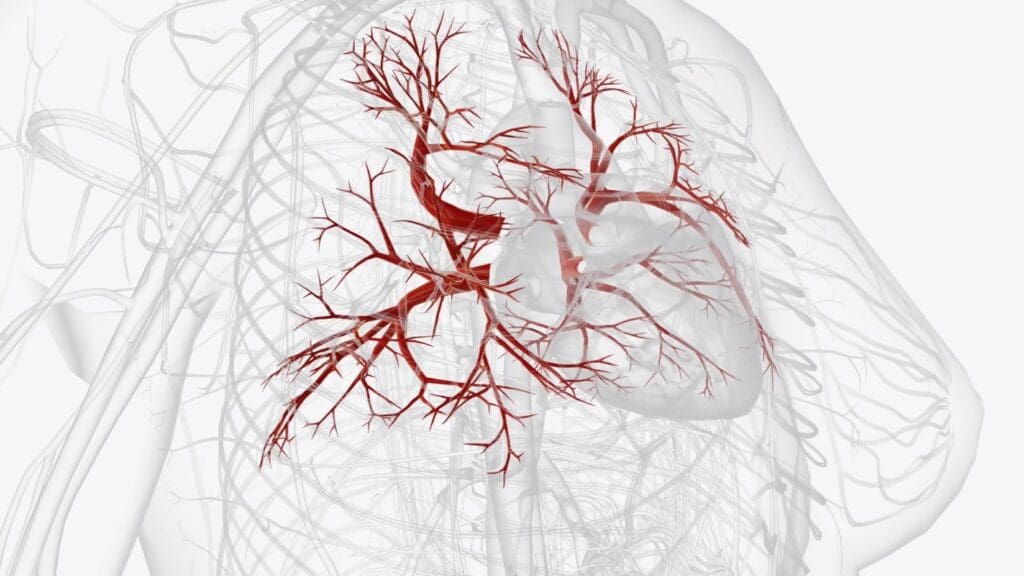
Knowing the difference between angiogram, arteriogram, and arteriography is key for good vascular health. At Liv Hospital, we use these advanced tools to give top-notch care to our patients from around the world.
Recent studies show these tests are very helpful. They help doctors make better decisions for their patients. We’ll explain the differences and similarities, so our patients know about their vascular health.
Our team is all about giving the best diagnostic results. We use the newest medical methods to make sure our care is trusted.
Key Takeaways
- Angiogram, arteriogram, and arteriography are diagnostic imaging techniques used in vascular medicine.
- These procedures are minimally invasive and improve patient outcomes.
- Liv Hospital utilizes advanced diagnostic tools for world-class healthcare.
- Understanding the differences between these terms is key for making informed choices.
- Our team is dedicated to delivering high-quality diagnostic outcomes.
Understanding Vascular Imaging Basics
Diagnostic imaging is key to keeping our blood vessels healthy. It helps doctors see inside our bodies and find problems early. This way, they can treat us better.
The Role of Diagnostic Imaging in Vascular Medicine
The Role of Diagnostic Imaging in Vascular Medicine
Diagnostic imaging is at the heart of vascular medicine today. It lets us look at blood vessels without surgery. We use vascular arteriogram and arteriography to find issues like blockages and aneurysms.
- Enables accurate diagnosis of vascular diseases
- Guides treatment planning and interventions
- Monitors disease progression and treatment efficacy
Thanks to these tools, we can make treatment plans that really help patients.
Evolution of Blood Vessel Visualization Techniques
Seeing blood vessels has changed a lot over time. We’ve moved from old angiography to new digital subtraction angiography. This makes pictures clearer and safer.
New tech keeps coming, making it easier to find and fix vascular problems.
Some big steps include:
- Improved image resolution
- Reduced contrast dye volumes
- Enhanced procedural safety
Defining Key Terms in Vascular Imaging
It’s important for patients to know the terms used in vascular imaging. This knowledge helps them understand their health results. Vascular imaging uses different methods to see blood vessels. Knowing these terms can help patients grasp their health issues and treatments.
What is an Angiogram?
An angiogram shows the blood vessels in the body. It uses X-ray technology and contrast dye. This dye is injected into the blood vessels to make them visible.
An angiogram can spot blockages, aneurysms, or other problems in blood vessels.
What is an Arteriogram?
An arteriogram is a special angiogram for arteries. It gives detailed views of the arteries. This helps doctors find any narrowings or blockages.
Like an angiogram, an arteriogram uses contrast dye and X-ray technology.
Understanding Angiography and Arteriography
Angiography and arteriography are the procedures for making angiograms and arteriograms. A catheter is inserted into a blood vessel. Through it, contrast dye is given.
