Thrombosis occlusion is a big health issue worldwide. It affects up to 900,000 people in the United States every year. At Liv Hospital, we are committed to providing world-class care for those with this condition. It’s linked to diseases like cardiovascular disease, deep vein thrombosis, and venous thromboembolism.
Knowing the key facts about thrombosis occlusion is key to managing it well. We understand the need for awareness and new ways to treat it. Our focus on patient care makes us a leader in treating thrombosis.
Key Takeaways
- Thrombosis occlusion affects a large number of individuals worldwide.
- Liv Hospital is committed to providing world-class care for thrombosis patients.
- Thrombosis is closely related to cardiovascular disease and other conditions.
- Awareness and modern protocols are key for managing thrombosis well.
- Patient-centered care is vital for better patient outcomes.
The Global Burden of Thrombosis Occlusion
Thrombosis occlusion is a big health issue worldwide. It needs our attention and good ways to handle it. Knowing how big of a problem it is helps us tackle it better.
Understanding the Scale: 900,000 Annual Cases in the United States
In the United States, there are about 900,000 cases of venous thromboembolism (VTE) each year. This includes deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). These issues cause serious problems and cost a lot in healthcare. We need to find ways to stop and manage these problems better.
Thrombosis as a Leading Preventable Cause of Hospital Death
Thrombosis occlusion is a top reason for hospital deaths that could be prevented. Research shows that using proven methods can lower the number of blood clots. We stress the need for pharmacological and mechanical prevention in people at high risk.
- Spotting high-risk patients early is key to stopping problems.
- Quick diagnosis and treatment can greatly help patients.
- Having clear management plans is vital to avoid more issues.
By grasping the global issue of thrombosis occlusion and its role in hospital deaths, we can aim to better patient care. This is through spreading awareness, prevention, and effective treatment.
Understanding Thrombosis Occlusion: Pathophysiology and Mechanisms
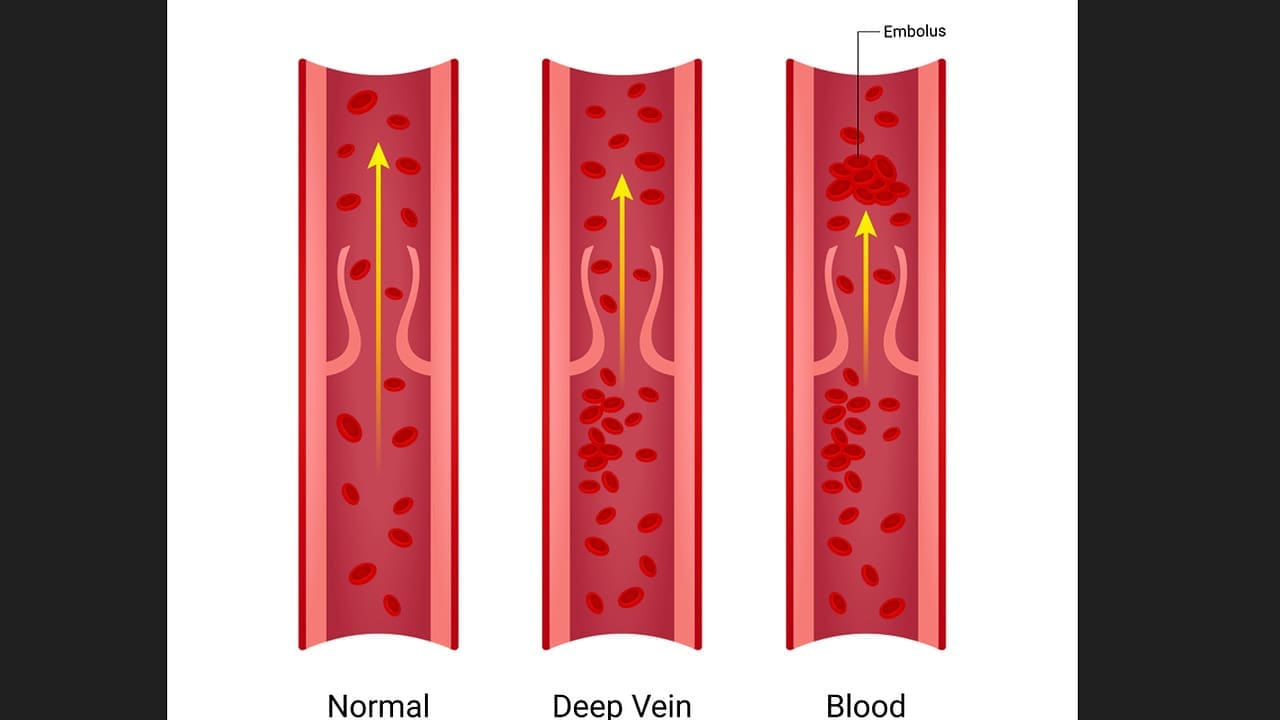
To understand thrombosis occlusion, we must explore its mechanisms and pathophysiology. It’s a condition where a blood clot blocks a blood vessel, stopping blood flow.
