Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
Back pain and nerve discomfort can signal a deeper spinal problem, like a disc protrusion. At Liv Hospital, we offer top-notch advice on spinal health. We also provide advanced medical care for patients from around the world.
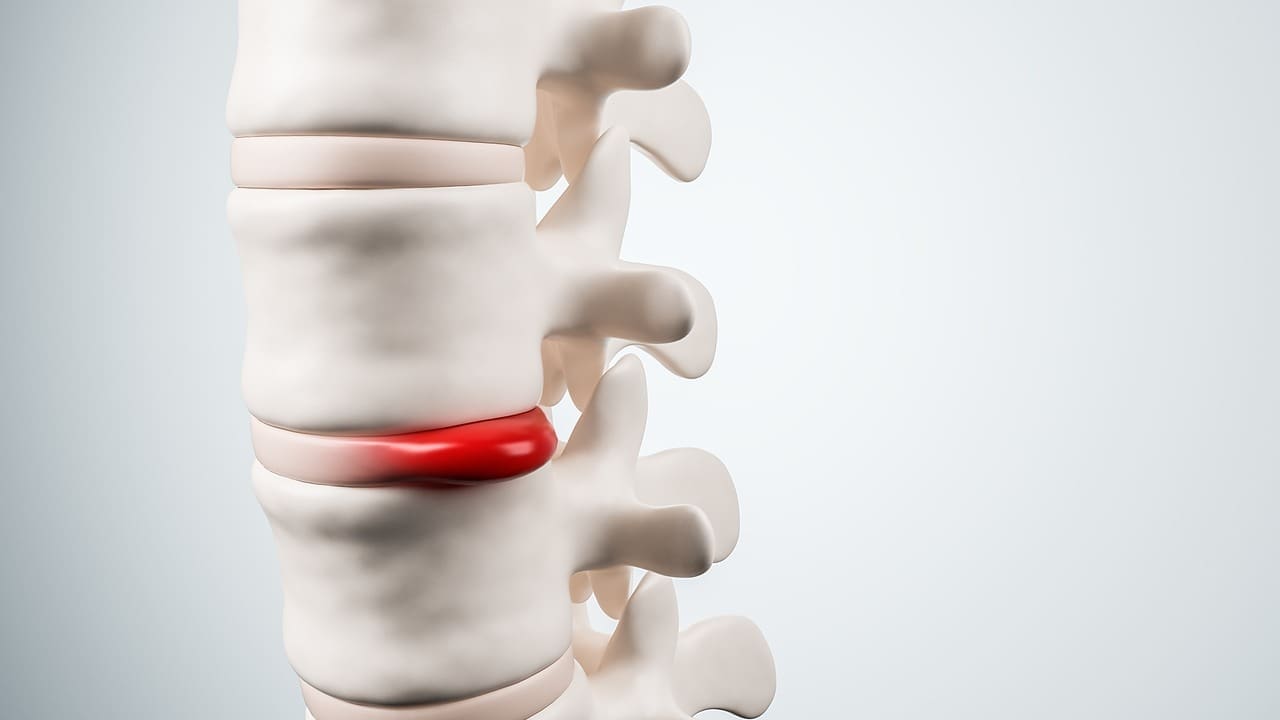
A disc protrusion happens when the outer layers of the intervertebral disc bulge into the spinal canal. This doesn’t mean the disc has torn completely. It can lead to pain, numbness, or weakness, depending on where it is and how bad it is.
We’ll dive into what a disc protrusion is and how it impacts the spine. We’ll use the latest medical research and expert opinions to guide us.
To understand spinal health, knowing what disc protrusion is key. It affects the intervertebral discs, which are vital for spine flexibility and shock absorption. This condition is also known as protrusão discal or protusion discal.
We will look into the anatomy of spinal discs and how disc protrusion is different from herniation. This will give a full grasp of this condition.
The spine has many vertebrae, with discs in between. These discs have a tough outer layer called the annulus fibrosus and a soft center, the nucleus pulposus. They help the spine move and absorb shock.
Disc protrusion and herniation are not the same. Protrusion happens when the disc bulges out but stays intact. Herniation, on the other hand, is when the disc ruptures, letting the soft center leak out. Knowing the difference is important for treatment.
Studies show that over a quarter of adults without back pain may have disc protrusion on MRI scans. This shows how common it is and why it’s important to understand its effects on the spine.
Disc protrusion can happen anywhere in the spine but is most common in the lower back. This is because the lower back carries a lot of weight and stress.
