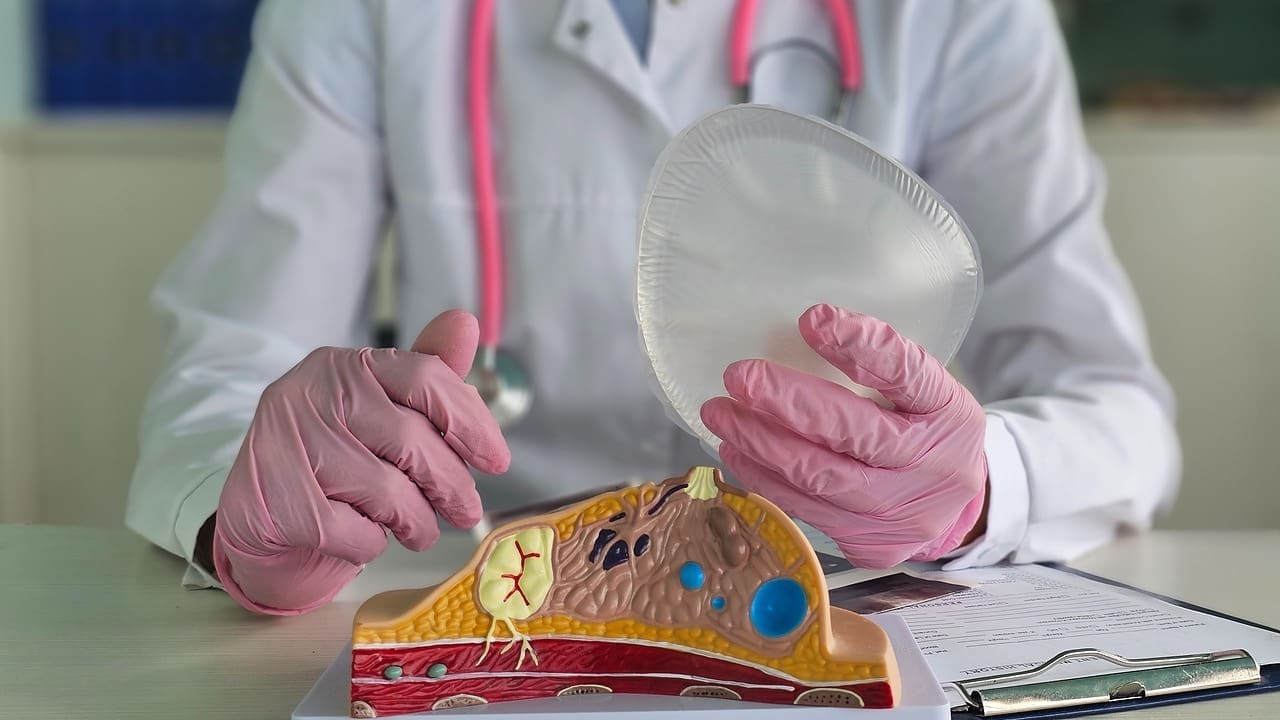
At Liv Hospital, we know how important it is to treat arterial blockages. Atherosclerosis medical procedures and arteriosclerosis surgeries are key to managing these issues.
Recent studies, like the TEMP-PREVENT trial, have looked into new ways to treat arterial calcification. This has brought to light new methods for handling atherosclerosis. We offer cutting-edge treatments like angioplasty, stent placement, atherectomy, and bypass surgery. These help prevent complications and improve patient results.
Key Takeaways
- Effective treatments for arterial blockages are key for patient success.
- Liv Hospital offers top-notch treatments, including angioplasty andbypass surgery.
- New ways to manage atherosclerosis are being explored.
- Our team is dedicated to providing quality, innovative, and patient-focused care.
- It’s important to understand the role of atherosclerosis medical procedures.
Understanding Atherosclerosis and Arteriosclerosis
Atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis are two related but different conditions that affect the arteries. They need a deep understanding for effective management. These terms are often mixed up, but they describe different parts of arterial disease.
The Pathophysiology of Arterial Plaque Buildup
Atherosclerosis is when plaque builds up in the artery walls, making them hard and narrow. This buildup includes lipids, inflammatory cells, and fibrous elements. The process is complex, involving problems with the inner lining of the artery, lipid infiltration, and inflammation.
