Last Updated on November 4, 2025 by mcelik

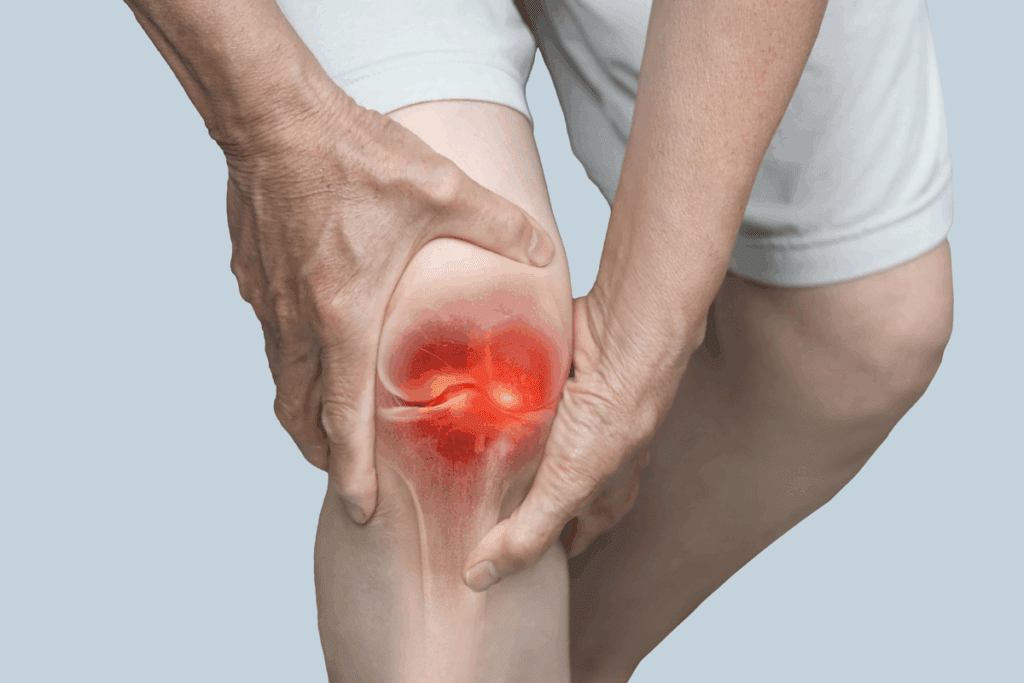
Tendonitis of the knee is a common issue among athletes. Jalen Royals, a wide receiver, had to sit out due to this condition. Tendonitis is when tendons get inflamed, leading to pain and discomfort.
Walking is seen as a low-impact exercise that can help manage pain and aid in healing. For those with knee tendonitis, gentle exercises like walking might offer some relief. But, is walking really good for tendonitis of the knee?
Knowing about knee tendonitis is key to managing it. This condition causes inflammation in the tendons around the knee. It can really hurt and make life harder.
Tendons connect muscles to bones. When they get inflamed, it leads to pain and discomfort.
Knee tendonitis affects the tendons near the knee. It’s often due to overuse or repetitive strain. This condition can hurt anyone, not just athletes.
There are several reasons for knee tendonitis. Overuse, poor training techniques, and inadequate equipment are common. Running, jumping, or quick changes can make it worse.
| Cause | Description |
| Overuse | Repetitive strain on the tendons without adequate rest. |
| Poor Training Techniques | Incorrect methods of performing exercises or sports. |
| Inadequate Equipment | Using improper or worn-out gear during activities. |
Symptoms include pain, swelling, and stiffness around the knee. Spotting these early is important for managing and recovering.
To manage knee tendonitis while walking, understand its causes and symptoms. Using knee tendonitis recovery exercises and tips can help. It’s also good to know the difference between walking vs running tendonitis to pick the right exercise.

There are several types of knee tendonitis, each with its own characteristics. Knowing these differences is key to creating a good exercise plan. This includes knee tendonitis exercise and low impact exercises knee.
Patellar tendonitis, also known as Jumper’s Knee, affects the tendon between the kneecap and shinbone. It’s common in athletes who jump a lot. Walking as therapy tendonitis can help if done right, as it improves blood flow without too much strain.
Quadriceps tendonitis is when the tendon that links the quadriceps muscle to the kneecap gets inflamed. It can happen from too much use or a direct hit. Proper walking technique tendonitis is important to not make it worse. Changing how you walk and adding strengthening exercises can help manage the symptoms.