It’s important to know the different types of disc protrusions for accurate diagnosis and treatment. These protrusions vary in how they bulge and how much, affecting symptoms and treatment choices.
A circular protrusion means the disc bulges out evenly in all directions. This is also called a diffuse disc protrusion. It can press on nerves, causing pain, numbness, and weakness.
A focal protrusion is when the disc bulges in one specific area. This type can cause more severe symptoms because it puts pressure on certain nerves.
A broad-based protrusion has a larger area of bulging but not as evenly as a circular one. It affects a big part of the disc and can also cause nerve compression and symptoms.
Research shows that different protrusions affect the spine and nerves in different ways. Knowing these differences helps doctors create better treatment plans. The size and location of the protrusion are key in deciding the best treatment.
Doctors can tailor treatments by identifying the specific type of disc protrusion. This approach improves patient outcomes by addressing each type’s unique characteristics and symptoms.
Disc protrusions can happen in different parts of the spine. The spine is split into three main areas: cervical, thoracic, and lumbar. Each area has its own features and is more prone to certain types of protrusions.
Cervical disc protrusions happen in the neck. They can cause a lot of pain, like neck pain and arm pain. You might also feel numbness or tingling in your hands.
“Cervical disc protrusions can lead to serious complications if not properly managed,” says a leading spine specialist. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are key to avoid long-term damage.
Thoracic disc protrusions are less common but can be serious. They happen in the mid-back and might cause pain around the rib cage. Sometimes, they can even press on the spinal cord, leading to more severe symptoms.
Lumbar disc protrusions are the most common, found in the lower back. They can lead to lower back pain and pain in the legs (sciatica). You might also feel numbness or weakness in your legs.
As a spine expert notes, “Lumbar disc protrusions can really affect a patient’s life, making simple tasks hard.” Treatment depends on how bad the symptoms are and how they affect daily life.
Knowing what causes disc protrusions is key to preventing and treating them. These protrusions can really affect a person’s life. Studies show that over a quarter of adults without symptoms may have disc protrusions on MRI scans.
Age is a big risk factor for disc protrusions. As we get older, our spinal discs wear out. They lose moisture and become less flexible, making them more likely to bulge. Research shows that aging is a major cause of these protrusions.
Getting hurt badly, like in a fall or car crash, can also cause disc protrusions. This can happen to anyone, not just those with spinal problems.
How we live can also affect our risk of disc protrusions. Heavy lifting, bending, or twisting increases the risk. Sitting too much and bad posture also play a part. Making lifestyle changes can help reduce these risks, as discussed in bulging disc wikipedia.
Our genes can also play a role. If your family has spinal issues, you might be more likely to get disc protrusions. Knowing this can help you take steps to prevent it.
In summary, disc protrusions come from a mix of aging, injuries, lifestyle, and genes. Understanding these factors helps us prevent and treat them. As disc herniation wikipedia and disc prolapse wiki show, knowing the causes is vital for managing the condition.
Disc protrusion symptoms can vary a lot from person to person. This depends on where and how severe the condition is. Some people might not feel any pain, while others have constant back pain or discomfort.
The pain from disc protrusion can show up in different ways. It might stay in the same spot or spread to other areas. For example, a disc in the lower back can cause pain that goes down to the legs.
Disc protrusion can also cause neurological symptoms. This happens when nerves get compressed or irritated. Symptoms can include:
Some people with disc protrusion might not feel any symptoms at all. Research shows that many people with this condition don’t show any signs. This makes it hard to diagnose just by symptoms.
Managing disc protrusion can be tough, but knowing the symptoms is a big step. By recognizing these signs and getting medical help, people can find relief and improve their life quality.
Disc protrusion can change daily life a lot. It affects how we move, work, and play. This condition makes the spinal disc bulge out, causing pain, numbness, or weakness. Let’s see how it impacts our daily lives.
Disc protrusion can really limit how we move. The pain and discomfort make simple tasks hard. Even walking or bending can be tough.
Reduced mobility might make us less active. This can make the problem worse.
Keeping mobile is key for health. So, we need to find ways to move better despite disc protrusion. Physical therapy and gentle exercises can help a lot.
Disc protrusion can also hurt our work. It makes some jobs harder to do. For jobs that are physically tough, it’s even harder.
Chronic pain and discomfort can make us less productive. We might miss more work too.
We think workplaces should help those with disc protrusion. Making workstations and tasks easier can help a lot.
