Last Updated on November 26, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir

A CT guided biopsy is a medical procedure. It uses computed tomography imaging to guide a needle to a targeted area for tissue sampling. This method is very helpful when other imaging tests don’t give clear results.
Healthcare professionals use CT scan guided biopsy to get tissue samples from areas that look suspicious. This is a small, non-invasive procedure. Many patients ask, “why CT guided biopsy is done?” It helps figure out if there’s an issue and what kind it is. This information is key for planning the right treatment.
Key Takeaways
- CT guided biopsy is a precise method for tissue sampling.
- It is used when conventional imaging is inconclusive.
- The procedure is minimally invasive.
- CT guided biopsy aids in determining the presence and nature of abnormalities.
- It enables timely and effective treatment planning.
Understanding CT Guided Biopsies

CT-guided biopsies are a key tool in medical diagnostics. They allow for precise targeting of areas of concern. This precision is vital for accurate diagnoses and effective treatment plans.
Definition and Basic Concept
A CT-guided biopsy uses CT scans to guide a needle into the body to collect tissue samples. This method ensures the sample is taken from the right spot. It uses real-time visualization for accuracy.
The idea behind CT-guided biopsies is to use CT scans’ detailed images. These images help doctors precisely locate the area to biopsy. This is true even if the area is deep or hard to reach.
How CT Imaging Works During Biopsies
During a CT-guided biopsy, the patient lies on a CT scanner table. A CT scan is done to find the area of interest. Then, the images guide the biopsy needle to the exact spot.
CT imaging uses X-rays to show detailed body images. For biopsies, this means the needle can be placed exactly. This reduces risks and boosts the chance of getting a good sample.
Difference Between CT Guided and Other Biopsy Methods
CT guided biopsies use CT imaging for guidance, unlike ultrasound-guided biopsies which use sound waves. This makes CT biopsies better for hard-to-reach areas.
CT scans provide more detail than other methods. This makes CT biopsies great for finding small or complex areas. Other methods might not be as precise, leading to less accurate results or needing more tests.
Primary Reasons Why CT Guided Biopsy Is Done
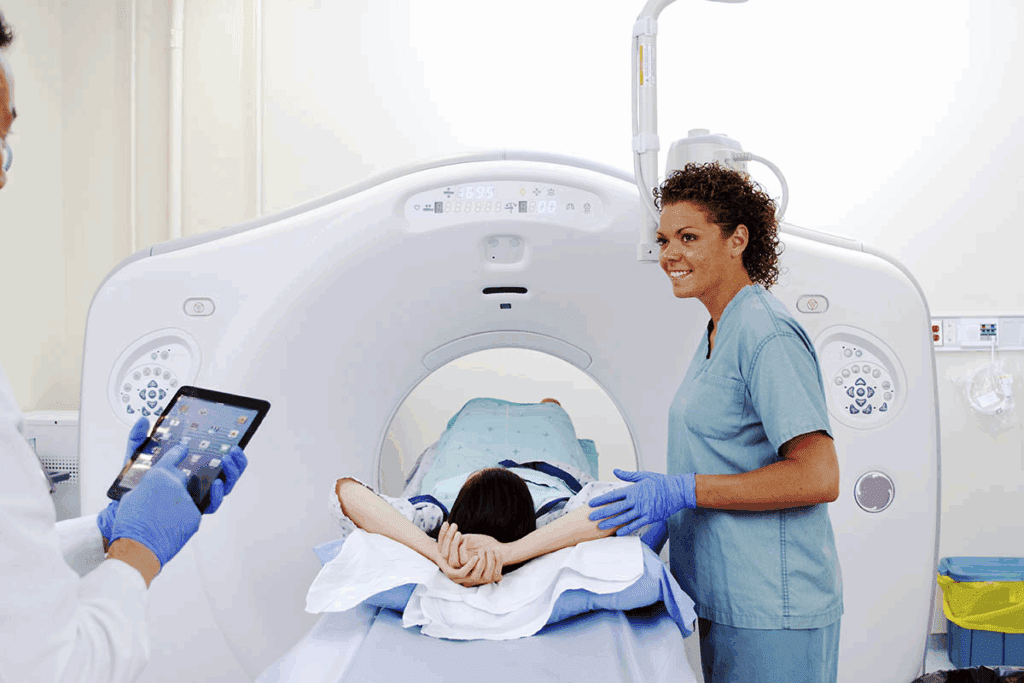
CT guided biopsies are done for many important reasons. They help doctors diagnose and manage health issues. These tests are key when other imaging methods don’t give clear results.
