Last Updated on November 25, 2025 by
When urine flow is blocked, it can lead to acute urinary retention. This is when you can’t control when you pee, causing your bladder to swell. It also brings on severe pain that can come on quickly.

This blockage can happen for many reasons. It might be because of a block in the ureter or other parts of the urinary system. This can cause obstructive uropathy. If not treated, it can lead to infections and even permanent damage to your kidneys.
It’s important to know why and what happens when urine flow is blocked. This knowledge helps in getting the right treatment early. It also helps avoid serious health problems later on.
Urinary obstruction happens when urine flow is blocked. This can be due to kidney stones, blood clots, or tissue growth. If not treated, it can cause serious problems like kidney damage and infections.
There are two main types of urinary blockage causes: congenital and acquired. Congenital conditions are present at birth. Acquired conditions develop later in life due to various factors.
Ureteral stones are a common cause of urinary blockage. They block urine flow from the kidney to the bladder. Another cause is ureteropelvic junction (UPJ) obstruction, a condition present at birth.
Other factors that can cause urinary blockage include bladder stones, blood clots, and tumors. Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is also a cause, as it can block urine flow.
The risk of urinary blockage varies based on the cause. But some groups are more at risk. For example, older people and men are more likely to get BPH, which can block urine.
Other risk factors include a history of kidney stones, urinary tract infections, and certain medical conditions like diabetes. Knowing these risk factors helps in preventing and treating urinary blockage.
It’s important to know how the ureter works and its structure to understand urinary blockages. The ureters are muscular tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
The ureters are about 10 inches long. They have mucous membranes to protect them from urine. Their muscles help move urine towards the bladder through waves.
The anatomy of the ureters includes three layers: mucosa, muscularis, and adventitia. The mucosa keeps urine from being absorbed. The muscularis layer moves urine through waves.
Ureteral blockages can be caused by kidney stones, tumors, and congenital conditions. These blockages can be partial or complete, depending on the cause.
Liv Hospital aims to use international standards and evidence-based treatments for ureteral blockages. Experts say, “Quick diagnosis and treatment are key to avoiding kidney damage.”
It’s important to know the symptoms and how doctors diagnose obstructive uropathy. This condition happens when urine flow is blocked. If not treated quickly, it can cause serious health problems.
Acute urinary retention is a serious sign of obstructive uropathy. People can’t urinate suddenly. This is very painful and needs immediate medical help.
About 10% of men in their 70s face this issue. It’s key to spot the symptoms early.
Other signs include pain in the lower abdomen or back, changes in urine, trouble urinating, blood in urine, and frequent infections. These signs depend on where and how bad the blockage is.
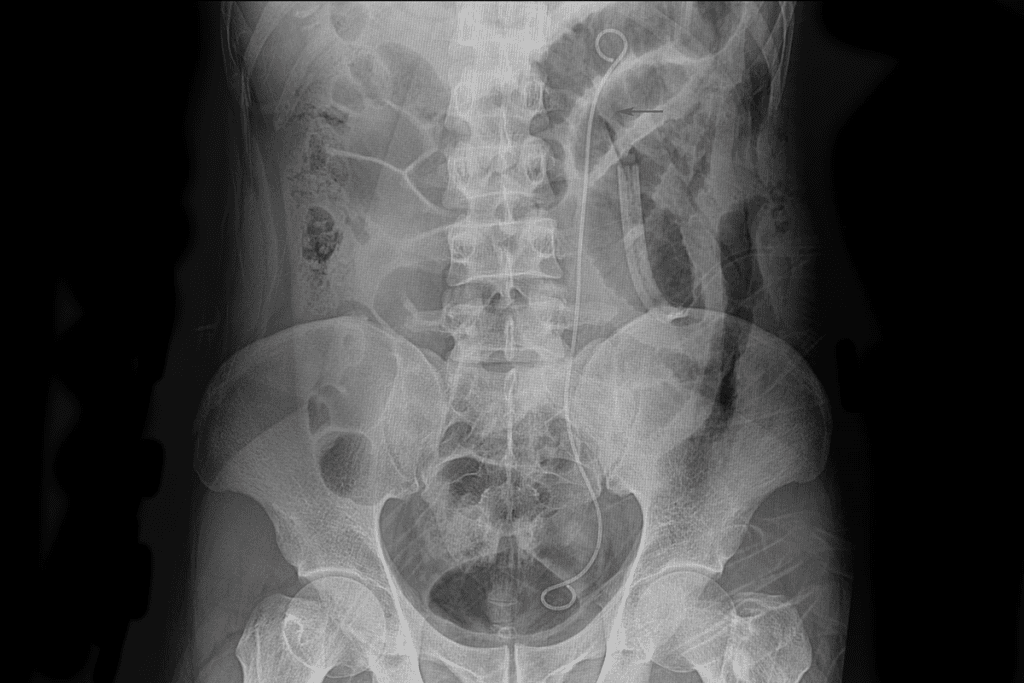
Doctors use imaging tests and other exams to find the blockage. They might use ultrasound, CT scans, or intravenous pyelography (IVP). These help see the urinary tract and find any blockages.
