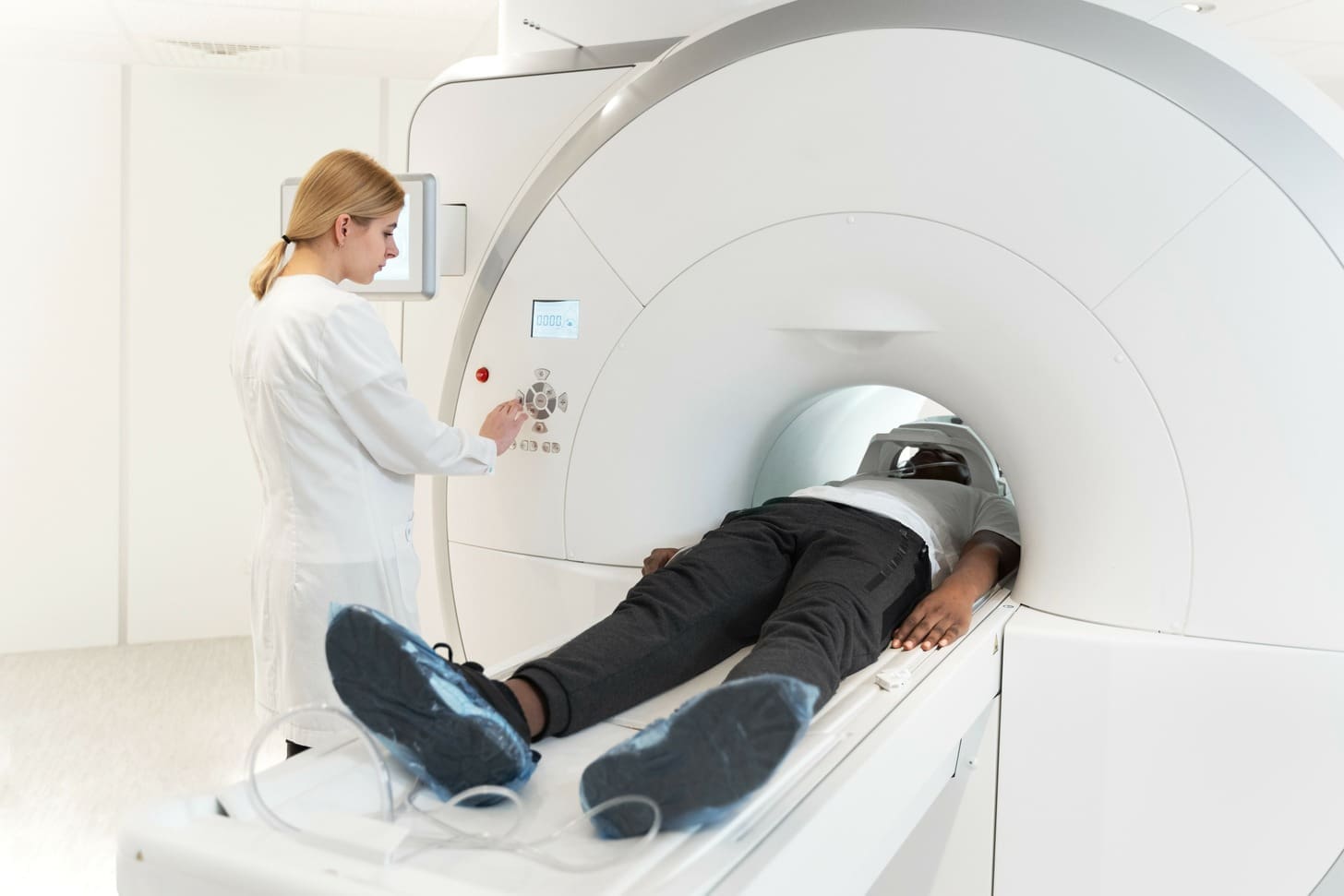
At Liv Hospital, we know how vital it is to check heart health fast and right. Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography (CCTA) is a key tool in cardiology. It’s a non-invasive way to look at coronary artery disease.
We use top-notch CCTA tech to give clear answers for heart issues. This test uses contrast dye and CT tech to show the heart’s blood vessels. It lets us check heart health fully.
