At Liv Hospital, we know how critical it is to tackle coronary ischemia. This is when the heart muscle doesn’t get enough blood. It usually happens because the coronary arteries are narrowed or blocked.
This issue is at the heart of ischemic heart disease. It’s a major reason for heart disease globally. We aim to give you a detailed look at this condition. We want to mix medical knowledge with empathy and understanding.
Our team is committed to top-notch healthcare. We support patients from all over the world. We’ll dive into the key facts about cardiac ischemia. This includes its causes, signs, and how it’s diagnosed. We want to help you understand this important health issue better.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding coronary ischemia and its impact on heart health.
- Recognizing the causes and risk factors associated with ischemic heart disease.
- Identifying the warning signs and symptoms of cardiac ischemia.
- Learning about the diagnostic approaches for coronary ischemia.
- The importance of seeking medical care from specialized institutions.
Understanding Coronary Ischemia: A Critical Heart Condition
Coronary ischemia is a serious heart condition where blood flow to the heart is reduced. It happens when the heart’s blood supply is blocked or narrowed. This blockage cuts down the oxygen reaching the heart.
Definition and Mechanism of Coronary Ischemia
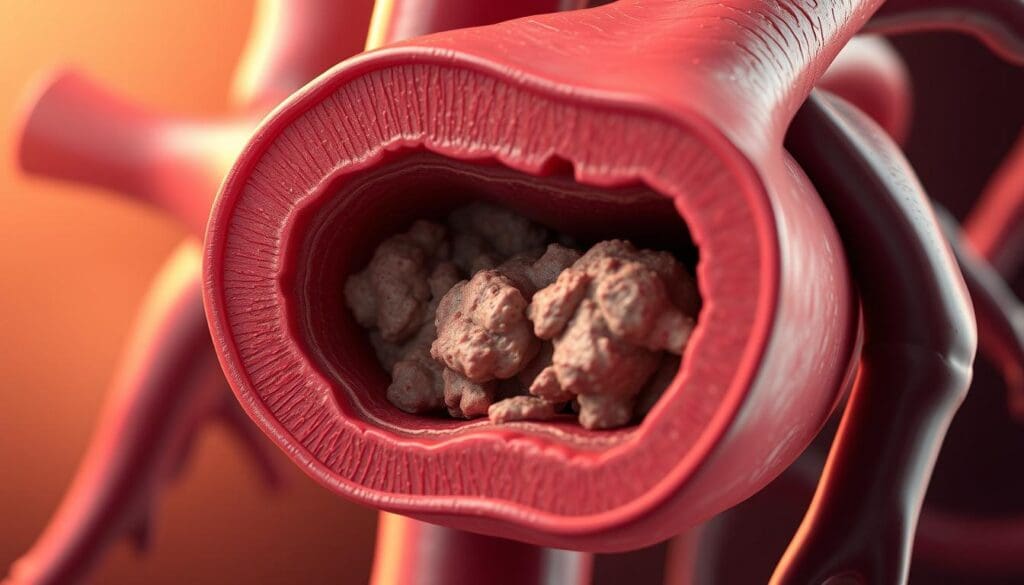
Coronary ischemia means the heart muscle doesn’t get enough oxygen-rich blood. This is because of a decrease in blood flow. Several things can cause this, like atherosclerosis, or plaque buildup in the heart’s arteries.