X-ray images taken during these procedures show important details about blood vessels. They help find any issues.
While often used together, angiography means imaging of both arteries and veins. Arteriography is for arteries only. Knowing this can help patients understand their diagnosis better.
Angiogram vs Arteriogram: Key Differences and Similarities
Angiogram and arteriogram are tools to see blood vessels. But they focus on different things. An angiogram looks at many blood vessels, like arteries and veins.
Anatomical Focus: Vessels vs Arteries
The main difference is where they look. An angiogram looks at all blood vessels, including arteries and veins. An arteriogram only looks at arteries.
Here’s a simple table to show the difference:
| Procedure | Focus | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| Angiogram | Blood vessels (arteries and/or veins) | General vascular assessment |
| Arteriogram | Arteries | Specific arterial disease diagnosis |
Common Misconceptions and Interchangeable Usage
People often mix up angiogram and arteriogram. This can confuse patients. It’s important to know that arteriograms are a type of angiogram, but not all angiograms are arteriograms.
When Physicians Choose One Term Over Another
Doctors might pick one term over the other. For example, they might choose arteriogram for looking at arteries. This shows the focus of the test.
Knowing the differences helps doctors and patients talk better. It shows how vascular imaging works.
The Science Behind Contrast-Enhanced Vascular Imaging
Contrast-enhanced imaging is key in vascular medicine. It gives us deep insights into blood vessel health. These advanced methods help us make accurate diagnoses and plan treatments.
How Contrast Dyes Work
Contrast dyes, or agents, make body structures clearer in medical images. During an arteriogram procedure, they absorb X-rays. This makes blood vessels stand out on images.
Iodine is a common ingredient in these dyes. It absorbs X-rays well. As it moves through blood vessels, it changes their look on X-ray images. This makes it easier to see the vessels.
X-ray Technology in Vascular Visualization
X-ray tech is the core of contrast-enhanced vascular imaging. X-rays pass through soft tissues but get blocked by denser materials like bone and dyes. This contrast lets us see blood vessels.
Today’s X-ray systems are advanced. They take high-quality images with little radiation. These systems are vital for arteriography, where seeing arteries clearly is essential.
Digital Subtraction Techniques
Digital subtraction techniques are a big leap in vascular imaging. They take two images: one with dye and one without. Then, they subtract the without-dye image from the with-dye one. This leaves us with a clear image of blood vessels.
This method is great for contrast dye procedures. It makes blood vessels easier to see against other tissues. Digital subtraction improves image quality, helping with better diagnoses and treatment plans.
Step-by-Step: The Arteriography Procedure Explained
Learning about the arteriography procedure can help reduce anxiety. We’ll walk you through what happens from start to finish. This includes preparation, the procedure itself, and care after it’s done.
Patient Preparation and Considerations
Before arteriography, there are steps to take. These include:
- Telling your doctor about any allergies, like to contrast dyes
- Sharing any medications you’re on, like blood thinners
- Following diet instructions before the procedure
- Having someone drive you home
Arteriography is done under local anesthesia. This means you’ll be awake but won’t feel pain.
Catheter Insertion Techniques
The next step is putting a catheter into an artery. This is done using the Seldinger technique. First, a needle is used to make a small hole in the artery. Then, a guidewire and catheter are inserted.
We make sure the catheter is placed correctly. This is key for getting clear images of the blood vessels.
Contrast Administration and Image Capture
With the catheter in place, contrast dye is given to highlight the blood vessels. We then take X-ray images as the dye moves through. This gives us detailed info about the vessels and any blockages.
| Step | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Patient Preparation | Involves dietary instructions, medication disclosure, and allergy information | Ensures patient safety and procedure success |
| 2. Catheter Insertion | Using Seldinger technique to place the catheter in an artery | Crucial for accurate image capture |
| 3. Contrast Administration | Injecting contrast dye through the catheter | Highlights blood vessels on X-ray images |
| 4. Image Capture | Taking X-ray images as contrast dye flows through vessels | Provides detailed information about vessel structure |
Post-Procedure Care
After arteriography, we watch you for a bit to check for any problems. You might be told to:
- Rest for a few hours
- Avoid heavy lifting or strenuous activities for a day or two
- Follow up with your doctor to discuss the results and any further treatment
Knowing about the arteriography procedure can make patients feel more at ease and prepared.
Common Applications of Angiography
Angiography is key in today’s healthcare, helping with heart and brain checks. It lets doctors see the blood vessels clearly. This helps them make accurate diagnoses and treatment plans.