Knowing about CCTA helps both patients and doctors. In this article, we’ll cover the main points about CT angiogram for coronary arteries. We’ll look into CCTA heart tests.
Key Takeaways
- CCTA is a non-invasive imaging test that uses contrast dye and advanced CT technology.
- It provides detailed images of the heart’s blood vessels, helping diagnose coronary artery disease.
- CCTA has become a key tool in cardiology, giving a safe and accurate way to check.
- Understanding CCTA helps patients and doctors see its value in modern heart care.
- Liv Hospital uses advanced CCTA tech for detailed heart health checks.
Understanding CT Angiogram for Coronary Arteries: The Basics
Learning about CT angiogram for coronary arteries is key for those thinking about this test. Coronary CT angiography, or CCTA, is a big deal in cardiology.
What is a Coronary CT Angiogram?
A coronary CT angiogram is a test that doesn’t hurt and uses X-rays to see the heart and blood vessels. It helps find and check coronary artery disease (CAD) by looking at the arteries and spotting any problems.
For a OCT-9217CCTA test, a special dye is put into your blood to make the arteries show up. Then, a CT scanner takes pictures of your heart. These pictures are turned into 3D models.
How CCTA Differs from Traditional Imaging
CCTA shows the coronary arteries directly, unlike stress tests or echocardiograms. This means it can spot heart disease more accurately and early on.
Unlike invasive tests, CCTA is safe and doesn’t hurt because it uses CT technology, not a catheter. This makes it easier for patients.
| Imaging Method | Invasiveness | Diagnostic Use |
|---|---|---|
| CCTA | Non-invasive | Direct visualization of coronary arteries |
| Invasive Coronary Angiography | Invasive | Detailed assessment of coronary artery disease |
| Stress Test | Non-invasive | Assesses heart function under stress |
The Evolution of Coronary Imaging Technology
Coronary imaging has changed a lot, thanks to better CT scanners. Now, images are quicker and clearer, cutting down on procedure time and radiation.
New contrast dyes have also made CCTA images better. This means doctors can see the arteries more clearly and make more accurate diagnoses.
The Science Behind CCTA: How the Technology Works

Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography (CCTA) is a cutting-edge medical technology. It gives us detailed views of the heart’s blood vessels. Advanced CT scanners take many images from different angles, then make detailed 3D pictures.
Advanced CT Technology Explained
CCTA heart tests use top-notch CT technology for clear artery images. Advanced CT scanners use multidetector computed tomography (MDCT). This lets them take many slices of the heart at once, making images sharp and quick.
Studies show CCTA gives high-quality heart images. This helps doctors diagnose and plan treatments well. The advanced CT tech in CCTA has greatly improved finding heart disease.
| Feature | Traditional CT | Advanced CT for CCTA |
|---|---|---|
| Detector Rows | Fewer than 64 rows | 64 rows or more |
| Scan Time | Longer scan times | Faster scan times |
| Image Resolution | Lower resolution | Higher resolution |
The Role of Contrast Dye in Visualization
The CCTA procedure uses contrast dye to make arteries visible. Contrast dye is injected into the blood. It makes the arteries show up clearly in CT images by absorbing X-rays differently.
Creating Three-Dimensional Heart Images
The images from CCTA are turned into detailed 3D heart models. This uses special software to combine CT slices into one image. The 3D images show the heart’s arteries clearly, helping doctors spot problems.
Understanding CCTA’s technology shows its importance in heart disease diagnosis and treatment. The mix of advanced CT and contrast dye lets doctors see the heart’s blood vessels clearly. This helps in making accurate diagnoses and treatment plans.
Key Benefits of CCTA Heart Scans
CCTA cardiac tests offer many advantages. They are safer, more detailed, and quicker than other tests. This makes CCTA a top choice for finding coronary artery disease.
Non-Invasive Nature: Comfort and Safety
CCTA heart scans are non-invasive. They don’t need to go inside the heart like old tests do. This lowers the risk of problems and makes patients feel better.
Superior Detail Compared to Standard X-rays
CCTA shows more detail than X-rays. It lets doctors see the heart’s arteries clearly. They can spot blockages or problems easily.
