Last Updated on November 17, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir
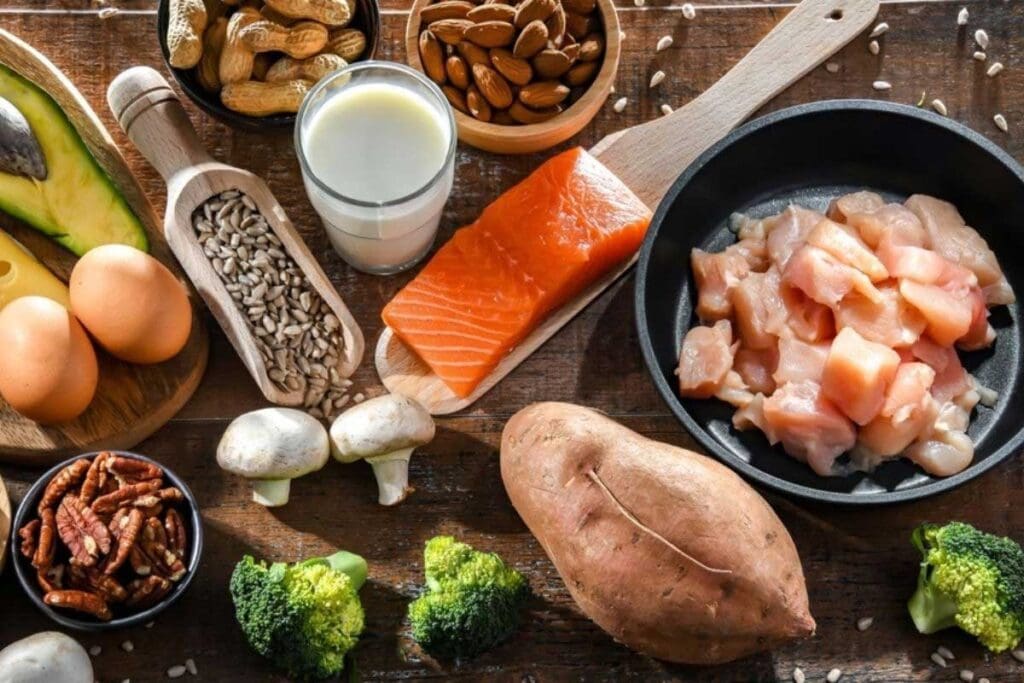

At LivHospital, we understand how vital Vitamin B is for your overall health. It’s a group of nutrients that support energy production, brain function, and cell metabolism. There are eight different vitamins in this group: B1 (thiamine), B2 (riboflavin), B3 (niacin), B5 (pantothenic acid), B6 (pyridoxine), B7 (biotin), B9 (folate or folic acid), and B12 (cobalamin).
These vitamins are essential for keeping your body energized, supporting brain health, and maintaining proper cell function. If you’re wondering what contains Vitamin B, the answer includes a variety of foods—from animal products to plant-based options. In this guide, we’ll explore 15 foods rich in B vitamins, discuss their benefits, and share simple ways to include them in your daily meals for a healthier lifestyle.

B vitamins are key for energy and brain health. They help our bodies turn food into energy and keep our nervous system working. Let’s dive into why B vitamins are so important for our health.
B vitamins are eight essential nutrients our bodies need. They help us turn food into energy and keep our skin and muscles healthy. B vitamins are vital for energy production, and not having enough can cause health problems.
The eight B vitamins are thiamine (B1), riboflavin (B2), niacin (B3), pantothenic acid (B5), vitamin B6, biotin (B7), folate (B9), and vitamin B12. Each vitamin has its own role, but they all work together to keep us healthy.
Here’s a quick look at what each does:
| B Vitamin | Function |
| Thiamine (B1) | Converts carbohydrates into energy |
| Riboflavin (B2) | Essential for energy production and can help reduce the risk of cataracts |
| Niacin (B3) | Important for skin health and converting carbohydrates into energy |
| Pantothenic acid (B5) | Necessary for synthesizing coenzyme-A (CoA) and producing energy |
The B vitamin complex includes eight vitamins, each with its own role in our health. These vitamins help with energy, nerve function, and heart health. They are key for many bodily processes.
B1, or thiamine, is vital for energy and nerve health. B2, or riboflavin, aids in energy production and can lower cataract risk. B3, or niacin, helps turn carbs, fats, and proteins into energy.
Key Functions:
B5, or pantothenic acid, is needed for making coenzyme-A (CoA), a key energy enzyme. B7, or biotin, is important for energy and keeping skin, hair, and nails healthy.