Obtaining Tissue Samples from Suspicious Masses
One main reason for CT guided biopsies is to get tissue samples from suspicious areas. This is vital to know if these areas are cancerous or not. The CT scan’s precision helps get accurate samples, even from hard-to-reach spots.
Key benefits of obtaining tissue samples include:
- Accurate diagnosis of suspicious masses
- Guiding treatment decisions based on the histological characteristics of the sampled tissue
- Reducing the need for more invasive diagnostic procedures
Diagnosing Unexplained Abnormalities
CT guided biopsies are also key for diagnosing unclear abnormalities seen on scans. When scans show something odd but its cause is unknown, a biopsy can help. This is very important for serious issues like tumors.
Medical experts say CT guided biopsies are a reliable way to check unclear abnormalities. This helps start the right treatment quickly.
Confirming or Ruling Out Malignancy
Another big reason for CT guided biopsies is to check if something is cancerous. By looking at the tissue samples, doctors can see if cancer is there and what kind. This info is vital for planning treatment.
The ability to check for cancer with CT guided biopsies is very important. It lets doctors:
- Start the right treatment fast
- Avoid treatments that aren’t needed
- Give patients clear info about their health and future
In summary, CT guided biopsies are very important in today’s medicine. They help get accurate tissue samples, diagnose unclear issues, and check for cancer. These tests are key for making the right treatment plans and helping patients get better.
Precision and Accuracy Advantages
CT guided biopsies are key in today’s medical world. They ensure accurate diagnoses. This is thanks to their high precision.
Targeting Small and Deep Lesions
CT guided biopsies are great at finding small and deep lesions. This is vital when lesions are hard to reach or in sensitive spots.
Doctors use CT imaging to precisely locate the needle. This reduces the chance of errors.
Accessing Hard-to-Reach Areas
CT guided biopsies let doctors reach hard-to-reach areas of the body. CT imaging gives a clear view, helping doctors navigate precisely.
This method avoids harming nearby tissues. It’s a big plus of CT guided biopsies.
Real-Time Visualization Benefits
CT guided biopsies offer real-time visualization. This lets doctors watch and adjust during the procedure.
Real-time imaging boosts the accuracy of the biopsy. It ensures the sample is from the right spot.
In summary, CT guided biopsies are a top choice for doctors. They offer many benefits over other methods.
Common Anatomical Targets for CT Guided Biopsies
CT guided biopsies target various parts of the body. They are key for diagnosing many conditions. These biopsies help get tissue samples from areas that look abnormal.
Lung Biopsies
Lung biopsies are very common. They help find out if lung nodules or masses are cancer. CT guidance makes it easier to hit small spots, lowering the chance of problems.
Liver and Kidney Procedures
CT guided biopsies are also used for the liver and kidneys. Liver biopsies can spot cirrhosis and cancer. Kidney biopsies help find diseases like tumors or inflammation by looking at tissue samples.
Bone and Adrenal Gland Applications
Bone biopsies check for tumors or lesions. CT helps reach hard-to-get bone areas. Adrenal gland biopsies look for tumors, which might not work right.
