Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
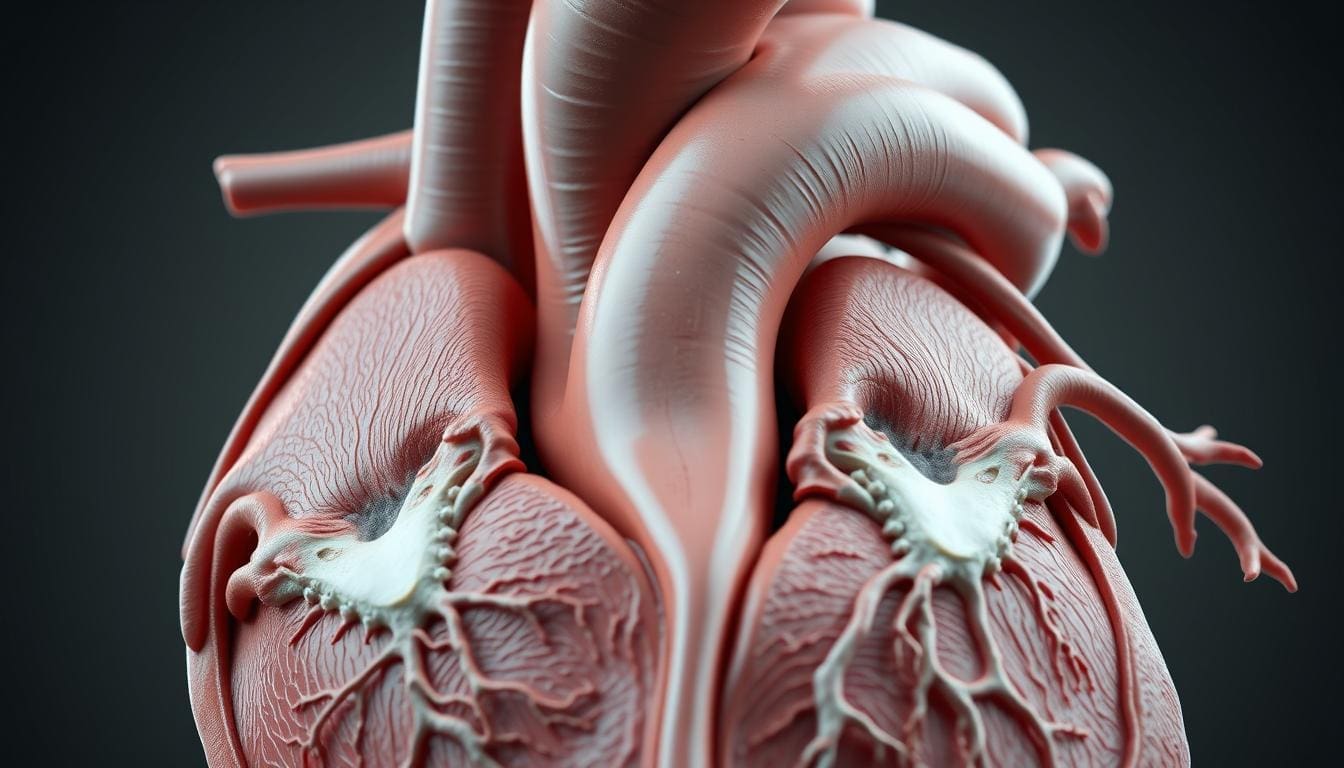
At Liv Hospital, we know how key the aortic root is. It’s the first part of the aorta, linking the heart to the rest of the body. The aortic root sits at the heart’s base, where the left ventricle meets the aorta.
Knowing how this important part works is vital for finding and fixing problems. We offer top-notch heart care at Liv Hospital. We make sure we get every detail of the aortic root right.
The aortic root is key to the heart’s pumping power. It’s a complex part of the heart that keeps it healthy.
The aortic root connects the left ventricle to the aorta. It has parts like the aortic valve and sinuses of Valsalva. These parts help the heart work right.
Its main job is to let blood flow from the left ventricle to the aorta. It stops blood from flowing back. This is thanks to its different parts working together.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Aortic Valve | Regulates blood flow between the left ventricle and the aorta |
| Sinuses of Valsalva | Provide a space for the aortic valve leaflets to open into during systole |
| Interleaflet Triangles | Support the aortic valve leaflets and contribute to the root’s structural integrity |
| Sinotubular Junction | Marks the boundary between the aortic root and the ascending aorta |
The aortic root has evolved to improve heart function. Studying vascular structures is vital. Its development is linked to the heart’s growth, and problems can cause serious heart issues.
