Last Updated on November 25, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir
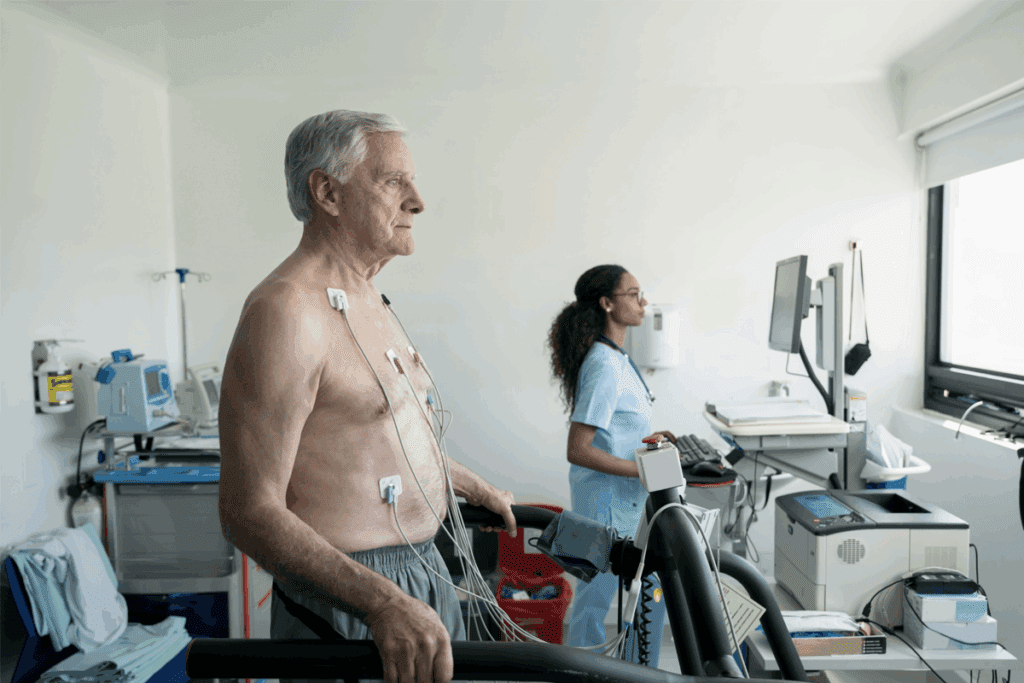
At Liv Hospital, we know how vital it is to check heart health with detailed tests. A cardiac stress test is key. It shows how well the heart works when it’s under more stress. This helps us spot signs of heart problems, like blockages and irregular beats.
Find out what does a cardiac stress test show and how it helps detect blocked arteries and heart problems.
This test is non-invasive and gives us important clues. It shows how the heart acts during exercise. This helps us figure out if someone has heart disease or irregular heartbeats. It also tells us if treatment is needed.
When you get a cardiac stress test, you learn more about your heart. You find out what you need to do to keep it healthy or make it better.
Cardiac stress tests are key in cardiology. They give insights into heart function and help decide treatments. We’ll dive into what these tests are, how they work, and when they’re used.
The main goal of a cardiac stress test is to see how the heart works under stress. This stress is usually from exercise or medicine. It’s vital for spotting coronary artery disease and heart risk.
“A stress test shows how well your heart handles activity,” says a top cardiologist. It checks the heart’s performance when it’s working harder. This can uncover problems not seen when the heart is at rest.
During a cardiac stress test, several things are watched, like heart rate and blood pressure. The test also looks at electrocardiogram (ECG) readings. It checks how well the heart muscle gets blood, mainly when stressed.
It spots areas of the heart that don’t get enough blood, which could mean coronary artery disease. The test’s skill in finding these problems under stress makes it very useful.
Doctors suggest cardiac stress tests for many reasons. They help find coronary artery disease, check how severe heart issues are, and see if treatments work.
People with chest pain or shortness of breath when active might get a stress test. Also, those at risk for heart disease, like those with high blood pressure or diabetes, might get tested too.
Understanding cardiac stress tests helps patients see their value. We’ve covered how they check heart function and when they’re needed. This gives a full picture of their role in cardiology.
A cardiac stress test is key for checking heart health. It shows how the heart works when stressed, usually during exercise.
The main goal of a cardiac stress test is to find cardiac ischemia. This is when the heart muscle doesn’t get enough oxygen-rich blood. We watch the heart’s electrical activity and blood flow to spot any problems.
Finding ischemia early is important. It can mean there’s a blockage in the heart’s arteries. We can then take steps to manage it and prevent more issues.
A cardiac stress test also spots heart rhythm abnormalities, or arrhythmias. These can happen when the heart is stressed, like during exercise.
By checking the heart’s electrical activity, we can find arrhythmias that aren’t seen when the heart is at rest. This is key for diagnosing and treating heart rhythm problems.
The test also shows how well the heart handles exercise. It checks if the heart can keep up with physical demands.
This info is useful for diagnosing heart issues and making exercise plans. It helps figure out safe levels of physical activity, which is important for people with heart disease.
