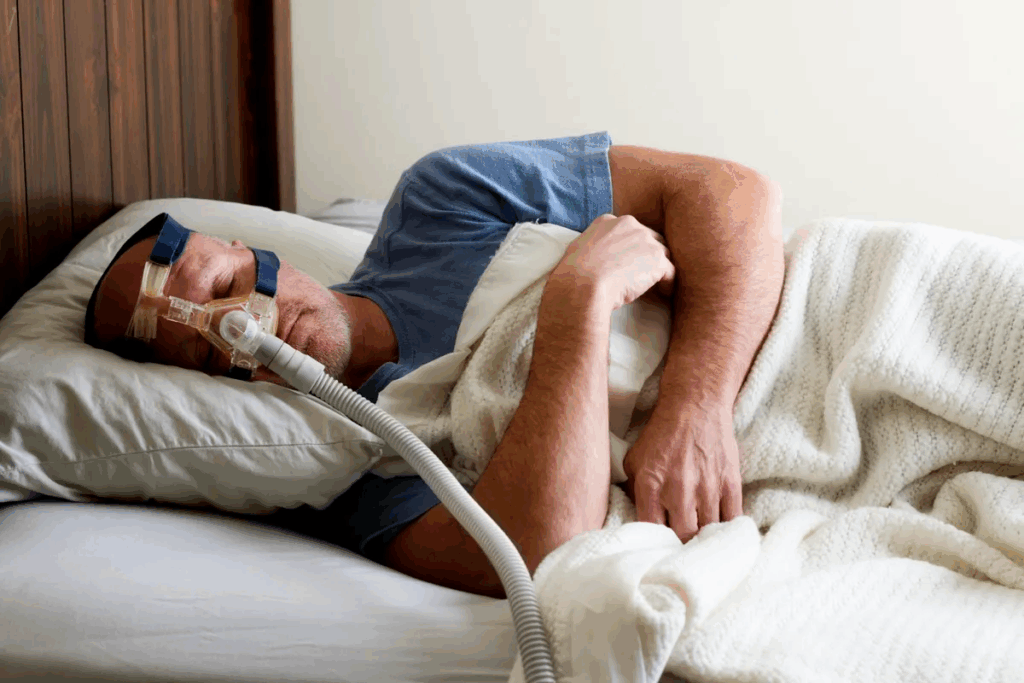
Sleep apnea is a serious condition where breathing stops many times during sleep. It often happens because the airway collapses. People with sleep apnea may snore, have morning headaches, feel tired, get irritable, and have trouble focusing.
Even though CPAP therapy is the main treatment, surgical options are there for those who can’t use it. At Liv Hospital, we use our advanced surgical skills to help patients sleep better and feel healthier.
What is the best surgery for sleep apnea? A comparison of UPPP, MMA, and Inspire for maximum efficacy.
Key Takeaways
- Sleep apnea is a disorder involving lapses in breathing during sleep.
- Multiple surgical treatment options exist for patients who do not respond to conservative therapies.
- Understanding the causes and symptoms of sleep apnea is key to finding the best surgery.
- Liv Hospital offers top-notch care for international patients looking for sleep apnea treatments.
- Surgical options can greatly improve sleep quality and overall health.
Understanding Sleep Apnea and Its Impact
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder that affects millions. It disrupts sleep quality and health. It causes pauses in breathing or shallow breathing during sleep.
Types of Sleep Apnea: Obstructive, Central, and Mixed
Sleep apnea has three main types: Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA), Central Sleep Apnea (CSA), and Mixed Sleep Apnea. Obstructive Sleep Apnea happens when the airway is blocked during sleep. This is often due to the throat muscles relaxing too much. Central Sleep Apnea is when the brain can’t send the right signals to the breathing muscles. Mixed Sleep Apnea is a mix of OSA and CSA.
Type of Sleep Apnea | Description | Common Causes |
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) | Airway obstruction during sleep | Relaxation of throat muscles, obesity |
Central Sleep Apnea (CSA) | Brain signaling issue | Neurological disorders, heart conditions |
Mixed Sleep Apnea | Combination of OSA and CSA | Complex, involving both physical and neurological factors |
Common Symptoms and Diagnosis Methods
Symptoms of sleep apnea include loud snoring and stopped breathing during sleep. You might also wake up with a dry mouth or sore throat. Morning headaches are common too.
To diagnose sleep apnea, a sleep study is done. This can be at home or in a sleep lab. It monitors breathing and oxygen levels during sleep.
A doctor will also look at your medical history and do a physical exam. They check for things like obesity or nasal congestion that might be causing the sleep apnea.
Health Consequences of Untreated Sleep Apnea
Not treating sleep apnea can cause serious health problems. These include high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke. It can also make you very tired during the day and affect your thinking.