The Process of Pathological Blood Clot Formation
The formation of a blood clot involves several steps. These include platelet adhesion, activation, and aggregation. Also, thrombin and fibrin are generated. This complex process starts with injury to the blood vessel’s lining.
Arterial vs. Venous Thrombosis: Key Differences
Arterial and venous thrombosis have different causes and symptoms. Arterial thrombosis is linked to atherosclerosis and cardiac conditions. On the other hand, venous thrombosis is often caused by immobility, cancer, and genetic predispositions.
The Clotting Cascade and Occlusive Processes
The clotting cascade is a series of biochemical reactions that form a fibrin clot. Understanding this process is key to managing thrombosis. Interestingly, one in five cases of thrombosis is related to cancer therapy, showing the importance of careful management in oncology.
Major Types of Thrombosis Occlusion and Their Clinical Manifestations
Thrombosis occlusion is a complex condition with various clinical manifestations. These require prompt diagnosis and treatment. We will discuss the major types of thrombosis occlusion, including deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and arterial thrombosis, and their clinical manifestations.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): Pathology and Symptoms
Deep vein thrombosis occurs when a blood clot forms in the deep veins, typically in the legs. Risk factors for DVT include age, hospitalization, and pregnancy. Symptoms may include leg pain, swelling, and warmth.
- Pain or tenderness in the leg
- Swelling in the affected limb
- Warmth or redness in the affected area
Pulmonary Embolism: A Critical Complication
Pulmonary embolism is a life-threatening complication of DVT, occurring when a blood clot breaks loose and travels to the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath, chest pain, and rapid heart rate. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent serious consequences.
Arterial Thrombosis: Cerebral, Coronary, and Peripheral Manifestations
Arterial thrombosis occurs when a blood clot forms in an artery. This can lead to serious complications such as stroke, heart attack, or peripheral artery occlusion. Clinical manifestations vary depending on the location of the thrombosis. For example, cerebral arterial thrombosis can cause stroke, while coronary arterial thrombosis can cause myocardial infarction.
Key Risk Factors for Developing Thrombotic Events
It’s important to know the risk factors for thrombotic events to prevent and treat them well. These events, like deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism, can happen more often due to various factors.
Age as a Significant Risk Factor
As people get older, the risk of thrombotic events goes up. This is because older adults often move less, have other health issues, and their blood vessels change with age.
Cancer and Cancer Therapy: The 20% Connection
Cancer and its treatment raise the risk of blood clots. About one in five blood clot cases is linked to cancer treatment. So, it’s key to watch closely for signs in cancer patients.
Hospitalization and Immobility Risks
Being in the hospital or stuck in bed for a long time can lead to blood clots. People having big surgeries or those who can’t move much need special care to prevent this.
Pregnancy and Postpartum Period
Pregnancy and after giving birth are times when blood clots are more likely. The body’s changes, like more blood and higher pressure in veins, make this risk higher.
Other Contributing Factors: Genetics, Lifestyle, and Comorbidities
Other things that can raise the risk of blood clots include genes, lifestyle choices like smoking and being overweight, and other health problems like high blood pressure and diabetes. Knowing these can help in managing and assessing risks better.
Diagnostic Approaches to Thrombosis Occlusion
Diagnosing thrombosis occlusion needs a detailed plan. This includes checking the patient, using imaging, and lab tests. We will look at each step closely.
Clinical Assessment and Risk Stratification
First, we assess the patient clinically. We use tools to find out who might get thrombosis. These tools look at age, medical history, and current health.
Imaging Techniques: Ultrasound, CT, MRI, and Angiography
Imaging is key to confirming the diagnosis. Ultrasound, CT scans, MRI, and angiography give us clear images.
| Imaging Technique | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Ultrasound | Non-invasive, quick, and cost-effective | Limited depth penetration, operator-dependent |
| CT Scan | High sensitivity, detailed images | Radiation exposure, contrast required |
Laboratory Tests and Biomarkers
Laboratory tests help confirm the diagnosis. D-dimer assays and other biomarkers show if there’s thrombotic activity. We look at these results with the patient’s symptoms and imaging.
Recent studies show we need to do better in managing thrombosis. A thorough diagnostic approach can lead to better patient care and fewer complications.
