Ultrasound technology is key in finding cancers early. A recent study showed ultrasound can spot cancerous tumors very accurately. This change is big for cancer care and helps answer an important question ” can you see cancer in the abdomen with ultrasound?
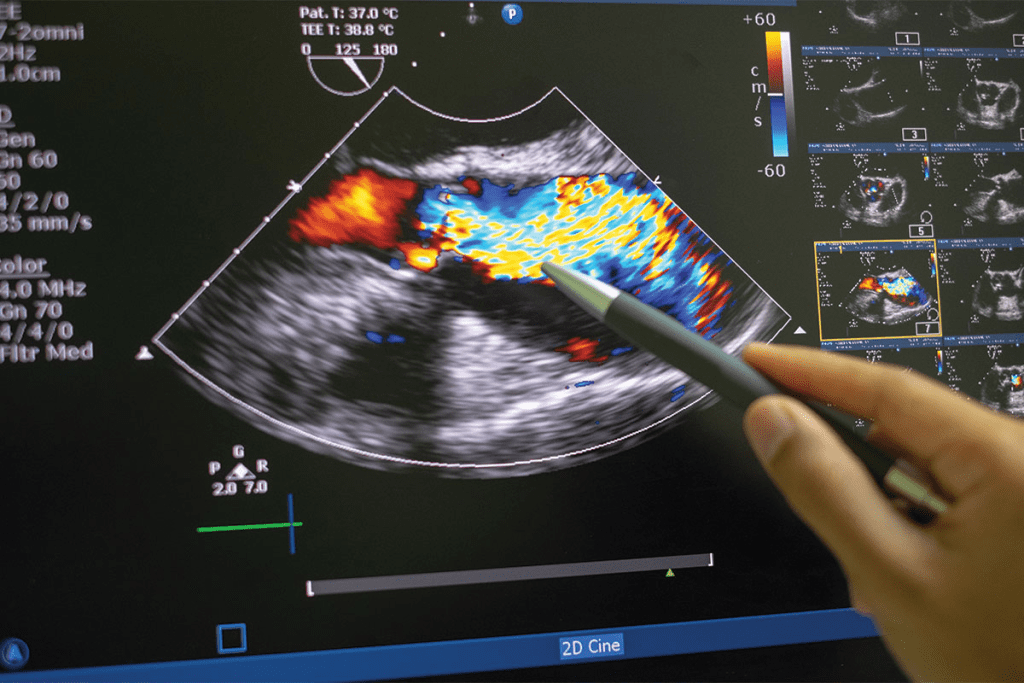
Ultrasound is great for finding tumors without surgery. The colors on ultrasound pictures, like red and blue, are often not understood. These colors show blood flow direction, which helps figure out if a tumor is cancerous.
It’s important to know what these colors mean and how ultrasound works. As we explore ultrasound’s role in finding cancer, it’s clear it’s a game-changer. It helps catch cancer early, which can save lives.
Key Takeaways
- Ultrasound technology is increasingly used for detecting various types of cancers.
- The colors on an ultrasound image indicate blood flow direction.
- Early detection of cancer significantly improves treatment outcomes.
- Understanding ultrasound images is critical for accurate diagnosis.
- Ultrasound offers a non-invasive method for cancer detection.
Understanding Ultrasound Imaging Technology
Ultrasound technology is key in modern medicine. It gives valuable insights without needing invasive procedures. This tool is vital in healthcare, helping doctors see inside the body and track health issues.
How Ultrasound Works
Ultrasound imaging uses high-frequency sound waves to see inside the body. A device called a transducer sends these sound waves and catches the echoes from inside. These echoes turn into electrical signals, creating images on a screen in real-time.
Different tissues reflect sound waves in different ways. For example, fluid-filled areas look dark because sound waves pass through easily. Denser tissues like bone reflect more sound and look brighter.
Types of Ultrasound Techniques
There are many ultrasound techniques, each for different uses:
- B-mode Ultrasound: The most common, showing two-dimensional images of inside structures.
- Doppler Ultrasound: Helps check blood flow and find vascular problems.
- 3D and 4D Ultrasound: These advanced methods show three-dimensional images and moving video.
Limitations of Ultrasound Technology
Ultrasound is a great tool, but it has limits. Image quality depends on the operator’s skill and the patient’s body type. It’s hard for ultrasound to go through bone or gas-filled areas, making some structures hard to see. It also might not work as well in people with a higher BMI.
