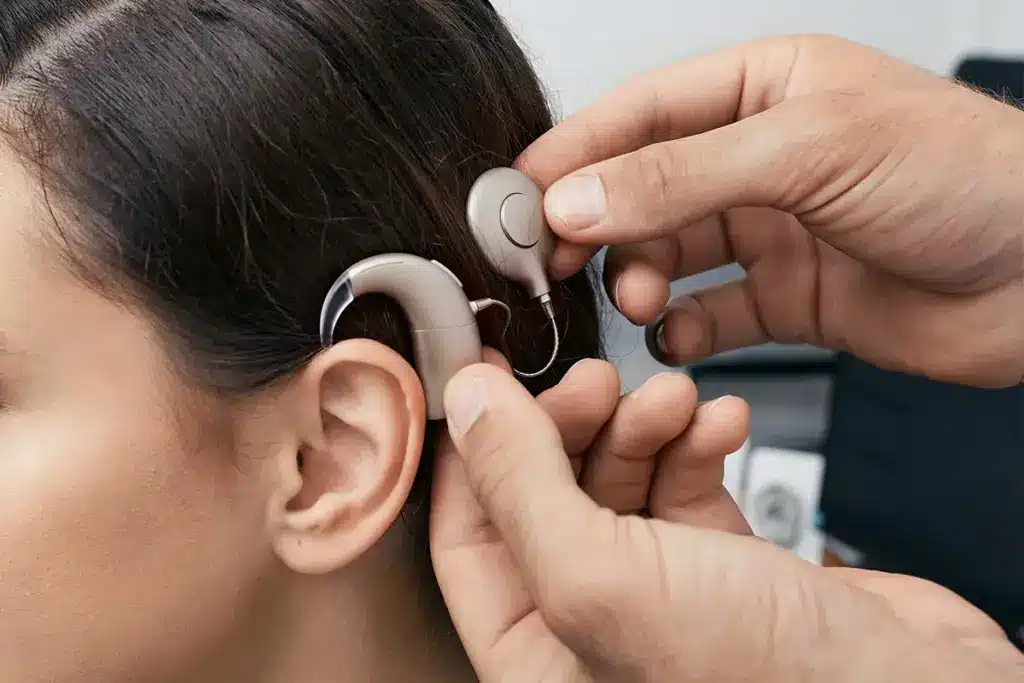
Hearing loss affects millions worldwide. Thanks to technology, we now have new solutions. Cochlear implants are a big step up from traditional hearing aids. They directly stimulate the auditory nerve, helping people hear meaningful sounds again.
New innovations are making implants smarter, with upgradable firmware. For those with severe to profound hearing loss, cochlear implants and other devices are changing lives. Three FDA-approved makers – Cochlear, Advanced Bionics, and MED-EL – offer different models. Each has its own special features and benefits.
Key Takeaways
- Cochlear implants directly stimulate the auditory nerve.
- Recent innovations include smart implant systems.
- Three FDA-approved manufacturers offer distinct devices.
- Implantable hearing devices are a viable alternative for severe hearing loss.
- These devices can significantly improve quality of life.
