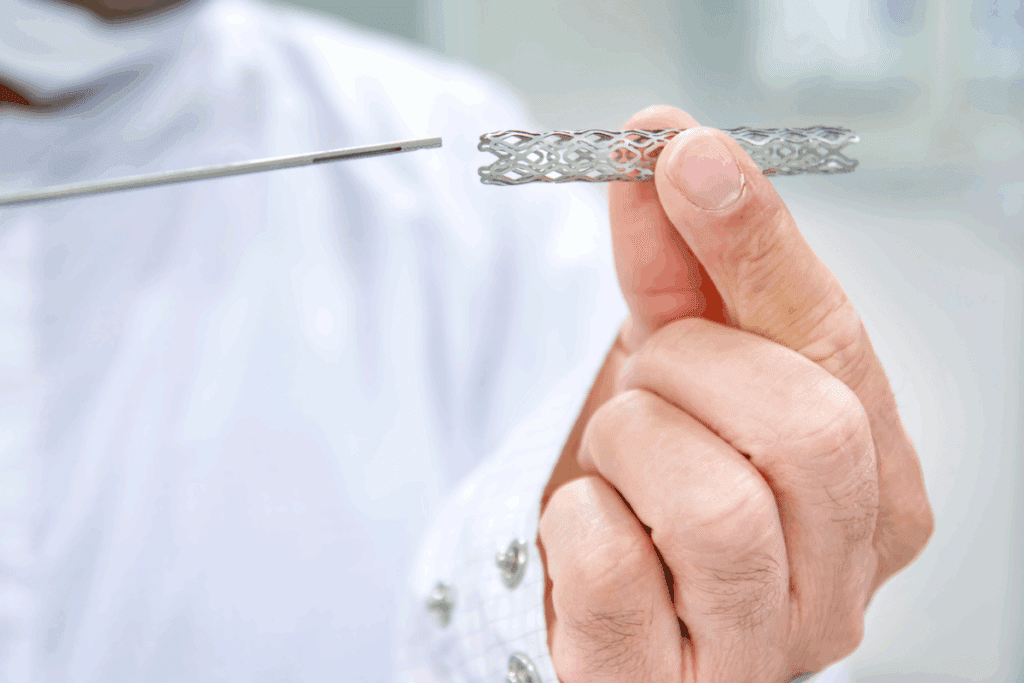
At Liv Hospital, we know how vital it is to grasp medical procedures. Aheart stent is a small, mesh tube that keeps arteries open. This improves blood flow to the heart. We use the latest technology to get the best results for our patients.
A stent is usually made of fine metal, like stainless steel, platinum-chromium, or cobalt-chromium. It’s made to expand. When put in, it looks like a tiny fishing net. It helps keep the artery open, improving blood flow.
Our team of experts is committed to giving personalized care and guidance. We help you from start to finish, making sure you’re okay.
See what does a heart stent look like, its size, and how it is inserted in the artery.
Key Takeaways
- Heart stents are small, mesh tubes used to keep arteries open.
- Stents are typically made of fine metals like stainless steel or platinum-chromium.
- The stent is designed to be expandable and resembles a tiny fishing net.
- Our team provides personalized care and guidance throughout the process.
- Liv Hospital uses advanced technology to ensure the best outcomes for patients.
Understanding Heart Stents: A Life-Saving Medical Device
Heart stents are key in treating coronary artery disease. They help keep blood flowing in narrowed arteries. This is important because narrowed arteries can cause chest pain, shortness of breath, or even heart attacks.
Stents help the heart get the oxygen and nutrients it needs. They play a big role in treating coronary artery disease. They not only restore blood flow but also prevent arteries from narrowing again after treatment.