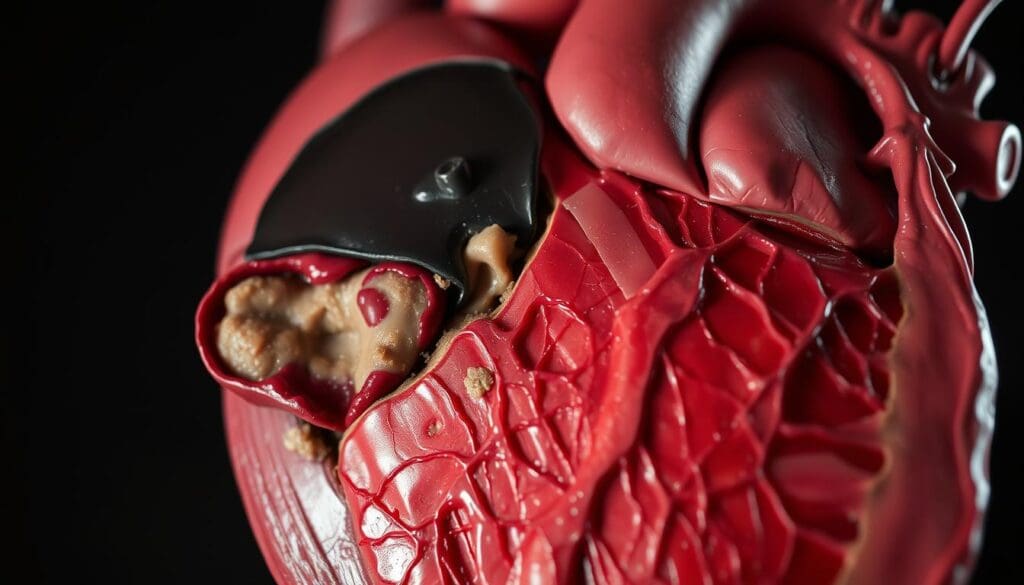
The heart’s arteries get narrowed or blocked. This can cause the heart muscle to become ischemic. Symptoms include chest pain (angina) or, in severe cases, a heart attack.
Global Prevalence and Impact
Coronary ischemia is a big health issue worldwide. Millions of people suffer from coronary artery disease, a main cause of this condition.
| Region | Prevalence of Coronary Ischemia | Impact on Mortality |
|---|---|---|
| North America | High | Significant contributor to cardiovascular deaths |
| Europe | Moderate to High | Major cause of mortality |
| Asia | Varies by country | Increasingly significant due to rising cardiovascular risk factors |
The global effect of coronary ischemia is huge. It affects not just death rates but also healthcare costs and the quality of life for those with it. It’s important to understand and tackle the risk factors to lessen its impact.
The Relationship Between Coronary Ischemia and Ischemic Heart Disease
Coronary ischemia is a key step towards ischemic heart disease. This disease is a major cause of illness and death worldwide. It happens when the heart doesn’t get enough blood, causing damage to the heart muscle. We will look at how coronary ischemia leads to ischemic heart disease and the differences between acute and chronic ischemia.
How Coronary Ischemia Leads to Ischemic Heart Disease
Coronary ischemia happens when the heart’s blood supply is cut off. This is due to narrowed or blocked coronary arteries. Without enough blood, the heart muscle doesn’t get enough oxygen, leading to ischemia. If this goes on for too long, it can damage the heart muscle, causing ischemic heart disease.
The process involves several key steps:
- Atherosclerosis: The buildup of plaque in the coronary arteries.
- Narrowing of the arteries: Plaque buildup reduces the diameter of the arteries.
- Reduced blood flow: Narrowed arteries restrict blood flow to the heart.
- Ischemia: Insufficient blood flow leads to oxygen deprivation.
- Cardiac damage: Prolonged ischemia damages the heart muscle.
Differentiating Between Acute and Chronic Ischemia
Ischemia can be acute or chronic. Knowing the difference is key for the right treatment.
| Characteristics | Acute Ischemia | Chronic Ischemia |
|---|---|---|
| Onset | Sudden | Gradual |
| Duration | Short-term | Long-term |
| Causes | Often due to thrombosis or spasm | Typically due to progressive atherosclerosis |
| Symptoms | Severe chest pain, potentially leading to myocardial infarction | Stable angina, shortness of breath |
Acute ischemia needs quick medical help to avoid serious problems like heart attacks. Chronic ischemia can be managed with lifestyle changes and medicine, but it also needs careful watch.
Understanding the link between coronary ischemia and ischemic heart disease is vital. It helps us give better care and improve patient results.
Key Fact #1: Atherosclerosis Is the Primary Cause of Coronary Ischemia
Atherosclerosis is the main reason for coronary ischemia, affecting millions globally. We’ll look at how this disease causes coronary ischemia. We’ll focus on plaque formation and its effect on blood flow.