Knowing these limits helps doctors understand ultrasound images better. This is key for making the right decisions about further tests or treatments.
Interpreting Colors on Ultrasound Images
Colors on ultrasound images are key in medical diagnosis. Ultrasound technology now shows not just what’s inside but also how things work. This is thanks to color imaging.
Grayscale Ultrasound: The Basic View
Grayscale ultrasound is the basic ultrasound view. It shows different shades of gray based on echo intensity. This helps doctors see structures and find problems.
But, it doesn’t show blood flow. This is important for checking blood vessel health and tumor activity.
Color Doppler: What Red and Blue Actually Represent
Color Doppler adds blood flow info to the grayscale image. Red means blood is moving towards the transducer, and blue means it’s moving away. This helps doctors check blood vessel health and tumor blood supply.
The color’s brightness shows how fast the blood is moving. Brighter colors mean faster blood flow. This is useful for spotting problems like stenosis or vascular malformations.
Power Doppler and Other Color Variations
Power Doppler is great for finding slow blood flow in small vessels or tumors. It doesn’t show flow direction like regular color Doppler does. It just shows there’s flow.
Other variations, like directional power Doppler, add flow direction to power Doppler’s sensitivity. These advanced methods help doctors understand blood vessel health better.
Can You See Cancer in the Abdomen with Ultrasound?
Ultrasound imaging is key in finding and diagnosing abdominal cancers early. It uses sound waves to show the inside of organs. Doctors can spot problems and tumors with this method.
Abdominal Ultrasound Capabilities
Ultrasound is great for looking at organs in the belly. It checks the liver, pancreas, kidneys, and spleen. It’s fast, doesn’t hurt, and doesn’t use harmful radiation.
Types of Abdominal Cancers Detectable by Ultrasound
Ultrasound can spot some cancers in the belly, like:
- Liver cancer: It finds liver tumors and checks the liver’s shape.
- Pancreatic cancer: It can see big pancreatic tumors, but it’s hard.
- Kidney cancer: It’s good for finding kidney masses and cysts.
But, how well it works depends on the tumor’s size, where it is, and the ultrasound expert.
Limitations in Abdominal Cancer Detection
Ultrasound has its limits in finding cancers. These include:
- It needs a skilled person to get good images and make accurate diagnoses.
- Things like being overweight or having gas in the bowels can mess up the images.
- Small or hidden tumors are hard to see with ultrasound.
Knowing these limits helps understand what ultrasound results mean. It also tells us when we need more tests.
Characteristics of Cancer on Ultrasound Images
Ultrasound imaging is key in finding cancer. It shows specific signs of bad tumors. Techniques like Color Doppler help tell good from bad tumors by looking at blood flow.
Common Visual Features of Malignant Tumors
Malignant tumors show certain signs on ultrasound. These include irregular shapes, heterogeneous echotexture, and ill-defined borders. Seeing these signs means more tests are needed.
The size and location of tumors also matter. Big tumors or those in certain spots might be cancerous.
Benign vs. Malignant: Differentiating Features
Telling benign from malignant tumors is key for right treatment. Benign tumors have well-defined borders and uniform echotexture. Malignant ones look irregular and heterogeneous.
- Benign tumors have clear boundaries.
- Malignant tumors show invasive traits.
The Role of Blood Flow Patterns in Cancer Diagnosis
Blood flow patterns seen with Color Doppler ultrasound are vital in cancer diagnosis. Malignant tumors show increased vascularity and abnormal blood flow patterns. This shows their aggressive nature.
Using advanced ultrasound like Power Doppler helps see blood flow better. This helps tell if a tumor is benign or malignant.
Does Red and Blue on Ultrasound Mean Cancer?