The Evolution of Hearing Restoration Technology
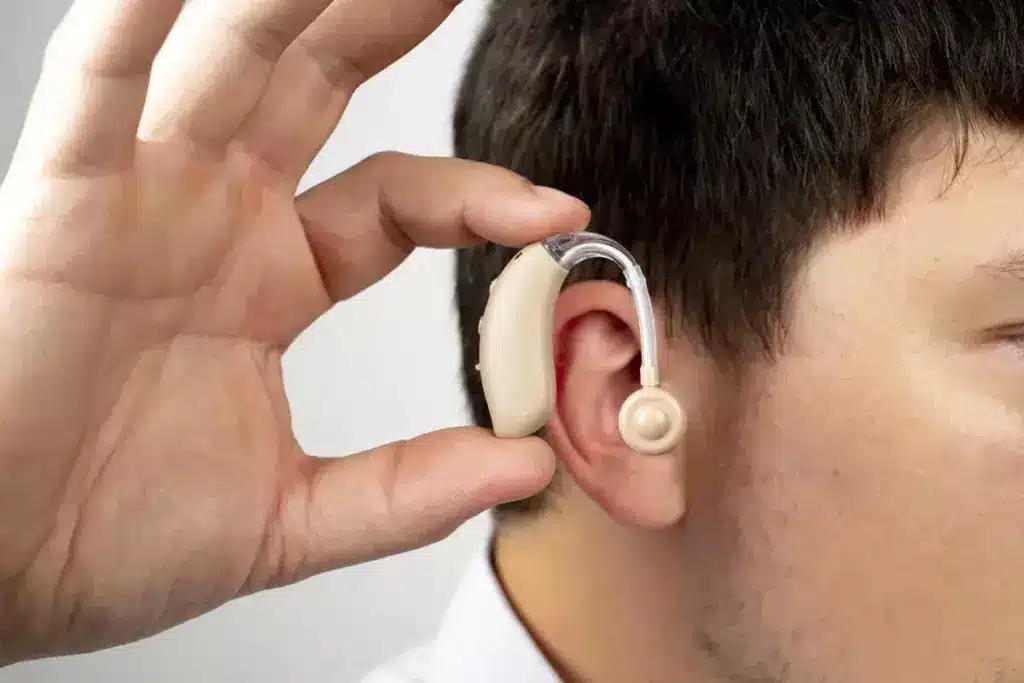
Technology for hearing restoration has made big strides, leading to advanced cochlear implants. These devices have changed lives for people with severe hearing loss. They offer better hearing and a higher quality of life.
How Modern Cochlear Implants Function
Modern cochlear implants use advanced digital signal processing to help people hear. The Nucleus Nexa System is a recent example. It has upgradeable firmware for future improvements without more surgery. These implants bypass damaged parts of the ear and directly stimulate the auditory nerve, giving a sense of sound.
Digital signal processing is key to how these implants work. It helps filter and prioritize sounds. This makes it easier for users to understand speech and interact with their surroundings.
Clinical Outcomes and Global Market Growth
Clinical results for cochlear implants are very positive. Research shows that up to 80 percent of kids who got implants before 12 months old saw big gains in understanding words. This shows how important early treatment is.
| Age at Implantation | Improvement in Receptive Vocabulary |
| Before 12 months | Up to 80% |
| 1-2 years | Significant improvement |
| 2-3 years | Notable improvement |
The global market for cochlear implants is growing fast. This growth is thanks to new technology and more people knowing about hearing restoration. As technology keeps getting better, we’ll see even more ways to help those with hearing loss.
5 Types of Cochlear Implants from Leading Manufacturers
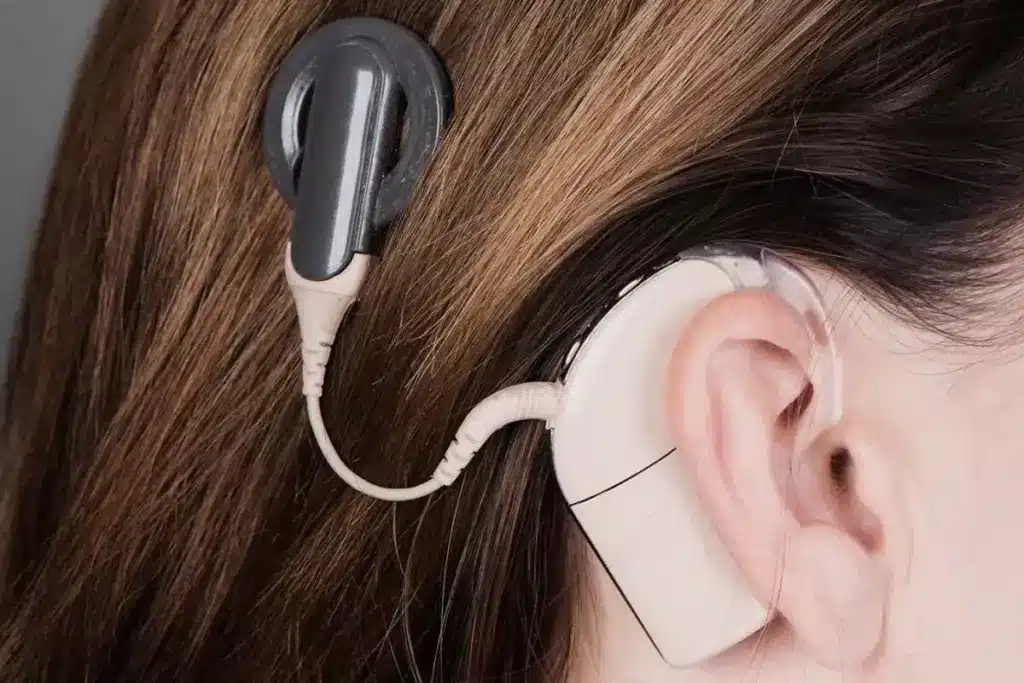

Cochlear implants have changed a lot, thanks to top makers. These devices help people who can’t hear well or are deaf. They work by sending sound straight to the auditory nerve.
