Last Updated on November 27, 2025 by Bilal Hasdemir
Nuclear stress tests are key for finding heart problems. But, they also have risks, like getting too much radiation. Millions of people get these tests every year. Even though they’re mostly safe, there are dangers.
Getting a nuclear stress test can worry you, thinking about the risks. We aim to give you a full guide on these tests. We’ll talk about their good sides and the dangers. This way, you can make smart choices about your health.
Key Takeaways
- Nuclear stress tests are used to diagnose heart conditions.
- The procedure involves radiation exposure.
- There are possible risks with nuclear stress tests.
- We offer a balanced view to help patients make informed decisions.
- Knowing the risks and benefits is key for international patients.
What is a Nuclear Stress Test?
The nuclear stress test is a detailed test that shows how well the heart works when stressed. It’s key for spotting heart problems like coronary artery disease.
Definition and Basic Principles
This test uses a small amount of radioactive material, like thallium or technetium. It makes images of the heart. These images show how well blood flows to the heart muscle, even when you’re active or stressed.
The test works by comparing how the heart functions at rest and when stressed. It finds out if parts of the heart get enough blood when stressed, a sign of ischemia.
Nuclear Test for Heart vs. Regular Cardiac Testing

A nuclear stress test is different from regular heart tests like an ECG or echocardiogram. Here’s why:
- Detailed Imaging: It gives detailed heart images for better diagnosis.
- Blood Flow Assessment: It checks blood flow to the heart muscle, something not all tests can do.
- Stress and Rest Comparison: It compares heart function at rest and under stress, giving insights into heart health.
It’s important to understand nuclear stress test results, including how they change by age. For example, results can vary a lot between younger and older people. This is because of health differences and other medical conditions.
The Purpose of Nuclear Stress Tests
Nuclear stress tests are key in diagnosing and managing heart disease. They show how well the heart works when stressed, usually through exercise or medicine.
These tests help us understand a patient’s heart health. A small amount of radioactive material is injected into the blood. This lets us see the heart’s function and blood flow with special imaging.
What Does a Nuclear Stress Test Show?
A nuclear stress test gives us important info about the heart. It shows if some heart areas get too little blood. It also checks for coronary artery disease and heart attack risk.
The test results can tell us:
- How well the heart muscle works
- Any damaged or underperforming heart areas
- How well the heart’s blood flow is during stress
- How much coronary artery disease there is
This info helps doctors decide the best treatment for a patient.
Why Would a Doctor Order a Nuclear Stress Test?
Doctors order these tests for many reasons, mainly to diagnose and manage heart issues. Some main reasons are:
| Reason | Description |
| Diagnosing Coronary Artery Disease | To find blockages or narrowings in the coronary arteries. |
| Assessing Heart Attack Risk | To see the risk of a heart attack and what to do next. |
| Evaluating Heart Function | To check how well the heart pumps blood, under stress. |
| Monitoring Treatment Effectiveness | To see if treatments for heart conditions are working. |
Knowing the purpose and benefits of nuclear stress tests helps patients understand their importance in heart health.
Nuclear stress tests are a vital tool for diagnosis. They give insights that help improve patient care. We use them to make accurate diagnoses and effective treatment plans.
Types of Nuclear Cardiac Testing
Nuclear cardiac testing includes various protocols for different patients. It’s a key tool in cardiology for checking heart function and finding problems.
Exercise Nuclear Stress Test
The most common test is the exercise nuclear stress test. It involves walking on a treadmill or biking to stress the heart. A radioactive tracer is then used to see how the heart works under stress.
This test is great for those who can exercise. It helps find heart problems in active patients.
Chemical Nuclear Stress Test
For those who can’t exercise, a chemical test is an option. It uses medicine to stress the heart, like exercise does. This lets doctors check heart function without needing to exercise.
This test is good for many patients. It’s useful for those with mobility issues or chronic conditions.
Two-Day Nuclear Stress Test Protocol
The two-day test is done over two days. First, a resting scan is done, then a stress scan on the second day. This is for detailed assessments or when tests need to be done on different days.
This method gives clearer results. It shows how the heart changes from resting to stressed states.
Choosing the right test depends on the patient’s health and ability to exercise. Knowing the different tests helps doctors tailor care for each patient.