Research shows CCTA catches heart disease early. This helps doctors act fast and stop big heart problems.
Speed and Efficiency of Diagnosis
CCTA is fast and efficient. It only takes a few minutes. This quickness helps doctors make quick decisions for patients.
It also makes the whole process smoother. Doctors don’t need to do as many tests. This helps them plan treatment faster.
In short, CCTA heart scans are great. They’re safe, show more detail, and are quick. These reasons make CCTA a key tool for heart disease diagnosis.
Medical Indications: When Doctors Recommend a CCTA Test
Doctors use CCTA to see the coronary arteries clearly. This helps them diagnose and manage heart disease well. The CCTA test is key in cardiology, guiding treatment choices. We’ll look at why doctors suggest a CCTA test, its role in patient care.
Evaluating Chest Pain and Symptoms
Doctors often suggest a CCTA test for chest pain and symptoms of heart disease. Chest pain, or angina, means less blood to the heart. CCTA spots blockages or narrowings in the arteries. It lets doctors see how bad the problem is and choose the best treatment.
Following Up on Ambiguous Stress Test Results
Stress tests sometimes don’t give clear results, making diagnosis hard. A CCTA test can give more info for a clear diagnosis. It shows the arteries in detail, helping doctors decide on treatment.
Screening High-Risk Patients
CCTA is also for screening high-risk patients. This includes those with heart disease in the family, diabetes, or other risk factors. Early detection with CCTA can spot problems before symptoms show, leading to early treatment.
The Complete CCTA Procedure: What to Expect
Learning about the CCTA procedure can ease your worries. We’ll guide you through everything, from getting ready to recovering. This way, you’ll know what to expect at every step.
Before Your Appointment: Preparation Guidelines
Getting ready for a CCTA test is easy. Just follow what your doctor tells you. Don’t have caffeine or take certain meds before the test. Wear comfy clothes and take off any metal or jewelry.
Tell your doctor about any allergies or sensitivities, like to contrast dye. Our team will give you all the details you need.
During the Scan: Step-by-Step Process
The CCTA scan is quick. Here’s what happens during it:
- You’ll lie on a table that slides into the CT scanner.
- A contrast dye is given through an IV to see your coronary arteries.
- The scanner takes pictures of your heart from different angles.
- You might need to hold your breath for a few seconds for clear images.
- The whole thing usually takes 10-30 minutes.
After the Test: Recovery and Next Steps
After the scan, you’ll be watched for a bit to check for any dye reactions. Most people can go back to normal right away. Your doctor will talk about the results and what to do next.
“The CCTA procedure is a valuable diagnostic tool that provides critical information about the health of our patients’ coronary arteries. By understanding the process, patients can feel more comfortable and prepared for their test.”
Getting a medical test can be scary, but knowing what to expect helps. Our team is here to support you every step of the way through the CCTA procedure.
Interpreting CCTA Images: What Specialists Look For
Reading CCTA images is key to spotting coronary artery disease. Experts look at these images for important details. They check for blockages, plaque, and any unusual shapes in the heart’s arteries.
Identifying Coronary Artery Blockages
Spotting blockages in the heart’s arteries is a main goal. Specialists use CCTA images to find any narrowing or blockages. This helps them decide the best treatment for the patient.
CCTA images give a close look at the heart’s arteries. This lets experts find blockages that other tests might miss. Knowing about these blockages is key to treating the patient right.
Assessing Plaque Buildup and Composition
Experts also check the type and amount of plaque in the arteries. This info is vital for understanding the patient’s heart risk. It helps doctors plan a treatment that fits the patient’s needs.
Studies show CCTA images can show the details of plaque. This includes both hard and soft plaque. Knowing this helps doctors tailor treatments for each patient.
Evaluating Anatomical Abnormalities
CCTA images also help spot unusual shapes in the arteries. This includes looking at where the arteries start and how they run. It’s important for understanding the heart’s structure.
By looking at these shapes, doctors get a full picture of the heart. This helps them plan treatments and ensure the best care for the patient.
