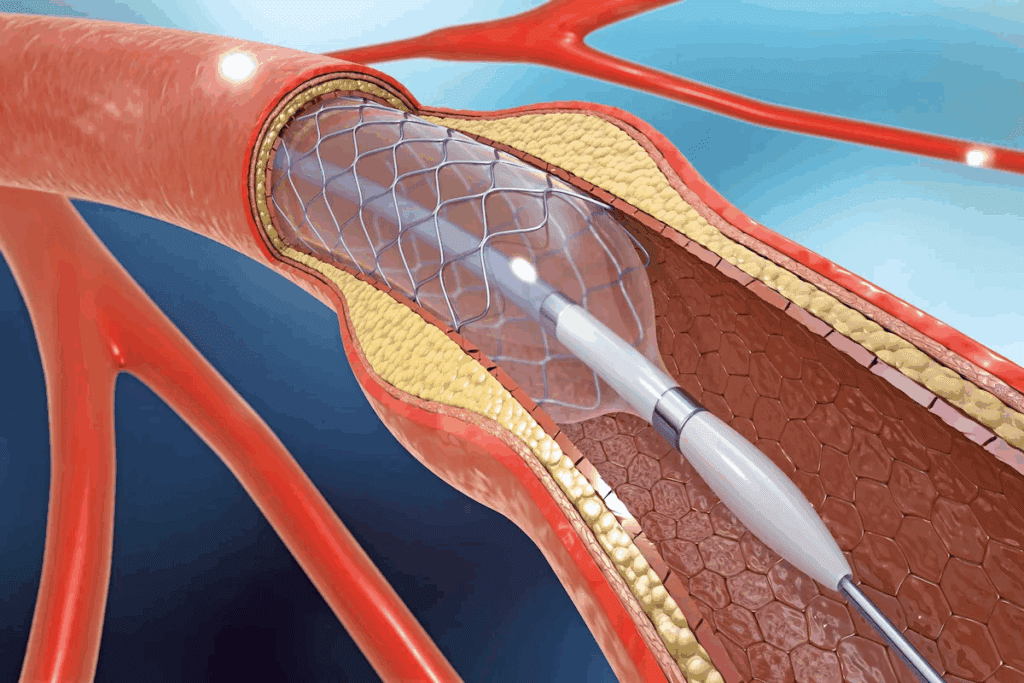
At Liv Hospital, we know how vital it is to keep blood flowing well to the heart. A stent is a tiny, metal mesh tube. It’s used to keep narrowed or blocked arteries open. This improves blood flow and lowers the risk of heart disease.
When a coronary artery gets blocked, it can cause serious health problems, like heart attacks. By putting in a stent, we can get blood flowing right again. This relieves symptoms and boosts heart health.
Our team at Liv Hospital uses cutting-edge, safe methods to put in stents. We aim for the best results for our patients. We focus on top-notch care and support to help patients reach their best heart health.
Discover what does a stent do in the heart and how it is used to improve blood flow.
Key Takeaways
- A stent is a small metal mesh tube used to hold open blocked arteries.
- Stents improve blood flow to the heart, reducing the risk of heart disease.
- Stent insertion is a safe and effective procedure for treating coronary artery disease.
- Liv Hospital provides innovative and internationally recognized heart stent procedures.
- Our team is dedicated to delivering world-class care and support to patients.
Understanding Coronary Artery Disease and Its Treatments
When plaque builds up in the coronary arteries, it can cause coronary artery disease. This condition happens when the arteries narrow or block, reducing blood flow to the heart. Symptoms include chest pain, known as angina.
If not treated, coronary artery disease can lead to heart attacks. A heart attack happens when a clot blocks blood flow to the heart muscle. Knowing the treatments for coronary artery disease is key to managing it and preventing heart attacks.
The Impact on Heart Health
Coronary artery disease affects heart health by reducing the heart’s function. The buildup of plaque restricts blood flow and can cause blood clots. The severity of coronary artery disease can vary, but its impact on heart health is always significant.
Overview of Treatment Options
Treating coronary artery disease involves lifestyle changes, medications, and sometimes surgery like stent placement. Medications help manage symptoms and slow disease progression. Lifestyle changes, like diet and exercise, are also important.
Stent placement is a common treatment for narrowed or blocked arteries. A stent is a small, mesh-like device that keeps the artery open. The choice of treatment depends on the disease’s severity and the patient’s health.
| Treatment Option | Description | Benefits |
| Medications | Drugs to manage symptoms and slow disease progression | Reduces symptoms, slows disease progression |
| Lifestyle Changes | Diet, exercise, and smoking cessation | Improves overall health, reduces disease severity |
| Stent Placement | Minimally invasive procedure to insert a stent | Restores blood flow, reduces angina |
Understanding these treatment options is essential for patients to make informed decisions about their care. By working closely with healthcare providers, individuals can develop a treatment plan that best suits their needs.