It can even lead to accidents. Sleep apnea is also linked to diabetes and other metabolic disorders. This shows why it’s important to get it treated early.
Knowing about sleep apnea and its effects is key. It helps find the right treatment, which might include surgery. Surgery depends on the person’s anatomy and where the airway is blocked. This makes treatment very personal.
Non-Surgical Treatments and Their Limitations
Non-surgical treatments are often the first choice for sleep apnea. They help manage symptoms and improve life quality. But, their success can vary.
CPAP Therapy: Effectiveness and Compliance Issues
CPAP therapy is a common first step for sleep apnea. It uses a mask to deliver air, keeping the airway open. Despite its effectiveness, many struggle with using it due to discomfort and other issues.
Studies show that sticking to CPAP therapy is key. But, many find it hard. New CPAP machines have features like ramp settings and heated humidifiers to make it more comfortable.
Oral Appliances and Positional Therapy
Oral appliances move the jaw forward, keeping the airway open. They’re good for mild to moderate sleep apnea and are more comfortable than CPAP for some. Positional therapy helps by preventing sleeping on the back, which can worsen sleep apnea.
Oral appliances and positional therapy can work well. But, their success depends on the sleep apnea’s severity and the patient’s situation. For example, oral appliances might not work for severe cases or certain dental issues.
Lifestyle Modifications and Their Impact
Lifestyle changes are important for managing sleep apnea. Losing weight, exercising regularly, avoiding alcohol and sedatives, and quitting smoking can help. These changes can reduce symptoms, mainly if obesity is a factor.
A study found that losing 10% of body weight can greatly improve symptoms. We suggest working with healthcare professionals to create a weight loss and exercise plan.
If non-surgical treatments don’t help enough, surgery might be an option. The table below shows the effectiveness and limitations of non-surgical treatments.
Treatment | Effectiveness | Limitations |
CPAP Therapy | Highly effective for reducing apnea episodes | Compliance issues due to discomfort and side effects |
Oral Appliances | Effective for mild to moderate sleep apnea | Not suitable for severe sleep apnea or certain dental conditions |
Positional Therapy | Effective for patients who sleep on their backs | May not be effective for patients who sleep in other positions |
Lifestyle Modifications | Can significantly reduce symptoms | Requires consistent effort and may not be sufficient on its own |
When to Consider Surgical Intervention
For many patients, surgical intervention is considered when conservative treatments fail to provide adequate relief from sleep apnea symptoms. This decision is made after a thorough evaluation of the patient’s condition and the effectiveness of previous treatments.
Failed Conservative Treatment Scenarios
Conservative treatments for sleep apnea include CPAP therapy, oral appliances, and lifestyle modifications. When these treatments fail to adequately manage symptoms, surgical options become a viable alternative. Failed conservative treatment scenarios may include:
- Inability to tolerate CPAP therapy due to discomfort or claustrophobia
- Oral appliance therapy that is ineffective or causes significant side effects
- Lifestyle modifications that do not result in significant weight loss or other desired changes
Anatomical Indications for Surgery
The decision to proceed with surgical intervention also depends on the presence of specific anatomical indications. These may include:
- Narrowing or obstruction of the airway due to anatomical abnormalities
- Presence of a large tongue or tonsils that obstruct the airway
- A deviated septum or other nasal obstructions that contribute to sleep apnea
The Pre-Surgical Evaluation Process
Before undergoing surgical intervention, patients must undergo a thorough pre-surgical evaluation. This process involves a detailed assessment of the patient’s overall health, the severity of their sleep apnea, and the specific anatomical characteristics that may be contributing to their condition.
The evaluation may include sleep studies, imaging tests such as CT or MRI scans, and consultations with specialists including otolaryngologists and sleep specialists. The goal of this evaluation is to determine the most appropriate surgical approach for each individual patient.
What Is the Best Surgery for Sleep Apnea? Key Determining Factors
To find the best surgery for sleep apnea, we look at many factors. These factors help us choose the right treatment for each patient. The success of the surgery depends on these elements.
Identifying the Site of Obstruction
The first step is to find where the obstruction is. Sleep apnea can happen at different places, like the nose or tongue. We use tools like sleep endoscopy to see where it is.
Severity of Sleep Apnea and AHI Scores
The severity of sleep apnea is key. It’s measured by the Apnea-Hypopnea Index (AHI). Higher AHI scores mean more severe sleep apnea. This helps us choose the right surgery.
Patient-Specific Considerations
Patient-specific considerations are also important. We look at the patient’s health and what they prefer. For example, some might need nasal surgery, while others might need jaw surgery.
By looking at these factors, we can find the best surgery for sleep apnea. This improves the patient’s life and health.
Maxillomandibular Advancement (MMA): Highest Success Rates
Maxillomandibular Advancement (MMA) surgery is a top choice for treating sleep apnea. It has success rates between 80% to 90%. This surgery moves the upper and lower jaws forward to widen the airway. This makes it harder for the airway to block during sleep.