Coronary Angiography for Heart Disease
Coronary angiography is vital for heart disease diagnosis and treatment. It shows the coronary arteries’ condition. This helps spot blockages and narrow spots, guiding treatments like angioplasty and stenting.
This test is key for doctors to plan treatments that improve heart blood flow. It’s important for patient care.
Cerebral Angiography for Brain Conditions
Cerebral angiography looks at brain blood vessels. It helps find issues like aneurysms, AVMs, and stenosis. This is important for brain health checks.
It gives neurologists and neurosurgeons clear images. They use this to plan treatments, like surgery or endovascular procedures.
Pulmonary Angiography for Lung Assessment
Pulmonary angiography checks lung blood vessels. It’s mainly for diagnosing pulmonary embolism or other issues. The test uses contrast material in the pulmonary arteries.
This test is great for lung health checks. It’s used for patients with symptoms of pulmonary embolism or other lung problems.
Specialized Arteriogram Procedures
Specialized arteriogram procedures have changed vascular medicine a lot. They let doctors see specific parts of the blood vessels clearly. This helps them find the right treatment for each patient.
Leg Arteriogram for Peripheral Artery Disease
A leg arteriogram helps find peripheral artery disease (PAD). PAD happens when the arteries in the legs get narrow or blocked. This can cause pain and make it hard to move.
Key benefits of leg arteriograms include:
- Accurate diagnosis of PAD severity
- Guiding treatment decisions, such as angioplasty or stenting
- Monitoring disease progression over time
Renal Arteriogram for Kidney Evaluation
Renal arteriograms check the blood flow to the kidneys. They help find problems like renal artery stenosis. This is when the main artery to the kidney gets narrow.
The information obtained from a renal arteriogram can be critical for:
- Diagnosing renovascular hypertension
- Planning interventions to improve kidney function
- Assessing the need for surgical or endovascular repair
Mesenteric Arteriogram for Digestive System Assessment
Mesenteric arteriograms look at the blood vessels of the digestive system. They help find problems like mesenteric ischemia. This is when the intestines don’t get enough blood.
| Procedure | Primary Use | Key Diagnostic Information |
|---|---|---|
| Leg Arteriogram | Diagnosing Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) | Extent of arterial blockages or narrowing in the legs |
| Renal Arteriogram | Evaluating kidney blood supply | Renal artery stenosis, renovascular hypertension |
| Mesenteric Arteriogram | Assessing digestive system blood flow | Mesenteric ischemia, blockages in intestinal blood vessels |
These arteriogram procedures are big steps forward in vascular medicine. They give doctors clear images of the blood vessels. This helps them make better diagnoses and treatments.
From Diagnosis to Treatment: How Arteriography Guides Interventions
Arteriography is key in guiding medical treatments by showing detailed images of blood vessels. It’s vital for vascular specialists to see the patient’s vascular anatomy. This helps them plan and do complex treatments.
Planning for Angioplasty and Stent Placement
Arteriography is mainly used for planning angioplasty and stent placement. It shows doctors where blockages are in arteries. This helps pick the right stent size and type.
During the procedure, arteriography helps by showing the stent’s placement in real-time. This makes sure the stent is in the right spot. It also opens the artery well, improving blood flow.
Guiding Embolization Procedures
Arteriography is also key for embolization procedures. These block blood flow to certain body parts. This is needed for treating things like aneurysms or tumors getting too much blood.
Doctors use arteriography to find the right spot for embolization. They guide the catheter to the exact place. This is important for the procedure’s success and to avoid problems.
Evaluating Treatment Success
After treatments like angioplasty or stent placement, arteriography checks if they worked. It shows if blood flow is restored or bleeding stopped.
This check is very important. It lets doctors know if the treatment worked. It also helps spot any issues early. And it helps plan for more treatments if needed.
Risks, Complications, and Safety Considerations
Arteriography, like any invasive procedure, comes with risks and safety concerns. It’s a valuable tool for diagnosis, but knowing its risks is key for making informed choices.
Potential Complications of Catheter-Based Procedures
Arteriography involves putting a catheter into blood vessels. This can lead to bleeding or hematoma at the catheter site, infection, and vascular damage. Rarely, the catheter might cause a dissection or perforation of the blood vessel, needing immediate care.
To lower these risks, we stick to strict protocols for catheter insertion and patient monitoring. Our team is ready to handle any complications that might come up during or after the procedure.
Contrast Dye Reactions and Kidney Concerns
The contrast dye in arteriography can cause reactions in some patients. These can range from mild allergic responses to severe anaphylactic reactions. It can also harm those with pre-existing kidney disease, leading to contrast-induced nephropathy.