Plaque Composition: Plaque can be stable or unstable. Unstable plaques, rich in lipids and with a thin fibrous cap, are more likely to cause heart attacks.
Differentiating Between Atherosclerosis and Arteriosclerosis
Arteriosclerosis is when the artery walls harden and thicken, often due to aging or high blood pressure. Atherosclerosis is a specific type of arteriosclerosis caused by plaque buildup. Knowing the difference is key to choosing the right atherosclerosis treatment or arteriosclerosis management.
| Characteristics | Atherosclerosis | Arteriosclerosis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Plaque buildup in arterial walls | Hardening and thickening of arterial walls |
| Causes | Lipid infiltration, inflammation | Aging, hypertension, various pathological processes |
| Clinical Implications | Risk of plaque rupture, acute cardiovascular events | Reduced arterial compliance, increased cardiovascular risk |
Risk Factors and Disease Progression
Many factors can lead to atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis, like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and smoking. Knowing these risk factors is key to preventing and treating atherosclerosis effectively.
These diseases can lead to serious heart problems and death. It’s important to manage risk factors early to slow disease progression and lower the risk of complications.
Healthcare providers can create better treatment plans by understanding the disease, knowing the difference between atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis, and identifying risk factors. This helps improve patient outcomes.
Diagnosis and Assessment Methods
Managing atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis starts with accurate diagnosis. We use various diagnostic techniques to find out how much arterial disease there is. This is key for creating a treatment plan that fits each patient.
Non-Invasive Diagnostic Techniques
Non-invasive tests are often the first step in checking for atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis. These include:
- Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to create images of the arteries. It helps spot plaque buildup and check blood flow.
- Computed Tomography (CT) scans: Gives detailed images of the arteries. It helps find calcification and plaque.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Offers clear images of the arteries without using harmful radiation.
The TEMP-PREVENT trial used CT scans to measure arterial calcification. It shows how important imaging is in diagnosing atherosclerosis.
Invasive Diagnostic Procedures
When non-invasive tests show serious arterial disease, more detailed tests are needed. These include:
- Angiography: Involves injecting a contrast agent into the arteries. It helps see the lumen and find blockages or stenosis.
- Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS): Uses a catheter with an ultrasound probe. It gives detailed images of the arterial walls and plaque.
Determining Treatment Eligibility
The results from these tests help decide the best treatment. We look at how much plaque there is, if there are symptoms, and the patient’s health. This helps figure out if a patient is eligible for treatment.
By using clinical evaluation and advanced diagnostic techniques, we can accurately diagnose atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis. This leads to effective management and better outcomes for patients.
Angioplasty: The Most Typical Treatment for Arteriosclerosis
Angioplasty is a key treatment for arteriosclerosis. It’s a way to open up blocked arteries without surgery.
Getting a medical procedure can seem scary. But angioplasty is a common and effective way to treat arteriosclerosis. It uses a balloon to widen arteries, improving blood flow and easing symptoms.
The Balloon Angioplasty Procedure Explained
Balloon angioplasty involves inserting a small balloon into a narrowed artery. The balloon is then inflated to widen the artery. This is done under local anesthesia and guided by imaging.
The steps of balloon angioplasty are:
- Insertion of a catheter into the artery
- Guiding the catheter to the narrowed section
- Inflating the balloon to widen the artery
- Deflating the balloon and removing the catheter
Types of Angioplasty Approaches
There are different angioplasty methods, each suited for different needs. Some common ones are:
- Plain Old Balloon Angioplasty (POBA)
- Cutting Balloon Angioplasty
- Scoring Balloon Angioplasty
- Drug-Coated Balloon Angioplasty
Each method has its own benefits. The choice depends on the patient’s condition and the blockage.
Recovery and Post-Procedure Care
After angioplasty, patients need to rest and be watched. They should follow a recovery plan. This might include:
- Monitoring the puncture site for any signs of bleeding or infection
- Avoiding strenuous activities for a specified period
- Taking prescribed medications to prevent clotting and manage symptoms
- Attending follow-up appointments to check on the progress of the treated artery
Success Rates and Possible Complications
Angioplasty works well for many people, improving blood flow and symptoms. But, like any procedure, it can have risks. These include:
- Restenosis (re-narrowing of the artery)
- Bleeding or hematoma at the catheter site
- Vascular complications
We focus on choosing the right patients and careful post-procedure care. This helps avoid risks and get the best results.