Procedure Details and Surgical Approach
The MMA surgery is complex and needs a team of experts. They plan carefully to find the best jaw position for each patient. The surgery is done under general anesthesia. The jawbones are accessed through incisions and moved forward before being secured.
Recovery Timeline and Post-Operative Care
Recovering from MMA surgery takes weeks to months. Patients stay in the ICU for a day or two after surgery. They use pain meds and cold compresses to manage swelling and pain. Eating soft foods for weeks helps with healing and comfort.
Success Rates of 80-90% and Long-Term Outcomes
Research shows MMA surgery works well, with success rates of 80% to 90%. Success means a big drop in the Apnea-Hypopnea Index (AHI). Most patients see lasting improvements in their sleep and health.
Ideal Candidates for MMA Surgery
People with moderate to severe sleep apnea who haven’t improved with other treatments are good candidates. A detailed check, including sleep studies and images, is needed. The team looks at where the blockage is, how severe the apnea is, and the patient’s overall health.
Surgical Procedure | Success Rate | Recovery Time |
MMA Surgery | 80-90% | Several weeks to months |
UPPP | 40-70% | Few weeks |
Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation | 80%+ | Variable, often quicker than MMA |
In conclusion, MMA surgery is a top choice for sleep apnea. It greatly improves sleep quality and health for the right patients.
Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP): Targeting the Soft Palate
For years, Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) has been a key treatment for sleep apnea. It removes extra tissue in the throat to make the airway wider. This helps lessen sleep apnea symptoms.
Traditional vs. Modified UPPP Techniques
UPPP methods have changed over time. The old way removed the uvula, parts of the soft palate, and sometimes the tonsils. Now, modified techniques aim to keep more of the natural anatomy. This helps reduce complications and improve results.
The main differences between old and new UPPP are:
- How much tissue is removed
- Keeping or removing the uvula
- Adding procedures like tonsillectomy
Success Rates and Predictive Factors
UPPP success rates vary, from 40% to 70%. Several things affect these rates, including:
- How severe the sleep apnea is
- Where the blockage is
- The patient’s unique anatomy
Knowing these factors helps find the best candidates for UPPP. It also sets realistic expectations for results.
Recovery Process and Possible Complications
Recovering from UPPP can be tough. Patients often face pain, trouble swallowing, and voice changes. Post-operative care is key to avoiding problems like infection, bleeding, and velopharyngeal insufficiency.
To help with recovery, patients should:
- Eat soft foods
- Avoid hard activities
- Go to all follow-up visits
Combining UPPP with Other Procedures
UPPP is sometimes paired with other surgeries to boost results. These can include:
- Genioglossus advancement
- Hyoid suspension
- Other airway surgeries
Doing more than one surgery at a time can tackle more blockages. This might make treatment for sleep apnea more effective.
Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation: A Modern Alternative
Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation has changed how we treat sleep apnea. It involves a device that stimulates the hypoglossal nerve. This nerve controls the tongue, keeping the airway open at night.
Device Functionality
The device senses when you breathe and moves your tongue forward. This keeps your airway open. It’s a personalized stimulation that reduces sleep apnea episodes.
Implantation and Activation
To implant the device, a small generator goes in your chest and a lead on your nerve. It’s turned on when you sleep. Clinical studies have shown it’s very effective.
Clinical Outcomes and Success Rates
Many studies have shown Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation works well, with over 80% success. Here are some key findings from recent trials.
Study | Number of Patients | Success Rate |
STAR Trial | 126 | 83% |
French Study | 104 | 85% |
German Study | 60 | 82% |
Patient Selection and Contraindications
Not everyone can get Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation. You need to have severe sleep apnea and a certain body mass index. A comprehensive evaluation is needed to see if you’re a good candidate.
Every patient is different, and a detailed check is key to finding the right treatment. Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation is a good option for those who haven’t found relief with other treatments.
Transoral Robotic Surgery (TORS): Precision Treatment
Transoral Robotic Surgery (TORS) has changed how we treat sleep apnea. It precisely targets the tongue base and epiglottis, common blockages in sleep apnea.
Targeting the Tongue Base and Epiglottis
TORS uses robotic tech to remove or reshape tissues with great precision. This method tailors treatment to each patient’s unique needs.
Benefits of Robotic Precision
The robotic system in TORS offers many benefits. It provides better visualization, precise dissection, and less bleeding. These features make the surgery safer and more effective.
Key Benefits of TORS:
- Precision in targeting obstructive tissues
- Minimally invasive, reducing recovery time
- Enhanced visualization for the surgeon
Effectiveness Data and Patient Selection
Research shows TORS can greatly improve sleep apnea symptoms in the right patients. Choosing the right patients is key. It depends on the sleep apnea’s severity and where the blockage is.
