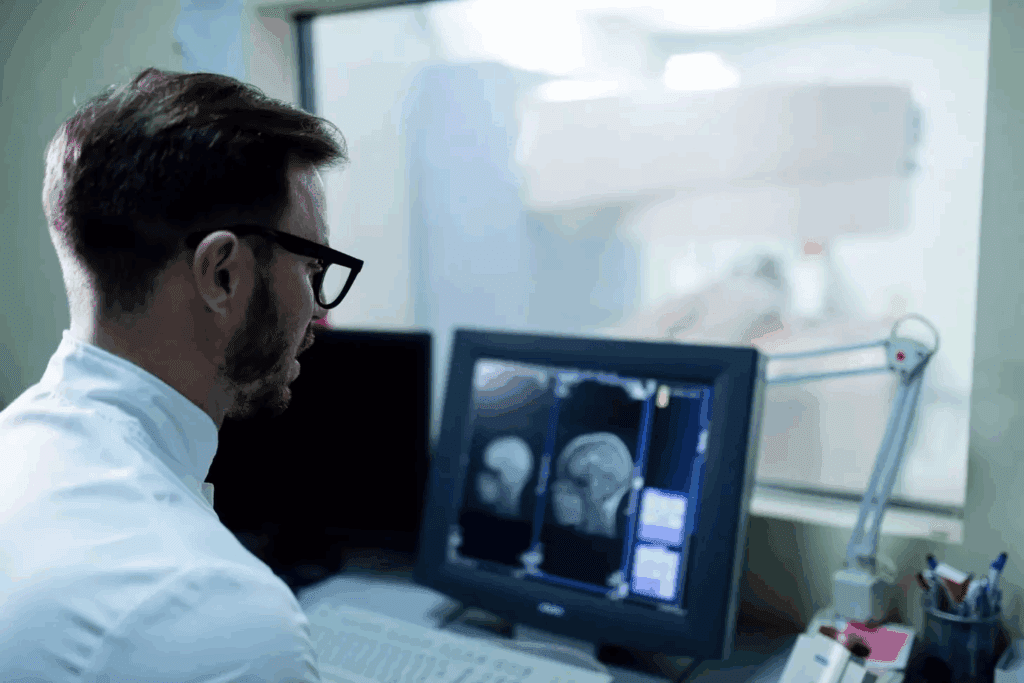
At Liv Hospital, we know how complex neurological conditions like multiple sclerosis (MS) can be. Damage to the myelin sheath around nerve fibers can cause brain lesions. These are abnormal tissue areas that MRI scans can show.
It’s key to know what MS lesions on brain MRI look like to diagnose and manage MS. We use MRI scans to spot the differences between an MS-affected brain and a normal one. This helps us tailor care for our patients.
Key Takeaways
- MS lesions are areas of abnormal tissue caused by damage to the myelin sheath.
- MRI scans are used to visualize brain lesions in MS patients.
- The appearance of MS lesions on MRI differs significantly from a normal brain.
- Understanding these differences is key for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
- At Liv Hospital, we use advanced MRI technology to provide personalized care for MS patients.
Understanding Brain Lesions in Multiple Sclerosis
It’s important to know about brain lesions to manage multiple sclerosis well. Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic disease that harms the central nervous system (CNS). This leads to many neurological symptoms. Brain lesions in MS are damaged areas caused by the disease’s effect on the CNS.
Definition and Formation of MS Lesions
MS lesions happen when the protective covering around nerve fibers, called myelin, is lost. This disrupts how nerves send signals. The immune system mistakenly attacks the myelin, causing inflammation and damage.
The exact reasons for this immune attack are not known. But, it’s thought that genetics and environment play a part. This leads to demyelination and the formation of lesions, seen on MRI scans.
The Role of Myelin Damage in Lesion Development
Myelin damage is key in creating MS lesions. Myelin helps nerves send signals quickly. When it’s damaged, signals slow down or stop, causing symptoms like vision problems and muscle weakness.
The damage to myelin in MS is complex. It involves inflammation, demyelination, and damage to nerve fibers. This can create lesions in the CNS, including the brain and spinal cord.
Inflammatory Processes in MS Lesion Formation
Inflammation is a major part of MS lesion formation. The immune system’s attack on myelin causes inflammation and tissue damage. This inflammation affects not just the lesion but also the surrounding areas, impacting CNS function.
Understanding the inflammation in MS is key to finding treatments. Treatments aim to reduce inflammation and control the immune response to prevent more damage.
What Does a Brain Lesion Look Like on MRI?