Fun activities are important for a good life, but disc protrusion can limit them. Hobbies and sports that need a lot of effort can hurt too much. Adapting recreational activities can help us keep enjoying our favorite things.
We suggest talking to doctors to find new ways to have fun. This way, we can keep enjoying life without making the problem worse.
To diagnose disc protrusion, doctors use a mix of clinical checks and tests. We’ll look at how they do it to make sure patients get the right care.
A physical check is key in finding disc protrusion. Doctors look at range of motion, muscle strength, and reflexes. They might also do special tests to see if they can make the patient’s symptoms worse.
For example, a straight leg raise test can check for sciatic pain, which often comes with a bulging disc in the lower back. By watching how the patient reacts, doctors can figure out what’s going on.
Imaging tests are very important to confirm disc protrusion. The main ones are:
MRI is great for seeing soft tissues like discs and nerves. A study in the BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders journal shows MRI gives clear details about disc shape and nerve pressure.
| Imaging Modality | Key Features | Clinical Utility |
|---|---|---|
| MRI | Excellent soft tissue visualization | Detailed assessment of disc protrusion and nerve root compression |
| CT scans | Good for bony structures | Useful for evaluating bony abnormalities and spinal stenosis |
| X-rays | Basic assessment of spinal alignment | Limited use in diagnosing disc protrusion, but helpful for ruling out other conditions |
Neurological tests are key to see how disc protrusion affects nerves. They check sensory function, motor strength, and reflexes. This helps doctors understand how much nerves are involved and if there are any nerve problems.
For instance, someone with a bulging disc in the lower back might feel numbness or weakness in their legs. By noting these symptoms, doctors can plan the best treatment for the patient.
Non-surgical treatments are great for those with disc protrusion. They help manage symptoms and improve life quality. They also try to avoid surgery when possible.
Managing pain is key in treating disc protrusion. We suggest over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen. For severe cases, we might prescribe muscle relaxants or oral steroids.
Key pain management medications include:
Physical therapy is essential for disc protrusion treatment. It includes exercises to improve flexibility and strengthen muscles. Techniques like heat or cold therapy and electrical stimulation help reduce pain.
“Physical therapy is often a cornerstone of treatment for disc protrusion, helping patients regain mobility and strength.”
– Spine Health Expert
Chiropractic care is another non-surgical option. Chiropractors use spinal manipulation to improve alignment and reduce pressure. This helps in promoting healing.
For those not helped by other treatments, injection therapies can be effective. Corticosteroid injections reduce inflammation and pain. Other injections target specific pain areas.
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best treatment plan for your specific condition.
When other treatments don’t work, surgery might be needed for severe disc protrusion. Surgery can help by fixing the problem disc directly.
Research shows surgery can help with severe disc protrusion. It’s useful when symptoms or pain don’t go away. “Surgery is considered when the condition severely impacts the patient’s quality of life and conservative management has failed,” as noted in medical literature.
Microdiscectomy is a small surgery to remove the herniated disc part. It’s used for lumbar disc herniations. It’s effective in easing pain and shortening recovery time.
A study found microdiscectomy works well for disc herniation symptoms. This makes it a top choice for spine surgeons.
Laminectomy removes part or all of the lamina to relieve nerve pressure. It’s used for spinal stenosis or severe disc protrusion.
Laminectomy can help those with severe disc protrusion. It’s good for nerve symptoms.
Spinal fusion joins two or more vertebrae together. It’s used for severe disc protrusion and spinal instability.
Spinal fusion can ease pain and stabilize the spine. It’s for more serious cases or when other options fail.
Artificial disc replacement swaps the damaged disc with an artificial one. It aims to keep spinal mobility and reduce pain.
Artificial disc replacement is a good alternative to spinal fusion for some. It keeps more spinal motion and lowers disease risk.
In conclusion, surgery offers many options for severe disc protrusion. The right procedure depends on the condition’s severity, the patient’s health, and the surgeon’s advice.
Recovery and rehabilitation after disc protrusion treatment are key. A structured approach leads to the best results. These steps are vital for returning to normal activities and maintaining spinal health.
Studies show that a well-planned rehabilitation program can greatly improve outcomes.
The recovery time varies based on the disc protrusion’s severity, treatment type, and individual factors. Patients usually need several weeks to a few months to recover. Following a healthcare provider’s advice is essential for a smooth recovery.