We take steps to reduce these risks by checking patients’ kidney function before the procedure. We also use other imaging methods when needed. Patients with allergies or kidney disease are closely watched during and after the procedure.
Radiation Exposure Considerations
Arteriography involves X-ray radiation, which carries a small risk of injury. We use the least amount of radiation needed to get clear images, following the ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) principle.
The radiation from arteriography is similar to other imaging procedures. We talk to our patients about the benefits and risks. We also take steps to reduce exposure, like in children and pregnant women.
Understanding arteriography’s risks and complications helps patients make better choices. Our team aims to provide safe and effective diagnostic services. We balance the benefits of arteriography with its possible risks.
Technological Advancements in Vascular Imaging
New technologies are making vascular imaging more precise. We’re seeing big improvements in this area. These changes are making diagnoses more accurate and safer for patients.
Digital and 3D Angiography
Digital angiography has changed vascular imaging a lot. It gives us clear images with less noise. The main benefits are:
- Enhanced image quality: This means doctors can make more accurate diagnoses.
- Reduced radiation exposure: This makes patients safer.
- Improved diagnostic accuracy: It helps doctors plan better treatments.
Also, 3D angiography gives a detailed view of blood vessels. This helps with complex procedures.
Hybrid Imaging Systems
Hybrid imaging systems mix different imaging types for a full view of blood vessels. They offer:
- Integration of anatomical and functional information: This boosts diagnostic skills.
- Enhanced diagnostic capabilities: Doctors can make more precise diagnoses.
- Better treatment planning: This leads to more effective treatments.
Reducing Radiation and Contrast Exposure
It’s important to cut down on radiation and contrast for patient safety. Ways to do this include:
- Using low-dose protocols: This reduces the radiation patients get.
- Implementing advanced image processing techniques: These improve image quality without needing high doses of radiation or contrast.
- Developing alternative contrast agents: This gives safer options for patients, like those with kidney problems.
Conclusion: The Future of Vascular Imaging
The future of vascular imaging is bright. New research and tech are changing how we find and treat vascular problems. At Liv Hospital, we’re all about using the latest imaging tech for our patients.
Arteriography will keep being key in vascular imaging. New tools like digital and 3D angiography give us clearer images. This helps us see the vascular system better.
We’re excited for more innovation in vascular imaging. This will lead to better ways to diagnose and treat patients. We’re committed to keeping up with these advancements. This way, we can give our patients the top care.
What is the difference between an angiogram and an arteriogram?
Angiograms and arteriograms are tests that use dye and X-rays to see blood vessels. An angiogram looks at all blood vessels. An arteriogram focuses on arteries.
What is arteriography?
Arteriography is a way to see arteries with dye and X-rays. It’s the method used for arteriograms.
Are angiography and arteriography the same?
Angiography looks at all blood vessels, including arteries and veins. Arteriography is just for arteries. But, they’re often used to mean the same thing.
What is the purpose of using contrast dye in vascular imaging?
Contrast dye makes blood vessels stand out in images. It absorbs X-rays, making vessels clearer.
What are the possible risks of arteriography?
Risks include dye reactions, kidney issues, radiation, and problems at the catheter site. These can be bleeding or infection.
How is arteriography used in planning treatments?
It gives detailed artery images. Doctors use these to plan treatments like angioplasty and stent placement. It helps them treat more effectively.
What advancements have been made in vascular imaging technology?
New tech includes digital and 3D angiography, and hybrid systems. These reduce radiation and dye use, making it safer and more accurate.
What is a leg arteriogram used for?
It’s for diagnosing leg artery disease. It shows artery problems in the legs, helping doctors find blockages or narrowing.
How does digital subtraction angiography improve image clarity?
It removes background, showing just the blood vessels with dye. This makes it easier to see and diagnose.
What is the role of X-ray technology in vascular imaging?
X-rays capture images of blood vessels during tests. They work with dye to show the vascular system clearly.
References
- Coronary angiography. Retrieved from: https://www.pennmedicine.org/treatments/coronary-angiography
- Catheter angiography. Retrieved from: https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info/angiocath
- Angiogram (Cardiac Catheterization). Retrieved from: https://www.ottawaheart.ca/test-procedure/angiogram-cardiac-catheterization
- Arteriogram. Retrieved from: https://www.healthline.com/health/arteriogram
- Angiogram/Arteriogram. Retrieved from: https://stanfordhealthcare.org/medical-tests/a/angiogram-arteriogram.html
- Peripheral Angiography. Retrieved from: https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/peripheral-artery-disease/diagnosing-pad/peripheral-angiogram