The Process of Plaque Formation
Plaque formation starts with damage to the artery’s inner layer. This damage lets lipids get in and build up. Over time, these lipids get oxidized, causing inflammation.
This inflammation brings in immune cells. As the plaque grows, it can become unstable. This can lead to a heart attack.
How Atherosclerosis Restricts Blood Flow
Atherosclerosis narrows arteries by building up plaque. This buildup reduces the artery’s size. It limits blood flow to the heart muscle.
This reduced blood flow can cause ischemia, which is worse during exercise or stress. It can also lead to chronic ischemia and symptoms like angina. In severe cases, it can cause a heart attack.
| Stage of Atherosclerosis | Effect on Blood Flow | Clinical Manifestation |
|---|---|---|
| Early-stage plaque formation | Minimal reduction in blood flow | Often asymptomatic |
| Advanced plaque buildup | Significant narrowing of the artery | Angina or chest discomfort during exertion |
| Plaque rupture | Acute blockage of the artery | Myocardial infarction (heart attack) |
Knowing how atherosclerosis causes coronary ischemia is key. It helps us find ways to manage it. By tackling the root causes, we can prevent atherosclerosis and lower the risk of coronary ischemia.
Key Fact #2: Major Risk Factors That Contribute to Coronary Ischemia
Several major risk factors contribute to the likelihood of developing coronary ischemia. Understanding these risk factors is key for prevention and management.
Modifiable Risk Factors
Modifiable risk factors are those we can change. The main ones for coronary ischemia are hypertension, high cholesterol, and smoking.
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, can damage blood vessel linings. This makes them more likely to block. High cholesterol, mainly LDL, helps form plaques in arteries. Smoking harms the heart and reduces blood flow.
| Modifiable Risk Factor | Description | Impact on Coronary Ischemia |
|---|---|---|
| Hypertension | High blood pressure | Damages blood vessel lining, increasing the risk of blockage |
| High Cholesterol | Elevated LDL cholesterol | Contributes to plaque formation in arteries |
| Smoking | Tobacco use | Damages cardiovascular system, reduces blood flow to the heart |
Non-Modifiable Risk Factors
Non-modifiable risk factors are those we can’t change. These include age, gender, and family history of heart disease. As we age, the risk of coronary ischemia grows. Men are generally at higher risk than pre-menopausal women, though women’s risk increases after menopause.
Having a family history of heart disease also raises your risk. While these can’t be changed, knowing them helps in preventing other risk factors.
| Non-Modifiable Risk Factor | Description | Impact on Coronary Ischemia |
|---|---|---|
| Age | Increasing age | Increases risk due to accumulation of other risk factors |
| Gender | Male or female | Men are at higher risk; women’s risk increases post-menopause |
| Family History | History of heart disease in family | Increases individual risk |
By tackling both modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors, we can lower the risk of coronary ischemia. This improves our overall heart health.
Key Fact #3: Recognizing the Warning Signs of Coronary Ischemia
Knowing the warning signs of coronary ischemia is key to better patient care. We’ll look at classic symptoms, secondary symptoms, and atypical presentations in different groups.
Classic Symptoms: Angina and Chest Discomfort
The most common sign of coronary ischemia is angina. It feels like chest pain or discomfort. This pain can feel like squeezing, pressure, or heaviness in the chest.
It often happens when you’re active or stressed. Rest or medicine can help ease it. It’s important to notice these signs to get help quickly.
Secondary Symptoms: Shortness of Breath and Fatigue
People with coronary ischemia might also feel shortness of breath and fatigue. This is because their heart isn’t getting enough oxygen. This makes it hard for the heart to pump blood well.
Shortness of breath can happen when you’re active or even when you’re resting. Fatigue is feeling very tired, even when you’re not active.
Atypical Presentations in Different Populations
Coronary ischemia can show up differently in different people. Women, older adults, and those with diabetes might have different or less obvious symptoms than the usual chest pain.