Physical therapy is critical in the rehabilitation process. It includes exercises to boost flexibility, strengthen spine-supporting muscles, and improve posture. Consistency and patience are important as patients follow their personalized plans.
Some common physical therapy protocols include:
Returning to normal activities should be gradual and under healthcare provider guidance. Avoid heavy lifting, bending, or twisting in the early recovery stages. Gradually increasing activity levels helps prevent re-injury and supports a lasting recovery.
By sticking to a structured rehabilitation program, patients can achieve the best recovery outcomes. This approach also reduces the risk of future disc protrusion problems.
To prevent disc protrusion, it’s important to use a few key strategies. These include keeping your posture right, doing exercises that strengthen your core, and making lifestyle changes. By doing these things, you can lower your chances of getting disc protrusion and feeling pain.
Keeping your body in the right position is key to avoiding disc protrusion. This means standing and sitting correctly, lifting safely, and not twisting too much. Always lift with your knees, keep your back straight, and take breaks when sitting for a long time.
Key Tips for Proper Body Mechanics:
Doing exercises that strengthen your core can help your spine stay healthy. Focus on exercises that work your abdominal and back muscles. Try planks, bridges, and pelvic tilts to keep your spine strong.
Sample Core Strengthening Exercises:
| Exercise | Description | Repetitions |
|---|---|---|
| Plank | Hold a position with your body in a straight line from head to heels | 3 sets of 30-second hold |
| Bridge | Lie on your back with knees bent and lift your hips towards the ceiling | 3 sets of 15 repetitions |
| Pelvic Tilt | Lie on your back with knees bent and tilt your pelvis upwards | 3 sets of 10 repetitions |
Changing your lifestyle can also help prevent disc protrusion. This means staying at a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and being active. Eating a balanced diet is also important for your spine’s health.
Having an ergonomic workspace is important too. Use a good chair, keep your computer at eye level, and have things you use often within reach. This can help prevent disc protrusion.
By following these tips, you can take steps to prevent disc protrusion and keep your spine healthy.
Understanding what a disc protrusion is is key to managing it well. We’ve looked into what it is, its types, and how it affects daily life. A disc protrusion, often linked to disc herniation, can cause pain and discomfort in the spine.
Protrusions can happen in different parts of the spine, leading to different symptoms. To manage disc protrusion, a full plan is needed. This includes getting a proper diagnosis, treatment, and making lifestyle changes. Studies show that with the right treatment and lifestyle changes, people can manage their condition and live better.
A bulging disc is another condition that affects spinal health, as explained on Wikipedia. Knowing the causes, symptoms, and treatments for disc protrusion helps people prevent it and take care of their spine.
Managing disc protrusion requires a complete approach, including non-surgical and surgical treatments, and lifestyle changes. Working with healthcare experts and being proactive helps people manage their condition. This way, they can stay healthy and active.
A disc protrusion happens when the soft center of a spinal disc bulges out. This is due to a tear or weakness in the outer layer. It can press on nerves, causing pain and discomfort.
Both involve disc material displacement, but they differ in severity. A disc protrusion is a milder condition where the disc bulges but stays intact. In contrast, a disc herniation is a more severe rupture, allowing the gel-like center to leak out.
There are several types, including circular, focal, and broad-based protrusions. Each type has unique characteristics and treatment implications.
They can happen anywhere in the spine, but most often in the lumbar region. The cervical and thoracic regions are also common.
Causes include age-related wear, injuries, lifestyle choices, and genetics. These factors can increase the risk of developing disc protrusions.
Symptoms include pain, numbness, tingling, and sometimes no symptoms at all. This is known as an asymptomatic disc protrusion.
Diagnosis involves a physical exam, imaging tests like MRI or CT scans, and neurological assessments.
Non-surgical treatments include pain meds, physical therapy, chiropractic care, and injections. Surgery options include microdiscectomy, laminectomy, and spinal fusion.
Recovery time varies based on treatment and individual factors. It usually involves physical therapy and rehabilitation.
Some risks can’t be avoided, but proper body mechanics and exercises can help. Lifestyle changes and ergonomic considerations also play a role.
Physical therapy is key in treating and preventing disc protrusion. It helps alleviate symptoms, improves mobility, and strengthens spine-supporting muscles.
Yes, it can recur if risk factors are not managed. Preventive measures are essential to reduce recurrence risk.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Disc_protrusion
https://www.institutoclavel.com/en/blog/disc-protrusion-what-it-is-and-how-it-can-be-treated
https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/back-pain-disc-problems
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!