MRI scans are key in finding MS by showing brain lesions. These lesions are a key sign of Multiple Sclerosis. They can be seen through different MRI sequences.
Appearance on T2-Weighted Images
On T2-weighted images, MS lesions look bright. This is because they have more water due to inflammation and damage. These images are great for spotting lesions in the brain’s white matter.
“Black Holes” on T1-Weighted Images
Some MS lesions show up dark on T1-weighted images, called “black holes.” These dark spots mean severe damage and loss of brain tissue. Seeing black holes can mean the disease is getting worse.
Gadolinium Enhancement and Active Lesions
Gadolinium enhancement on T1-weighted images shows active MS lesions. When a lesion lights up with gadolinium, it means inflammation and damage are happening. This shows the disease is active.
Size and Shape Characteristics of MS Lesions
MS lesions come in different sizes and shapes. They are often shaped like an oval and face the ventricles. Their size can be small or quite large, sometimes merging with others.
| Characteristic | Description |
| Appearance on T2-weighted images | Hyperintense (bright) areas |
| Appearance on T1-weighted images | Hypointense (dark) areas, potentially “black holes” |
| Gadolinium Enhancement | Indicates active inflammation and blood-brain barrier disruption |
| Size and Shape | Ovoid, variable size, often perpendicular to ventricular surface |
Common Locations of MS Brain Lesions
Knowing where MS lesions usually show up is key for diagnosing and treating the disease. These lesions can pop up in different parts of the brain. Where they appear often matches the symptoms patients feel.
Periventricular White Matter
MS lesions often hit the periventricular white matter. This area wraps around the brain’s ventricles. Lesions here can cause a range of symptoms because they mess with nerve fibers.
Corpus Callosum
The corpus callosum, a thick band of nerve fibers, connects the brain’s two hemispheres. It’s a common spot for MS lesions. Lesions here can mess with coordination and thinking skills.
Juxtacortical Regions
Juxtacortical regions, near the cortex, are also often affected. Lesions here can lead to problems with thinking and moving, depending on where they are.
Infratentorial Areas
Infratentorial areas, like the cerebellum and brainstem, are vital for keeping us balanced and controlling basic functions. MS lesions in these spots can cause big problems with movement and basic functions.
The spot where MS lesions appear can really affect the symptoms and how the disease moves. Here’s a table that shows where MS lesions usually pop up and what symptoms they can cause:
| Location | Common Symptoms |
| Periventricular White Matter | Vision problems, cognitive issues |
| Corpus Callosum | Coordination problems, cognitive decline |
| Juxtacortical Regions | Motor symptoms, cognitive issues |
| Infratentorial Areas | Balance issues, coordination problems, autonomic dysfunction |
It’s important for doctors to know where MS lesions usually appear and what they mean. This helps them diagnose and manage MS better. Because lesions can show up in different places, MS symptoms and how the disease progresses can vary a lot.
Types of MS Lesions and Their Characteristics
In multiple sclerosis, the brain shows lesions that can be classified into types. These are seen on MRI scans and are key in diagnosing and understanding the disease.
Periventricular Lesions
Periventricular lesions are found around the brain’s ventricles. They are common in MS and show up as bright spots on T2-weighted MRI images. These lesions are a key sign of MS.
Dawson’s Fingers
Dawson’s fingers are a type of periventricular lesion. They look like fingers extending from the ventricles. Named after a neurologist, they are a strong sign of MS.
Juxtacortical Lesions
Juxtacortical lesions are near the brain’s outer layer, the cerebral cortex. They can cause cognitive problems and seizures. These lesions are important because they show the disease affects the brain’s outer layer.
Infratentorial Lesions
Infratentorial lesions are below the tentorium cerebelli. They can be in the cerebellum, brainstem, or other areas. These lesions can cause balance issues and problems with cranial nerves.
Each type of MS lesion has its own characteristics and effects. Knowing these differences helps doctors understand symptoms and plan treatment.
Key Characteristics of MS Lesion Types:
- Periventricular Lesions: Occur around the ventricles, common in MS.
- Dawson’s Fingers: Radial periventricular lesions, highly suggestive of MS.
- Juxtacortical Lesions: Adjacent to the cerebral cortex, associated with cognitive and seizure symptoms.
- Infratentorial Lesions: Located below the tentorium, can cause ataxia and balance issues.
MS Lesions vs. Normal Brain Appearance
It’s important to know the difference between MS lesions and normal brain tissue for accurate diagnosis. Multiple sclerosis (MS) is marked by lesions in the brain and spinal cord. These can be seen with MRI scans.