These can include pain in the upper body, nausea, feeling lightheaded, or even no symptoms at all. It’s important to know these variations to diagnose and treat correctly.
| Symptom | Classic Presentation | Atypical Presentation |
|---|---|---|
| Chest Pain | Squeezing or pressure in the chest | Pain in the upper body, not necessarily in the chest |
| Shortness of Breath | Occurs during exertion | Can occur at rest |
| Other Symptoms | Fatigue, nausea | Lightheadedness, dizziness |
Understanding all symptoms of coronary ischemia helps doctors make better diagnoses and treatment plans. Spotting these signs early is key to better patient care.
Key Fact #4: Silent Myocardial Ischemia Can Occur Without Symptoms
Silent myocardial ischemia is a serious issue where the heart gets less blood flow without any pain. This can be very dangerous because it often goes unnoticed until a major heart problem happens.
Understanding Silent Ischemia
Silent myocardial ischemia means the heart muscle gets less blood flow without any pain. Doctors can find it with tests like electrocardiograms (ECG) during stress tests or by constant monitoring.
Key characteristics of silent myocardial ischemia include:
- No noticeable symptoms despite reduced blood flow to the heart
- Often detected during routine medical examinations or stress tests
- Can be a precursor to more severe cardiac events if left unmanaged
Populations at Higher Risk for Silent Ischemia
Some groups are more likely to get silent myocardial ischemia. People with diabetes might not feel the usual pain because of nerve damage. Older adults and those with heart disease history are also at higher risk.
| Risk Factor | Description | Impact on Silent Ischemia Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Diabetes | Presence of diabetes mellitus, potentially leading to neuropathy | Increases risk due to possible symptom masking |
| Age | Older adults, typically above 65 years | Higher risk due to possible comorbidities and decreased symptom perception |
| History of Heart Disease | Previous myocardial infarction or coronary artery disease | Increases risk due to possible undetected ischemia |
It’s important to understand and spot silent myocardial ischemia early. By knowing the risk factors and using the right tests, doctors can help prevent serious problems.
Key Fact #5: Diagnostic Methods for Coronary Ischemia
Diagnosing coronary ischemia requires several important methods. These help doctors find the condition accurately. They are key for choosing the right treatment and improving patient care.
Electrocardiogram (ECG) Findings in Coronary Ischemia
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a basic tool for detecting coronary ischemia. It shows the heart’s electrical activity. ECG findings can indicate coronary ischemia through changes like ST-segment depression or T-wave inversion.
The ECG is very useful during chest pain episodes. But, a normal ECG doesn’t mean there’s no ischemia. Ischemia can be intermittent.
Stress Testing and Imaging Techniques
Stress testing is another essential method for diagnosing coronary ischemia. It watches the heart’s activity under stress, usually through exercise or medicine. Stress testing can reveal ischemia that’s not seen at rest.
Imaging like echocardiography or nuclear stress testing is often used with stress testing. These methods show the heart’s structure and function. They help spot ischemia or infarction areas.
- Nuclear Stress Testing: Uses small amounts of radioactive material to visualize blood flow to the heart muscle.
- Echocardiography: Employs ultrasound waves to create images of the heart, assessing its function and structure.
Biomarkers for Detecting Myocardial Damage
Biomarkers are vital for diagnosing myocardial damage from coronary ischemia. Troponin levels are a key biomarker for cardiac injury. High troponin levels show heart muscle damage, often from ischemia.
Other biomarkers, like creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB), are also used. But troponin is more specific and sensitive for myocardial infarction. Biomarkers help diagnose acute coronary syndromes and measure cardiac damage severity.
By using ECG findings, stress testing, imaging, and biomarkers, doctors can accurately diagnose coronary ischemia. They can then create a treatment plan that fits the patient’s needs.
Key Fact #6: Advanced Imaging Techniques Improve Diagnosis Accuracy
Advanced imaging has changed cardiology, making diagnosing coronary ischemia better. These methods let doctors see the heart and blood vessels clearly. This leads to better diagnoses and treatment plans.
Coronary Angiography
Coronary angiography is top for finding coronary artery disease, a big cause of ischemia. It’s an invasive method where a contrast agent is injected into the arteries. This shows blockages or issues on an X-ray.
