Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by aysenuurcakir
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of inherited blood disorders. It can cause severe pain and complications all over the body. For sickle cell sufferers, symptoms can range from mild to severe.
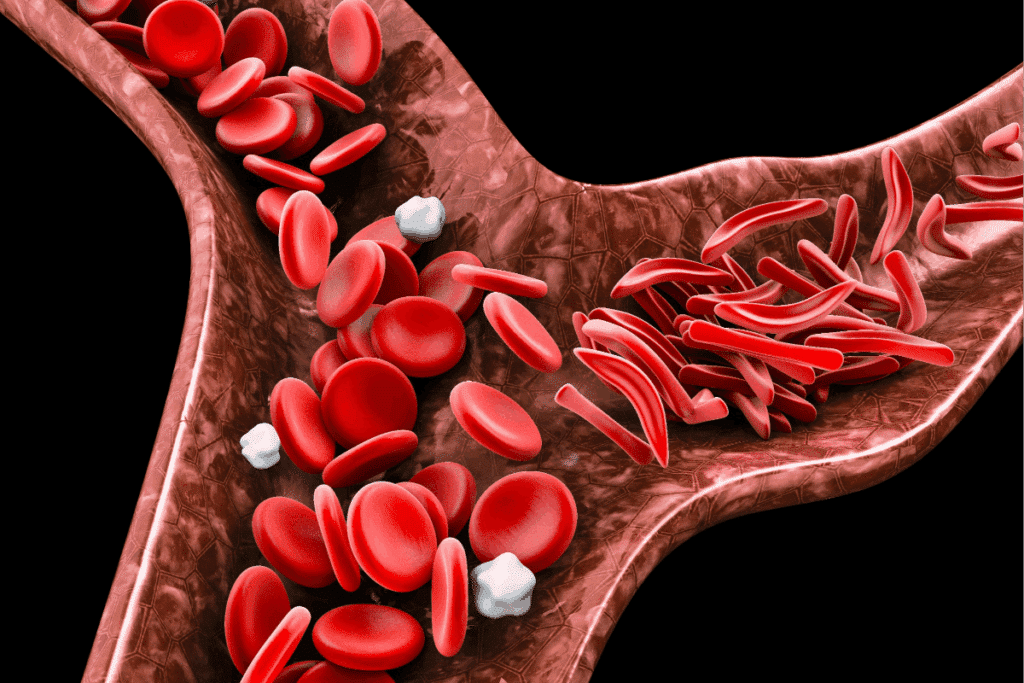
A sickle cell pain crisis can be triggered by many things. This includes infections and sudden changes in respiratory conditions. These can lead to dangerous infections and sudden respiratory distress. Knowing what triggers these crises is key to managing the condition well.
By understanding the risk factors for pain and sickle cell disease, people can take steps to lessen the crisis’s impact.
It’s important to understand sickle cell disease to manage its crises well. Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a genetic disorder that affects how red blood cells make hemoglobin. This leads to several health problems.
SCD makes red blood cells sickle, making them stiff and prone to breaking down. This causes anemia and other complications. It also leads to vaso-occlusive crises, where sickled cells block blood vessels. This results in tissue ischemia and pain.
A sickle cell pain crisis happens when sickled cells block blood vessels. This causes tissue ischemia and severe pain. Dehydration, infection, and stress can trigger these crises.
Dehydration is a big risk for sickling in SCD patients. When the body is dehydrated, hemoglobin S concentration goes up, leading to sickling. It’s key to stay hydrated to avoid dehydration-induced sickling.
Keeping well-hydrated is a major preventive step for SCD patients. We suggest drinking lots of water and avoiding diuretics like caffeine and alcohol. Checking urine output and colour can help see if you’re hydrated.
SCD patients face a higher risk of infections. These can cause acute crises and long-term health problems. We’ll look at common infections that lead to crises and how to prevent them.
SCD patients are more likely to get infections like pneumonia. These infections can start a chain of events leading to a sickle cell crisis. Research in Frontiers in Pediatrics shows understanding infections is key to managing SCD.
SCD patients have a weakened immune system. This makes them more prone to infections. Preventive measures are vital to lower the risk of infections and crises.