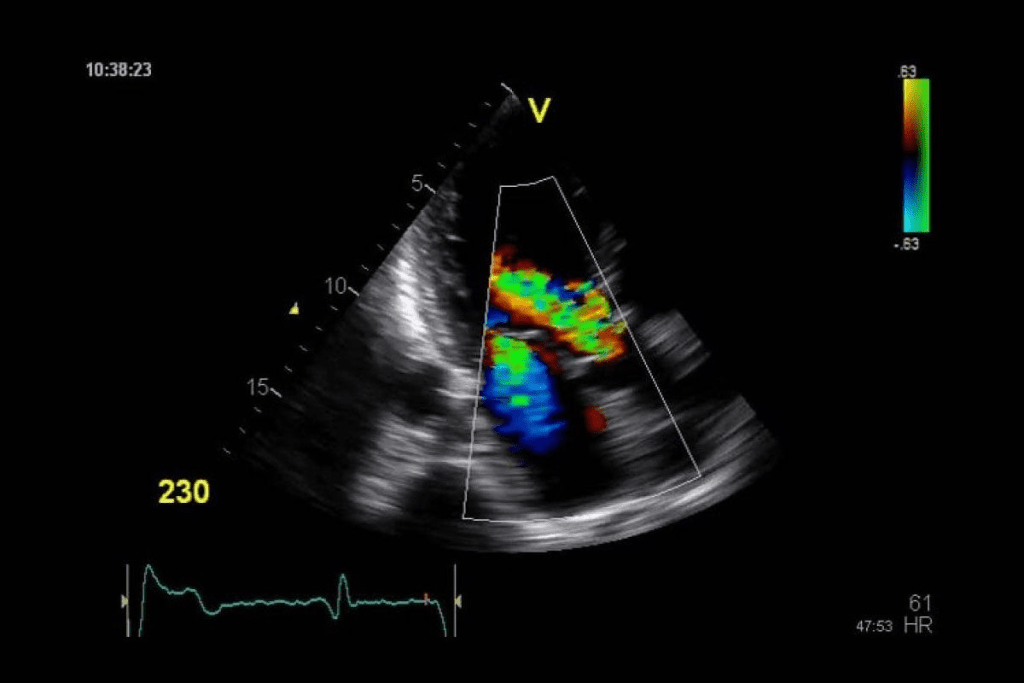
Red and blue colors on ultrasound images show blood flow. They don’t directly mean cancer. Instead, they show the blood flow’s direction and speed in the body’s vessels.
Understanding Doppler Flow Signals
Doppler ultrasound technology uses Doppler shift to check blood flow. Sound waves change frequency when they hit moving blood cells. This change is shown as colors on the ultrasound: red for flow towards the transducer, and blue for flow away.
Doppler flow signals help check vascular conditions. Doctors use these signals to find blood flow problems. This can help spot issues like cancer.
Tumor Vascularity and Blood Flow Patterns
Tumors grow and spread by getting a blood supply. Tumor vascularity is when new blood vessels form in a tumor. Doppler ultrasound can spot these vessels and check their blood flow.
Malignant tumors have special blood flow patterns. They have more blood vessels and irregular shapes. Doctors can learn about the tumor by looking at these patterns.
When Red and Blue Patterns May Indicate Malignancy
Red and blue on an ultrasound don’t always mean cancer. But, some Doppler flow signal traits can hint at cancer. For example, fast or chaotic blood flow in a tumor might suggest cancer.
| Characteristics | Benign Tumors | Malignant Tumors |
| Vascularity | Less vascular or peripheral vascularity | Highly vascular with irregular vessels |
| Blood Flow Pattern | Normal or slightly altered flow | High-velocity or chaotic flow |
| Doppler Signals | Typically uniform | Often irregular or turbulent |
Knowing these patterns is key for accurate diagnosis and treatment. Ultrasound is a helpful tool, but it’s often used with other tests to confirm cancer.
Ultrasound Detection of Specific Cancer Types
Ultrasound technology has gotten better at finding different cancers. This helps patients get better care. It’s now a key tool for spotting and diagnosing many cancers.
Liver Cancer on Ultrasound
Liver cancer, or hepatocellular carcinoma, can be found with ultrasound. It shows up as a darker or lighter spot. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound makes these spots easier to see.
Ovarian Cancer Ultrasound Findings
Ovarian cancer is spotted with ultrasound by looking for certain signs. Color Doppler ultrasound checks blood flow. This helps tell if a tumor is cancerous or not.
Detecting Lymph Node Involvement
Ultrasound checks lymph nodes for cancer signs. Big or odd-looking nodes might mean cancer has spread. Ultrasound-guided biopsies can confirm this.
Colon and Stomach Cancer Visualization
Ultrasound isn’t the main way to find colon and stomach cancers. But it can spot cancer spread or metastasis. Endoscopic ultrasound is better for looking at the stomach and intestines.
Knowing how ultrasound shows different cancers helps doctors make better diagnoses. This leads to more effective treatments.
