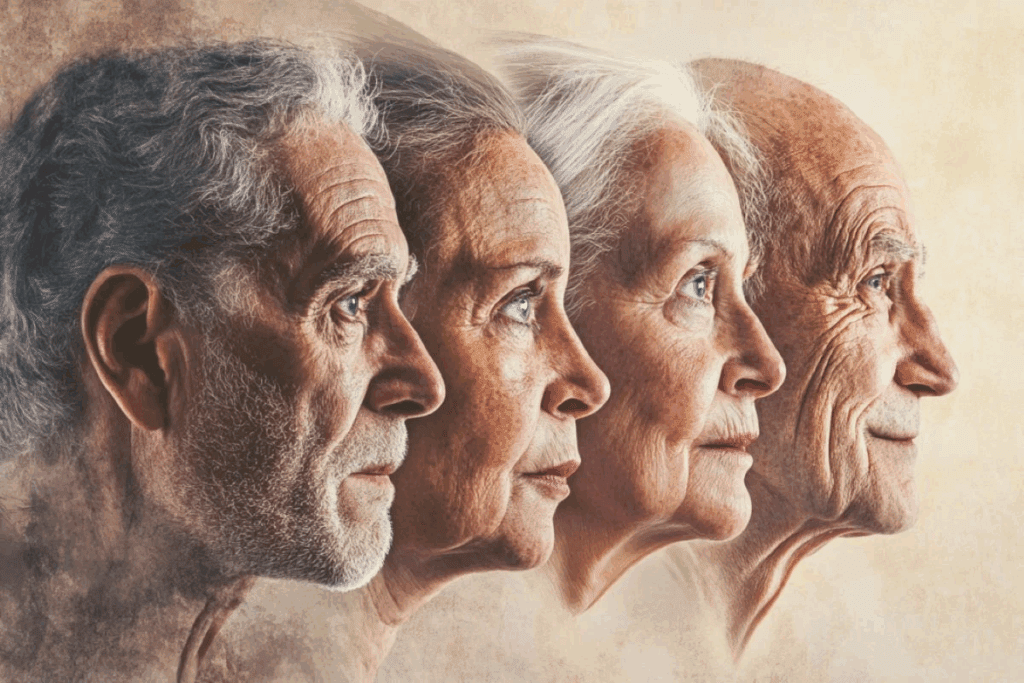
The world is seeing a big change as more people get older. By 2050, the number of people over 60 will almost double, reaching 2.1 billion. This big increase in older people puts a lot of pressure on healthcare systems everywhere. Older adults are more likely to get chronic diseases and lose physical and mental strength. What is aging? This essential guide defines the process and reveals 7 alarming health challenges facing the aging population today.
As we live longer, we need to tackle the complex health needs of the aging population worldwide. The seven major health problems include heart disease, Alzheimer’s, diabetes, and more. These issues are key to understanding how to help the growing number of older people.
Key Takeaways
- The global population is aging rapidly, with the proportion of people over 60 expected to nearly double by 2050.
- The aging population faces a higher risk of chronic diseases and declining physical and mental capacity.
- Seven major health problems are prevalent among the older population: cardiovascular disease, Alzheimer’s disease, diabetes, multi-morbidity, geriatric syndromes, mental health issues, and healthcare access inequities.
- Effective healthcare strategies are key to support the growing older population.
- Understanding the health challenges faced by the aging population is essential to meet their complex needs.
The Global Aging Phenomenon: Understanding the Demographic Shift
The world’s population is getting older, and it’s key to understand this shift. This change means more older adults, affecting healthcare, social services, and economies globally.
Current Statistics and Future Projections
By 2050, the number of people over 60 will nearly double to 22% of the world’s population. The number of those 80 or older will triple, reaching 426 million.
This growth highlights the urgent need for readiness. The global population ageing trend affects society deeply, beyond just numbers.