Both types of tendonitis need a careful approach to exercise and activity. By knowing the specific condition and its effects, people can follow a safer and more effective walking as therapy tendonitis plan.
It’s key to know how tendonitis and movement work together for good rehab plans. Tendonitis in the knee causes inflammation and damage to tendons. This can really hurt your ability to move and enjoy life.
Tendons heal slowly because they don’t get much blood. This makes the recovery process longer than for other tissues.
Tendons go through three healing stages: inflammation, repair, and remodeling. The first stage, inflammation, brings more blood and growth factors to start healing.
| Healing Phase | Characteristics | Role of Movement |
| Inflammation | Increased blood flow, growth factors | Limited movement to avoid excessive strain |
| Repair | Tissue regeneration, collagen synthesis | Gradual introduction of controlled movement |
| Remodeling | Tissue strengthening, alignment | Progressive loading and movement |
Movement, like walking, is very important for tendon healing. It helps bring blood, which is needed for nutrients and healing factors.
Rehabilitation walking tendonitis programs mix rest with movement. Physical therapy walking benefits include better blood flow, less stiffness, and stronger tendons.
Knowing how tendons heal and how movement helps is key for knee tendonitis recovery. This knowledge helps people make smart choices about their treatment and recovery.
Gentle walking is a low-impact exercise that can help with knee tendonitis. It offers relief and supports healing. Walking can bring many benefits that help in recovery.
Walking boosts blood flow to the affected area, which is key for healing. This increased blood flow brings oxygen and nutrients to the damaged tendons. It supports the repair process.
Using a knee support like RecovrKnee while walking can also help. It provides stability and reduces strain on the knee.
Regular walking keeps the joint mobile, reducing stiffness and improving flexibility. This is vital for those with knee tendonitis. Reduced mobility can make the condition worse.
Walking helps maintain functional ability and reduces pain. It keeps the knee joint mobile.
Walking can have big psychological benefits. It helps reduce stress and anxiety related to chronic pain. It also improves mood and overall well-being.
The gentle exercise of walking is great for mental health during recovery. It helps keep the mind healthy while the body heals.
In conclusion, walking is good for those with knee tendonitis. It improves blood flow, maintains joint mobility, and offers psychological benefits. By walking regularly and using knee support, individuals can aid their recovery and improve knee health.
Walking with knee tendonitis needs careful steps to avoid making it worse. “Understanding your body’s limits and progressing slowly is key,” says an orthopedic specialist.
Before you start walking, check your pain levels. Know how bad your knee tendonitis is and how it affects you. Pain assessment helps decide how long and how hard your walks should be.
It’s important to tell the difference between normal exercise pain and pain that means you’re hurting yourself more. Paying attention to your body and knowing your pain helps adjust your walks.
Start with short walks on flat ground when you have knee tendonitis. Slowly add more distance and intensity over time. This progressive approach lets your tendons get used to walking without getting too stressed.
Try to increase your walking by 10% each week. This slow increase helps prevent injuries and lets your tendons heal and get stronger.
Keep an eye on how your body reacts to walking. Notice any changes in pain or discomfort. If your symptoms get worse, you might need to change your walking plan.
Keeping a symptom journal helps track your progress and spot any patterns. This info is key to making smart choices about your walking.
In summary, walking with knee tendonitis can be good if done right. By checking your pain, starting slow, and watching your body, you can walk safely and enjoy its benefits.
Walking can be both a blessing and a curse for those with knee tendonitis. It’s often suggested as a low-impact way to manage the condition. Yet, there are times when it might make things worse.
Walking can make knee tendonitis symptoms worse if the tendon gets too much stress or strain. This is more likely if you suddenly start walking more or harder.
It’s important to listen to your body when walking. If you notice any of these signs, it’s time to stop and see a doctor:
Ignoring these signs can cause more harm and make recovery take longer.
| Signs to Watch For | Action to Take |
| Sharp knee pain | Stop walking, rest, and consult a healthcare professional |
| Increased swelling | Apply ice, elevate the knee, and seek medical advice |
| Persistent pain | Modify your walking routine, consider alternative exercises |
Knowing the risks and listening to your body can help you manage knee tendonitis. This way, you can stay active without hurting yourself.
For those with knee tendonitis, learning the right walking technique is key. Walking is good for the knees, but wrong steps can make things worse.
Foot placement and stride length are important. Try to land on your midfoot or forefoot, not your heel. Avoid overstriding to lessen knee stress. Go for a stride that feels natural and smooth.