Accuracy and Limitations of Ultrasound in Cancer Diagnosis
It’s important to know how accurate ultrasound is for cancer diagnosis. This technology helps doctors find and diagnose cancers. But, its success depends on several things.
Sensitivity and Specificity Rates
The success of ultrasound in finding cancer changes with the type and location of the cancer. Sensitivity is how well it finds people with the disease. Specificity is how well it finds people without the disease. Ultrasound works well for some cancers, like liver cancer, but not as well for others.
Factors Affecting Ultrasound Accuracy
Many things can change how well ultrasound works for cancer diagnosis. These include:
- The skill and experience of the person doing the ultrasound
- The size, location, and depth of the tumor
- The quality of the ultrasound machine
- Things about the patient, like their body shape and any gas or other things that might get in the way
The person doing the ultrasound is very important. They affect how good the images are and how well they can be understood.
When Ultrasound Misses Cancer
Ultrasound might not find cancer sometimes. This can happen if the tumor is small or hard to see, like deep inside the body or near the lungs. Also, some cancers are hard to tell apart from normal tissue with ultrasound alone.
Knowing these limits helps doctors decide when to use other tests or imaging methods.
Comparing Ultrasound to Other Imaging Methods for Cancer Detection
Many imaging methods are used to find cancer, each with its own benefits and drawbacks. Ultrasound is popular because it’s non-invasive and shows images in real-time. It’s important to compare ultrasound with other methods to see how well it works for finding cancer.
Ultrasound vs. CT Scan
CT scans give detailed images and can spot cancers early. They show internal organs, bones, soft tissue, and blood vessels clearly. But, CT scans use radiation and might not be safe for everyone, like pregnant women. Ultrasound is safer and can be used more often without radiation risks.
Key differences: CT scans have higher resolution images, while ultrasound is non-invasive and doesn’t use radiation.
Ultrasound vs. MRI
MRI gives detailed images of the body’s internal structures. It’s great for soft tissue imaging and can find cancers that ultrasound or CT scans might miss. But, MRI is more expensive and takes longer than ultrasound. Some people might feel claustrophobic or have metal implants that make MRI not possible.
Considerations: MRI is better for soft tissue imaging but is pricier and less accessible than ultrasound.
Ultrasound vs. PET Scan
PET scans show how tissues are working, which helps find cancerous tissues. They can also show how cancer has spread and if treatment is working. PET scans give functional information, but they don’t show anatomy as well as ultrasound, CT, or MRI. Using PET with CT (PET-CT) can give both functional and anatomical details.
Advantages: PET scans provide metabolic information, while ultrasound offers real-time anatomical imaging.
Choosing the Right Imaging Method
Choosing an imaging method depends on the cancer type, patient health, and clinical situation. For example, ultrasound is often first used for liver or thyroid cancers because it’s safe and easy to use. MRI might be better for soft tissue tumors, and CT scans for a wider view of internal organs.
Decision-making: The right imaging method depends on the clinical situation, patient factors, and the cancer’s characteristics.
When Is Ultrasound Most Appropriate for Cancer Screening?
Ultrasound technology is key in finding and managing cancer early. It’s safe and works well for checking different parts of the body. It doesn’t use harmful radiation, making it a good first choice for many cancers.
First-Line Screening Applications
Ultrasound is often the first choice for screening. It’s safe and doesn’t use radiation, so it can be used many times without harm. This is great for checking organs like the liver, gallbladder, kidneys, and reproductive organs.
For example, ultrasound can spot liver cancer and check the liver’s shape. It also helps with thyroid nodules, figuring out if they’re solid or fluid and what to do next.
Monitoring Known Tumors
After finding a tumor, ultrasound helps track its size and type over time. This is key in seeing how well treatments like chemotherapy or radiation are working. For liver or kidney tumors, ultrasound shows if the tumor is getting smaller or growing.
Being able to do ultrasound tests often is helpful. It lets doctors keep an eye on tumors closely and change treatment plans if needed.
Special Populations and Considerations
Some groups really benefit from ultrasound for cancer screening. Pregnant women, for example, use ultrasound to check on the baby or look for health issues in the mom. It’s safe for the baby and gives important info without radiation.
Ultrasound is also good for people who can’t have other tests because of health issues. For example, those with severe kidney disease might not be able to have MRI with contrast.
