of bleeding and hematuria. These include anticoagulants, antiplatelet drugs, and some antibiotics. It’s vital for patients to tell their healthcare providers about all meds they’re taking to check for bleeding risks.
Blood clots in urine need a detailed check to find the cause. Doctors use many steps to figure out why these clots happen. This helps them choose the best treatment.
The first step is a full medical history and physical check. We look at symptoms, past health, and lifestyle to find possible causes. A physical exam might show signs like belly pain or a big prostate.
Labs are key in finding blood clot causes. Tests include:
These tests give important info and guide next steps.
Imaging helps see the urinary tract and find problems. Common tests are:
Some cases need special urology tests. These include:
These tests give a clear picture of the condition. They help doctors plan the best treatment.
Knowing when to get medical help for blood clots in urine is key for your health. Blood clots in urine, or hematuria, can signal many health issues. Some of these may need quick medical care.
Certain signs with blood clots in urine mean you need to see a doctor right away. Severe pain could mean a kidney stone or blockage. Inability to urinate is also a big warning sign that needs fast action.
Fever is another sign of infection. If you have any of these symptoms with blood clots in your urine, get medical help fast.
Urinary blockage can happen when blood clots block urine flow. You might feel painful urination, need to urinate often, or have trouble starting or stopping urine flow. If you notice these signs, see a doctor.
Other symptoms that need quick attention include vomiting, dizziness, and severe abdominal or back pain. These can mean serious issues like infection or severe bleeding.
Even without severe symptoms, blood clots in urine need a doctor’s check-up. It’s best to make an appointment with a healthcare provider. They will do a physical exam and might run tests or scans to find out why you have blood in your urine.
In short, while some cases are urgent, any blood clots in urine should be checked by a doctor. This ensures you get the right treatment on time.
Blood clots in urine can signal serious health issues. This article has covered the main causes, like infections, stones, and cancers. Knowing these causes is key to finding the right treatment.
It’s vital to see a doctor if you notice blood in your urine. Quick diagnosis and treatment are critical, as they can greatly improve your health. By being aware of the symptoms and risk factors, you can take care of your health early on.
To wrap it up, blood clots in urine are concerning but manageable. Understanding their causes and how to diagnose them can ease worries. If you’re experiencing hematuria, don’t hesitate to talk to a healthcare professional. They can help find the cause and provide the right care.
Blood clots in urine can come from many health issues. These include urinary tract infections, kidney stones, kidney diseases, and cancers of the urinary tract.
Hematuria is when blood is in your urine. It can be tiny or big enough to see with your eyes. Big hematuria might have blood clots.
UTIs can make your urinary tract inflamed and irritated. This can cause bleeding and blood clots.
Yes, kidney stones can cause bleeding. This is more likely when they move or get stuck in the urinary tract.
Signs include pain when you pee, needing to pee a lot, and sometimes seeing blood in your urine.
UTIs are treated with antibiotics. Sometimes, other steps are needed to help with symptoms.
Yes, cancers like bladder and kidney cancer can cause blood in your urine and blood clots.
Seeing blood in your urine is a common sign of bladder cancer. Other urinary symptoms can also occur.
Get medical help right away if you have severe pain, trouble peeing, or a fever. Also, if you see blood clots in your urine.
Doctors use a medical history, physical exam, and lab tests like urine analysis. They also do imaging studies and urological procedures.
Yes, an enlarged prostate can lead to bleeding and blood clots in your urine.
Bleeding disorders can make it more likely to bleed and form clots in the urinary tract.
Yes, some medications can make bleeding and clotting more likely.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!