Good posture and body alignment are vital. Keep your head up, shoulders relaxed, and engage your core. Ensure your body is aligned from head to heels. Avoid slouching or leaning forward to prevent knee strain.
“Good posture is the foundation of efficient and safe walking.”
An Orthopedic Specialist
The pace and intensity of your walk matter too. Start with a gentle pace and increase it slowly. Avoid sudden speed changes or long walks that can hurt your knees. Pay attention to how your body feels and adjust your walks as needed.
By focusing on proper walking technique, people with knee tendonitis can reduce knee strain. They can enjoy walking without making their condition worse.
For those with knee tendonitis, picking the right walking shoes is key. It’s not just about feeling comfortable. The right shoes also support your knee health. This makes walking less painful and more enjoyable.
When looking for walking shoes for knee tendonitis, focus on a few important features. Good arch support is essential. It spreads out your body’s weight and lessens knee strain. Cushioning is also vital; it softens the impact of each step, easing knee stress. Plus, shoes with a stable and supportive heel counter help stop the heel from moving too much, which can irritate the tendon.
| Feature | Benefit |
| Good Arch Support | Reduces strain on the knee by distributing weight evenly |
| Cushioning | Absorbs impact, reducing stress on the knee joint |
| Stable Heel Counter | Prevents excessive heel movement, reducing irritation to the tendon |
It’s important to know when to swap out your walking shoes. They should be replaced every 300 to 500 miles or every 3 to 6 months, based on how much you use them. Look for signs like worn-out soles, less cushioning, and visible wear on the heel counter.
By picking the right shoes and knowing when to replace them, people with knee tendonitis can manage their condition better. They can enjoy walking without making their symptoms worse.
The surface you walk on is key in managing knee tendonitis. Different surfaces can either lessen or increase the impact on your knees. This affects how severe the condition is.
Soft, even surfaces are best for walking with knee tendonitis. These include:
Walking on these surfaces can help reduce the repetitive stress on your knee tendons.
On the other hand, some surfaces can make knee tendonitis worse and should be avoided:
By choosing the right walking surface, you can manage your knee tendonitis more effectively.
Managing pain while walking with knee tendonitis needs a careful plan. This plan should cover before and after walking. Good pain management helps keep you active, even with this condition.
Before you start walking, think about how to ease knee tendonitis pain. Here are some ways to do it:
Table: Pre-Walking Pain Relief Methods Comparison
| Method | Effectiveness | Duration of Relief |
| Applying Ice | High | 2-3 hours |
| Topical Creams/Gels | Moderate | 4-6 hours |
| Over-the-counter Pain Relievers | High | 6-8 hours |
After walking, it’s key to use recovery methods to manage pain. Here are some good ones:
By using these strategies, you can handle knee tendonitis better. This way, you can stay active and enjoy your walks.
Stretching and warm-up exercises are key for safe and effective walking, even more so for those with knee tendonitis. They boost blood flow to the tendons, enhance flexibility, and lower injury risk.
Knee mobility exercises are vital for keeping or boosting knee range of motion. Simple knee bends and straightening exercises can be done while holding onto a chair. The knee extension stretch is also helpful, done by sitting on the floor with legs straight out and leaning forward slightly.
A dynamic warm-up routine before walking boosts performance and cuts injury risk. Begin with leg swings to loosen hip and knee joints. Then, do high knees and butt kicks to warm up your muscles and get blood flowing.
Adding these stretching and warm-up exercises to your routine prepares your knees for walking. This can help reduce pain and improve knee health.
Strengthening exercises are key to keeping your knees healthy and easing tendonitis pain. When you have knee tendonitis, it’s not just about easing the pain. It’s also about making the muscles around your knee stronger to avoid more injuries. This way, you can keep walking and doing physical activities without worrying about making your condition worse.
The quadriceps muscles are very important for keeping your knee stable. Making these muscles stronger can help lessen tendonitis symptoms. Quadriceps strengthening exercises like straight leg raises and squats are very helpful. To do a straight leg raise, lie on your back, tighten your quadriceps, and lift your leg about 12 inches off the ground. Hold for a few seconds and then lower it back down.
It’s also important to work on hamstring and calf exercises. Hamstring curls and calf raises can improve knee function and lessen tendon strain. For hamstring curls, stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and slowly bend one knee, bringing your heel towards your buttocks. Calf raises involve standing on the edge of a step and raising up onto your tiptoes.