Patient Selection Criteria | Importance |
Severity of Sleep Apnea | High |
Site of Obstruction | High |
Overall Health | Medium |
Recovery Timeline and Speech Considerations
After TORS, patients may feel some swelling and discomfort. These feelings usually go away in a few weeks. Some may notice changes in speech or swallowing, but these usually get better as they heal.
Post-operative care is key for a smooth recovery. It includes managing pain, speech therapy if needed, and follow-up visits to check on healing.
Comparing Surgical Options: Risk-Benefit Analysis
When looking at different surgeries for sleep apnea, it’s important to weigh the options carefully. You need to think about how invasive the surgery is, how long it takes to recover, how successful it is, and the cost. These factors help you choose the best surgery for your needs.
Invasiveness and Recovery Comparison
Sleep apnea surgeries vary in how invasive they are and how long it takes to get better. For example, Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) is less invasive than Maxillomandibular Advancement (MMA). MMA moves the upper and lower jaws.
- UPPP: This surgery removes extra tissue from the throat. It takes a few weeks to recover, with some pain and swelling.
- MMA: Being more invasive, MMA takes longer to recover, often several months. This is because it changes the face’s structure a lot.
- Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation: This involves putting in a device that helps control the tongue. Recovery is quicker than MMA but adjusting to the device takes time.
Success Rate Comparison Across Procedures
The success of sleep apnea surgery is measured by how much it lowers Apnea-Hypopnea Index (AHI) scores. Different surgeries have different success rates:
Procedure | Success Rate |
MMA | 80-90% |
UPPP | 40-70% |
Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation | 80%+ |
MMA and Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation have higher success rates than UPPP. But, the success also depends on who gets the surgery.
Cost and Insurance Considerations in the US
The cost of sleep apnea surgery varies a lot. It depends on the surgery, where you are, and your insurance. In the US, insurance might cover part of the cost if it’s deemed necessary.
“Insurance coverage for sleep apnea surgery varies by provider and policy. It’s essential to check with your insurance company to understand what is covered.” – Medical Expert, Sleep Apnea Specialist
Combining Surgical Approaches for Better Outcomes
At times, mixing different surgeries can lead to better results. For example, combining UPPP with genioglossus advancement can improve outcomes for some patients.
We think a personalized approach is key. It considers each patient’s unique needs and conditions for the best sleep apnea surgery outcome.
Conclusion: Making an Informed Decision About Sleep Apnea Surgery
When thinking about sleep apnea surgery, patients need to carefully consider their choices. It’s important to know about the different surgeries, their benefits, and risks. This knowledge helps in making a smart choice for treating sleep apnea.
We’ve looked at several surgical options, like Maxillomandibular Advancement (MMA) and Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP). We also talked about Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation and Transoral Robotic Surgery (TORS). Each has its own success rates, possible problems, and things to think about for each patient.
To make the right choice, patients should talk to their healthcare provider about their needs. This way, they can pick the best treatment for them and get the best results.
In the end, deciding on sleep apnea surgery needs a full understanding of the options and what they mean. We suggest patients work with their healthcare team to find the best treatment for their situation.
FAQ
What is the success rate of sleep apnea surgery?
The success of sleep apnea surgery varies. It depends on the procedure and the patient. For example, Maxillomandibular Advancement (MMA) works for 80-90% of patients. Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) works for 40-70%.
What is the best surgery for sleep apnea?
The best surgery for sleep apnea depends on several factors. These include where the blockage is, how severe the sleep apnea is, and the patient’s health. MMA is often very effective, but the right surgery for a patient is decided by a doctor.
Is there an operation for sleep apnea?
Yes, there are many surgeries for sleep apnea. These include MMA, UPPP, Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation (HNS), and Transoral Robotic Surgery (TORS). The right surgery depends on the patient’s sleep apnea and health.
Can surgery fix sleep apnea?
Surgery can greatly improve sleep apnea for many people. But, it depends on the surgery, how severe the sleep apnea is, and the patient’s health. Some might need more treatments after surgery.
What are the surgical options for sleep apnea?
Surgical options include MMA, UPPP, HNS, and TORS. Each targets different parts of the airway. They have different benefits and risks.
Does removing adenoids help sleep apnea in adults?
Adenoid removal is more common in kids. In adults, it’s less common but can help if adenoids are big. How well it works in adults varies.
What is Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation?
Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation is a surgery. It implants a device that moves the tongue. This keeps the airway open during sleep, reducing sleep apnea.
How does Transoral Robotic Surgery (TORS) work?
TORS uses a robotic system to remove tissue. It helps widen the airway and reduce blockages in sleep apnea. It allows for precise removal of tissues.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2025). What Is the Best Surgery for Sleep Apnea. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC11476387/