What Does a Stent Do in the Heart?
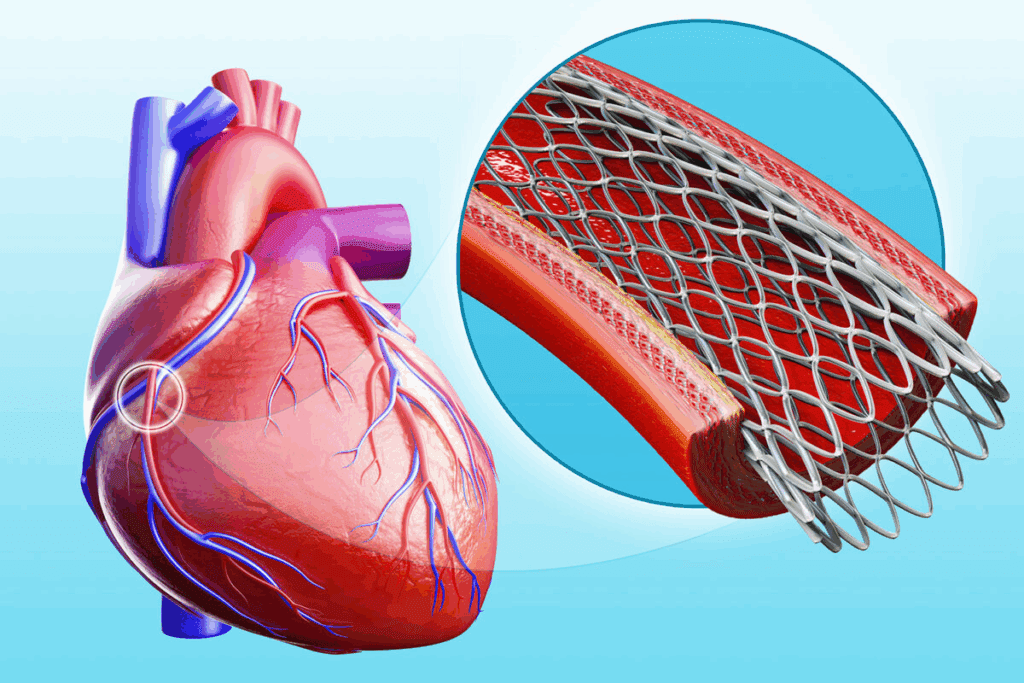
Stents are medical devices that keep arteries open. This improves blood flow to the heart. Understanding their role helps patients grasp how they manage coronary artery disease.
The Primary Function of Cardiac Stents
Cardiac stents provide structural support to blood vessels. They keep arteries open after angioplasty. This is key for healthy blood flow to the heart muscle.
Stents are made from materials like stainless steel and cobalt-chromium alloys. The material choice depends on the patient’s condition and stent needs.
How Stents Support Arterial Health
Stents are vital for arterial health. They ensure arteries stay open for unobstructed blood flow. This is critical after angioplasty to prevent artery narrowing.
Modern stents, like drug-eluting stents, release medication. This prevents scar tissue growth inside the artery. This advancement boosts stent success rates.
Stents keep arteries open, reducing chest pain (angina) symptoms. They improve patients’ quality of life. Regular check-ups are key to monitor stent performance and heart health.
The Evolution of Cardiac Stent Technology
Cardiac stent technology has changed a lot over the years. It has moved from simple designs to advanced devices today. This change aims to make treatments better, safer, and more effective.
Limitations of Early Stent Designs
Early stents were just metal mesh tubes. They helped keep arteries open but had big problems. One major issue was restenosis, or arteries getting narrow again. This often meant more surgeries, which was risky for patients.
Advancements in Modern Stent Technology
New stent technologies have made big improvements. Drug-eluting stents release medicine that helps prevent arteries from narrowing. This has greatly helped patients, making treatments more effective and lasting longer.
Bioabsorbable stents are another big step forward. They are temporary and dissolve after a few months. They support healing and then disappear, which could reduce long-term problems.
The growth of cardiac stent technology shows our dedication to better heart care. As we keep improving stent designs, we expect even better results and fewer risks for patients.
Types of Heart Stents Available Today
Today, there are many types of heart stents, each for different heart problems. The right stent depends on the patient’s health, the disease’s severity, and the blockage’s type.
Bare-Metal Stents: Structure and Applications
Bare-metal stents are made of metal mesh. They help keep the artery open. They’re good for people with a low risk of artery narrowing.