Key Functions:
B6, B12, and folate are vital for brain, blood, and heart health. B6 helps with many reactions, B12 makes red blood cells, and folate prevents birth defects.
| B Vitamin | Primary Functions | Food Sources |
| Thiamine (B1) | Energy production, nerve function | Whole grains, legumes, nuts |
| Riboflavin (B2) | Energy production, eye health | Dairy products, leafy greens, almonds |
| Niacin (B3) | Energy production, skin health | Meat, fish, whole grains |
| Pantothenic Acid (B5) | Energy production, hormone synthesis | Meat, vegetables, whole grains |
| Biotin (B7) | Energy production, skin, hair, and nail health | Nuts, seeds, eggs, dairy |
| B6 | Brain function, immune system | Meat, fish, vegetables, whole grains |
| B12 | Red blood cell production, nerve function | Animal products, fortified plant-based milk |
| Folate (B9) | Preventing birth defects, red blood cell production | Leafy greens, legumes, fortified cereals |
B vitamins are key for energy and nerve health. Animal-based foods are top sources. They offer B vitamins and other nutrients for health.
Salmon is a great source of B vitamins, like B12 and B6. A 3-ounce cooked salmon has lots of these vitamins. They help your heart and brain.
Tuna is full of B vitamins, including B12, B6, and niacin. It’s easy to add to many dishes, like salads and sandwiches.
Liver, like beef liver, is packed with B vitamins. It has folate, B12, and riboflavin. It’s a food that boosts your B vitamin intake.
Eggs are a complete source of B vitamins. They have many vitamins in one serving. They’re high in B12 and folate, making them a great choice.
| Food | B Vitamin Content | Nutritional Benefits |
| Salmon | Rich in B12 and B6 | Supports heart health and brain function |
| Tuna | High in B12, B6, and Niacin | Versatile and supports energy production |
| Liver | Rich in Folate, B12, and Riboflavin | Nutrient-dense, boosts B vitamin intake |
| Eggs | Complete B vitamin profile | High in B12 and Folate, supports overall health |
B vitamins are found in plenty in poultry and dairy. These foods are key to a healthy diet. They offer important nutrients and make meal planning easy.
Chicken is a favorite in many diets. It’s an excellent source of B6 and niacin. These vitamins help with energy and keeping skin healthy. A 3-ounce cooked chicken breast gives a lot of B6 and niacin you need each day.
Milk is also packed with B vitamins, like B12 and riboflavin. These vitamins are important for nerves and making red blood cells. Drinking a glass of milk helps meet your daily B vitamin needs.
Yogurt and cheese, being fermented, are full of B vitamins. They’re great for riboflavin and B12. Adding yogurt and cheese to your diet boosts B vitamins and supports gut health.
| Food Item | B Vitamin Content | Nutritional Benefit |
| Chicken | B6, Niacin | Energy metabolism, healthy skin |
| Milk | B12, Riboflavin | Nerve function, red blood cell production |
| Yogurt/Cheese | Riboflavin, B12 | Gut health, nerve function |
B vitamins are found in many plant-based foods. These foods help with energy, brain function, and heart health. Let’s look at some of the best plant-based sources of B vitamins.
Legumes are packed with folate and B6. You’ll find lentils, chickpeas, and black beans in this group. They’re not just good for B vitamins but also for fiber and protein.
Whole grains are a treasure trove of B vitamins. Brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread are top picks. They’re full of thiamine, niacin, and folate, among others.
Fortified cereals are also rich in B vitamins. They often have B12, folate, and other B vitamins. They’re a quick and easy breakfast that can help you get your daily B vitamins.
When picking fortified cereals, choose ones with little added sugar and lots of fiber. This way, you get the most nutritional benefits.
Leafy greens and some vegetables are full of B vitamins. They are key to a balanced diet. These foods give us important nutrients and health benefits when we eat them regularly.
Spinach is famous for its folate. It’s great for boosting your folate intake. Folate helps with cell growth, DNA making, and preventing birth defects. Add spinach to salads, smoothies, or sautéed dishes for its health perks.
Nutritional Highlight: One cup of cooked spinach has lots of folate and other B vitamins like B2 and B6.
Avocados are full of healthy fats and B vitamins. They have folate, B6, and B5. Their creamy texture is perfect for sandwiches, salads, and dips.
Health Benefit: Avocado’s B vitamins help with energy and keep skin and nerves healthy.
Asparagus and Brussels sprouts are rich in folate. They’re great for B vitamin intake. Asparagus also has B1 and B2, while Brussels sprouts have B6 and folate.
Culinary Tip: Roasting or steaming these veggies brings out their taste and keeps their nutrients.
| Vegetable | Primary B Vitamins | Nutritional Benefits |
| Spinach | Folate (B9), B2, B6 | Supports cell division and DNA synthesis |
| Avocados | Folate (B9), B6, B5 | Contributes to energy production and healthy skin |
| Asparagus | Folate (B9), B1, B2 | Essential for nervous system function and energy production |
| Brussels Sprouts | Folate (B9), B6 | Supports heart health and immune function |
Knowing how much B vitamins you need is key to staying healthy. B vitamins help with energy, nerve function, and heart health. The amount you need changes with age, sex, and other factors.
We’ll look at the daily needs for B12, B6, and folate. We’ll also talk about what’s different for different ages. Remember, your needs might be unique, so always talk to a doctor for advice.