Knowing about angioplasty helps patients make informed choices for treating arteriosclerosis.
Stent Placement Procedures for Arterial Support
Stents have changed how we treat heart problems. They help keep arteries open, ensuring blood flows well to important organs. We’ll look at the different stents, how they’re placed, and caring for arteries with stents long-term.
Bare Metal Stents vs. Drug-Eluting Stents
Stents are mainly two types: bare metal stents (BMS) and drug-eluting stents (DES). Bare metal stents are made of metal and support the artery. Drug-eluting stents release medicine to stop cells from growing, which lowers the chance of the artery narrowing again.
Choosing between BMS and DES depends on the patient’s health and the artery’s condition. Drug-eluting stents are often used in more complex cases or when there’s a high risk of the artery narrowing again.
| Stent Type | Characteristics | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bare Metal Stents | Metal mesh structure | Lower risk of late thrombosis with prolonged dual antiplatelet therapy | Higher risk of restenosis |
| Drug-Eluting Stents | Releases medication to prevent cell proliferation | Lower risk of restenosis | Requires prolonged dual antiplatelet therapy |
Stent Deployment Techniques
Putting in a stent requires careful techniques for accurate placement. We use advanced tools like intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) and optical coherence tomography (OCT) to guide the process. These tools help us check the stent’s position and make sure it’s expanded right.
Long-term Management of Stented Arteries
After a stent is placed, managing it long-term is key to avoid problems. Patients usually take antiplatelet drugs to lower the risk of blood clots. Regular check-ups and scans are done to keep an eye on the artery and catch any issues early.
We stress the importance of healthy habits like eating right, exercising, and quitting smoking. These actions help keep the heart healthy and improve outcomes over time.
Atherectomy: Removing Arterial Plaque
The atherectomy procedure removes plaque from arterial walls. It’s a key step in fighting atherosclerosis and avoiding more problems. This method is a minimally invasive way to tackle arterial plaque buildup.
Rotational Atherectomy Techniques
Rotational atherectomy uses a high-speed device to grind plaque away. It’s great for dealing with hard, calcified lesions.
We use this method for patients with tough blockages. It’s precise in removing plaque and improving blood flow.
Laser Atherectomy Procedures
Laser atherectomy uses a laser to vaporize plaque. This makes it easy to remove. It works well in different parts of the arteries.
Directional Atherectomy Methods
Directional atherectomy uses a cutting catheter to shave off plaque. Then, it’s removed. This method controls how plaque is taken out.
Patient Selection and Outcomes
Choosing the right patients for atherectomy is key for good results. We look at the plaque’s location and type, and the patient’s health. This helps decide if the procedure is right for them.
Here’s a quick look at the different atherectomy methods and what they do:
| Atherectomy Technique | Description | Primary Use |
|---|---|---|
| Rotational Atherectomy | High-speed rotational device to grind or abrade plaque | Calcified lesions |
| Laser Atherectomy | Laser catheter to vaporize or break down plaque | Plaque in various arterial locations |
| Directional Atherectomy | Catheter with a cutting device to shave or excise plaque | Controlled removal of plaque |
Knowing about the different atherectomy techniques helps us tailor treatments. This way, we meet each patient’s unique needs. It improves their outcomes and quality of life.
Bypass Surgery for Severe Arterial Blockages
Bypass surgery is a lifeline for those with severe arterial disease. It’s a key treatment for both coronary and peripheral artery disease. It helps patients with complex blockages.
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) improves blood flow to the heart. A surgeon uses a healthy blood vessel to bypass a blocked artery. This boosts blood flow to the heart muscle, easing symptoms.
CABG is best for those with many blockages or complex disease. It can be done through open-heart surgery or minimally invasive methods.
Peripheral Artery Bypass Procedures
Peripheral artery bypasses fix blocked or narrowed arteries in the legs. This surgery boosts blood flow, easing pain and cramping.
A graft from a healthy blood vessel is used. It’s attached above and below the blockage, allowing blood to bypass it.