What a Healthy Brain Looks Like on MRI
A healthy brain looks clear on MRI scans. Its structure, including white and gray matter, is symmetrical and clear. But, a brain with MS shows lesions, mainly in the white matter.
Age-Related Changes vs. MS Lesions
It’s key to tell apart age-related changes from MS lesions. Age can cause small vessel disease, seen as white matter hyperintensities on MRI. But, these changes don’t look like MS lesions.
Key Differences in Appearance and Distribution
MS lesions are unique and different from age-related changes. They are often found near the ventricles, near the brain’s surface, or below the tentorium. They appear as bright spots on T2-weighted MRI images.
| Characteristics | MS Lesions | Age-Related Changes |
| Location | Periventricular, juxtacortical, infratentorial | Subcortical, deep white matter |
| Appearance on T2 MRI | Hyperintense | Hyperintense, but often more diffuse |
| Distribution | Ovoid, perpendicular to ventricles | More random, not necessarily related to ventricles |
Normal Variants That May Mimic MS Lesions
Some normal brain features can look like MS lesions on MRI. For example, certain perivascular spaces can resemble MS lesions. But, more detailed imaging can tell them apart.
Accurate diagnosis needs a full check-up, including MRI scans and medical history. Knowing the difference between MS lesions and normal brain tissue helps doctors make better choices.
How Many Brain Lesions Are Normal in MS?
Knowing how many brain lesions are normal in MS is key for doctors to diagnose and treat the disease. MS affects everyone differently, and the number of lesions can vary a lot.
Variability in Lesion Load Among MS Patients
The number of brain lesions in MS patients varies. Some have few, while others have many. This difference is due to several factors, like the disease stage and immune system strength.
Research shows that the number of lesions can differ a lot among MS patients. This highlights the need for treatments tailored to each person.
Relationship Between Lesion Number and Disease Severity
There’s a general link between lesion number and disease severity, but it’s not always true. Some with many lesions may have mild symptoms, while others with fewer lesions may have severe symptoms. This is because the location and type of lesions matter, as well as individual brain differences.
Studies suggest that where lesions are located is more important than how many there are. For example, lesions in key areas like the spinal cord or optic nerve can cause significant symptoms, even if there are only a few.
The McDonald Criteria for MS Diagnosis
The McDonald criteria help doctors diagnose MS. They look for lesions on MRI scans, symptoms, and other tests. Having lesions in different parts of the brain and spinal cord is a key sign of MS.
According to the McDonald criteria, MS is diagnosed when lesions are found in different areas of the central nervous system at different times. This shows the disease is ongoing and chronic.
Clinically Isolated Syndrome vs. Definite MS
Some people have a single episode of neurological symptoms, known as clinically isolated syndrome (CBS). If MRI scans show lesions that could be MS, there’s a higher chance of developing MS. Seeing multiple lesions on MRI scans can help predict if someone will get MS after a CIS episode.
It’s important to understand the difference between CIS and definite MS. CIS might not meet all MS criteria, but it can lead to MS. So, it’s important to watch closely to decide the best treatment.
Correlation Between Lesion Location and MS Symptoms
It’s key to know how MS lesion location affects symptoms for better care. Where lesions are can change how severe symptoms are.
Visual Disturbances and Optic Nerve Lesions
Damage to the optic nerve can cause vision problems, common in MS. These can be anything from blurry vision to losing sight in one eye. The optic nerve is easily damaged because of its myelin sheath, which MS attacks.
Visual symptoms often show up first in MS. Inflammation of the optic nerve, or optic neuritis, is a big reason for these vision issues. Quick treatment can help, but repeated attacks can cause lasting vision loss.
Motor Symptoms and Corticospinal Tract Lesions
Motor symptoms like weakness and trouble with balance can come from lesions in the corticospinal tract. This tract is key for controlling movement. Damage here can really affect how well a person can move and live independently.
How bad motor symptoms are can depend on where and how big the lesions are. Spinal cord lesions might cause more severe symptoms than lesions elsewhere.
Cognitive Impairment and Cerebral Lesions
Cerebral lesions can hurt memory and thinking skills. The cerebral cortex handles many important brain functions. Damage here can make thinking hard.
Up to 70% of MS patients face cognitive problems. White matter lesions in the brain can mess up communication between brain areas, leading to thinking issues.
Balance Issues and Cerebellar Lesions
Lesions in the cerebellum can cause trouble with balance and movement. The cerebellum is key for keeping balance and coordinating movement. Damage here can really affect a person’s life quality.
