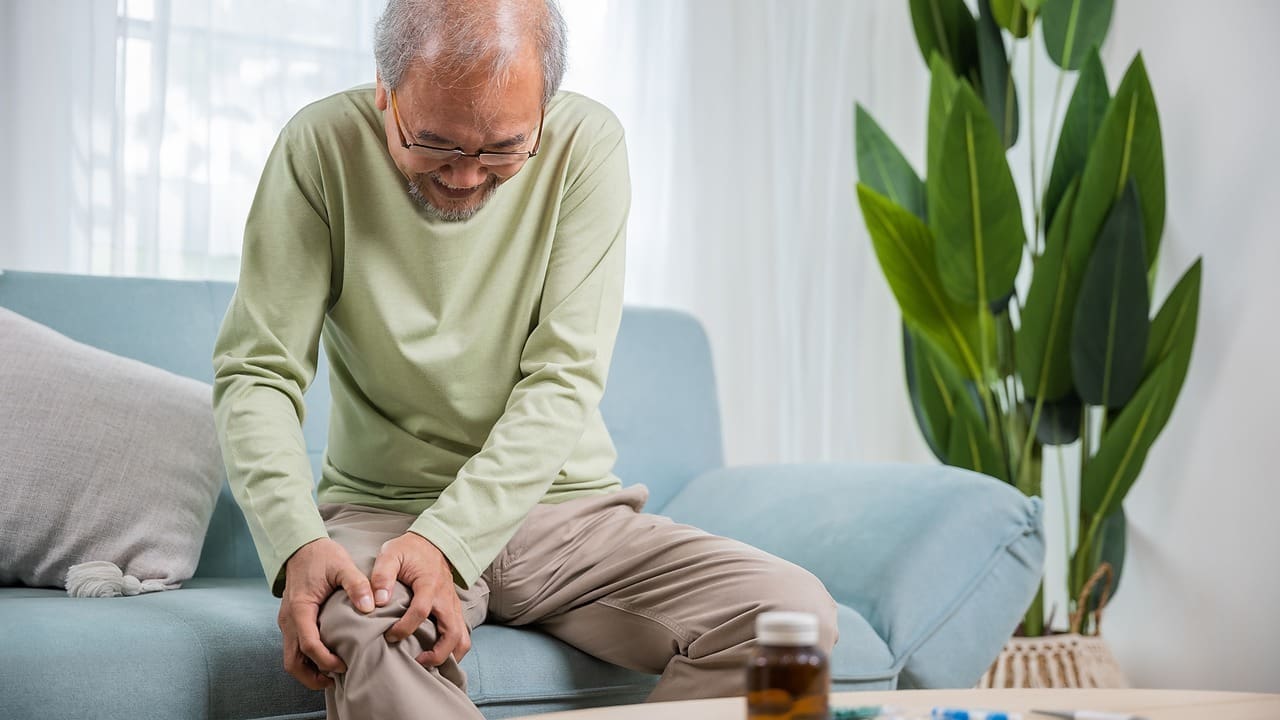
Osteoarthritis in the knee is a big problem for the elderly, causing a lot of pain. At Liv Hospital, we know how hard it is and want to help. We offer ways to manage this condition.
Effective pain relief is key for those with osteoarthritis. We look at the best pain relief choices, from over-the-counter to prescription drugs.
Finding the right pain reliever can be tough. Our article gives you the latest advice on treating osteoarthritis knee pain.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding osteoarthritis and its impact on the elderly
- Exploring effective pain relief options for osteoarthritis
- Overview of available treatment options for arthritis knee pain
- Importance of choosing the right pain reliever for osteoarthritis
- Evidence-based guidance for managing osteoarthritis knee pain
Understanding Osteoarthritis and Knee Pain
It’s important to know what causes osteoarthritis knee pain to manage it well. Osteoarthritis is a disease that wears down cartilage, causing knee pain and stiffness.
What Causes Arthritis Knee Pain
Arthritis knee pain comes from cartilage wear and knee joint inflammation. Cartilage breakdown means bones rub together, causing pain and less mobility.
Cartilage Breakdown and Inflammation
Cartilage in our knees cushions the bones. When it breaks down, we get osteoarthritis. The body’s repair efforts cause more inflammation and pain.
Risk Factors for Developing Osteoarthritis
Several things can raise your risk of osteoarthritis. These include age, being overweight, past knee injuries, and family history. For more on managing osteoarthritis, check out WebMD’s guide on medicines to treat.