Surgical Approaches and Techniques
There are many ways to perform bypass surgery. The method chosen depends on the blockage’s location and severity, and the patient’s health.
| Surgical Approach | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Open-Heart Surgery | Involves a large incision in the chest to access the heart | Allows for complex repairs and multiple grafts |
| Minimally Invasive CABG | Uses smaller incisions and specialized instruments | Reduces recovery time and scarring |
| Robotic-Assisted Surgery | Utilizes robotic systems for enhanced precision | Improves accuracy and reduces trauma to surrounding tissues |
Recovery Timeline and Rehabilitation
The recovery time for bypass surgery varies. Patients usually spend several days in the hospital.
Rehabilitation is key for a smooth recovery. It includes physical therapy, dietary advice, and lifestyle changes to improve heart health.
Knowing about bypass surgery and recovery helps patients make informed choices. It leads to better outcomes.
Atherosclerosis Medical Procedures for Aortic Disease
Managing aortic atherosclerosis needs both surgery and endovascular methods. These treatments are key to dealing with the condition’s complexity and stopping further problems.
Open Surgical Repair for Aortic Atherosclerosis
Open surgery is a common way to treat aortic atherosclerosis, mainly for severe cases. It involves opening the chest to replace the damaged part with a graft. This method lets doctors directly see and fix the problem, which is vital for complex cases.
The TEMP-PREVENT trial is important for understanding how to treat aortic disease. It shows the need to tackle the root causes of aortic atherosclerosis.
Endovascular Approaches for Aortic Treatment
Endovascular methods are a less invasive option for treating aortic atherosclerosis. They use stent grafts to block off the diseased part of the aorta. This is great for patients who can’t handle open surgery because of other health issues.
- Endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR)
- Stent graft placement
- Angioplasty with stenting
These procedures are done under imaging, ensuring the stent graft is placed correctly. This reduces the chance of complications.
Complications and Their Management
It’s vital to manage complications from aortic atherosclerosis treatment to improve patient results. Issues like endoleaks, graft migration, and systemic problems need attention. Regular checks and follow-up care help catch and handle these problems early.
- Regular imaging studies to monitor graft position and function
- Clinical follow-up to assess for signs of complications
- Management of risk factors to prevent disease progression
By using both surgery and endovascular methods, and managing complications, we can better care for patients with aortic atherosclerosis.
Thoracic Aorta Atherosclerosis Treatment Options
Atherosclerosis of the thoracic aorta needs advanced treatments. These are tailored to each patient’s needs. We know how complex this condition is and the need for a detailed approach.
Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair (TEVAR)
TEVAR is a minimally invasive method for treating thoracic aortic disease. It involves placing a stent-graft in the aorta. This blocks the diseased part from blood flow, preventing further growth or rupture.
Benefits of TEVAR: It has fewer risks than open surgery, a quicker recovery, and is less invasive.
Open Surgical Techniques for Thoracic Aorta
Open surgery is a key treatment for thoracic aorta atherosclerosis. It’s for those not fit for TEVAR. The surgery involves opening the chest to replace the diseased part with a prosthetic graft.
Advantages of Open Surgery: It allows for direct repair and can be more durable.
Hybrid Procedures for Complex Cases
For complex cases, a hybrid approach is used. It combines open and endovascular techniques. This treats complex aortic problems that other methods can’t handle.
Hybrid procedures are flexible and tailored to each patient’s needs.
Post-Operative Monitoring and Follow-up
After treatment, patients need close monitoring for the best results. This includes regular imaging to check the repair and watch for complications.
| Treatment Option | Key Benefits | Post-Operative Care |
|---|---|---|
| TEVAR | Minimally invasive, reduced risk of complications, shorter recovery | Regular imaging, surveillance for endoleaks |
| Open Surgical Repair | Direct visualization, potentially more durable | Monitoring for surgical complications, long-term follow-up |
| Hybrid Procedures | Flexible, tailored to complex cases | Combination of endovascular and surgical follow-up protocols |
We know each patient is different. We’re dedicated to personalized care and support throughout treatment.
Comprehensive Arteriosclerosis Management Strategies
Managing arteriosclerosis is best done with a mix of medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and surgery when needed. We know that treating arteriosclerosis needs a detailed plan. This plan must tackle the disease’s complex nature.