Cochlear Corporation Systems
Cochlear Corporation leads in cochlear implants. They have many types for different needs. The Nucleus Series stands out, with the Nucleus Nexa System being the latest. It has new sound processing and electrode tech.
The Nucleus Series is known for being reliable and flexible. It comes with different electrode arrays for each person’s ear. Cochlear’s sound processors, like the Nucleus 7 Sound Processor, bring the latest tech for better hearing.
Cochlear Corporation
Advanced Bionics Systems
Advanced Bionics is known for its HiRes technology. It offers high-resolution sound processing. Their HiRes Ultra and HiRes Ultra 3D systems are great for clear sound and precise location.
The HiRes Ultra 3D has a special electrode design for better nerve stimulation. Advanced Bionics’ sound processors, like the Naída CI Q90, have cool features like wireless and strong noise reduction.
MED-EL Implant Systems
MED-EL is famous for its Synchrony system. It’s special because it’s safe for MRIs without removing magnets. MED-EL’s implants offer flexible hearing solutions with various electrode lengths.
The SONNET audio processor from MED-EL is a top feature. It has wireless audio streaming and an easy-to-use interface.
| Manufacturer | Implant System | Notable Features |
| Cochlear Corporation | Nucleus Nexa System | Advanced sound processing, electrode technology |
| Advanced Bionics | HiRes Ultra 3D | High-resolution sound, precise sound localization |
| MED-EL | Synchrony | MRI compatibility, flexible electrode options |
Alternative Hearing Solutions for Different Hearing Needs
There are many hearing solutions beyond cochlear implants. These options help people with different types of hearing loss. They offer choices for those not suited for cochlear implants or need other types of hearing help.
Bone Anchored Hearing Systems
Bone anchored hearing systems help those with conductive or mixed hearing loss. They send sound vibrations through the skull to the inner ear. This way, they bypass the outer and middle ear, improving sound quality and comfort.
Key features of bone anchored hearing systems include:
- Direct sound transmission through the skull
- Suitable for conductive or mixed hearing loss
- Improved sound quality and comfort
Middle Ear Implants
Middle ear implants are for those with sensorineural hearing loss. They directly stimulate the ossicles or inner ear, providing natural sound. They offer better sound quality and less feedback than traditional hearing aids.
Characteristics of middle ear implants include:
- Direct stimulation of the ossicles or inner ear
- Improved sound quality and reduced feedback
- Suitable for sensorineural hearing loss
Auditory Brainstem Implants
Auditory brainstem implants are for severe to profound hearing loss. They bypass damaged parts of the ear and directly stimulate the auditory brainstem. This provides some sound perception.
The main benefits of auditory brainstem implants include:
- Direct stimulation of the auditory brainstem
- Suitable for severe to profound hearing loss
- Potential for improved sound perception
Emerging Hearing Technologies
The field of hearing restoration is always growing. New technologies include regenerative medicine, novel implants, and better signal processing. As research advances, we’ll see more innovative solutions for hearing loss.