Core and hip strengthening are also essential for knee health. Weak core and hip muscles can cause poor walking mechanics, which can stress your knee tendons more. Exercises like bridges and planks can strengthen these areas. Bridges involve lying on your back with your knees bent and lifting your hips towards the ceiling. Planks require holding a position with your body in a straight line from head to heels.
By adding these strengthening exercises to your routine, you can support your knee health better. This way, you can walk with less discomfort from tendonitis.
The right knee support can help those with knee tendonitis who love walking. It offers stability and relief. This makes it a great choice for staying active.
There are many knee braces and supports out there. Each one meets different needs and preferences. Here are a few examples:
RecovrKnee is a great example of a product that offers specific support. It’s perfect for those with knee tendonitis. When picking a knee support, think about your activity level and support needs.
Getting the most from your knee support means using it right. Here are some tips:
Choosing the right knee support and using it correctly helps those with knee tendonitis. It lets them walk comfortably and aids in recovery.
Low-impact exercises can change the game for those with knee tendonitis. They help manage the condition and keep you fit without harming your knee.
Swimming is a top choice for knee tendonitis. Water’s buoyancy eases joint stress, making it a safe workout. Water aerobics is also great.
Swimming and water exercises boost heart health and strengthen knee muscles. They’re better than high-impact activities like running or jumping.
Stationary cycling is great for knee tendonitis. It lets you control your pace and adjust to your comfort. Cycling improves knee movement and strengthens muscles.
For the best results, make sure the bike fits you well. Start with low resistance.
Elliptical training offers a low-impact, smooth motion. It’s like running but easier on the knees. It’s good for heart health and leg strength.
Keep the right posture and stride length on an elliptical. This avoids knee strain.
Adding these low-impact exercises to your routine can help with knee tendonitis. They also boost knee health overall.
To stop knee tendonitis from coming back, it’s key to make long-term plans. This includes changing your lifestyle and staying active. Good management helps with current symptoms and keeps your knees healthy.
Changing your lifestyle can greatly help your knee health. Keeping a healthy weight is important because it lessens knee tendon strain. Also, adding anti-inflammatory foods to your diet can help fight inflammation.
Regular exercise is key for keeping your knees healthy and preventing tendonitis. You should do strengthening, flexibility, and low-impact exercises.
| Exercise Type | Benefits | Examples |
| Strengthening Exercises | Builds muscle around the knee | Quadriceps and hamstring strengthening |
| Flexibility Routines | Improves knee mobility | Leg swings, knee bends |
| Low-Impact Activities | Reduces stress on knee tendons | Swimming, cycling |
By mixing lifestyle changes and regular exercise, you can manage knee tendonitis well. This helps prevent it from coming back.
Managing knee tendonitis while walking is all about finding a balance. It’s important to stay active but avoid making things worse. Knowing what causes and symptoms of knee tendonitis are is a good start.
Walking can be good for your knees if done right. It helps with blood flow and keeps joints moving. Using the right walking techniques, wearing the right shoes, and using knee supports can help a lot.
To keep your knees healthy, you need to do more than just walk. Adding exercises, stretches, and low-impact activities is key. This way, you can lower the chance of getting knee tendonitis again and stay healthy overall.
Getting the right balance is essential for managing knee tendonitis and keeping your knees healthy for a long time. Paying attention to how your body feels and making changes as needed is important. This way, you can enjoy walking without worrying about harming your knees.
Walking can help with knee tendonitis by improving blood flow and keeping joints mobile. It also has mental health benefits. But, start slowly and watch for pain to avoid making it worse.
Walking can hurt patellar and quadriceps tendonitis more. The impact varies based on how severe and what type of tendonitis you have.
To manage knee pain, use stretches and warm-ups before walking. After, try icing and compression to recover.
Grass or trails are softer and better for your knees than hard surfaces like concrete or asphalt.
Yes, a knee support like a brace can help. Make sure to use it correctly for the best results.
Yes, swimming, cycling, and using an elliptical are good alternatives. They put less stress on your knee.
To prevent it, stay healthy and exercise regularly. Focus on strengthening your quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles.
Stop if your knee hurts more, swells, or feels unstable. It’s time to try something else or see a doctor.
Change your shoes every 300-500 miles or 3-6 months. This keeps your knees supported and cushioned.
Yes, exercises for your quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles can help. They support your knee and reduce pain.
Yes, stretching before walking is key. It prepares your knee and muscles, reducing the risk of making tendonitis worse.
Gentle walking and low-impact exercises help keep your joints moving. Adding exercises that improve flexibility is also good.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!