Other Organ Systems
CT guided biopsies can also target other areas. This includes the pancreas, lymph nodes, and soft tissue. Its wide use makes it a key tool in many medical fields.
| Anatomical Target | Common Conditions Diagnosed |
| Lung | Lung cancer, pulmonary nodules |
| Liver | Liver cirrhosis, liver cancer |
| Kidney | Kidney disease, renal tumors |
| Bone | Bone tumors, metastatic bone disease |
| Adrenal Gland | Adrenal tumors, hyperaldosteronism |
Clinical Scenarios Requiring CT Guided Procedures
CT guided biopsies are key in many medical situations. They provide precise results when other methods fail. This is often the case when a clearer look is needed.
When Conventional Imaging Is Inconclusive
Ultrasound or MRI might not always give a clear picture. CT guided biopsies help by taking precise tissue samples. This is vital when other images don’t show enough.
- Identifying the exact nature of suspicious masses or lesions
- Determining the cause of unexplained abnormalities detected on other imaging tests
- Providing a definitive diagnosis when other methods are inconclusive
Following Abnormal Blood Test Results
Abnormal blood tests hint at health issues that need checking. CT guided biopsies help look into problems with organs like the liver or kidneys. This is when blood tests show something’s off.
Some common scenarios include:
- Elevated liver enzymes that may indicate liver disease
- Abnormal kidney function tests that could suggest kidney disease
- Unexplained changes in blood cell counts that may require bone marrow biopsy
For Treatment Planning in Oncology
In oncology, CT guided biopsies are vital for planning treatments. They give detailed info about tumors. This helps doctors create targeted plans.
The info from CT guided biopsies helps in many ways:
- Determine the stage and grade of cancer
- Identify genetic markers that may influence treatment choices
- Monitor the effectiveness of ongoing treatments
Advantages Over Surgical Biopsies
CT guided biopsies have many benefits over traditional surgical biopsies. They are less invasive, causing less damage and pain to the patient.
Minimally Invasive Nature
CT guided biopsies need smaller cuts than surgical biopsies. This means less scarring and a lower chance of infection.
Reduced Pain and Complications
These biopsies cause less pain and fewer complications than surgical ones. The CT scan helps target the area accurately, reducing harm to nearby tissues.
Shorter Recovery Times
CT guided biopsies also have shorter recovery times. Because they are less invasive, patients can get back to their daily lives faster than after surgery.
Suitability for High-Risk Patients
These biopsies are great for high-risk patients. They are safer than surgery for those with serious health issues because they are less invasive.
| Advantages | CT Guided Biopsies | Surgical Biopsies |
| Invasiveness | Minimally invasive | Invasive |
| Pain and Complications | Reduced pain and fewer complications | More pain and higher risk of complications |
| Recovery Time | Shorter recovery times | Longer recovery times |
The CT Guided Biopsy Procedure: What to Expect
Learning about the CT guided biopsy procedure can ease worries for those about to undergo it. This method is used to get tissue samples from different body parts. It’s a precise way to help doctors diagnose diseases.
Pre-Procedure Preparation
Before the biopsy, patients go through several steps. They might stop taking blood thinners and avoid eating or drinking for a few hours. This helps ensure the procedure goes smoothly.
A CT scan is done first to find the exact spot for the biopsy. This scan helps the doctor plan the best way to get the tissue sample.
Step-by-Step Process
The CT guided biopsy procedure has several important steps:
- The patient lies down on the CT table.
- A CT scan is done to find the target area.
- The skin is cleaned and numbed with local anesthesia.
- A small incision is made, and a needle is inserted under CT guidance.
- Tissue samples are collected and sent for examination.
- The needle is removed, and pressure is applied to stop bleeding.
Post-Procedure Care
After the procedure, patients are watched for a short time to check for any issues. Some might feel a bit of pain or discomfort. This can usually be managed with over-the-counter pain meds.
A follow-up appointment is set to talk about the biopsy results. Recovery is usually quick, and most can go back to their normal activities within a day or two.
| Procedure Stage | Key Activities | Patient Experience |
| Pre-Procedure | Stop certain medications, CT scan for planning | May feel anxious or concerned |
| During Procedure | Local anesthesia, needle insertion under CT guidance | Mild discomfort or pressure |
| Post-Procedure | Monitoring, pain management | Mild pain, short recovery time |
Potential Risks and Complications
It’s important to know the risks of CT guided biopsies before you decide. The procedure is usually safe, but knowing the risks helps everyone stay safe.