The main benefit of bare-metal stents is their simplicity and lower risk of complications from antiplatelet therapy. But, they have a higher chance of artery narrowing than drug-eluting stents.
Drug-Eluting Stents: Mechanism and Benefits
Drug-eluting stents have a coating that slowly releases medicine. This medicine stops new tissue growth that can narrow arteries. This technology has greatly lowered the chance of artery narrowing compared to bare-metal stents.
Drug-eluting stents are best for complex lesions or high-risk patients.
- Reduced risk of restenosis
- Effective for complex lesions
- Improved long-term outcomes
Bioabsorbable Stents: The Next Generation
Bioabsorbable stents dissolve over time. This new technology provides temporary support to the artery while it heals, without a permanent implant. They aim to reduce long-term problems from metal stents.
Specialized Stents for Complex Cardiac Conditions
For complex heart conditions, there are specialized stents. These include stents for specific features or high-risk patients. The development of these stents shows the ongoing effort to match treatments to each patient’s needs.
- Stents for bifurcated lesions
- Stents for chronic total occlusions
- Stents with unique coatings for enhanced biocompatibility
Materials Used in Heart Stent Manufacturing
Stents in cardiology are made from metals and biodegradable compounds. The material used is key because it affects how well the stent works and how safe it is for the body.
For a long time, stents were made from metals because they are strong and can be made thin and flexible. But, the metals used have changed over time to make stents better and safer.
Stainless Steel and Cobalt-Chromium Alloys
At first, stents were often made from stainless steel because it’s safe and strong. Today, stainless steel stents are used for some procedures. But, newer materials have become more common.
Cobalt-chromium alloys are now often chosen for stents. They are stronger, more flexible, and show up better on X-rays than stainless steel. This makes it easier to place the stent and reduces risks.
Platinum-Chromium and Other Metal Alloys
Platinum-chromium alloys are another big step forward in stent technology. They are clearer on X-rays, which helps doctors place the stent correctly and check on it later.
Other metal alloys are also being used in stents. Each has its own benefits. The search for new alloys is always ongoing, improving stent technology.
Biodegradable Materials in Modern Stents
Recently, biodegradable stents have become more popular. These stents dissolve over time, helping the artery heal before they disappear.
These stents are made from polymers and magnesium alloys. They might help avoid problems that can happen with permanent stents, like blood clots.
| Material | Properties | Benefits |
| Stainless Steel | Biocompatible, durable | Established track record, widely available |
| Cobalt-Chromium Alloys | Strong, flexible, radiopaque | Improved stent delivery, reduced complications |
| Platinum-Chromium Alloys | High radiopacity, biocompatible | Enhanced visibility, precise placement |
| Biodegradable Materials | Gradually absorbed by the body | Potential reduction in long-term complications |
As stent technology keeps getting better, we can expect even safer and more effective stents in the future.
“The future of stent technology lies in the development of materials that not only provide immediate relief but also ensure long-term health benefits for patients.”
The Cardiac Stent Procedure Explained
The cardiac stent procedure is a key treatment for heart blockages. It involves using a thin tube called a catheter to reach the heart. This tube carries a stent, a small mesh tube, to the blocked area.
Once in place, the stent is expanded to keep the artery open. This helps blood flow freely again. The stent also helps prevent the artery from getting blocked again.
Angioplasty is often done with stent placement. It uses a balloon to widen the artery. The stent is then placed to keep the artery open.
Recovery after a stent procedure is important. It helps the body heal and ensures the stent works well. Doctors will give specific instructions for recovery.
Is a stent a surgery? While it’s not a traditional surgery, it’s a medical procedure. It’s done in a hospital setting with a team of doctors and nurses.
Overall, the cardiac stent procedure is a common and effective treatment for heart blockages. It helps improve blood flow and prevent future blockages.
Benefits and Risks of Heart Stent Placement
Choosing to get a heart stent means looking at the good and bad sides. Heart stents help with coronary artery disease by making blood flow better to the heart.
Immediate and Long-Term Benefits
Heart stent placement has many benefits. Improved blood flow is one key advantage, easing symptoms like angina. Over time, stents can lower the risk of heart attack by keeping arteries open.
People often feel better after getting a stent. It can even be life-saving during a heart attack by quickly opening up the heart’s blood flow.
Potential Complications and Risks
Even though stent placement is usually safe, there are risks. These include blood clots forming in the stent, allergic reactions, and restenosis, or the artery narrowing again.
Other risks are bleeding or bruising at the catheter site, damage to blood vessels, and kidney problems from the dye used. Rarely, serious issues like stroke or heart attack can happen.
Factors Affecting Stent Success Rates
The success of a heart stent depends on several things. These include the patient’s health, other medical conditions, and following care instructions after the procedure. Lifestyle changes like not smoking, exercising, and eating well can help a lot.