The aortic root’s development is vital for heart health. Its proper formation is essential for the heart’s function throughout life.
The aortic root is at the heart’s center, surrounded by all four chambers. This key spot shows its vital role in heart anatomy and function.
The aortic root sits between the left ventricle and the ascending aorta. It’s a vital link between the heart’s main pump and the body’s blood flow. Its central spot means it’s near the right atrium, left atrium, and right ventricle. It’s also close to the pulmonary valve.
The aortic root’s edges are marked by important structures. These include:
Knowing these boundaries is key for doctors and researchers. The way these parts work together shows how vital the aortic root is.
| Anatomical Structure | Description | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Aortic Valve Leaflets | Three semilunar leaflets that control blood flow | Regulate blood flow from the left ventricle to the aorta |
| Sinuses of Valsalva | Dilations in the aortic root wall | Provide space for the aortic valve leaflets to open |
| Sinotubular Junction | Transition zone between the aortic root and ascending aorta | Marks the end of the aortic root |
Understanding the aortic root’s detailed anatomy is vital. It’s essential for both medical professionals and researchers. The aortic root’s complex design is key to its role in health and disease.
To understand the aortic root’s role, we need to look at its parts. The aortic root is a complex structure that is key to the heart’s function. Knowing its components helps us grasp its anatomy and how it works.
The aortic valve is a key part of the aortic root. It has three cusps or leaflets that open and close to control blood flow. The aortic valve’s proper function is essential for the heart’s normal output and to avoid problems like aortic regurgitation.
Aortic Valve Leaflets: These leaflets are thin, fibrous structures attached to the aortic root. They open fully during systole, letting blood flow into the aorta. They close tightly during diastole, stopping backflow into the left ventricle.
The sinuses of Valsalva are dilations in the aortic root that house the aortic valve leaflets. These sinuses are vital for the aortic valve’s proper functioning. They provide the space needed for the leaflets to open and close effectively.
Function of the Sinuses: The sinuses of Valsalva reduce stress on the aortic valve leaflets and help with smooth blood flow. They also house the coronary artery ostia, the openings for the coronary arteries.
The interleaflet triangles are small, triangular areas between the aortic valve leaflets. These triangles are part of the ventricular outflow tract. They are important for the aortic root’s structure and function.
The sinotubular junction is the boundary between the sinuses of Valsalva and the tubular portion of the ascending aorta. This junction is a critical landmark in the aortic root. It marks the transition from the aortic root to the ascending aorta.
| Component | Function | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Aortic Valve | Regulates blood flow from the heart into the aorta | Dysfunction can lead to aortic stenosis or regurgitation |
| Sinuses of Valsalva | Houses the aortic valve leaflets and coronary artery ostia | Abnormalities can lead to aortic root dilation or aneurysm |
| Interleaflet Triangles | Part of the ventricular outflow tract | Important for overall aortic root structure and function |
| Sinotubular Junction | Boundary between the sinuses and the ascending aorta | Critical landmark for surgical interventions |
In conclusion, the aortic root is a complex structure with several essential components. Each part plays a vital role in its function. Understanding these components is key to appreciating the aortic root’s anatomy and physiology. It’s also important for diagnosing and treating related cardiac conditions.
The aortic root is key in coronary circulation. It’s where the coronary arteries start. This connection is vital for the heart’s health.
The coronary arteries start at the aortic root, in the sinuses of Valsalva. The left and right main coronary arteries branch off here. They carry blood to the heart muscle.
The coronary arteries bring oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle. This is essential for the heart to pump well. The coronary circulation makes sure the heart gets what it needs.
The heart’s blood supply is complex. The coronary arteries are at its center. Any problem here can cause serious heart issues.
Coronary anatomy varies a lot among people. Variations in the origin and course of the coronary arteries affect health and treatment. Knowing these variations is key for good care.
Using detailed imaging and diagnostic methods is important. They help spot and manage these variations. This way, doctors can give care that fits each person’s needs.
The aortic root’s hemodynamics are key to its role in the heart. Knowing these dynamics helps us see how the heart keeps blood flowing well.
Blood flow in the aortic root follows complex patterns for efficient circulation. Flow dynamics are shaped by the root’s anatomy, like the sinuses of Valsalva and the aortic valve.
The sinuses of Valsalva are vital for blood flow. They help ensure the heart gets enough blood during its rest phase. This shows how important the aortic root is for heart function.