Social and Healthcare Implications
The aging population brings big challenges to healthcare, like more demand for age-related services. We need strategies to handle these issues and prepare healthcare for the future.
The impact of ageing on healthcare is complex. It requires a broad approach, including prevention, treatments, and support for older adults.
What Is Aging? The Biological Process and Its Effects
As we age, our bodies change at the cellular and molecular level. Aging is a complex process influenced by genetics, lifestyle, and environment.
The biological process of aging comes from molecular and cellular damage over time. This damage can cause a decline in physical and mental abilities. It makes older adults more susceptible to health issues.
Cellular and Molecular Changes
At the cellular level, aging brings changes like telomere shortening, epigenetic alterations, and loss of proteostasis. These changes impact how cells work and divide, contributing to aging.
Molecular changes, including DNA damage and mitochondrial dysfunction, also play a big role in aging. Knowing about these changes is key to finding ways to age healthily.
Normal Aging vs. Pathological Aging
It’s important to know the difference between normal aging and pathological aging. Normal aging is the natural process, while pathological aging includes age-related diseases.
Lifestyle choices and environmental factors can affect whether someone ages normally or pathologically. Understanding these can help us find ways to age healthily and prevent or manage age-related diseases.
Cardiovascular Disease: The Leading Threat to Elderly Health
The elderly face a big threat from cardiovascular disease, a major cause of death worldwide. As more people get older, this disease will become even more common. It’s a serious issue that needs quick action and good ways to manage it.
Heart Disease and Stroke in Older Adults
Heart disease and stroke are big problems for older adults. Heart disease affects the heart’s structure and function. This includes conditions like coronary artery disease and heart failure. Stroke happens when the brain doesn’t get enough blood, either because of a blockage or a blood vessel rupture.
Older adults are more likely to get these diseases because of age-related changes. These changes include higher blood pressure and less efficient heart function. Risk factors include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, smoking, and not being active enough.
Condition | Risk Factors | Prevention Strategies |
Heart Disease | Hypertension, Hyperlipidemia, Diabetes | Healthy Diet, Regular Exercise, Medication Adherence |
Stroke | Hypertension, Atrial Fibrillation, Smoking | Anticoagulation Therapy, Blood Pressure Management, Lifestyle Modifications |
Prevention and Management Strategies
To fight cardiovascular disease in older adults, we need a plan that includes lifestyle changes, medical care, and teaching patients. Lifestyle changes like eating well, staying active, and not smoking can help a lot. These actions can lower the chance of heart problems.
Medical management means controlling high blood pressure and high cholesterol with medicine and regular checks. Teaching patients is also key. It helps them take charge of their health, follow treatment plans, and make smart health choices.
By knowing the risks and using good prevention and management plans, we can lessen the harm of cardiovascular disease on older adults. This will help improve their health and quality of life.
Neurodegenerative Disorders and Cognitive Decline
The aging population faces more neurodegenerative disorders, leading to cognitive decline. As people get older, they often face several conditions at once. This includes neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s disease. It’s important to understand these conditions to offer effective care and support.
Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Dementias
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common dementia among older adults. It causes progressive memory loss and cognitive impairment. Early detection and diagnosis are key for managing the disease and improving life quality. Other dementias, like vascular dementia and Lewy body dementia, also affect older adults.
Dementia cases are rising worldwide, highlighting the need for better care strategies. These strategies include cognitive training, lifestyle changes, and medication. A multi-faceted approach can better support those with dementia.
Delirium and Cognitive Impairment
Delirium is a serious condition often seen in older adults, mainly in hospitals. It is marked by sudden confusion, altered consciousness, and disorganized thinking. Delirium can signal underlying medical issues and needs quick attention.
Cognitive impairment, from mild to full-blown dementia, affects many older adults. It’s important to know the difference between delirium and dementia. Delirium is usually acute and can be reversed, while dementia is chronic.
- Identify underlying causes such as infections or medication side effects.
- Implement strategies to prevent delirium, such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule and reducing sensory impairments.