The Role of Stents in Treating Coronary Artery Disease
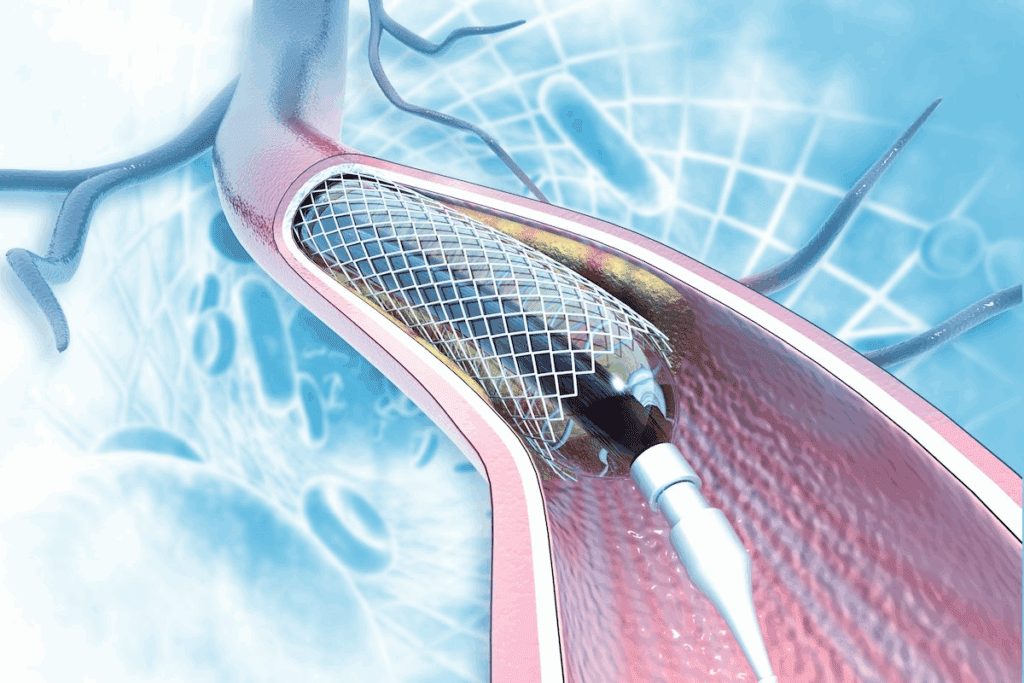
Stents are often used with balloon angioplasty to open blocked arteries. A catheter guides a balloon to widen the artery. Then, a stent is placed to keep it open, improving blood flow.
This procedure has changed how we treat coronary artery disease. It allows for faster recovery times compared to old surgical methods.
Evolution of Stent Technology
Stent technology has come a long way. Early stents were made of bare metal and sometimes caused arteries to narrow again. Now, we have stents that are safer. Drug-eluting stents, for example, release medicine to prevent arteries from narrowing.
Newer stents are made from materials like platinum-chromium and cobalt-chromium. These materials are more flexible and durable, making stents more effective.
Stent technology keeps getting better. Researchers are working on bioabsorbable stents and other new designs. These efforts aim to improve patient outcomes and lower the risk of complications.
What Does a Heart Stent Look Like?

Heart stents are small, wire mesh tubes. They are designed to keep an artery open. This helps increase blood flow to the heart.
The Cylindrical Mesh Design
A heart stent is a thin, wire mesh tube. It’s made to be flexible and expandable. This fits it snugly in the artery.
The mesh is usually made from metal alloys like stainless steel or platinum and chromium. This makes the stent strong and safe for the body.
Visual Comparison to Everyday Objects
Comparing a heart stent to everyday objects helps us understand it better. It’s like a tiny spring or a small mesh tube. It expands to keep a narrow passage open, just like a stent in an artery.
| Object | Size Comparison | Similarities |
| Spring | Similar diameter | Coiled structure |
| Mesh tube | Comparable length | Mesh design |
| Stent | – | Cylindrical, expandable |
By comparing a heart stent to familiar objects, we can grasp its appearance and function. Its cylindrical mesh design is key. It supports the artery and improves blood flow.
Materials Used in Modern Heart Stents
Modern heart stents are made from different materials, each with its own benefits. The material used affects how well the stent works and lasts.
Stainless Steel Stents
Stainless steel is a common choice for heart stents. It’s strong, doesn’t corrode easily, and shows up well under X-rays. Stainless steel stents have been a go-to for many years, helping patients with heart issues.
Platinum-Chromium and Cobalt-Chromium Stents
Newer stents are made from platinum-chromium and cobalt-chromium. These materials are more flexible and thinner, with better X-ray visibility. This makes them easier to place correctly, which can lead to better results for patients.
Benefits of Different Materials
Each material has its own advantages. For example, platinum-chromium stents are flexible and show up well on X-rays, making them easier to use. Cobalt-chromium stents are strong and thin, which can make them easier to insert and may lower the risk of problems.
It’s important for doctors and patients to know about the materials in heart stents. The type of stent used can impact how well the procedure goes and the patient’s long-term health. As technology gets better, we’ll likely see even more improvements in stent materials, leading to better care for patients.