Pressure in the aortic root is carefully managed to keep the heart stable. The aortic valve and nearby structures work together to control these changes.
When the heart beats, the aortic valve opens. This lets blood move into the aorta. When the heart rests, the valve closes to stop blood from flowing back. This is key for keeping proper blood pressure and ensuring organs get enough blood.
The aortic root’s hemodynamics greatly affect the heart’s overall function. Good blood flow and pressure control are vital for the heart’s best performance.
Any issues with these processes can cause heart problems. So, understanding and managing aortic root hemodynamics is critical. It helps us diagnose and treat heart diseases better.
Diagnostic imaging is key in checking the aortic root. It helps doctors spot and treat problems early. The aortic root is complex, so seeing it clearly is very important.
Echocardiography is a main tool for looking at the aortic root. It uses sound waves to show the heart’s details. Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) is often used first because it’s easy and doesn’t hurt.
Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) gives clearer pictures by being closer to the heart. It’s great for when you need exact measurements.
Other advanced tools also help check the aortic root. Computed Tomography (CT) scans give sharp pictures of the aortic root and nearby areas. They help doctors measure and check for problems.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is also useful. It shows detailed images without using harmful radiation. MRI can look at blood flow and heart function, giving a full view of the aortic root.
Getting the right size of the aortic root is very important. It helps find issues like dilation or aneurysm. Different tools measure it in different ways.
| Imaging Modality | Measurement Technique | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Echocardiography | Leading edge to leading edge | Widely available, non-invasive |
| CT Scan | Inner edge to inner edge | High-resolution images, precise measurements |
| MRI | Inner edge to inner edge | No radiation, assesses blood flow and cardiac function |
Using these imaging methods helps doctors make the best choices for treating aortic root problems.
It’s key to know about the aortic root’s health issues for good heart care. The aortic root is vital to the heart’s structure. Any problems here can affect heart health a lot.
Aortic root dilation and aneurysm are serious issues. Aortic root dilation means the aortic root gets bigger. This can lead to more serious problems. An aortic root aneurysm happens when it gets big enough to form a bulge, which can burst if not treated.
Early spotting and watching of aortic root dilation is very important. Tests like echocardiography and advanced imaging help find and manage these issues.
Aortic root dissection is a very dangerous condition. It’s when there’s a tear in the aorta’s inner layer, letting blood leak between the layers. It needs quick medical help.
Finding aortic root dissection can be hard because its symptoms are like other heart problems. We use tools like CT angiography and MRI to find and treat it right.
| Condition | Description | Diagnostic Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Aortic Root Dilation | Enlargement of the aortic root | Echocardiography, CT Angiography |
| Aortic Root Aneurysm | Significant dilation forming an aneurysm | Advanced Imaging (MRI, CT) |
| Aortic Root Dissection | Tear in the inner layer of the aorta | CT Angiography, MRI, Transesophageal Echocardiography |
Genetic disorders can cause problems with the aortic root. Conditions like Marfan syndrome and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome can make the aortic root bigger and increase the risk of a tear.
We stress the need for genetic tests and looking at family history to find at-risk people. Finding problems early and taking steps to prevent them can help patients with genetic risks a lot.
Understanding how genetics and aortic root problems are linked helps us give better care and plans for those affected.
Surgery is key in treating aortic root disorders. It gives patients a chance for a better life. New surgical methods have made treatment more tailored and effective.
This surgery keeps the patient’s own aortic valve. It replaces the diseased aortic root. It’s good for those with aortic root aneurysms or dissections and a working valve.
Benefits of Valve-Sparing Root Replacement:
This surgery replaces both the aortic root and valve with a graft. It’s for those with severe aortic root disease and valve problems.
| Procedure | Indications | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Composite Root Replacement | Aortic root disease with valve dysfunction | Effective for complex aortic root issues, durable |
| Valve-Sparing Root Replacement | Aortic root aneurysms or dissections with functioning valve | Preserves native valve, reduces anticoagulation need |
Less invasive surgeries are now used for aortic root surgery. They promise quicker recovery and less harm to the patient.
“Minimally invasive aortic root surgery represents a significant advancement in the treatment of aortic root disorders, providing patients with a less invasive alternative to traditional open surgery.” – Cardiothoracic Surgeon
Outcomes after aortic root surgery have gotten better. This is thanks to new surgical methods and better care before and after surgery. Patients need close follow-up to watch for complications and ensure they recover well.