Comparison of Ultrasound Applications in Different Cancer Types
| Cancer Type | Ultrasound Utility | Limitations |
| Liver Cancer | Highly effective for detecting and monitoring liver tumors | May not detect very small tumors or those deep within the liver |
| Ovarian Cancer | Useful for evaluating ovarian morphology and detecting masses | May not differentiate between benign and malignant masses |
| Thyroid Cancer | Effective in assessing thyroid nodules and guiding fine-needle aspiration | Limited in evaluating the extent of disease or lymph node involvement |
The Ultrasound Procedure for Cancer Detection
Cancer detection often uses an ultrasound procedure. This method is non-invasive and helps see inside the body. Knowing how to prepare for it can make it more effective.
Preparing for an Ultrasound
Getting ready for an ultrasound is simple. You might need to fast before it, if it’s for your abdomen. Wear comfy clothes that let you move easily.
Drinking water might be asked of you. This helps get clearer images. Pre-procedure instructions can change based on the ultrasound type and area. Always follow what your healthcare provider says.
What to Expect During the Procedure
A sonographer will put gel on your skin during the ultrasound. This gel helps sound waves work better. They’ll then use an ultrasound probe to take pictures that show on a screen.
The process is painless and non-invasive. You might feel some pressure. It usually takes 30 minutes to an hour.
Types of Ultrasound Probes and Their Uses
There are many ultrasound probes, each for different uses. Here are a few:
- Linear probes: Good for the surface and give clear images.
- Curvilinear probes: Great for wider views, often used for the belly.
- Endocavitary probes: For looking inside organs like the prostate or uterus.
Knowing about the probe used can help you understand the procedure better.
Advanced Ultrasound Technologies in Cancer Detection
Advanced ultrasound technologies are changing how we find and diagnose cancer. These new tools make ultrasound better for spotting cancer. It’s now a key part of cancer care.
New ultrasound methods are making cancer detection more accurate. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound, elastography, and 3D/4D ultrasound are leading the way.
Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) uses special agents to see blood flow better. It’s great for looking at liver lesions and tumor blood vessels. This is key for cancer diagnosis.
CEUS helps spot and understand cancerous lesions. It gives doctors real-time images without harmful radiation. This makes it a valuable tool for cancer diagnosis.
Elastography: Measuring Tissue Stiffness
Elastography checks how stiff tissues are, which can show if they’re cancerous. Stiffer tissues often mean cancer. It helps tell if a lesion is benign or malignant.
This method is useful for checking thyroid nodules, liver fibrosis, and breast lesions. Elastography adds to ultrasound’s ability to find cancer by showing tissue stiffness.
3D and 4D Ultrasound Applications
3D and 4D ultrasound give clearer images than 2D ultrasound. 3D makes a 3D image from 2D ones. 4D adds time, showing real-time 3D images.
These technologies help with complex body structures. They help find and understand tumors better. This is important for planning treatments.
In summary, new ultrasound technologies like CEUS, elastography, and 3D/4D ultrasound are boosting ultrasound’s role in cancer detection. They improve accuracy and give doctors more detailed info for treatment plans.
When to Seek Further Testing After an Ultrasound
Ultrasound results that are unclear or suspicious need more testing. If an ultrasound doesn’t give a clear answer, it’s important to know what to do next. This helps figure out the cause of the problem.
Understanding Inconclusive Results
Inconclusive ultrasound results happen when images don’t give enough info for a clear diagnosis. This can be due to:
- The area of concern is not clearly visible due to the patient’s body type or the location of the issue.
- The technology or technique used may not be sufficient to capture the necessary details.
- The presence of other medical conditions that complicate the interpretation of the ultrasound images.
It’s essential to remain calm and follow your doctor’s recommendations for further testing or evaluation.
Follow-up Procedures After Suspicious Findings
When an ultrasound shows suspicious findings, more tests are needed to confirm the diagnosis. Some common next steps include:
- Additional Imaging Tests: Such as CT scans, MRI, or PET scans to provide more detailed images.
- Blood Tests: To check for tumor markers or other indicators of disease.
- Biopsy: To collect tissue samples for pathological examination.
The choice of follow-up procedure depends on the initial findings and the patient’s overall health condition.
The Role of Biopsy in Confirming Diagnosis
A biopsy is often the key test when other tests are unclear. It involves taking a tissue sample from the suspicious area for detailed examination under a microscope.
The biopsy results can confirm whether a tumor is benign or malignant. They also provide information on the type of cancer. This is vital for choosing the right treatment plan.