Comparing CT Angiogram Coronary Arteries to Other Cardiac Tests
Cardiac imaging has grown a lot, with tests like CCTA each having their own role. We’ll look at CCTA against other tests, like invasive angiography and stress tests. This will help us see their differences and when to use them.
CCTA vs. Invasive Coronary Angiography
Invasive coronary angiography is top for finding coronary artery disease. But, it’s a big deal because it needs a catheter in the arteries. CCTA, on the other hand, is non-invasive and uses CT scans to see the arteries. It’s as good as invasive angiography for some patients, but safer.
Key differences between CCTA and invasive coronary angiography include:
- Non-invasive vs. invasive procedure
- Use of contrast dye in both, but different administration methods
- Ability to visualize not just the lumen but also the vessel wall and surrounding structures with CCTA
CCTA vs. Stress Tests and Echocardiograms
Stress tests and echocardiograms check heart function and find ischemia. But, they don’t show blockages in arteries. CCTA, though, gives clear pictures of the arteries, showing plaque and stenosis.
The choice between these tests depends on the patient’s specific condition and the clinical question being addressed. Stress tests are great for finding ischemia. But, CCTA is better for seeing how bad coronary artery disease is.
When Each Test is Most Appropriate
Choosing a test depends on the patient’s symptoms, history, and what’s suspected. CCTA is good for those with coronary artery disease doubts who can’t have stress tests or invasive angiography. It’s also great for checking how severe the disease is.
In conclusion, CCTA is a big help in diagnosing and managing coronary artery disease. Knowing what CCTA can do helps doctors make better choices for their patients.
Potential Risks and Limitations of CCTA Heart Tests
CCTA heart tests are very useful for diagnosing heart disease. But, it’s important to know their risks and limits. Like any medical test, CCTA has its downsides.
Radiation Exposure Considerations
One big worry with CCTA is radiation. The test uses X-rays to see the heart’s arteries. Even though the dose is lower now, it’s a concern, mainly for young people or those needing many scans.
The radiation from a CCTA scan is like years of natural background radiation. But, the dose can change based on the scanner and the patient’s size.
| Scanner Technology | Average Radiation Dose (mSv) |
|---|---|
| Traditional CT | 10-15 |
| Advanced CT (High-Pitch Mode) | 1-3 |
Contrast Dye Reactions and Precautions
Another risk is reactions to the contrast dye. The dye contains iodine, which can cause allergies in some. Though rare, it’s key to tell doctors about any allergies or kidney issues.
To lower the risk of dye reactions, patients with kidney disease or diabetes might need special care. This could include drinking more water before the test or using different dyes.
Accuracy Limitations in Certain Patients
CCTA is usually very good at finding heart disease. But, it’s not perfect for everyone. For example, those with a lot of calcium in their arteries or who have had heart bypass surgery might have harder-to-read images.
Also, people with irregular heartbeats or who can’t hold their breath might struggle with image quality.
In summary, CCTA heart tests are very useful but come with risks and limits. Knowing these helps doctors and patients make better choices about when and how to use CCTA.
Advancements in CCTA Cardiology: Latest Developments
Technology in CCTA is changing how we find and treat heart disease. The field of CCTA cardiology is growing fast. We’re seeing better images, less radiation, and more use of artificial intelligence.
Improved Image Resolution Technologies
New CT tech has made images clearer. This lets doctors see the heart’s arteries better. High-resolution CCTA images help doctors make better choices for patients.
Reduced Radiation Exposure Techniques
One big problem with CCTA was the radiation. But new methods are cutting down on this risk. Prospective ECG gating and iterative reconstruction algorithms help lower doses without losing image quality. This makes CCTA safer for patients.
Artificial Intelligence in CCTA Interpretation
Artificial intelligence (AI) is now helping with CCTA. AI can spot tiny problems that humans might miss. This tech could make diagnoses more accurate and help doctors work faster.
As CCTA cardiology keeps getting better, we’ll see even more advanced tech. This will help doctors care for patients better. It will lead to better health outcomes and more effective heart disease management.
Cost and Insurance Coverage for Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography
Understanding the cost and insurance coverage for a CCTA test is key for patients and healthcare providers. It’s important to know these details to make smart choices in healthcare.