Having surgery can be scary. Our team is here to give full care and support. We aim for the best results for our patients.
Medical research is changing how we treat aortic root diseases. We’re seeing big improvements in treatments, making life better for patients.
Transcatheter interventions are a new way to treat aortic root conditions. They’re less invasive than traditional surgery, cutting down recovery time and risks. Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) is a big success in treating aortic valve diseases.
Bioengineering is helping create bioprosthetic valves that can grow with the body. These new valves aim to last longer than current options, helping patients with aortic root replacement.
Medicine is key in treating aortic root conditions, early on or alongside surgery. Beta-blockers and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) help control blood pressure and slow aortic wall dilation.
New research is looking into regenerative medicine and gene therapy for aortic root diseases. These areas could lead to more effective, tailored treatments. We’re dedicated to keeping up with these advances for our patients.
The aortic root is key to keeping the heart healthy. It’s located at the top of the heart and has important parts. These parts help with blood flow and keeping the heart working right.
Problems with the aortic root, like it getting too big or tearing, can harm the heart. Finding and fixing these issues early is very important. It helps avoid serious damage later on.
New ways to fix the aortic root have made treatment better. These include surgeries that save the heart valves and new, less invasive methods. More research is needed to find even better ways to treat these heart problems.
Knowing how vital the aortic root is helps us take better care of our hearts. With better treatments and understanding, we can help more people. This way, we can make sure everyone gets the best care for their heart health.
The aortic root is a key part of the heart. It connects the heart to the rest of the body. It makes sure blood flows properly from the heart to the body.
The aortic root is in the center of the heart. Its exact location is important for doctors and surgeons.
The aortic root has several important parts. These include the aortic valve, sinuses of Valsalva, and the sinotubular junction. Each part is vital for the aortic root’s function.
The aortic root is connected to the coronary arteries. These arteries supply blood to the heart. Changes in the coronary anatomy can happen.
Doctors use echocardiography and other imaging to see the aortic root. Measuring its size is key for diagnosing problems like dilation or aneurysm.
The aortic root can face issues like dilation, aneurysm, dissection, and genetic disorders. Knowing about these conditions helps doctors treat them right.
There are surgeries like valve-sparing root replacement and minimally invasive options. These help treat aortic root problems. The success of these surgeries is important.
New treatments include transcatheter interventions and bioengineered valves. Research is also looking into new ways to manage aortic root issues.
Dilation or aneurysm can harm the heart’s function. It can cause problems like aortic regurgitation or dissection. Understanding the aortic root’s hemodynamics is key to managing these issues.
The sinotubular junction is vital in the aortic root. It marks the transition from the sinuses of Valsalva to the ascending aorta. Its health is essential for the aortic root’s function.
Yes, genetic disorders like Marfan syndrome can affect the aortic root. Understanding these conditions is important for proper care.
The aortic root is a key part of the heart. It connects the heart to the rest of the body. It makes sure blood flows properly from the heart to the body.
The aortic root is in the center of the heart. Its exact location is important for doctors and surgeons.
The aortic root has several important parts. These include the aortic valve, sinuses of Valsalva, and the sinotubular junction. Each part is vital for the aortic root’s function.
The aortic root is connected to the coronary arteries. These arteries supply blood to the heart. Changes in the coronary anatomy can happen.
Doctors use echocardiography and other imaging to see the aortic root. Measuring its size is key for diagnosing problems like dilation or aneurysm.
The aortic root can face issues like dilation, aneurysm, dissection, and genetic disorders. Knowing about these conditions helps doctors treat them right.
There are surgeries like valve-sparing root replacement and minimally invasive options. These help treat aortic root problems. The success of these surgeries is important.
New treatments include transcatheter interventions and bioengineered valves. Research is also looking into new ways to manage aortic root issues.
Dilation or aneurysm can harm the heart’s function. It can cause problems like aortic regurgitation or dissection. Understanding the aortic root’s hemodynamics is key to managing these issues.
The sinotubular junction is vital in the aortic root. It marks the transition from the sinuses of Valsalva to the ascending aorta. Its health is essential for the aortic root’s function.
Yes, genetic disorders like Marfan syndrome can affect the aortic root. Understanding these conditions is important for proper care.
Radiopaedia: Aortic Root (Informational Radiology Resource)
Annals of Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery: Anatomy of the Aortic Root: Surgical Considerations
PCRonline (EAPCI): Anatomy of the Aortic Valvar Complex: Aortic Root
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!