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Age | Increased risk with advancing age |
| Obesity | Excess weight puts additional stress on knee joints |
| Previous Injuries | Knee injuries can lead to osteoarthritis later in life |
| Genetics | Family history can play a role in developing osteoarthritis |
How Osteoarthritis Affects Daily Life
Osteoarthritis knee pain makes everyday tasks hard. It can make walking, climbing stairs, or standing for long hard. Without proper management, it can lower your quality of life.
Why Effective Pain Management Matters
Managing pain well is key to keeping mobility and improving life quality for those with osteoarthritis. Knowing the causes and risk factors helps us manage the condition better and lessen its daily impact.
What Is the Best Pain Reliever for Osteoarthritis?
Finding the best pain reliever for osteoarthritis means understanding how different medicines work. It’s about comparing the best options for managing osteoarthritis pain.
Comparing Effectiveness of Different Medications
For osteoarthritis pain, two main types of medicines are used: NSAIDs and acetaminophen. NSAIDs are often seen as more effective because they reduce pain and inflammation. This is key in slowing down osteoarthritis.
NSAIDs vs. Acetaminophen: The Evidence
Studies show NSAIDs work better than acetaminophen for osteoarthritis pain. A study in the American Family Physician journal found NSAIDs offer better pain relief than acetaminophen. But, the right choice depends on the patient’s health and risks.
Oral vs. Topical Treatments
There are oral and topical treatments for osteoarthritis pain. Oral NSAIDs help but can upset the stomach. Topical NSAIDs, like diclofenac gel, target pain locally and might have fewer side effects. The best choice depends on the patient’s needs and health history.
Latest Research on Osteoarthritis Pain Relief
New studies back NSAIDs as a top choice for osteoarthritis pain. But, there’s growing interest in other treatments. This includes topical options and combinations to manage pain better and reduce side effects.
Factors That Determine “Best” for Individual Patients
The best pain reliever for osteoarthritis changes from person to person. It depends on their medical history and age-related risks.
Medical History Considerations
Those with stomach problems might face more risks with NSAIDs. For them, acetaminophen or topical NSAIDs could be safer.
Age and Risk Factors
Older adults might face more risks from NSAIDs, like kidney problems and stomach bleeding. Age and individual risks are key in picking the right pain relief.
Healthcare providers can help patients with osteoarthritis find the best pain reliever. They consider various factors and compare medicines to meet each patient’s needs.
NSAIDs: The First-Line Treatment Option
NSAIDs are a top choice for treating osteoarthritis. They balance being effective and safe. We’ll look at how they fight arthritis pain and the benefits of specific NSAIDs.
How NSAIDs Work Against Arthritis Pain
NSAIDs stop the body from making prostaglandins. These chemicals cause inflammation and pain. By cutting down inflammation, NSAIDs help ease osteoarthritis pain. Recent studies show NSAIDs are key in treating osteoarthritis pain.
Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) for Knee Pain
Ibuprofen is often used for knee pain from osteoarthritis. It’s good at reducing pain and swelling, making it a favorite among patients.
Recommended Dosages and Effectiveness
The usual dose of ibuprofen for osteoarthritis pain is 1200 mg to 3200 mg a day. It’s split into several doses. Research shows it can lessen knee pain and improve function in osteoarthritis patients.
Potential Side Effects
Ibuprofen is usually okay, but it can upset your stomach. It might cause nausea, stomach pain, or diarrhea. Taking it for a long time can also raise the risk of bleeding in the stomach. It’s important to stick to the recommended dose and talk to a doctor to avoid side effects.
Naproxen (Aleve) Benefits and Usage
Naproxen offers longer-lasting relief for osteoarthritis pain. It releases its active ingredient slowly, giving longer pain relief.
Longer-Acting Relief Options
Naproxen’s longer half-life means you only need to take it twice a day. This helps keep pain under control all day long.
Safety Profile
Naproxen’s safety is similar to ibuprofen, with stomach problems being the main concern. But its longer action might mean fewer doses and less risk of side effects from frequent use.
Diclofenac: Superior Pain Relief Option
Diclofenac is known for its strong pain relief, best at higher doses. It comes in both prescription and over-the-counter forms.
150 mg/day Dosage Effectiveness
A 150 mg/day dose is effective for osteoarthritis pain. Doctors often prescribe it when other NSAIDs don’t work well enough.