Pharmacological Interventions
Medicines are key in fighting arteriosclerosis. We use statins, beta-blockers, and antiplatelet drugs to manage risk factors and slow the disease. The TEMP-PREVENT trial shows how important it is to treat arterial calcification with medicine. It shows how drugs can help patients get better.
Statins help lower cholesterol and prevent heart problems. Beta-blockers control blood pressure and heart rate. Antiplatelet agents stop blood clots that can cause heart attacks.
Lifestyle Modifications for Disease Management
Changing your lifestyle is vital for managing arteriosclerosis. We suggest eating healthy, exercising regularly, and not smoking. These steps help control risk factors, improve heart health, and make medicines work better.
- Eat more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Do regular aerobic exercises like walking or cycling
- Keep a healthy weight to lower heart risk
- Stay away from tobacco to prevent more damage
Integrating Medical Therapy with Surgical Approaches
Sometimes, surgery is needed to manage arteriosclerosis well. We consider angioplasty, stenting, and bypass surgery to improve blood flow and ease symptoms. Combining medicine with surgery gives patients the best care for their needs.
Deciding on surgery depends on how severe the arteriosclerosis is and if symptoms are present. Mixing medicine and surgery helps patients get better and live better lives.
Monitoring Disease Progression and Treatment Response
Keeping an eye on the disease is key to managing arteriosclerosis. We use tests to check how the disease is doing and how treatments are working. This helps us adjust our plans as needed. It lets us catch problems early and act fast to avoid bigger issues.
By taking a complete approach to managing arteriosclerosis, we can help patients get better and lower the risk of heart problems. Our goal is to give each patient care that fits their needs, improving their health and happiness.
Conclusion: Selecting the Optimal Treatment Approach
Choosing the right treatment is key to managing atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis. Treatments like angioplasty, stent placement, atherectomy, and bypass surgery help manage arterial disease. Each option has its own benefits.
At Liv Hospital, we focus on top-notch healthcare for international patients. Our team works together to find the best treatment for atherosclerosis or atherosclerotic treatment for each patient. This ensures the best results for everyone.
Knowing the different treatment for arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis treatment options helps patients make better choices. We aim to give personalized care that meets each patient’s unique needs. Our goal is to help patients achieve their best health and well-being.
What is atherosclerosis, and how is it different from arteriosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis is when plaque builds up in arteries. Arteriosclerosis is when arteries harden. We treat each differently based on the condition.
What are the risk factors for developing atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis?
High blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, and family history are risks. Knowing these helps us manage the disease better.
What diagnostic techniques are used to assess atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis?
We use ultrasound and CT scans for non-invasive checks. Angiography is used for more detailed views of blockages.
What is angioplasty, and how is it used to treat arteriosclerosis?
Angioplasty is a procedure to widen narrowed arteries. It helps restore blood flow and prevent complications.
What are the different types of stents used in stent placement procedures?
We use bare metal stents and drug-eluting stents. The choice depends on the patient’s needs.
What is atherectomy, and how is it used to remove arterial plaque?
Atherectomy removes plaque from arteries. We use it to manage plaque buildup.
What is bypass surgery, and when is it used to treat severe arterial blockages?
Bypass surgery creates a detour around blocked arteries. It’s used for severe blockages to restore blood flow.
What are the treatment options for aortic atherosclerosis?
We treat aortic atherosclerosis with open surgery and endovascular methods. We also manage complications.
What is TEVAR, and how is it used to treat thoracic aorta atherosclerosis?
TEVAR is a procedure to place a stent graft in the thoracic aorta. It repairs damaged sections.
How can pharmacological interventions and lifestyle modifications help manage arteriosclerosis?
Medications manage risk factors and slow disease. Diet and exercise improve cardiovascular health.
How do you integrate medical therapy with surgical approaches for managing arteriosclerosis?
We combine medical therapy with surgery for complete care. This optimizes patient outcomes.
What is the importance of monitoring disease progression and treatment response?
Regular monitoring helps adjust treatment plans. It ensures the best outcomes for patients.
Reference:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29573979
https://ajronline.org/doi/full/10.2214/ajr.174.4.1741119



