Balance problems are a big worry for MS patients. They can lead to falls and injuries. Cerebellum lesions or problems with its connections can cause these issues, making special rehab plans important.
| Lesion Location | Common Symptoms |
| Optic Nerve | Visual disturbances, optic neuritis |
| Corticospinal Tract | Motor weakness, spasticity |
| Cerebral Cortex | Cognitive impairment, memory issues |
| Cerebellum | Balance issues, ataxia, tremors |
Knowing how lesion location and symptoms are linked helps doctors make better treatment plans. These plans are made to fit each patient’s needs.
Evolution of MS Lesions Over Time
Understanding how MS lesions change is key to managing the disease well. As MS progresses, lesions can change in many ways. This affects the severity of symptoms and the disease’s course.
Acute vs. Chronic Lesions
MS lesions are divided into acute and chronic types. Acute lesions show active inflammation and are linked to new or worsening symptoms. Chronic lesions are older, have less inflammation, and may show permanent damage.
Can MS Lesions Disappear?
Some MS lesions may seem to disappear on MRI scans over time. This might look like good news. But, it’s important to know that disappearing lesions don’t always mean a cure or big improvement. They might just mean less inflammation, with some damage left behind.
Lesion Changes During Disease Progression
As MS gets worse, lesions can change in nature and location. New lesions might form, while old ones evolve or disappear. Watching these changes helps understand the disease’s activity and guides treatment.
The Role of MRI Monitoring in MS Management
MRI scans are vital in managing MS. They help track changes in lesions and disease progression. Regular scans spot new lesions, track existing ones, and check treatment success. This info is key for patient care and adjusting treatment plans.
| Lesion Characteristic | Acute Lesions | Chronic Lesions |
| Inflammation Level | High | Low |
| Association with Symptoms | Often associated with new or worsening symptoms | May represent areas of permanent damage |
| Appearance on MRI | Typically enhanced with gadolinium | Usually non-enhanced |
Conclusion: The Significance of Brain Lesions in MS Diagnosis and Management
Understanding brain lesions in multiple sclerosis (MS) is key for accurate diagnosis and effective management. We’ve looked at how MS lesions show up on MRI scans. We’ve also talked about their common locations and how they relate to symptoms.
Brain lesions in MS can look different, and MRI scans give us important clues for diagnosis. Lesions in certain areas, like the periventricular white matter or corpus callosum, hint at MS. The number and location of these lesions can affect how severe symptoms are and how fast the disease progresses.
By looking at what a brain lesion looks like on MRI, doctors can see the extent of damage and inflammation. This info is vital for creating treatment plans and keeping an eye on the disease’s activity over time.
Managing MS well means understanding brain lesions and their impact on a patient’s life. We stress the need for MRI monitoring to track changes in lesions. This helps in adjusting treatment plans as needed.
FAQ
What does a brain lesion look like on MRI in MS?
On MRI, MS brain lesions show up as bright spots on T2-weighted images. They are usually in the brain’s white matter. On T1-weighted images, they look like “black holes,” showing more damage.
How are MS lesions different from a normal brain on MRI?
MS lesions stand out on MRI because of their unique look and where they are. They are often shaped like an oval and found near the brain’s center. They also show up bright with gadolinium, showing they are active.
What is the significance of lesion location in MS?
Where lesions are located in MS matters a lot. For example, lesions in the optic nerve can cause vision problems. Lesions in the corticospinal tract can lead to muscle weakness.
How many brain lesions are normal in MS?
The number of brain lesions in MS varies a lot. Some people have just a few, while others have many. The McDonald criteria look for multiple lesions to confirm MS.
Can MS lesions disappear?
Yes, some MS lesions can fade away or get smaller over time, thanks to treatment. But, some stay the same, and new ones can appear.
What is the role of MRI monitoring in MS management?
MRI monitoring is key in managing MS. It helps track the disease, see how lesions change, and adjust treatment plans.
What do MS lesions look like on T2-weighted images?
On T2-weighted images, MS lesions are bright and often have an ovoid or periventricular shape.
What are “black holes” on T1-weighted images?
“Black holes” on T1-weighted images show severe damage and loss of axons. They are dark and linked to more disability and severe disease.
What is the significance of gadolinium enhancement in MS lesions?
Gadolinium enhancement means there’s active inflammation and damage to the blood-brain barrier. It’s seen in new or active lesions.
How do age-related changes differ from MS lesions on MRI?
Age-related changes can look like MS lesions on MRI but are more spread out. MS lesions are more distinct and found near the brain’s center.