Prescription vs. OTC Formulations
Diclofenac is available without a prescription, but prescription versions may have higher doses or combinations. Talking to a doctor is key to finding the right version and dose for you.
Topical Pain Relievers for Localized Knee Pain
Topical pain relievers are a great way to handle knee pain from osteoarthritis. They are applied directly to the skin, giving targeted relief.
Diclofenac Gel (Voltaren): Effectiveness and Application
Diclofenac gel, or Voltaren, is a topical NSAID that works well for knee pain from osteoarthritis. It works by penetrating the skin and acting on the pain site.
Proper Application Techniques
To get the most out of diclofenac gel, applying it right is key. Apply a thin layer to the affected area and rub it in until it’s fully absorbed. Follow the dosage and frequency as advised by your doctor or the product label.
Absorption and Local Action
The gel form of diclofenac is absorbed locally, providing pain relief right where it’s needed. This local action means less of the drug goes into your system, lowering the chance of side effects.
Other Topical NSAIDs and Their Benefits
There are other topical NSAIDs out there, each with its own benefits for osteoarthritis patients. They come in different forms and have various active ingredients, catering to different needs and preferences.
Advantages for Elderly Patients and Those with GI Concerns
Topical NSAIDs, like diclofenac gel, are great for older adults and those with stomach issues. Their localized action means fewer systemic side effects.
Reduced Systemic Side Effects
Topical NSAIDs have fewer systemic side effects than oral ones. This is because they are absorbed locally, reducing the risk of stomach problems.
Combining with Oral Medications
In some cases, using topical NSAIDs with oral pain meds can help more. This combo can offer better pain relief for those with more severe osteoarthritis.
Acetaminophen (Tylenol): A Safer Alternative?
Acetaminophen is seen as a safer choice for osteoarthritis pain relief compared to NSAIDs. We’ll look at how it differs from NSAIDs and its effectiveness. This will help us understand when it’s a better option.
How Acetaminophen Differs from NSAIDs
Acetaminophen and NSAIDs work in different ways. NSAIDs fight inflammation, while acetaminophen targets the brain to lessen pain. This means acetaminophen doesn’t have NSAIDs’ anti-inflammatory powers.
Effectiveness for Osteoarthritis Pain
Research shows acetaminophen can help with osteoarthritis pain, but it’s not as strong as NSAIDs. It offers modest benefits for mild to moderate pain.
Modest Benefits for Mild to Moderate Pain
Acetaminophen can significantly reduce pain for some with mild to moderate osteoarthritis. But, its effects can differ from person to person.
When to Choose Acetaminophen Over NSAIDs
There are times when acetaminophen is better than NSAIDs. This is true for patients with specific health issues.
Kidney, Heart, and GI Considerations
For those with kidney disease, heart problems, or stomach issues, acetaminophen is safer. It has a different side effect profile than NSAIDs. It’s key to think about these when picking a pain reliever.
Safe Usage Guidelines
To safely use acetaminophen, stick to the recommended dose. Taking too much can harm your liver. Always talk to a doctor for advice tailored to you.
In summary, acetaminophen might not be as effective as NSAIDs for osteoarthritis pain. Yet, it’s safer for some patients. Knowing its differences and following safe use guidelines helps patients make better choices for managing their pain.
Over-the-Counter Options for Arthritis Pain Management
Understanding over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers is key when managing arthritis pain. We’ll look at the different options, their benefits, and how to pick the best one for you.
Comparing OTC Pain Relievers for Knee Pain
OTC pain relievers are often the first choice for arthritis knee pain. The main options are acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen and naproxen.
Strength and Duration Differences
OTC pain relievers vary in strength and how long they last. Acetaminophen is good for mild to moderate pain. NSAIDs work better for pain caused by inflammation.
Cost Considerations
Cost is important too. Acetaminophen is usually cheaper than NSAIDs. But, prices can change based on the brand and type.
Combination Therapies Available Without Prescription
Some OTC products mix pain relievers with other ingredients. For example, some products have both acetaminophen and NSAIDs. But, be careful not to take too much of either.
Reading Labels and Choosing the Right Strength
It’s vital to read and understand OTC pain reliever labels. We need to look at the active ingredients and how much to take.
Active Ingredients to Look For
When picking an OTC pain reliever, check the active ingredients. Look for acetaminophen, ibuprofen, and naproxen.