- Provide supportive care to manage symptoms and improve outcomes.
By focusing on detecting, diagnosing, and managing neurodegenerative disorders, we can greatly improve the lives of older adults. Our approach should be diverse, including medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and supportive care. This addresses the complex needs of this population.
Musculoskeletal Conditions and Mobility Issues
As the world’s population ages, musculoskeletal conditions become more common. They affect the lives of millions of older adults worldwide. These issues not only harm their physical health but also have big social and emotional impacts.
Osteoporosis and Bone Health
Osteoporosis is a big problem for older adults. It makes bones weaker and more likely to break. To fight osteoporosis, we can make lifestyle changes and use medical treatments.
Eating foods rich in calcium and vitamin D helps. So does doing exercises that make bones stronger. These steps can keep bones healthy.
Prevention strategies for osteoporosis include not smoking and drinking less alcohol. These habits can make bones weaker. Also, preventing falls is key, as falls often lead to fractures in older adults with osteoporosis.
Arthritis and Joint Disorders
Arthritis is another big issue for older adults. It causes pain, stiffness, and makes moving harder. The most common types are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Effective management of arthritis needs a mix of treatments. This includes medicines, physical therapy, and changes in lifestyle. For example, staying at a healthy weight helps joints. Exercises that improve flexibility and strength can also help manage symptoms.
We suggest that older adults team up with their doctors to create a plan for their musculoskeletal conditions. By being proactive about their health, older adults can greatly improve their quality of life and stay independent.
Geriatric Syndromes: Complex Health Challenges
As the world’s population ages, older adults face complex health issues. These are called geriatric syndromes. They come from age-related changes, chronic diseases, and environmental factors.
Geriatric syndromes affect the quality of life and function of older adults. We will look at key issues like frailty, falls, urinary incontinence, and pressure ulcers.
Frailty and Physical Vulnerability
Frailty makes older adults more vulnerable to health problems. It’s linked to weight loss, weakness, and less activity. Understanding frailty is key to helping them.
Managing frailty involves nutrition, exercise, and managing chronic diseases. This approach can improve their health and well-being.
Falls and Their Consequences
Falls are a big worry for older adults, causing injuries and disability. Muscle weakness, balance issues, and environmental hazards increase the risk. Knowing these risks helps prevent falls.
To prevent falls, we can modify homes and improve lighting. Exercise programs also help. These steps can lower the number of falls.
Urinary Incontinence and Pressure Ulcers
Urinary incontinence and pressure ulcers are common and affect quality of life. Urinary incontinence needs a full management plan, including therapies and products.
Pressure ulcers happen from too much pressure on the skin. Prevention includes moving patients often, good nutrition, and using support surfaces. We must tackle these issues to better patient outcomes.
Understanding and tackling geriatric syndromes helps us support older adults better. This improves their health and well-being.
Metabolic and Endocrine Disorders in Aging
As the world’s population ages, more older adults face metabolic and endocrine disorders. These issues can greatly affect their health and happiness. It’s important to know what causes them, their symptoms, and how to manage them.
Diabetes and Glucose Regulation
Diabetes is a big problem for older adults. It’s vital to keep blood sugar levels in check to avoid serious health issues. Managing diabetes well means making healthy lifestyle choices and possibly taking medication.
Older adults with diabetes are more likely to have low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia. Hypoglycemia is very dangerous if not treated right away. It’s key for them and their caregivers to know the signs and how to act fast.
Management Strategy | Description | Benefits |
Balanced Diet | Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins | Helps regulate blood sugar levels |
Regular Physical Activity | Engaging in activities such as walking, swimming, or cycling | Improves insulin sensitivity and overall health |
Medication/Insulin Therapy | Using medications or insulin as prescribed by a healthcare provider | Helps control blood sugar levels |
Thyroid Dysfunction and Hormonal Changes
Thyroid problems are common in older adults. Both underactive and overactive thyroid can affect energy, weight, and heart health.