The Clinical Impact of Thrombosis on Patient Outcomes
Thrombosis has a big impact on patient outcomes. It can cause serious health problems and even death. It affects patients in many ways.
Acute Complications and Management Challenges
Thrombosis can lead to serious conditions like pulmonary embolism and stroke. These are life-threatening. Treating them quickly is key to prevent lasting damage.
We need to know about these risks to give the best care.
Long-term Sequelae: Post-Thrombotic Syndrome and Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension
Thrombosis can also cause long-term problems. Post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS) and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) are examples. PTS can cause pain and swelling, while CTEPH can lead to heart failure.
Quality of Life and Functional Impairments
Thrombosis can greatly affect a patient’s life. It can lead to less mobility, pain, and a lower quality of life. Using proven treatments can help lessen these effects.
| Condition | Impact on Quality of Life | Management Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Post-Thrombotic Syndrome | Chronic pain, swelling | Compression therapy, pain management |
| Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension | Progressive right heart failure | Anticoagulation, pulmonary endarterectomy |
Understanding thrombosis’s impact helps us manage it better. This can reduce complications and improve life quality.
Evidence-Based Management Protocols for Thrombosis Occlusion
Managing thrombosis occlusion involves several key protocols. These are vital for ensuring patients get the best treatment for their condition.
Anticoagulation Therapy: Options and Considerations
Anticoagulation therapy is a mainstay in treating thrombosis occlusion. We have many anticoagulants, like heparin and warfarin, and newer options like DOACs. The right choice depends on the patient’s health, risk of bleeding, and the situation.
DOACs are often chosen for their ease of use and less need for blood tests. Warfarin might be better for those needing close blood test monitoring.
Thrombolytic Therapy and Interventional Approaches
Thrombolytic therapy is used for severe cases like massive pulmonary embolism or stroke. It aims to quickly dissolve clots and restore blood flow.
Interventional methods, like catheter-directed thrombolysis, target the clot directly. This can be more effective and safer than traditional methods.
Surgical Interventions: Thrombectomy and Vascular Procedures
Surgery is considered for those not helped by other treatments or with large clots. Thrombectomy removes the clot, while vascular procedures like angioplasty or stenting fix stenotic lesions.
These surgeries are often part of a larger treatment plan. They require careful patient selection and teamwork among healthcare professionals.
Protocol 1536: Emerging Classification and Management Updates
New protocols, like Protocol 1536, are changing how we manage thrombosis. This protocol helps standardize treatment, giving doctors a clearer guide for managing thrombotic events.
| Management Protocol | Description | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Anticoagulation Therapy | Use of anticoagulants to prevent clot formation | Renal function, bleeding risk, patient compliance |
| Thrombolytic Therapy | Dissolution of existing clots | Severity of condition, time to treatment, bleeding risk |
| Surgical Interventions | Surgical removal of clots or vascular repair | Clot burden, limb ischemia, patient comorbidities |
As we learn more about thrombosis occlusion, a multi-faceted approach to management is key. Keeping up with the latest evidence-based protocols ensures we provide the best care for our patients.
Inconsistencies in Thrombosis Management and Awareness
Recent studies have shown that there are big gaps in how we manage and talk about thrombosis worldwide. These gaps can lead to less than ideal care for patients. We know that managing thrombosis is complex. It involves many people and needs a wide range of solutions.
Gaps in Implementation of Evidence-Based Protocols
Even though we have good protocols for managing thrombosis, we struggle to use them. Healthcare workers often find it hard to follow guidelines in real life. This leads to different ways of treating patients.
This difference comes from not knowing enough, not getting enough training, and not having enough resources.
The Impact of Standardized Approaches on Reducing Complications
Using the same methods for managing thrombosis can really help. It makes care better, lowers the chance of blood clots, and improves overall care quality. We think everyone should use the same guidelines to fix the gaps in managing thrombosis.
Prevention Strategies and Risk Reduction Approaches
Preventing thrombosis occlusion is key to reducing its impact. It’s a complex task that involves many people and methods. We need to tackle it from all angles.
Pharmacological Prophylaxis in High-Risk Populations
For those at high risk, like surgery patients or those with clot history, medicine is a big help. Anticoagulant medications stop clots from forming. The right medicine depends on the patient’s health and other factors.
Mechanical Prophylaxis Methods
Methods like graduated compression stockings and intermittent pneumatic compression devices are also effective. They help blood flow better in the legs, which lowers the risk of clots.