The test also looks at how blood pressure changes with exercise. A normal response is important to make sure the heart isn’t overworked.
Abnormal blood pressure changes during exercise can mean heart problems. For example, too high blood pressure might show there’s high blood pressure or other heart issues.
| Aspect | Normal Response | Abnormal Response |
| Cardiac Ischemia | No signs of ischemia | Presence of ischemia indicated by ECG changes or symptoms |
| Heart Rhythm | Normal sinus rhythm | Arrhythmias or other rhythm disturbances |
| Exercise Tolerance | Good exercise capacity | Reduced exercise capacity or early fatigue |
| Blood Pressure | Appropriate increase in blood pressure with exercise | Exaggerated or inadequate blood pressure response |
Cardiac stress testing isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. Different tests are used based on what each patient needs. The choice of test depends on the patient’s health, how mobile they are, and what the doctor needs to know about their heart.
Exercise stress tests are the most common. Patients walk on a treadmill or bike while their heart is monitored. The workout gets harder to stress the heart more.
Benefits of Exercise Stress Tests: They show how well the heart works under stress. They help find coronary artery disease, check heart attack risk, and see if treatments work.
For those who can’t exercise, pharmacological stress tests are used. These tests give medication that makes the heart work like it’s exercising, without the actual exercise.
When to Use Pharmacological Stress Tests: They’re great for patients with physical limits or who can’t get their heart rate up through exercise alone.
Imaging stress tests add imaging like echocardiography or nuclear cardiology to the standard stress test. They give detailed pictures of the heart at rest and under stress.
| Type of Stress Test | Description | Used For |
| Exercise Stress Test | Physical exertion on a treadmill or bike | Diagnosing coronary artery disease, assessing heart attack risk |
| Pharmacological Stress Test | Medication simulates exercise effects | Patients unable to exercise; assessing heart function |
| Imaging Stress Test | Combines stress test with imaging technology | Detailed assessment of heart structure and function |
Knowing about the different cardiac stress tests helps both patients and doctors pick the best test for each person’s needs.
A stress test can show signs of blockages in arteries, even if it can’t see them directly. It checks how well the heart works when stressed, usually through exercise or medicine. It looks at the heart’s electrical activity, blood flow, and overall performance.
During a stress test, several signs can point to coronary artery disease or blocked arteries. These signs include:
These signs mean the heart might not get enough blood when stressed, hinting at blockages.
Stress tests compare the heart’s function at rest and during stress. For example, a nuclear stress test uses radioactive material to show where blood flow drops during stress. A stress echocardiogram also compares heart function at rest and during stress, highlighting areas with poor blood flow.
Key diagnostic features include:
Stress tests are useful but have limits in finding blocked arteries. Not all blockages are big enough to show up on a stress test. Some people might have blockages that don’t affect blood flow enough to be detected.
Stress tests might miss blocked arteries in certain cases. For example:
In these cases, more tests might be needed to find coronary artery disease.
It’s important to know how accurate cardiac stress tests are. These tests help doctors diagnose heart issues. But, their results can vary based on different factors.
Stress tests can detect heart disease with about 67 to 80 percent accuracy. Sensitivity means the test can spot those with the disease. Specificity means it can also spot those without it.
Studies show stress tests are 68% to 85% sensitive. This means 68% to 85% of people with heart disease are correctly diagnosed. They are 70% to 90% specific, meaning 70% to 90% of people without heart disease are correctly identified.
Several things can affect how accurate stress tests are. These include:
Stress tests are not perfect and can give false positives or false negatives. False positives can cause unnecessary tests and worry. False negatives can give a false sense of security.
| Test Result | Actual Condition | Implication |
| Positive | Disease Present | True Positive – Correct Diagnosis |
| Positive | Disease Absent | False Positive – Unnecessary Further Testing |
| Negative | Disease Present | False Negative – Missed Diagnosis |
| Negative | Disease Absent | True Negative – Correct Reassurance |
It’s good to compare stress tests to other methods. For example, coronary angiography is very accurate but is more invasive. Stress tests are non-invasive and can be a first step in diagnosis.
Other methods like cardiac MRI or coronary CT angiography are very accurate but cost more. They’re not as common as stress tests. The right test depends on the patient’s condition and risk factors.
Understanding the cardiac stress test procedure can ease your anxiety. We’ll walk you through each step, from preparation to after the test. This ensures your comfort and safety.
Proper preparation is essential for accurate results and safety. We provide guidance on what to eat and drink before the test. You’ll also need to inform us about your medications.
During the test, your heart activity is closely monitored. You’ll exercise on a treadmill or stationary bike. If you can’t exercise, we’ll use medication instead.
The test lasts about 30-60 minutes. But, you’ll spend more time at the facility due to preparation and monitoring after the test.
After the test, we continue to monitor your heart activity. This ensures it returns to its resting state. It helps us check for any changes and keep you safe.
Cardiac stress tests are generally safe, but there are risks and complications. These include abnormal heart rhythms, heart attack, or other heart problems. But, these are rare, and our team is ready for any situation.