How Big Is a Heart Stent? Dimensions Explained
Heart stents come in different sizes to fit various coronary arteries. Knowing the size of a heart stent helps us see how it fits and works. It’s key to restoring blood flow.
Length Variations: 8mm to 48mm
Stents vary in length to match different blockages and artery sizes. They usually range from 8 to 48 millimeters long. This flexibility helps in treating many blockage lengths.
Diameter Range: 2mm to 5mm
The diameter of a heart stent is also important. It must match the artery’s diameter for a good fit and function. Stents are usually 2 to 5 millimeters wide. This range fits the different sizes of coronary arteries.
Stents are made to be precise and adaptable. Their dimensions are chosen carefully for each patient’s anatomy. This ensures the best results.
The Heart Stent Insertion Procedure
Putting in a heart stent is called percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or angioplasty. It’s a way to fix blocked heart arteries without surgery. This method is less invasive and helps keep the heart working right.
Pre-Procedure Preparation
Before the stent is put in, tests are done to check the heart and arteries. These tests include blood work, electrocardiograms, and angiograms. Doctors also tell patients what to do before, like fasting or stopping some medicines.
Access Points: Wrist vs. Groin
Doctors choose where to put the catheter, either through the wrist or groin. Radial access, through the wrist, is preferred for less bleeding and faster recovery. But, it depends on the patient and the doctor’s choice.
Navigation to the Blockage Site
A thin, flexible tube called a catheter is used to reach the blockage. Real-time X-ray imaging helps guide it. When it gets to the blockage, a balloon is used to open the artery.
“The use of advanced imaging techniques during PCI has significantly improved the accuracy and safety of stent placement,” says a leading cardiologist.
Duration of the Procedure: What to Expect
The time it takes for a stent procedure varies. It can be from 30 minutes to several hours. Patients are usually awake and can go home the same day or next.
Knowing about the stent procedure can make patients feel better. It shows how doctors use new tech to help hearts and improve lives.
How Does a Heart Stent Work?
It’s important for patients to know how heart stents work. We’ll look at how stents are deployed, their immediate effects, and their long-term role in the artery.
Balloon Angioplasty and Stent Deployment
A heart stent is put in place with a balloon catheter. First, a catheter with a balloon is guided to the narrowed artery. The balloon is then inflated, expanding the stent against the artery walls.
The stent stays in place after the balloon is deflated and removed. This keeps the artery open. This method is called balloon angioplasty with stent placement.
Immediate Effects on Blood Flow
After the stent is in, it boosts blood flow right away. The expanded stent widens the artery, helping blood reach the heart muscle better.
This quick fix can lessen symptoms like chest pain and shortness of breath. It improves the patient’s life quality.
Long-Term Function Within the Artery
Over time, the stent keeps the artery open. It becomes part of the artery wall, with tissue growing around it. This makes it stable.
Drug-eluting stents release medicine to stop tissue growth. This helps keep the artery open for longer, improving the stent’s success.
Types of Heart Stents and Their Benefits
There are many types of heart stents, each with its own benefits. The right stent depends on the patient’s health, the blockage’s location and severity, and overall health.
Bare Metal Stents
Bare metal stents are made from metals like stainless steel. They help keep the artery open. They are simpler and cheaper than drug-eluting stents. But, they can cause tissue growth, leading to artery narrowing.
Drug-Eluting Stents
Drug-eluting stents release medicine into the artery wall. This reduces artery narrowing. They greatly improve outcomes for patients with complex blockages. The medicine prevents cell growth, keeping the artery open.
Specialized Stent Designs
There are also specialized stents for specific needs. Bioresorbable stents dissolve over time. Stents with unique shapes improve flexibility. These designs aim to reduce complications and improve outcomes. Bioresorbable stents, for example, may lower risks of long-term problems.
Choosing the right stent can be confusing. But, our medical team helps patients pick the best one. By doing so, we can greatly improve treatment success and patient quality of life.
Recovery and Life After Stent Placement
Understanding the recovery process and life after stent placement is key to a patient’s well-being. We’ll guide you through the hospital stay, medication, and lifestyle changes.
Hospital Stay and Immediate Recovery
After stent placement, patients usually stay in the hospital for a short time. This lets doctors watch for any problems and make sure the patient is okay. Most patients go home in 24 to 48 hours.
Right after, patients should rest and not do too much. Your healthcare team will tell you how to care for your wound, what activities are okay, and when to come back for more checks.