Common Minor Side Effects
Most people have minor side effects after a CT guided biopsy. These side effects usually go away on their own. They might include:
- Pain or discomfort at the biopsy site
- Bruising or swelling
- Mild bleeding
Table 1: Common Minor Side Effects
| Side Effect | Frequency | Typical Outcome |
| Pain or discomfort | Common | Resolves with pain management |
| Bruising or swelling | Common | Resolves on its own |
| Mild bleeding | Occasional | Usually stops spontaneously |
Rare but Serious Complications
Even though they’re rare, serious complications can happen. These might include:
- Infection
- Significant bleeding needing a blood transfusion
- Pneumothorax (collapsed lung) in lung biopsies
Risk Factors That May Increase Complications
Some factors can make complications more likely during or after a CT guided biopsy. These include:
- Patient’s overall health and any other health issues
- Medications that affect bleeding, like anticoagulants
- The location and type of the lesion being biopsied
- They carefully choose who to do the biopsy on
- They use the latest imaging tech for precise guidance
- They follow strict clean technique to avoid infection
- They watch the patient closely during and after the procedure
By knowing these risks and taking steps to prevent them, doctors can make sure CT guided biopsies are done safely and well.
Conclusion: The Vital Role of CT Guided Biopsies in Modern Medicine
CT guided biopsies have changed how we diagnose diseases. They are precise and don’t hurt much. This makes it easier for doctors to find and treat problems early.
These biopsies are great because they can reach small and deep spots. They also show what’s happening in real time. This means less pain, quicker healing, and better results for patients.
In short, CT guided biopsies are key in today’s medicine. They help doctors find and treat diseases accurately. Their ability to be precise and reach hard spots makes them essential for better patient care.
FAQ
What is a CT guided biopsy?
A CT guided biopsy uses CT imaging to guide a needle into a body area. It collects tissue samples for diagnosis.
Why is a CT guided biopsy performed?
A CT guided biopsy is done to get tissue samples from suspicious areas. It helps diagnose and confirm cancer.
How does CT imaging work during a biopsy?
During a CT guided biopsy, CT imaging shows the needle’s path in real-time. This ensures accurate sampling.
What are the advantages of CT guided biopsies over surgical biopsies?
CT guided biopsies are less invasive. They cause less pain and have shorter recovery times than surgery.
What are the common anatomical targets for CT guided biopsies?
Common targets include the lungs, liver, kidneys, bones, and adrenal glands. These are among the body’s organs.
What are the possible risks and complications of CT guided biopsies?
Risks include minor side effects like pain and bleeding. Serious complications like infection and tissue damage are rare but possible.
How is a CT guided biopsy procedure performed?
The procedure starts with preparation. It involves needle placement guided by CT imaging. Post-procedure care monitors for complications.
What can I expect during a CT guided biopsy?
You’ll be positioned on a CT table and receive local anesthesia. A needle will be guided into the target area under CT imaging.
Are CT guided biopsies suitable for all patients?
Most patients can undergo CT guided biopsies. But, those with certain conditions or high risk may not be recommended.
How do physicians minimize risks during CT guided biopsies?
Physicians evaluate patient risks and use precise imaging. They take steps to prevent complications.
What is the role of CT guided biopsy in oncology treatment planning?
CT guided biopsy is key in oncology. It provides accurate diagnosis and tissue sampling. This informs treatment plans.
Can CT guided biopsies be used for diagnosing conditions other than cancer?
Yes, CT guided biopsies can diagnose conditions like infections and inflammatory diseases. They obtain tissue samples for examination.
Reference
- Johansen, K. B. (2025). Diagnostic yield and complications of CT-guided biopsy in lung lesions. PMC, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11926819/