Respiratory issues, like sudden distress, can be deadly for SCD patients. Pneumonia can cause acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), needing quick medical help. Knowing the signs of respiratory distress is important for timely action.

Stopping infections is key in managing SCD. Vaccinations are important in preventing diseases like pneumococcal and flu. Good hygiene, like washing hands often, also helps a lot.
By knowing the risks of infections and using preventive steps, we can improve SCD patients’ lives. It’s important to work with healthcare providers to create a care plan that meets SCD patients’ needs.
Physical and emotional stress have a big impact on people with sickle cell disease. These stresses can trigger crises. It’s important to balance physical health and emotional well-being.
Physical activity can trigger sickle cell crises. When people with sickle cell disease do too much, their bodies need more oxygen. This can cause a crisis. Avoiding too much physical activity is key to preventing crises.
Simple changes, like taking breaks and staying in comfortable temperatures, can help. These steps can lower the risk of a crisis.
Psychological stress can also trigger a sickle cell crisis. Stress can change the body in ways that lead to sickling of red blood cells. Stress management techniques, like meditation and yoga, can help.
These methods can reduce how often crises happen.
Managing pain well is key during a crisis. Doctors often suggest a mix of medicine and other therapies. Pain management plans should fit each person’s needs.
They might include staying hydrated, resting, and using pain medicines.
Making lifestyle changes with sickle cell disease in mind can greatly improve life. Understanding and managing stress can help reduce crisis frequency and severity.
Recurrent sickle cell crises have a major impact on life expectancy with sickle cell anemia. But thanks to modern treatments, there’s hope for better outcomes. Sickle cell anemia is a genetic disorder that messes with hemoglobin production. This leads to red blood cells that are shaped incorrectly and can get stuck in blood vessels.
It’s key to know what affects life expectancy for patients and doctors. We’ll look into how new medicines and lifestyle changes can help those with sickle cell anemia.
New treatments, like hydroxycarbamide, are showing great promise. Hydroxycarbamide boosts fetal hemoglobin production. This type of hemoglobin is less likely to cause sickling. This means fewer painful crises and fewer complications.
“Hydroxycarbamide has been a big change for many with sickle cell disease,” says a top hematologist. “It cuts down on crises. This improves life quality and might even add years to their life.”
Along with medicine, some lifestyle changes are key. Avoiding extreme temperatures is important to prevent crises. Eating a healthy diet full of fruits, veggies, and whole grains also helps.
By making these lifestyle changes and sticking to treatment plans, people with sickle cell anemia can live better lives. This approach tackles both the physical and emotional sides of the disease.
Sharp pain, dangerous infections, and sudden breathing problems can be deadly in a sickle cell crisis. Knowing these risks is key to managing the disease well. To manage sickle cell disease, it’s important to understand what triggers it, take preventive steps, and get medical help quickly.
Working with healthcare providers and making smart lifestyle choices can greatly improve life for those with sickle cell disease. We stress the need for quality care to manage pain and sickle cell disease. This helps patients live more fulfilling lives.
Using effective management strategies, like preventing infections and managing stress, can lessen crisis frequency and severity. With the right approach, people with sickle cell disease can overcome its challenges and enjoy a better quality of life.
Dehydration, infections, too much physical activity, and stress can trigger a crisis. Knowing these triggers helps manage the condition better.
Dehydration lowers blood volume, making red blood cells more concentrated. This can cause sickling. Drinking enough water is key to avoiding this.
Drinking lots of water and avoiding caffeine and alcohol helps. Also, watch your urine to make sure you’re hydrated.
Pneumonia and other bacterial infections often trigger crises. Vaccines and good hygiene can lower these risks.
Use stress-reducing activities like meditation. Avoid too much physical activity. A healthy lifestyle and diet also help manage stress.
New medicines like hydroxyurea can reduce crisis frequency. Blood transfusions and pain meds are also options.
A healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can help manage the disease. Stress management is also important.
Frequent crises can shorten life expectancy. But with modern treatments and lifestyle changes, outcomes are getting better. Proactive management is key.
Use pain meds, stay hydrated, and rest. Work with your healthcare team to create a pain plan.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!