Key risks and complications include:
We take all precautions to minimize these risks and ensure your safety.
Understanding your cardiac stress test results is key to making smart choices about your heart health. These tests show how your heart works when it’s stressed. This info is vital for your doctor to assess your heart’s health.
Stress test results can be normal or abnormal. Normal findings mean your heart is working fine under stress, showing good health. But, abnormal findings might point to heart problems like coronary artery disease.
It’s important to know that abnormal results don’t always mean a serious issue. They just mean you need more tests or monitoring.
Your stress test report will have details on your heart rate, blood pressure, and any symptoms. It might also include images or graphs of your heart’s function.
Key components of your report may include:
Positive results might show coronary artery disease or other heart issues. These results mean your heart might not get enough blood flow when stressed. This could be due to blockages in the coronary arteries.
“A positive stress test result doesn’t necessarily mean you have a blockage, but it does indicate the need for further testing to determine the cause of the abnormal result.”
Negative results usually mean your heart is doing well under stress. But, it’s important to remember that a negative result doesn’t rule out heart disease completely. This is true, even if you have other risk factors.
| Result Type | Implication | Next Steps |
| Normal | Good heart health under stress | Continue regular check-ups |
| Abnormal | Potential heart issues, such as coronary artery disease | Further testing or monitoring |
Grasping your stress test results is a big step in managing your heart health. Always talk to your healthcare provider about your results. This will help you understand what they mean for you.
When a cardiac stress test shows abnormal results, we do more tests to understand your heart better. These findings don’t always mean you have a serious problem. But they do show you need more tests to figure out what to do next.
Coronary angiography gives detailed pictures of your heart’s arteries. It helps find any blockages or problems. This test uses a small tube and dye to see your arteries on an X-ray.
Benefits of coronary angiography include:
Coronary CT angiography is a non-invasive test. It uses CT technology to see your heart’s arteries. It helps find blockages or plaque buildup.
Coronary CT angiography is useful for:
Cardiac MRI is a non-invasive test. It uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed heart images. It checks heart function, finds scar tissue, and looks at the heart’s structure.
Cardiac MRI is great for:
In some cases, abnormal stress test results mean you need quick medical help. This could be due to severe heart disease, big ischemia, or other serious heart issues.
| Condition | Immediate Intervention | Follow-Up |
| Severe Coronary Artery Disease | Angioplasty or CABG | Regular monitoring and lifestyle changes |
| Significant Ischemia | Medical therapy adjustment | Repeat stress testing and imaging |
| Serious Heart Conditions | Hospitalization and further evaluation | Ongoing management and treatment |
It’s important to understand your cardiac stress test results and any follow-up tests. Our team will explain your results, talk about treatment options, and give ongoing care. We aim for the best outcomes for you.
Cardiac stress tests are key in checking heart health and spotting problems early. They show how the heart works when stressed, helping find issues like heart blockages and rhythm problems. They also check how well the heart handles exercise.
These tests are valuable because they catch problems before they get worse. But, it’s important to know their limits. They can’t see blocked arteries directly.
At times, more tests are needed to be sure of a diagnosis. Knowing both the good and bad of cardiac stress tests helps doctors make better choices. This leads to better health for their patients.
A cardiac stress test checks how well the heart works when it’s stressed. This stress can come from exercise or medicine. It helps find problems like heart blockages, rhythm issues, and how well the heart handles exercise.
A stress test might show signs of blocked arteries indirectly. It can reveal heart problems like ischemia. But, it doesn’t directly show blockages.
The accuracy of a stress test varies. It depends on the test type and the patient’s health. Other health issues can also affect its accuracy.
There are many types of cardiac stress tests. These include exercise tests, medicine tests, and imaging tests. Each is used based on the patient’s health and what’s needed.
Yes, a stress test can find heart rhythm problems. It watches the heart’s electrical activity during stress.
A stress test is a non-invasive test that checks the heart’s function under stress. Coronary angiography is an invasive test that looks directly at the heart’s arteries. It’s more precise for finding blockages.
To prepare for a cardiac stress test, avoid certain foods and drinks. Wear comfy clothes. Tell your doctor about any medicines or health issues.
During a cardiac stress test, you’ll first have an evaluation. Then, you’ll do exercise or take medicine. Your heart and other vital signs will be monitored.
Positive results might mean you have heart disease or ischemia. You might need more tests and treatment.
Yes, stress tests can give false results. This can happen due to technical issues, patient health, or other conditions.
After an abnormal test, you might need more tests. These could include coronary angiography, CT angiography, or MRI. They help check the heart and blood vessels more closely.
A stress test can hint at blockages but won’t show them directly. More tests, like coronary angiography, might be needed to confirm blockages.
A stress test can hint at blockages by showing signs of ischemia. But, it depends on the blockage’s severity and other factors.
The reliability of a stress test varies. It depends on the test type, patient health, and other conditions. While useful, stress tests have limits and might miss some heart problems.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!