Medication Requirements
Medicine is very important after stent placement. Patients often take antiplatelet therapy to stop blood clots. This might include aspirin and a P2Y12 inhibitor like clopidogrel. Taking your medicine as directed is key to avoiding problems.
How long you need to take your medicine can change based on your health and the stent type. Always talk to your doctor about your medication plan to understand its importance.
| Medication Type | Purpose | Duration |
| Aspirin | Antiplatelet therapy to prevent blood clots | Indefinitely |
| P2Y12 Inhibitor (e.g., clopidogrel) | Antiplatelet therapy to prevent blood clots | 6-12 months or longer |
Lifestyle Adjustments and Long-Term Outlook
After stent placement, making healthy choices is important for your heart. This means eating well, staying active, and managing stress. Work with your healthcare team to create a plan that fits your life and goals.
Key Lifestyle Adjustments:
- Diet: Eat a diet full of fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean proteins for heart health.
- Exercise: Do regular physical activity, like walking, as your doctor suggests.
- Smoking Cessation: Quit smoking to lower heart disease risk and other health problems.
- Stress Management: Use stress-reducing activities like meditation or deep breathing.
By making these lifestyle changes and following your medication plan, you can greatly improve your long-term health and lower heart disease risk.
Conclusion: The Vital Role of Heart Stents in Modern Cardiac Care
Heart stents are key in treating coronary artery disease. They help people with blockages in their coronary arteries. We’ve looked at how they’re made, what they’re made of, and how they’re put in.
Their main job is to keep arteries open. This improves blood flow and lowers the risk of heart attacks. Knowing how stents work helps patients understand their benefits and make smart choices about their health.
As we keep improving in cardiac care, stents will stay important. New stent technologies, like drug-eluting stents, are making treatments better. This means patients can expect even better results from stent procedures.
Heart stents have changed how we treat coronary artery disease. They offer a less invasive way to help people live better lives. We see how vital these devices are in today’s cardiac care. Their ongoing development will be key in improving heart health in the future.
FAQ
What is a heart stent and what is its purpose?
A heart stent is a small, mesh tube used to keep arteries open. This improves blood flow to the heart. It treats coronary artery disease by keeping arteries unblocked.
How big is a heart stent?
Heart stents come in different sizes. They can be 8mm to 48mm long and 2mm to 5mm wide. The size depends on the artery size and where the blockage is.
What does a heart stent look like?
A heart stent looks like a small, tube-like structure. It’s made from materials like stainless steel or cobalt-chromium. It’s designed to be flexible and expandable.
How is a heart stent inserted?
To insert a heart stent, a doctor uses a minimally invasive procedure. A catheter is guided through an artery to the blockage. Then, a balloon angioplasty expands the stent to keep the artery open.
How does a heart stent work?
A heart stent works by expanding into the blocked area of the artery. It’s expanded using balloon angioplasty. Once in place, it keeps the artery open, improving blood flow. Over time, it becomes part of the artery wall, providing long-term support.
What are the different types of heart stents available?
There are several types of heart stents. Bare metal stents provide structural support. Drug-eluting stents release medication to prevent re-narrowing. Specialized stents are for specific conditions or artery types.
What materials are used to make heart stents?
Heart stents are made from materials like stainless steel or cobalt-chromium. Each material has benefits like strength and flexibility. The choice depends on the patient’s needs.
How long does it take to insert a heart stent?
The time it takes to insert a heart stent varies. It can be from 30 minutes to several hours. This depends on the case’s complexity and the number of stents.
What is the recovery process like after stent placement?
After stent placement, patients usually stay in the hospital for a short time. They take medications to prevent clotting. They may also need to make lifestyle changes to keep their heart healthy.
What is a heart stent used for?
A heart stent is used to treat coronary artery disease. It keeps arteries open and ensures proper blood flow to the heart. It’s a key tool in managing heart disease and preventing heart attacks.
How is a stent inserted into the heart?
A stent is inserted through a minimally invasive procedure. A catheter is guided through an artery to the blockage site. A balloon angioplasty is then used to deploy the stent.
What does a stent do in the heart?
A stent in the heart keeps arteries open. This ensures blood flows freely to the heart muscle. It provides structural support to the artery wall, preventing it from narrowing or closing again.
References
- Neupane, S., et al. (2019). Meta-analysis of drug eluting stents compared with bare metal stents in high bleeding risk patients. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions, 94(7), 997-1005. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30585391/


