Testing the thyroid is key to finding these issues. Treatment usually means taking medicine to balance thyroid hormones. Older adults need regular check-ups to make sure their treatment works right.
Understanding and managing metabolic and endocrine disorders can help older adults stay healthy. This means making lifestyle changes, getting medical help, and keeping an eye on their health.
Mental Health and Social Well-being
Mental health issues among older adults are a growing concern worldwide. As people age, they face many challenges that can affect their mental well-being. These include chronic health conditions and social isolation.
Depression and Anxiety in Later Life
Depression and anxiety are common mental health challenges for older adults. These conditions can come from chronic illness, loss, and social isolation. Early detection and intervention are key to managing these conditions well.
- Recognizing the signs of depression and anxiety
- Understanding the impact of chronic illness on mental health
- The importance of social support networks
Older adults with depression or anxiety can benefit from therapy and medication. It’s essential to approach these conditions with compassion and understanding.
Social Isolation and Loneliness
Social isolation and loneliness are big concerns for older adults. These can severely affect both mental and physical health. Building and maintaining social connections is vital to prevent isolation.
- Encouraging community engagement
- Supporting family connections and friendships
- Utilizing technology to stay connected
We must focus on strategies to fight social isolation. This ensures older adults stay connected and supported in their communities.
Conclusion: Meeting the Healthcare Needs of an Aging World
The world is getting older, and we need a strong public health plan. This plan should help older people stay healthy and reduce the economic and social problems they face. We must focus on managing chronic diseases, geriatric syndromes, and mental health support for older adults.
We aim to provide top-notch healthcare and support for patients from around the world. The connection between an aging population and healthcare is strong. We need to address their health needs. By encouraging a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, exercise, and social activities, we can help older adults thrive.
Healthcare systems must change to meet the needs of an aging world. We all need to work together. This way, older adults can live happy and healthy lives.
FAQ
What are the major health challenges facing the aging population worldwide?
Older adults worldwide face many health challenges. These include heart disease, brain disorders, and muscle and bone issues. They also deal with metabolic problems, geriatric syndromes, and mental health issues.
How does the global aging phenomenon impact healthcare systems?
The aging of the global population strains healthcare systems. Older adults need more complex and expensive care. This includes managing chronic diseases and mental health support.
What is the difference between normal aging and pathological aging?
Normal aging is a natural process where physical and mental abilities gradually decline. Pathological aging, on the other hand, involves age-related diseases like Alzheimer’s or heart disease.
How can we reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease in older adults?
To lower the risk of heart disease in older adults, promote a healthy lifestyle. This includes eating well, staying active, and avoiding tobacco. Also, manage conditions like high blood pressure and high cholesterol.
What are the common musculoskeletal conditions affecting older adults?
Older adults often face osteoporosis, which increases fracture risk. They also deal with arthritis, causing joint pain and stiffness.
How can we prevent and manage geriatric syndromes, such as frailty and falls?
To prevent and manage geriatric syndromes, take a holistic approach. Encourage physical activity, improve nutrition, and address medical conditions. Also, implement strategies to prevent falls.
What are the mental health challenges faced by older adults?
Older adults face mental health issues like depression, anxiety, and social isolation. These can be caused by chronic illness, loss, and loneliness.
How can we support the mental health and well-being of older adults?
To support older adults’ mental health, use a multi-faceted approach. Promote social engagement, provide mental health support, and address medical conditions.
What is the impact of aging on the global population, and what are the projections for the future?
The global population is aging fast. By 2050, the number of people over 60 will nearly double to 2.1 billion. The number of those aged 80 and older will triple to 426 million.
How can healthcare systems adapt to meet the complex health needs of older adults?
Healthcare systems can adapt by prioritizing healthy aging. Encourage a balanced lifestyle, including diet, exercise, and social interaction. Provide complete care, including managing chronic diseases and mental health support.
References
World Health Organization. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ageing-and-health