They also do urine tests, blood tests, and physical checks. This helps understand the patient’s health and find any other issues that might be causing the blockage.
Early diagnosis is key to treating obstructive uropathy well. Knowing the symptoms and using the right tests helps doctors create effective treatment plans. This helps relieve the blockage and prevent damage to the urinary tract.
Ignoring urinary obstruction can lead to serious health problems. When urine can’t flow, it builds up, putting pressure on the urinary tract. This pressure can harm the kidneys and tissues around them.
In the short term, urinary obstruction causes a lot of discomfort. Pain is a common symptom, often due to urine backing up into the kidneys. This can lead to severe pain and an infection.
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a serious issue. They can turn into sepsis if not treated quickly.
“The risk of developing a UTI increases significantly with urinary obstruction, highlighting the need for prompt medical attention.” “ A Urologist
If not treated, urinary obstruction can cause long-term damage. It can lead to kidney damage or even failure. The prolonged buildup of urine can change the kidney’s structure, affecting its function.
Conditions like ureteral stones or upper-urinary-tract obstruction can cause an ongoing blockage. This can lead to chronic kidney disease.
A uvj stone can also block the ureterovesical junction for a long time. This makes the problem even worse.
The long-term effects show why it’s critical to treat urinary obstruction quickly. This can prevent permanent damage.
Treatment for urinary obstruction can include medical or surgical methods. The choice depends on the cause and how severe the blockage is. Quick and effective treatment is key to avoiding complications and improving health outcomes.
For many, the first step is medical treatment, like for those with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Alpha-blockers help relax muscles in the prostate and bladder neck. This makes it easier to urinate. Studies show a 68% chance of regaining normal urination for BPH patients treated with alpha-blockers.
Other patients, like those with ureteral obstruction from kidney stones, might get pain management and hydration. In some cases, ureteral stenting is needed to keep the ureter open.
When medical treatments fail, surgery might be needed. The type of surgery depends on the cause and location of the blockage. For BPH, transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) is common. For kidney stones, ureteroscopy with laser lithotripsy is used.
Recovery and success rates differ among various groups. Age, health, and the cause of the obstruction play big roles. Younger, healthier patients usually do better.
When treated quickly and correctly, most patients with urinary obstruction have a good prognosis. Both doctors and patients need to understand the treatment options and their effects.
Urinary obstruction, often related to issues with the ureter, can lead to severe complications if left untreated. Obstructive uropathy is a condition that requires prompt medical attention to prevent long-term damage.
Liv Hospital is committed to providing rapid intervention based on international standards and evidence-based protocols for treating urinary obstruction. Treatment options vary depending on the cause and severity of the obstruction, but timely intervention is key in all cases.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for obstructive uropathy can help patients receive the care they need to prevent complications.
By addressing urinary obstruction promptly, patients can avoid severe complications and improve their overall quality of life. Effective treatment of ureter-related issues is critical in managing obstructive uropathy and ensuring the best possible outcomes.
Ureteropelvic junction (UPJ) obstruction is a blockage at the junction of the renal pelvis and the ureter. It stops urine from flowing normally from the kidney to the ureter.
Symptoms of a ureteral stone include severe pain in the side or back, below the ribs. Pain can also radiate to the lower abdomen or groin. Other symptoms include nausea, vomiting, and painful urination.
Obstructive uropathy occurs when urine flow is blocked in the urinary tract. This can cause structural or functional changes. If not treated, it can lead to kidney damage.
To diagnose obstructive uropathy, doctors use imaging tests like ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI. These tests help see the urinary tract and find any blockages or abnormalities.
The ureters are muscular tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder. They do this through a process called peristalsis, which is key to the urinary system.
The ureter connects the kidney to the bladder. The urethra carries urine from the bladder out of the body. They are different parts of the urinary system with unique functions.
To dislodge a kidney stone stuck in the ureter, doctors may use pain management, hydration, or surgery. Procedures like lithotripsy or ureteroscopy can remove or break up the stone.
Untreated urinary obstruction can cause kidney damage, infection, and even kidney failure. This shows why it’s important to get medical help quickly.
Treatment for urinary obstruction depends on the cause and severity. Mild cases may be managed medically, while more complex cases may need surgery.
UPJ obstruction, or ureteropelvic junction obstruction, is a blockage at the junction of the renal pelvis and the ureter. It affects urine flow from the kidney to the ureter.
A UVJ stone is a kidney stone stuck at the ureterovesical junction (UVJ). This is where the ureter meets the bladder, causing an obstruction.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!