The type of stent used also matters. For example, drug-eluting stents release medicine to prevent artery narrowing.
Living with a Heart Stent: What to Expect
A heart stent is a lifesaver. Knowing how to live with it is key for good health. After getting a stent, patients must follow a detailed care plan. This ensures the stent works right and avoids problems.
Medication Requirements After Stent Placement
Patients with a heart stent usually take medicines to stop blood clots. Dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) is often given. It includes aspirin and a P2Y12 inhibitor. How long you take DAPT depends on your stent type and health risks.
It’s important to take your medicines as told. Talking to your doctor about any worries or questions is a good idea.
- Take medications as directed by your doctor.
- Do not stop taking your medications without consulting your healthcare provider.
- Report any side effects or concerns to your doctor.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Optimal Stent Function
Healthy lifestyle changes are key for a heart stent to work well. This includes:
- Dietary Changes: Eating a heart-healthy diet with lots of fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean proteins helps manage cholesterol and blood pressure.
- Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity, like walking, boosts heart health. But, always check with your doctor before starting new exercises.
- Stress Management: Stress-reducing activities like meditation or yoga can help manage stress.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is a must, as it greatly increases the risk of problems.
One patient said, “Making these lifestyle changes wasn’t easy, but it was worth it to ensure my stent worked properly and to improve my overall health.” — John, heart stent recipient
Follow-Up Care and Monitoring
Regular check-ups with your doctor are vital for monitoring your stent and heart health. Your doctor may do tests like:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Stress test
- Angiogram
These tests catch any issues early, allowing for quick action.
By following your medication, making lifestyle changes, and going to regular check-ups, heart stent patients can live active and healthy lives. We’re here to support our patients every step of the way, providing all the care and guidance they need.
Conclusion: The Life-Saving Role of Cardiac Stents
Cardiac stents are key in treating coronary artery disease. They help keep blood flowing well to the heart. For years, stents have helped prevent heart attacks and improved life for heart disease patients.
Stents support artery health and have evolved over time. Today, we have different types of stents. These include bare-metal, drug-eluting, and bioabsorbable stents. They offer various treatments for complex heart conditions.
The main goal of stents is to keep arteries open. This ensures a steady blood supply to the heart. By knowing how stents work, patients can see their vital role. As cardiology advances, stents remain essential for heart health.
FAQ
What is a stent and what is its purpose in the heart?
A stent is a small, mesh-like device. It’s inserted into a narrowed or blocked artery. This improves blood flow to the heart.
Its main job is to keep the artery open. This reduces the risk of heart attack and eases symptoms like chest pain.
What is coronary artery disease and how is it treated?
Coronary artery disease happens when arteries narrow or block due to plaque buildup. This reduces blood flow to the heart.Treatment includes lifestyle changes, medication, angioplasty, and stent placement. These options help manage the condition.
What are the different types of stents available?
There are several stent types, like bare-metal stents, drug-eluting stents, and bioabsorbable stents. Each has its own benefits and uses.
What materials are used to make stents?
Stents are made from materials like stainless steel, cobalt-chromium alloys, and platinum-chromium alloys. There are also biodegradable materials. The choice depends on the patient’s needs.
What is the cardiac stent procedure like?
The cardiac stent procedure involves inserting a stent into a narrowed or blocked artery. It’s done under local anesthesia and takes 30-60 minutes.
What are the benefits and risks of heart stent placement?
Heart stent placement improves blood flow and reduces symptoms. It also lowers the risk of heart attack. But, there are risks like bleeding, infection, and stent thrombosis.
What can I expect after receiving a heart stent?
After getting a heart stent, you’ll need to take blood clot-preventing medication. You’ll also need regular follow-up care. Lifestyle adjustments may be necessary to keep the stent working well.
How long do stents last?
The lifespan of a stent varies. It depends on the stent type, patient health, and lifestyle. With proper care, stents can last many years.
Can I undergo an MRI with a stent?
Most modern stents are MRI-compatible. But, it’s important to tell your doctor about your stent before an MRI scan.
What is the difference between a stent and an angioplasty?
Angioplasty involves inflating a balloon to widen a narrowed artery. A stent is often used during angioplasty to keep the artery open.
Are stents a permanent solution?
Stents can provide long-term relief but are not a cure for coronary artery disease. Patients with stents need to manage their condition through lifestyle changes and medication.
References
- Udriște, A. S., et al. (2021). Cardiovascular stents: A review of past, current, and future technologies. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine, 32(5), 45. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8151529/




