Average Costs in the United States
The price of a CCTA heart scan varies in the U.S. It can cost between $500 and $1,500. This depends on where you go, the location, and the technology used.
Several factors affect the cost:
- Facility Fees: Costs can differ between hospitals and outpatient centers.
- Geographic Location: Prices tend to be higher in cities than in rural areas.
- Technology and Equipment: More advanced CT scanners can raise the cost.
Insurance Coverage Guidelines
Insurance for CCTA varies by provider. Usually, Medicare and many private plans cover it if it’s medically needed.
To get coverage, patients should:
- Check their policy to see if CCTA is covered.
- Find out if they need pre-approval.
- Know any out-of-pocket costs, like deductibles and co-pays.
Questions to Ask Your Provider
When talking about a CCTA test, ask the right questions. This helps understand the financial side fully.
- What is the total cost of the CCTA procedure?
- Are there any extra fees for interpretation or consultation?
- How will my insurance cover the cost?
Being informed and proactive helps patients deal with the financial side of a CCTA test.
Conclusion: The Future of CCTA in Cardiac Care
CT angiogram coronary arteries, or CCTA heart scans, have changed cardiology a lot. They are now key in managing coronary artery disease (CAD).
Research shows CCTA will keep being important for CAD diagnosis and treatment. We’ll see better images, less radiation, and smarter analysis thanks to new tech.
The future of CCTA in cardiology is bright. It could lead to better diagnoses, better patient results, and more tailored care. As tech gets better, CCTA will stay a big part of heart care, helping doctors make smart choices.
Using CCTA well can help doctors give better care to patients with CAD. This can really improve people’s lives.
What is a CCTA test?
A CCTA (Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography) test is a non-invasive imaging method. It uses advanced CT technology and contrast dye to show detailed images of the heart’s blood vessels. This helps diagnose coronary artery disease.
How does CCTA differ from traditional imaging techniques?
CCTA is different because it’s non-invasive. It gives high-resolution images of the heart’s blood vessels. Traditional imaging might need invasive procedures or show less detail.
What is the role of contrast dye in CCTA?
Contrast dye in CCTA makes the heart’s blood vessels clearer. This helps doctors see blockages, plaque, and other issues more accurately. It’s key for diagnosing coronary artery disease.
Is CCTA a safe procedure?
CCTA is usually safe, but it involves radiation and contrast dye. Some people might react to the dye. Yet, the benefits often outweigh the risks for those with suspected coronary artery disease.
How do I prepare for a CCTA test?
To prepare for a CCTA test, avoid certain medications and fast as instructed. Remove metal objects and jewelry that could interfere with the scan. Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions.
What are the benefits of CCTA compared to other cardiac tests?
CCTA is non-invasive and provides high-resolution images. It can diagnose coronary artery disease without invasive procedures. It’s great for checking chest pain, ambiguous stress test results, and screening high-risk patients.
How is CCTA used in diagnosing coronary artery disease?
CCTA helps diagnose coronary artery disease by showing detailed images of the heart’s blood vessels. Specialists can spot blockages, assess plaque, and check for anatomical issues.
What are the potentially risks and limitations of CCTA?
Risks of CCTA include radiation exposure and dye reactions. There are also accuracy limits in some cases. But, technology advancements have reduced these risks, making CCTA a valuable tool in cardiac care.
How much does a CCTA test cost, and is it covered by insurance?
The cost of a CCTA test varies by location and provider. Insurance coverage also differs. It’s important to check with your provider to understand costs and coverage for CCTA.
What advancements have been made in CCTA technology?
Recent CCTA technology advancements include better image resolution and less radiation. Artificial intelligence is also being used in image interpretation. These improvements enhance CCTA’s diagnostic accuracy and safety.
References
- Coronary angiography. Retrieved from: https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/tests/coronary-angiography
- Coronary angiogram. Retrieved from: https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/coronary-angiogram
- Coronary angiography. Retrieved from: https://www.pennmedicine.org/treatments/coronary-angiography
- CT angiography. Retrieved from: https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info/angioct?PdfExport=1



