Benefits of Coronary Angiography:
- High accuracy in detecting coronary artery disease
- Ability to assess the severity of blockages
- Guiding interventional procedures like angioplasty
CT Coronary Angiography
CT coronary angiography is a non-invasive option. It uses CT scans to see the coronary arteries. It gives a detailed view of the heart’s blood vessels without needing a catheter.
According to a study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, “CT coronary angiography has emerged as a valuable tool for the non-invasive assessment of coronary artery disease.”
| Imaging Technique | Invasiveness | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Coronary Angiography | Invasive | High |
| CT Coronary Angiography | Non-invasive | High |
Nuclear Imaging and MRI
Nuclear imaging, like PET, and MRI give more info. They show how well the heart works and if it’s viable. This helps find ischemia areas.
“Nuclear imaging and MRI have become indispensable tools in the assessment of coronary ischemia, providing insights into both anatomy and function.”
Using these advanced imaging methods, doctors can better diagnose coronary ischemia. This leads to quicker and more fitting treatments.
Key Fact #7: Early Diagnosis Significantly Improves Patient Outcomes
Early detection of coronary ischemia can greatly change patient outcomes. We know that catching it early is key to managing it well. Here, we’ll look at why early diagnosis matters and how it affects patients.
The Golden Hour in Acute Coronary Ischemia
The “golden hour” is a big deal in medical emergencies, like acute coronary ischemia. It’s the first hour after symptoms start. Getting a diagnosis early in this time can lead to better treatment and survival.
During this hour, doctors can give treatments like thrombolysis or PCI. These help get blood flowing to the heart again. This can lessen damage and help patients do better.
Long-term Prognosis with Proper Management
With the right care, patients with coronary ischemia can have a better future. Treatments like lifestyle changes, medicines, and procedures can help manage symptoms. They can also slow the disease’s growth.
A good treatment plan can also lower the chance of heart problems later. By tackling risk factors and using proven treatments, doctors can make patients’ lives better.
| Outcome | Early Diagnosis & Treatment | Delayed Diagnosis & Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Survival Rate | High | Low |
| Complication Rate | Low | High |
| Quality of Life | Improved | Reduced |
In summary, catching coronary ischemia early is vital for better patient outcomes. By acting fast and knowing the importance of early detection, we can give patients the care they need. This improves their long-term health and quality of life.
Treatment Approaches for Coronary Ischemia
There are many ways to treat coronary ischemia. These include medicines, procedures, and surgery. The right treatment depends on how bad the condition is, the patient’s health, and other things.
Medication Strategies
Medicines are key in treating coronary ischemia. They help ease symptoms, slow the disease, and prevent serious problems.
- Antiplatelet therapy: Medications like aspirin and clopidogrel stop blood clots from forming.
- Beta blockers: These lower the heart’s workload and its need for oxygen.
- Nitrates: Nitroglycerin and other nitrates widen blood vessels to relieve angina.
- Statins: These lower cholesterol, slowing plaque buildup.
We often mix these medicines for the best results. For example, a patient might take aspirin to prevent clots and a beta blocker to lower heart rate and blood pressure.
Interventional Procedures
When medicines aren’t enough, we might need to do procedures. These procedures help get blood flowing to the heart again.
- Angioplasty and stenting: A balloon is used to widen the artery, and a stent keeps it open.
- Atherectomy: This removes plaque from the artery.
These procedures are often done during coronary angiography. This test shows detailed images of the coronary arteries. The choice of procedure depends on where and how bad the blockage is.
Surgical Options
In some cases, surgery is needed to treat coronary ischemia well.
- Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG): This surgery bypasses blocked arteries with grafts, improving blood flow.
- Heart transplant: In very severe cases, a heart transplant might be considered.
These surgeries are for patients with severe coronary ischemia or those who haven’t gotten better with other treatments. Doctors carefully decide if surgery is right for a patient.
Prevention Strategies to Reduce Coronary Ischemia Risk
To lower the chance of getting coronary ischemia, it’s key to use a full prevention plan. This plan should mix lifestyle changes with managing risk factors through medicine.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making lifestyle changes is vital in stopping coronary ischemia. Important steps include eating well and being more active.