Avoiding Duplicate Medications
To avoid taking too much of a medication, know that some products may have the same ingredient as others you’re taking.
| Medication | Primary Use | Duration of Action | Common Brand Names |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acetaminophen | Mild to Moderate Pain | 4-6 hours | Tylenol |
| Ibuprofen | Inflammatory Pain | 6-8 hours | Advil, Motrin |
| Naproxen | Inflammatory Pain | 8-12 hours | Aleve |
For more detailed info on comparing pain medications for osteoarthritis, visit the Arthritis Foundation website.
Special Considerations for Elderly Patients
Managing osteoarthritis in elderly patients is complex. We must consider medication interactions and safety concerns. It’s important to be careful when treating older adults with osteoarthritis.
Medication Interactions and Safety Concerns
Elderly patients often take many medications. This increases the risk of drug interactions. We need to watch out for these interactions to ensure safe treatment.
Common Drug Interactions
Some common interactions include those between NSAIDs and other medications. For example, NSAIDs and blood thinners can increase the risk of bleeding.
Monitoring for Side Effects
Regular monitoring for side effects is key. Elderly patients should be watched for signs of gastrointestinal bleeding or kidney damage.
Recommended Dosages for Older Adults
Dosage adjustments are often needed for older adults. This is because of changes in metabolism and kidney function with age. We start with lower doses and increase as needed.
Balancing Pain Relief with Side Effect Risks
Finding the right balance between pain relief and side effects is important. Topical options can be useful for localized pain.
When to Consider Topical Options
Topical NSAIDs, like diclofenac gel, are effective for knee osteoarthritis. They have fewer systemic side effects, making them a good choice for those at risk of gastrointestinal complications.
Working with Healthcare Providers
Collaboration with healthcare providers is essential. Regular follow-ups help adjust treatments as needed.
To illustrate the considerations for elderly patients, let’s examine a comparison of common osteoarthritis medications:
| Medication | Typical Dosage for Older Adults | Common Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Ibuprofen | 200-400 mg every 4-6 hours | Gastrointestinal upset, kidney strain |
| Naproxen | 250-500 mg twice daily | Gastrointestinal bleeding, fluid retention |
| Acetaminophen | 325-1000 mg every 4-6 hours | Liver damage (with high doses) |
| Diclofenac Gel | Apply to affected area 4 times daily | Local skin reactions |
Emerging Treatments for Osteoarthritis Pain
The treatment for osteoarthritis is changing fast with new medicines and methods. Scientists are learning more about the disease. This leads to new ways to treat it.
New Medications in Development
New medicines are being tested to help with osteoarthritis pain. Biologic agents aim to stop joint inflammation and damage. For example, interleukin-1 (IL-1) inhibitors might help reduce pain and slow the disease.
Alternative and Complementary Approaches
Along with new medicines, other treatments are also being used. These include things like exercise and natural remedies.
Exercise and Physical Therapy
Exercise and physical therapy are key for managing osteoarthritis. They keep joints moving and muscles strong. Personalized exercise programs can really help improve life quality.
Supplements and Natural Remedies
Some supplements, like glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate, might help with osteoarthritis. Even though results vary, some people find relief.
What to Expect in Osteoarthritis Treatment by 2025
By 2025, we expect big changes in treating osteoarthritis. Targeted therapies will likely play a bigger role.
Targeted Therapies on the Horizon
Research on gene therapy and stem cell therapy is exciting. These could lead to treatments that help repair or replace damaged tissue. This could be a game-changer for pain relief and treating the disease.
Conclusion: Creating Your Osteoarthritis Pain Management Plan
Creating a good plan for managing osteoarthritis pain is all about finding the right mix of treatments. We’ve looked at options like NSAIDs, topical pain relievers, and acetaminophen. Each has its own good points and things to watch out for.
It’s key to work with your healthcare team to make a plan that fits you. They’ll consider how bad your osteoarthritis is, your health history, and your lifestyle. By picking the right treatments and living a healthy lifestyle, you can manage your pain better.
Your pain management plan should be something you can change as needed. It’s a good idea to check and update your plan often. This way, you can keep getting the best pain relief and stay active and healthy, even with osteoarthritis.
FAQ
What is the best pain reliever for osteoarthritis?
The best pain reliever for osteoarthritis varies by person. Factors like medical history and age play a role. NSAIDs like ibuprofen and naproxen are often first choices. Diclofenac is seen as a top option. Acetaminophen works well for milder pain.