Patient Education and Self-Management Strategies
Teaching patients about thrombosis risks and signs is vital. It helps them catch problems early. Patients should stay active and follow their treatment plans closely.
| Prevention Strategy | Description | Target Population |
|---|---|---|
| Pharmacological Prophylaxis | Use of anticoagulant medications to prevent clot formation | High-risk surgical patients, patients with history of thrombotic events |
| Mechanical Prophylaxis | Use of graduated compression stockings and intermittent pneumatic compression devices | Hospitalized patients, patients at risk of immobility |
| Patient Education | Education on signs of thrombosis and self-management strategies | All patients at risk of thrombosis |
Liv Hospital’s Multidisciplinary Approach to Thrombosis Management
Liv Hospital’s thrombosis management program is all about teamwork. Our team of experts works together to give our patients the best care. This care goes from the first diagnosis to after treatment.
Global Competitiveness Through Academic Excellence
We aim to be the best globally by using the latest in thrombosis management. Our commitment to academic excellence keeps us ahead in medical science. This means our patients get the newest and most effective treatments.
Implementation of Latest Multidisciplinary Care Pathways
We use the latest care pathways to ensure top-notch care for our patients. Our care pathways are designed to be flexible and responsive to each patient’s needs. They follow the latest research and guidelines.
The ‘5-Star Tourism Healthcare’ Philosophy in Practice
Liv Hospital follows the ‘5-star tourism healthcare’ philosophy. We aim to give an amazing patient experience. We understand that international patients have unique needs, and we meet these needs with our support services.
Commitment to High Ethical Standards and Continual Improvement
At Liv Hospital, we stick to the highest ethical standards in thrombosis management. We continually review and improve our practices to ensure the best care for our patients. We follow international best practices and guidelines.
Conclusion: Advancing Thrombosis Care Through Awareness and Implementation
Improving thrombosis care needs a mix of awareness and using proven methods. Knowing the risks and how thrombosis works helps us manage and stop its problems. The study on venous thromboembolism shows how important it is to prevent blood clots in people at high risk, like those getting chemotherapy.
Using set management plans can greatly lower the number of blood clot events. Places like Liv Hospital show how a team effort can lead to better patient results. By using the latest research and guidelines, we can make thrombosis care better and help more patients.
Our goal to improve thrombosis care is key to lessening its global impact. By teaming up and following the best practices, we can make life better for those at risk of blood clots.
What is thrombosis occlusion?
Thrombosis occlusion is when a blood clot forms inside a blood vessel. This blockage can cause serious health problems.
What are the major types of thrombosis occlusion?
There are several types, including Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism, and arterial thrombosis. Each has its own symptoms.
What are the risk factors for developing thrombotic events?
Risk factors include age, cancer, and being in the hospital. Pregnancy and genetics also play a role.
How is thrombosis occlusion diagnosed?
Doctors use clinical assessment and imaging like ultrasound and CT scans. They also check lab tests and biomarkers.
What are the clinical impacts of thrombosis on patient outcomes?
Thrombosis can cause immediate problems and long-term issues like post-thrombotic syndrome. It can also affect quality of life and function.
What are the management protocols for thrombosis occlusion?
Treatment includes anticoagulation therapy and thrombolytic therapy. Surgery and vascular procedures may also be needed.
How can thrombosis occlusion be prevented?
Prevention includes using medicines and mechanical methods. Educating patients and teaching self-management is also key.
What is Liv Hospital’s approach to thrombosis management?
Liv Hospital uses a team approach. They focus on academic excellence and the latest care methods. They also aim for high ethical standards and improvement.
Why is awareness and implementation of evidence-based protocols important in thrombosis care?
Using proven protocols helps reduce complications and improves patient care. It shows the need for standard approaches.
What is venous thromboembolism?
Venous thromboembolism is when a blood clot forms in deep veins. It can travel to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism. It’s a big part of thrombosis occlusion.
How does clotting disorder affect thrombosis occlusion?
Clotting disorders can raise the risk of thrombosis. They affect how blood clots, leading to either too much bleeding or clotting.
References
- CDC (Blood Clots Facts & Stats) : https://www.cdc.gov/blood-clots/data-research/facts-stats/index.html
- National Blood Clot Alliance (Blood Clots in the United States) : https://www.stoptheclot.org/blood-clot-information/blood-clots-in-the-united-states
- NCBI Bookshelf (Venous Thromboembolism) : https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507708
- Thrombosis Canada (The Beat – February 2025) : https://thrombosis.org/patients/the-beat/the-beat-february-2025
- Barchart (New Survey Shows Management of Blood Clots is Inconsistent) : https://barchart.com/story/news/34691367/new-survey-shows-management-of-blood-clots-is-inconsistent-even-for-patients-with-the-same-risk-profile