Dietary Changes: Eating lots of fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean meats can cut down coronary ischemia risk a lot.
Increased Physical Activity: Exercising often boosts heart health. It also helps control weight, lowers stress, and keeps blood pressure in check.
Medical Management of Risk Factors
Managing risk factors well is also key in stopping coronary ischemia. This means keeping blood pressure in check, controlling diabetes, and fixing lipid problems.
| Risk Factor | Management Strategy |
|---|---|
| Hypertension | Medication, lifestyle changes |
| Diabetes | Blood glucose monitoring, medication |
| Dyslipidemia | Statins, dietary changes |
By mixing these lifestyle changes with medical management, people can greatly lower their risk of coronary ischemia.
Conclusion: The Importance of Awareness and Timely Intervention
Coronary ischemia is a serious heart condition that needs quick action. We’ve covered the main facts about its causes, symptoms, and how it’s diagnosed. Knowing about it and acting fast is key to better health outcomes.
It’s important to know the risk factors and watch for symptoms of coronary ischemia. Acting quickly can greatly help patients. It can lower the chance of serious problems and make life better.
We stress the importance of being aware of your risk and getting help if you notice symptoms. By spreading the word and acting fast, we can lessen the impact of coronary ischemia. This helps people all over the world stay healthier.
Cardiac ischemia, often caused by coronary ischemia, shows how vital good heart care is. Taking care of your heart early can prevent many problems. This approach helps fight against heart issues.
What is coronary ischemia?
Coronary ischemia happens when the heart doesn’t get enough blood. This is often because of a blockage in the heart’s arteries. It leads to less oxygen for the heart muscle.
What are the symptoms of coronary ischemia?
You might feel chest pain or discomfort, known as angina. You could also get short of breath or feel very tired. Sometimes, you might not feel any symptoms at all, called silent myocardial ischemia.
How is coronary ischemia diagnosed?
Doctors use several tests to find coronary ischemia. These include an electrocardiogram (ECG), stress tests, and imaging like coronary angiography. They also look at biomarkers for heart damage.
What is the relationship between coronary ischemia and ischemic heart disease?
Coronary ischemia can cause ischemic heart disease. This happens when the heart muscle gets damaged because of less blood flow.
What are the risk factors for developing coronary ischemia?
Several things can increase your risk. These include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and smoking. Diabetes, age, family history, and genetics also play a role.
Can coronary ischemia be prevented?
Yes, you can lower your risk. Eating well, exercising regularly, and quitting smoking are key. Managing conditions like high blood pressure and high cholesterol is also important.
What are the treatment options for coronary ischemia?
Doctors use several ways to treat it. They might prescribe medicine or do procedures like angioplasty and stenting. In some cases, surgery like coronary artery bypass grafting is needed.
What is silent myocardial ischemia?
Silent myocardial ischemia is when you have coronary ischemia but don’t feel any symptoms. It often affects people with diabetes or a history of heart disease.
Why is early diagnosis of coronary ischemia important?
Finding it early is key. It helps doctors act fast, which can save your heart and improve your chances of a better outcome.
What is the significance of the “golden hour” in acute coronary ischemia?
The “golden hour” is the first hour after a heart attack. Quick action during this time can greatly improve your chances of survival by getting blood flowing back to the heart.
How does atherosclerosis contribute to coronary ischemia?
Atherosclerosis is when plaque builds up in the arteries. This can narrow or block them, reducing blood flow to the heart and leading to ischemia.
Reference:
- “Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)” – StatPearls / NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK564304/ (NCBI)
- “Silent Myocardial Ischemia Revisited, Another Silent Killer…” – PMC article. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10699249/ (PMC)
- “Atherosclerosis” – Nature Reviews Disease Primers. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41572-019-0106-z (Nature)
- “Silent Myocardial Ischemia: From Pathophysiology to Diagnosis and Treatment” – MDPI Biomedicines. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12020259 (MDPI)
- “Translational pathophysiology of ischemic heart disease” – ScienceDirect. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2666634023004051 (ScienceDirect)
“From Atherosclerotic Plaque to Myocardial Infarction — The Molecular Biology” – MDPI. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137295 (MDPI)