A 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) is a key tool for checking heart health worldwide. It’s a non-invasive test that looks at the heart’s electrical activity from different sides. This gives us detailed information for making accurate diagnoses.
At Liv Hospital, we focus on our patients and use the latest ECG technology. This helps doctors spot heart problems fast and right. By looking at the heart’s electrical activity from 12 angles, we can find issues like arrhythmias and heart attacks.
Our ECG study is a big part of heart care. It lets doctors make smart choices about how to treat patients. The 12-lead ECG gives us deep insights into how the heart works. It’s a key part of diagnosing heart problems.
At the heart of modern cardiology is the 12 lead cardiogram technology. It gives us deep insights into how the heart works. An electrocardiogram (ECG) tracks the heart’s electrical signals, showing us its health. Discover how a 12 lead cardiogram helps diagnose heart conditions and what your test results mean.
Every heartbeat sends an electrical wave through the heart. This wave makes the heart muscle contract and pump blood. The 12 lead ECG captures this electrical activity from 12 angles, giving us a full picture of the heart’s signals.
The 12 lead electrocardiogram is a non-invasive test that tracks the heart’s electrical activity over time. It’s key in diagnosing heart issues like arrhythmias, coronary artery disease, and heart valve problems.
This test is vital in medical practice. It gives us instant and important info about the heart’s electrical signals. This info helps doctors diagnose and treat heart conditions well.
ECG technology has grown a lot over the years. From simple single-lead ECGs to today’s 12 lead systems, it’s become much better. Now, ECG machines are digital, with features like automated readings and record storage.
Improvements in electrode design, lead placement, and signal processing have also helped. These changes make diagnoses more accurate.
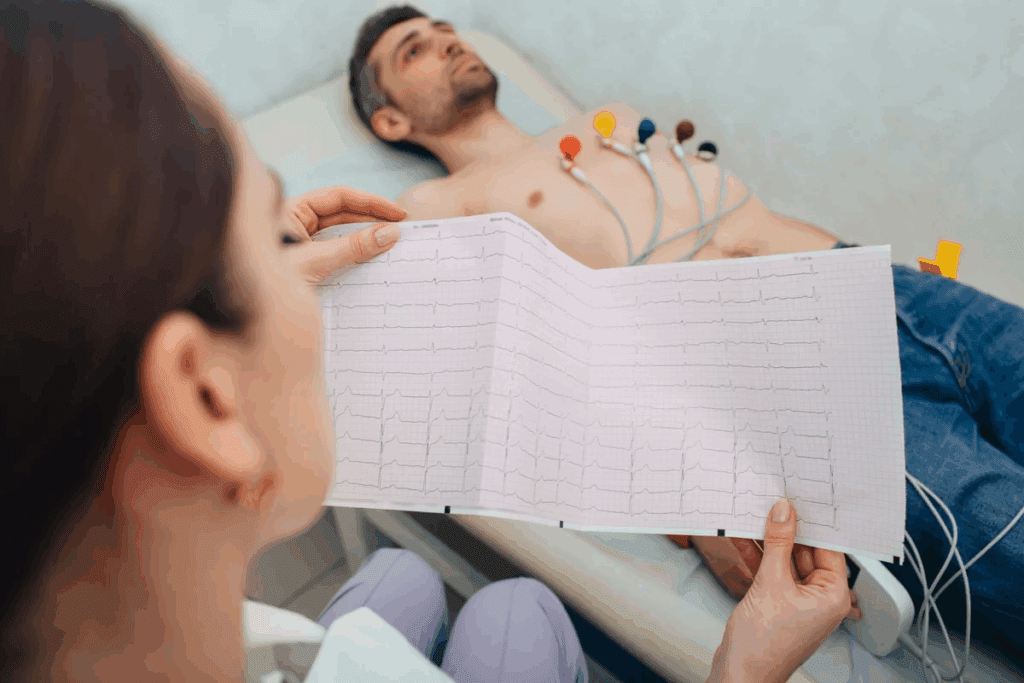
To diagnose heart conditions well, knowing how a 12 lead ECG works is key. It uses electrodes on the chest, arms, and legs to show the heart’s electrical activity. This gives a full view of the heart’s function.
A 12 lead ECG looks at the heart from twelve angles. These angles are split into limb leads and precordial leads. Each angle gives a special view of the heart’s electrical signals.
By looking at all twelve angles, doctors can understand the heart better. They can spot any problems.
Where you put the electrodes is very important for good ECG readings. The electrodes are placed on the chest, arms, and legs. This lets them capture the heart’s electrical signals from the right angles.
Getting the lead setup right is key for accurate ECG readings. This means paying close attention to where the electrodes are placed and how they connect to the ECG machine.