The amount of vitamin B12 you should take depends on your age. Adults need 2.4 micrograms (mcg) every day. Pregnant women should get 2.6 mcg, and breastfeeding women need 2.8 mcg.
Vitamin B12 is important for making red blood cells and keeping nerves healthy. Not getting enough can cause tiredness, weakness, and nerve problems.
| Age Group | RDA for Vitamin B12 (mcg) |
| Adults | 2.4 |
| Pregnant Women | 2.6 |
| Breastfeeding Women | 2.8 |
Adults need 1.3 milligrams (mg) of vitamin B6 each day. Folate, or vitamin B9, should be 400 micrograms (mcg) daily for adults.
Vitamin B6 helps with energy and nerve health. Folate is vital for fetal development and preventing birth defects.
“Folic acid is key to preventing neural tube defects in the fetus. Women of childbearing age should take 400 to 800 mcg of folic acid daily, along with eating foods rich in folate.”
Nutritional Guidelines
Each age group has different B vitamin needs. For example, older adults might need more vitamin B12 because their bodies absorb it less well.
Children and teens also have specific B vitamin needs. For instance, kids aged 1-3 need 0.5 mg of vitamin B6 daily.
It’s important to talk to a healthcare professional about your B vitamin needs. This is true for pregnant or breastfeeding women, and for anyone with special dietary needs or health conditions.
B6, B12, and folic acid together offer many health benefits. They are great for heart health. These vitamins work together to keep our bodies running smoothly.
B6, B12, and folic acid are key for heart health. They help control homocysteine levels. High homocysteine levels can lead to heart disease and stroke.
They help keep our hearts healthy by:
B6, B12, and folic acid are important for our brains and nerves. They help make neurotransmitters and keep our nervous system strong. Lacking these vitamins can cause fatigue, weakness, and brain fog.
They support brain health by:
B6, B12, and folic acid are essential for energy and cell health. They help our cells turn nutrients into energy. Having enough of these vitamins is key for energy and avoiding fatigue.
They boost energy by:
B vitamins are key for our health, but too much can be risky. Vitamin B complex is usually safe, but high doses from supplements can cause problems.
Too much Vitamin B can show in different ways. For example, too much Vitamin B6 can cause numbness and tingling in hands and feet. High doses of B12 are mostly safe, but too much folate (B9) can hide a B12 deficiency, leading to nerve damage.
Common signs of B vitamin excess include:
It’s important to know the difference between getting B vitamins from food and supplements. Food usually has safe amounts of B vitamins. But supplements can have much higher levels, raising the risk of too much.
| Vitamin B Type | Food Sources | Supplement Risks |
| B6 | Chicken, fish, potatoes | Neurological symptoms at high doses |
| B12 | Meat, fish, dairy products | Generally safe, but high doses can cause skin rashes |
| Folate (B9) | Leafy greens, legumes | Masking B12 deficiency at high doses |
Some people need to be careful with B vitamins. Pregnant women need folate but should avoid too much. People with kidney or liver disease should also watch their B vitamin levels closely.
Always talk to a healthcare professional before taking B vitamin supplements, even if you’re considering high doses. Knowing the risks and being careful with your intake can help you use Vitamin B complex safely for your health.
Adding B vitamins to your daily meals is key for staying healthy. Eating foods rich in B vitamins helps your body work better. This includes making energy, keeping your brain sharp, and keeping your heart healthy.
To get enough B vitamins, eat foods like salmon, tuna, and eggs. Also, include legumes, whole grains, and leafy greens in your meals. Don’t forget about fortified cereals, they’re good too.
Knowing how B vitamins help your body is important. By choosing the right foods, you can help your health. At LivHospital, we help you find the best foods for your health.
Adding B vitamins to your meals is easy and good for you. Just a few changes in your diet can make a big difference. This way, you can make sure you’re getting the B vitamins you need to stay healthy.
B vitamins are key for energy, brain health, and overall well-being. They help break down nutrients, support the nervous system, and help make red blood cells.
Yes, too much Vitamin B can be harmful. Taking too much, mainly from supplements, can cause nerve damage, skin issues, and stomach problems.
Vitamin B12 is found in animal products like salmon, tuna, liver, and eggs. B6 is in chicken, fish, and plant-based foods like legumes and whole grains.
Adults need about 2.4 micrograms of Vitamin B12 daily. Pregnant and breastfeeding women might need more.
Yes, plants like legumes, whole grains, spinach, and avocados are good sources of B vitamins.
B6, B12, and folic acid boost heart health, brain function, and energy. They help lower homocysteine levels, support brain health, and aid cell metabolism.
No, B6 and niacin are different vitamins with unique roles. They are both part of the B complex but serve different functions in the body.
Spinach, legumes, asparagus, and Brussels sprouts are rich in folic acid. Fortified cereals are also a good choice.
Eating a balanced diet is safer for B vitamins than supplements. But, some people might need supplements under doctor’s advice.
People with kidney or liver disease, and those on certain meds should be careful with B vitamins. Pregnant and breastfeeding women also need special care.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!