What are the most effective over-the-counter pain relievers for knee pain?
For knee pain, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and naproxen (Aleve) are good choices. Diclofenac gel (Voltaren) is also effective for knee pain. It’s applied directly to the area.
Are topical pain relievers effective for osteoarthritis pain?
Yes, topical pain relievers like diclofenac gel (Voltaren) are great for osteoarthritis pain. They work well for knee pain and have fewer side effects. They’re good for older adults and those with stomach issues.
How does acetaminophen compare to NSAIDs for osteoarthritis pain?
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) is safer than NSAIDs for osteoarthritis pain. It’s better for those with kidney, heart, or stomach problems. But NSAIDs are usually more effective.
What are the possible side effects of NSAIDs for osteoarthritis pain?
NSAIDs can cause stomach problems like ulcers and bleeding. They also raise the risk of heart attack and stroke. Older adults are more at risk.
Can I use combination therapies for osteoarthritis pain management?
Yes, you can use combination therapies without a prescription. But make sure to read labels. Choose the right strength to avoid duplicate medications and interactions.
What are the emerging treatments for osteoarthritis pain?
New treatments for osteoarthritis pain are being developed. There are also alternative and targeted therapies. Exercise and physical therapy help manage pain too.
How can I manage osteoarthritis pain effectively and safely?
To manage osteoarthritis pain well, work with your doctor. Create a plan that fits your needs. Use the most effective pain relief options.
What is the recommended dosage for older adults with osteoarthritis?
Dosage for older adults with osteoarthritis depends on the medication and individual factors. Always talk to your doctor to find the right dosage for you.
Are there any alternative and complementary approaches for osteoarthritis pain?
Yes, there are alternative and complementary approaches like supplements and natural remedies. They may help with osteoarthritis pain. But always check with your doctor first.
What is the best pain reliever for osteoarthritis?
The best pain reliever for osteoarthritis varies by person. Factors like medical history and age play a role. NSAIDs like ibuprofen and naproxen are often first choices. Diclofenac is seen as a top option. Acetaminophen works well for milder pain.
What are the most effective over-the-counter pain relievers for knee pain?
For knee pain, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and naproxen (Aleve) are good choices. Diclofenac gel (Voltaren) is also effective for knee pain. It’s applied directly to the area.
Are topical pain relievers effective for osteoarthritis pain?
Yes, topical pain relievers like diclofenac gel (Voltaren) are great for osteoarthritis pain. They work well for knee pain and have fewer side effects. They’re good for older adults and those with stomach issues.
How does acetaminophen compare to NSAIDs for osteoarthritis pain?
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) is safer than NSAIDs for osteoarthritis pain. It’s better for those with kidney, heart, or stomach problems. But NSAIDs are usually more effective.
What are the possible side effects of NSAIDs for osteoarthritis pain?
NSAIDs can cause stomach problems like ulcers and bleeding. They also raise the risk of heart attack and stroke. Older adults are more at risk.
Can I use combination therapies for osteoarthritis pain management?
Yes, you can use combination therapies without a prescription. But make sure to read labels. Choose the right strength to avoid duplicate medications and interactions.
What are the emerging treatments for osteoarthritis pain?
New treatments for osteoarthritis pain are being developed. There are also alternative and targeted therapies. Exercise and physical therapy help manage pain too.
How can I manage osteoarthritis pain effectively and safely?
To manage osteoarthritis pain well, work with your doctor. Create a plan that fits your needs. Use the most effective pain relief options.
What is the recommended dosage for older adults with osteoarthritis?
Dosage for older adults with osteoarthritis depends on the medication and individual factors. Always talk to your doctor to find the right dosage for you.
Are there any alternative and complementary approaches for osteoarthritis pain?
Yes, there are alternative and complementary approaches like supplements and natural remedies. They may help with osteoarthritis pain. But always check with your doctor first.
Références
- American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP) : https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2013/0301/p354.html
- GoodRx : https://www.goodrx.com/conditions/pain/popular-over-the-counter-pain-relievers
- Arthritis Foundation : https://www.arthritis.org/health-wellness/healthy-living/managing-pain/pain-relief-solutions/comparing-pain-meds-for-osteoarthritis
- PMC – PubMed Central : https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8586433/
- WebMD : https://www.webmd.com/osteoarthritis/medicines-treat-oa


