Key Considerations for Electrode Placement:
Understanding the anatomy and setup of a 12 lead ECG helps doctors use it well. They can then check the heart’s function and find any heart problems.
The 12-lead cardiogram is a key tool for checking the heart’s electrical activity. It looks at the heart from different angles. This helps doctors find and understand heart problems.
The heart’s electrical system controls its rhythm. It has parts like the SA node and AV node. These parts send out electrical signals that make the heart beat.
The ECG machine records these electrical signals. It turns them into graphs that show the heart’s activity.
Key components of the ECG waveform include:
Doctors use these graphs to spot heart issues like arrhythmias and ischemia.
Understanding the parts of an ECG waveform is key for doctors to spot heart problems. The electrocardiogram (ECG) is a vital tool that shows the heart’s electrical activity. It does this through different waveforms.
The ECG waveform has several important parts: the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave. Each part shows a different part of the heart’s electrical activity.
Looking at these parts is key to understanding the heart’s rhythm and spotting problems. For example, odd P waves can mean the upper chambers are too big or have issues.
Knowing the normal ECG waveform parameters is important for spotting heart issues. The normal size and time of P waves, QRS complexes, and T waves can vary. But big changes often mean there’s a heart problem.
| ECG Component | Normal Parameters | Common Variations |
| P Wave | Duration | Prolonged or inverted P waves may indicate atrial enlargement or abnormal rhythms. |
| QRS Complex | Duration | Prolonged QRS duration can signify ventricular conduction delays or bundle branch blocks. |
| T Wave | Generally upright in leads I, II, and V4-V6 | Inverted or flattened T waves can indicate ischemia or ventricular hypertrophy. |
By closely looking at these parts and their changes, doctors can make accurate diagnoses. They can then create the right treatment plans for patients with heart conditions.
The 12-lead ECG is key for spotting arrhythmias and seeing how they affect the heart. It gives a full view of the heart’s electrical activity. This helps doctors pinpoint arrhythmias accurately.
Arrhythmias are irregular heartbeats caused by many things like heart disease or medicines. The 12-lead ECG is great for finding arrhythmias. It looks at the heart’s electrical activity from different sides, giving a clearer picture of the rhythm.
There are several arrhythmia patterns seen on a 12-lead ECG, including:
These arrhythmias can be serious. Accurate diagnosis with the 12-lead ECG is key for treatment.
Critical rhythm problems need quick diagnosis and treatment. The 12-lead ECG is essential for spotting these by showing specific signs, like:
Spotting these signs is vital for doctors to manage serious arrhythmias well.
Using a 12 lead ECG is key in spotting acute coronary syndromes. These include ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), and unstable angina. This info is vital for patient care.
STEMI happens when a coronary artery is completely blocked. This shows up as ST-segment elevation on the ECG. We look for ST elevation over 1 mm in two or more leads.
The leads tell us where the heart is hurt. For example, ST elevation in leads II, III, and aVF points to an inferior wall STEMI. Leads V2-V4 suggest an anterior wall STEMI.
Locating STEMI is key for quick treatment. The 12 lead ECG helps pinpoint the damage and how big it is.
NSTEMI and unstable angina don’t show ST-elevation. Instead, they might have ST-segment depression, T-wave inversion, or no changes. We watch for ST segment or T wave changes over time, showing ischemia.
In unstable angina, the ECG might show brief ST-segment changes or T-wave inversion during pain. NSTEMI is marked by cardiac biomarkers showing heart muscle damage.
The 12 lead ECG is vital for diagnosing and treating acute coronary syndromes. It helps spot signs of heart trouble, find where it is, and guide treatment.
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is key in spotting chamber hypertrophy. It shows how the heart’s electrical activity and muscle thickness are doing. We use the 12 lead ECG to find signs of abnormal heart muscle thickness.
The 12 lead ECG spots left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) and right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH). It does this by looking at specific changes in the ECG waveform.
Atrial enlargement can also be seen on a 12 lead ECG.
The 12 lead ECG is a great tool for diagnosing chamber hypertrophy. It gives us important info that helps with treatment and management.
Spotting myocardial ischemia early is key to avoiding heart problems. The 12 lead ECG is a big help in this fight. It looks for specific changes in the ECG waveform to spot ischemia.
The ST segment and T wave are key parts of the ECG. ST segment depression or elevation can hint at ischemia. T wave inversion or flattening also points to possible ischemic changes. We check these parts closely for signs of ischemia.
ST segment changes can show different levels of ischemia. For example, downsloping ST segment depression often means more serious ischemia.
Regional ischemic patterns on a 12 lead ECG give us clues about where and how bad the ischemia is. We look at the ECG leads to spot patterns that show ischemia in different heart areas.