In conclusion, while an ultrasound is a valuable tool, unclear or suspicious results need more investigation. Knowing the next steps and the role of additional tests, including biopsy, is key. This helps get an accurate diagnosis and develop an effective treatment plan.
Conclusion: The Role of Ultrasound in Cancer Management
Ultrasound is key in fighting cancer, from finding tumors to tracking treatment. It’s safe and shows images in real-time. This makes it a powerful tool in the battle against cancer.
Ultrasound does many things in cancer care. It helps find tumors, guides biopsies, and checks how well treatments work. New ultrasound tech, like contrast-enhanced ultrasound and elastography, makes it even better.
As tech gets better, ultrasound’s role in cancer care will grow. It’s cheap and doesn’t use radiation. This makes it a great choice for both patients and doctors.
Knowing how ultrasound helps in cancer care helps patients make better choices. It lets doctors find tumors more accurately and plan treatments well.
FAQ
Can you see cancer in the abdomen with ultrasound?
Yes, ultrasound can spot cancers in the belly, like liver, ovarian, and stomach cancers. But, it works best when the cancer is not too advanced.
Does red and blue on ultrasound mean cancer?
Red and blue on an ultrasound indicate blood flow direction; they do not directly signify cancer. But, some patterns might hint at it.
Can ultrasound detect cancer?
Yes, ultrasound is great for finding cancers. It can spot tumors and check their size, location, and blood flow. This helps tell if it’s cancerous.
What does a cancerous tumor look like on an ultrasound?
Cancerous tumors look like irregular shapes on ultrasound. They might have different brightness levels. Color Doppler can show their blood flow patterns.
Can ultrasounds detect tumors in the abdomen?
Yes, ultrasounds can find tumors in the belly, like in the liver, pancreas, and ovaries. How well it finds them depends on the tumor’s size, where it is, and the skill of the person doing the ultrasound.
What is the difference between grayscale and Color Doppler ultrasound?
Grayscale ultrasound shows basic images in gray. Color Doppler adds color to show blood flow. This helps spot blood vessels and patterns.
How accurate is ultrasound in diagnosing cancer?
Ultrasound’s accuracy in finding cancer varies. It depends on the cancer type, where it is, and the person doing the ultrasound. It’s a good starting point but might not always be enough.
Can ultrasound detect colon cancer?
Ultrasound can sometimes see parts of the colon. But, it’s not the best way to find colon cancer. Colonoscopy is more effective for this.
What does liver cancer look like on ultrasound?
Liver cancer might look like a mass or nodule on ultrasound. It might be brighter or have a “target” shape. Color Doppler helps see the tumor’s blood flow.
Can abdominal ultrasound detect stomach cancer?
Ultrasound might find stomach cancer, but only if it’s big or has spread. Endoscopic ultrasound is better for checking stomach cancer.
What are the limitations of ultrasound in cancer detection?
Ultrasound has its limits. It depends on the person doing it, can’t see everything, and doesn’t always tell the difference between good and bad tumors.
When is ultrasound most appropriate for cancer screening?
Ultrasound is good for screening in certain groups, like those at high risk for liver cancer. It’s also used to watch known tumors and see how they’re responding to treatment.
What to expect during an ultrasound procedure for cancer detection?
During an ultrasound, a gel is applied, and a probe sends and receives sound waves. It’s painless and shows images in real-time on a screen.
Can ultrasound detect cancer in lymph nodes?
Yes, ultrasound can check lymph nodes for cancer signs, like being too big or looking different. It can also guide a biopsy to confirm.
What are the latest advancements in ultrasound technology for cancer detection?
New tech includes contrast-enhanced ultrasound, elastography, and 3D/4D ultrasound. These improve finding and understanding tumors, making diagnosis better.
What to do if ultrasound results are inconclusive or suspicious?
If ultrasound results are unclear or raise concerns, more tests are needed. This could be other imaging, biopsy, or procedures to confirm a tumor’s nature.
References
- American Cancer Society. (2024). Ultrasound for Cancer. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/screening-prevention/tests-and-procedures/ultrasound-for-cancer.html
- European Federation of Societies for Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology. (2020). Clinical applications of contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) in oncology: An update. https://www.efsumb.org/publications/guidelines/clinical-applications-of-contrast-enhanced-ultrasound-ceus-in-oncology-an-update