Emerging trends in hearing technologies include:
- Regenerative medicine for hearing restoration
- Advanced implant designs for improved outcomes
- Enhanced signal processing for better sound quality
Conclusion: Selecting the Optimal Hearing Solution
Choosing the right hearing solution is a personal choice. It depends on your hearing loss type and how severe it is. It also depends on what you prefer and need. We’ve looked at many options, like cochlear implants from Cochlear Corporation, Advanced Bionics, and MED-EL. We’ve also talked about other choices like bone anchored hearing systems and middle ear implants.
It’s important to talk to a hearing expert before making a decision. They can check your hearing and suggest the best device for you. Whether you’re thinking about a hearing ear implant or want to know more about hearing implants, getting a professional opinion is key.
Knowing about the different hearing implants and ear implant options helps you make a good choice. We aim to provide top-notch healthcare and support for patients from around the world. We urge you to get professional advice to find the best hearing solution for you.
FAQ
Hearing Solutions: Implants vs. Hearing Aids
When exploring options for hearing restoration, the technology typically falls into two categories: devices that amplify sound and devices that bypass the ear’s damaged anatomy.
Cochlear Implants vs. Traditional Hearing Aids
The fundamental difference lies in how they process sound. Hearing aids are acoustic devices that use a microphone and amplifier to make sound waves louder, relying on the remaining healthy hair cells in your ear to transmit that sound to the brain. Cochlear implants are electronic prosthetics that bypass those damaged hair cells entirely. They convert sound into electrical impulses that directly stimulate the auditory nerve, making them suitable for those whose hearing loss is too severe for amplification to be effective.
How Implants Work and Their Benefits
A cochlear implant consists of an external processor that captures sound and an internal electrode array placed inside the cochlea. This system provides a functional representation of sound that allows users to understand speech in noisy environments, talk on the phone, and hear environmental safety cues like sirens. The primary benefit is the restoration of communication, which significantly reduces the cognitive load and social isolation often associated with profound deafness.
Types of Implants and Variations
Cochlear implants vary mainly by the design of the external processor and the internal electrode array.
-
Behind-the-Ear (BTE) Processors: These look like traditional hearing aids and sit on the ear.
-
Off-the-Ear (OTE) Processors: These are single-unit circular devices, such as the Kanso 2 or the recently released Kanso 3 (2025), which sit entirely on the head, leaving the ear completely free.
-
Electrode Arrays: Variations include “slim” or “perimodiolar” shapes designed to protect the delicate internal structures of the cochlea, especially for patients who still have some natural low-frequency hearing.
Alternatives and Suitability for Different Types of Loss
Cochlear implants are specifically for sensorineural hearing loss (nerve-related). However, other implants exist for different types of loss:
-
Bone Anchored Hearing Systems (BAHA): Devices like the Baha 7 (released 2025) are used for conductive hearing loss (outer or middle ear issues) or single-sided deafness. They use bone conduction to send vibrations through the skull directly to the healthy inner ear.
-
Middle Ear Implants: These are recommended for patients with mild-to-moderate conductive or sensorineural loss who cannot wear traditional aids due to medical reasons like ear canal infections.
-
Auditory Brainstem Implants (ABI): These are for individuals with severely damaged or missing hearing nerves, where even a cochlear implant would not work.
Latest Advancements in 2026
Recent breakthroughs focus on hearing preservation and AI-driven automation. Surgeons now use robotic assistance to insert electrodes with microscopic precision, minimizing trauma to the cochlea. On the software side, 2026 technology features advanced AI-powered processors that automatically filter out background noise in real-time. Additionally, the rise of Auracast broadcast audio allows users to stream high-quality audio directly from public spaces to their implants, while “remote programming” via smartphone apps has become a standard for device adjustments.
Determining the Best Solution
The most suitable solution is determined through a multi-step evaluation. This includes an audiogram to measure hearing thresholds, a speech-in-noise test to evaluate clarity, and imaging (CT or MRI) to check physical anatomy. If a hearing aid is making things louder but not clearer, it is usually a sign that an implant evaluation is the appropriate next step.
References:
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK544280