ST segment elevation in leads II, III, and aVF points to ischemia in the inferior wall. ST segment depression in leads V1-V4 suggests ischemia in the anterior wall. Spotting these patterns is key for quick diagnosis and treatment.
By looking at ST segment and T wave changes and regional patterns, we can accurately find myocardial ischemia with a 12 lead ECG. This info is essential for more tests and treatment plans.
The 12 lead ECG is key in diagnosing heart problems. It needs to be read correctly and quickly. This is very important in emergencies where fast decisions are needed.
Emergency Evaluation Protocols for Chest Pain
In emergency rooms, doctors quickly check patients with chest pain using a 12 lead ECG. They should do this within 10 minutes of the patient arriving. This test is vital for spotting heart attacks.
The American Heart Association says the ECG is very important for diagnosing heart attacks.
“The ECG is the first step in the diagnosis of MI and should be performed and interpreted promptly.”
Time-Critical Pathways for Acute Cardiac Events
For heart attacks like STEMI, quick action is essential. Guidelines suggest a fast process. This includes quick ECG checks, calling the heart team, and fast treatments.
We stick to these rules to give our patients the best care. This means:
Following these steps helps us improve care for heart attack patients.
Advanced ECG analysis technologies have changed cardiology a lot. They make diagnosing better and faster. These tools help doctors understand ECGs more clearly, leading to better care.
Computer systems are now key in ECG analysis. They use smart algorithms to spot patterns and problems in ECGs. This makes it easier for doctors to quickly review complex ECGs.
These systems are great because they’re always consistent and accurate. Unlike doctors, who can vary, these systems apply the same rules to every ECG. This ensures top-notch results every time.
Third-party ECG services are a big help in busy hospitals. They have cardiologists who focus on ECGs, helping doctors keep up with the demand.
These services do more than just help doctors. They make sure ECGs are checked fast and right, even when doctors are really busy.
| Feature | Computer-Assisted Interpretation | Third-Party ECG Reporting Services |
| Expertise | Algorithm-based analysis | Human expertise by cardiologists |
| Turnaround Time | Immediate analysis | Varies, typically within hours |
| Accuracy | High consistency, possible errors | High accuracy, depends on the doctor |
Using both computer systems and third-party services is key. It makes ECG analysis better, faster, and more reliable. This leads to better care for patients.
The 12 lead ECG is key in modern cardiology. It gives a full view of how the heart works. We use it to spot heart problems like arrhythmias and acute coronary syndromes. It helps us decide on the best treatment.
Healthcare pros look at the 12-lead ecg to catch small changes in the heart. This lets them act fast and help patients get better sooner. The ecg tells us a lot about the heart’s electrical activity. This helps doctors treat patients quickly and well.
The 12 lead ECG has been a mainstay in cardiology for years. Its value comes from giving us lots of info about the heart. This makes it a vital tool for diagnosing and managing heart issues.
A 12 lead cardiogram, or 12-lead ECG, is a tool that checks the heart’s electrical activity. It looks at the heart from 12 different angles. This gives doctors a full picture of the heart’s health.
The 12 lead ECG helps find many heart problems. It can spot issues like arrhythmia, heart attack, and heart failure. It’s a key tool for diagnosing heart conditions.
Setting up a 12 lead ECG is important. Electrodes are placed on the chest and limbs. This lets doctors see how the heart’s lower and upper chambers work.
The ECG machine captures the heart’s electrical signals. It shows heart rate, rhythm, and any problems. Doctors use this info to diagnose heart issues.
Understanding ECG waveforms is key for diagnosing heart problems. Each part of the waveform tells doctors about different heart functions.
Yes, the 12 lead ECG is great for finding arrhythmias. It helps doctors decide on the right treatment. It can spot many arrhythmia patterns.
The 12 lead ECG is vital for spotting heart attacks. It can tell if it’s a STEMI or NSTEMI. This helps doctors act fast to treat it.
The 12 lead ECG shows a lot about the heart’s structure and function. It can spot hypertrophy and ischemia. This helps doctors understand the heart’s condition better.
Yes, there are new tools for ECG analysis. Computer systems and third-party services help improve diagnosis. They make ECGs more accurate and efficient.
There are rules for reading ECGs, like for chest pain. Quick and correct readings are key for good patient care.
ECG technology has grown a lot. It’s now a key part of heart care. The 12 lead ECG is a main tool in cardiology today.
The 12 lead ECG is very important for finding ischemia. It helps prevent heart problems. It shows important patterns that guide treatment.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2025). How Does a 12 Lead Cardiogram Diagnose Heart. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482520/
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!
WhatsApp us