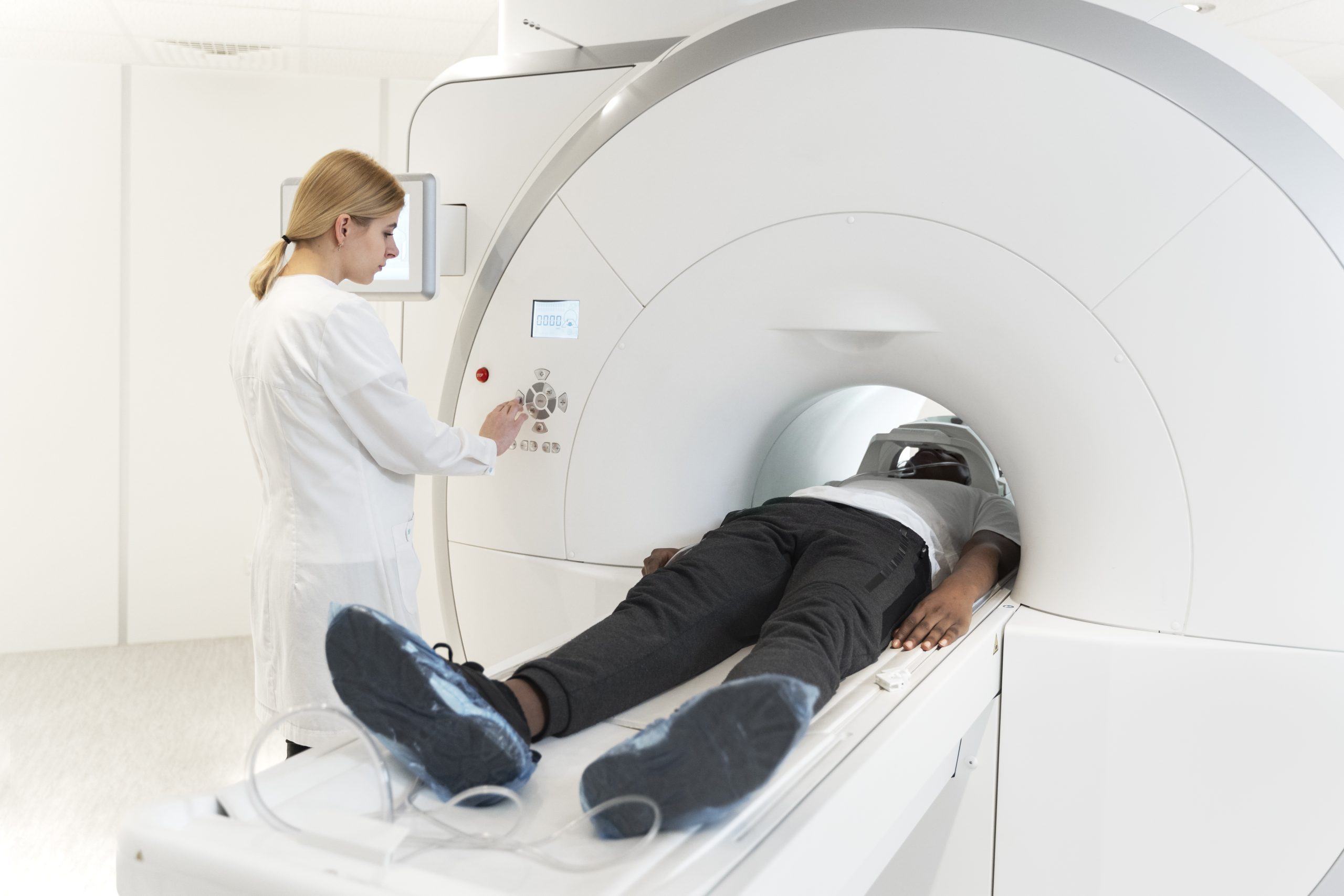
The Nuclear Stress Test Process
We will guide you through the nuclear stress test process. This includes preparation and recovery. Knowing each step can make you feel more at ease and ready for the test.
Before the Test: Preparation Requirements
Getting ready for a nuclear stress test involves several steps. You might need to skip certain foods and drinks, like caffeine, before the test. Also, tell your doctor about any medicines you’re taking. Some might need to be stopped before the test.
Wear comfortable clothes and shoes for the test. You’ll be walking on a treadmill. You’ll also need to arrive early to fill out paperwork and get ready. Your doctor will give you specific instructions, so it’s important to follow them closely.
During the Test: Step-by-Step Procedure
The test starts with an IV line in your arm. A small amount of radioactive tracer is then injected through this line. You’ll walk on a treadmill that gets faster and steeper to stress your heart. The tracer helps make images of your heart under stress.
When you reach the highest stress level, the tracer is given again. Then, you’ll lie down for imaging. A gamma camera takes pictures of your heart. This is done for both stress and rest images, taking several hours in total.
After the Test: Recovery and Follow-up
After the test, you’ll be watched for a bit to make sure you’re okay. The radioactive tracer will leave your body in a few days through urine and feces. Your doctor will tell you what to do next and schedule a follow-up to talk about your results.
It’s important to listen to your doctor about what to do and what not to do after the test. If you have any strange symptoms, like chest pain or trouble breathing, get help right away.
The Danger of Nuclear Stress Test: A Detailed Look
It’s important to know the risks of nuclear stress tests before getting one. These tests help find heart problems but have dangers that need to be thought about carefully.
Short-term Risks and Side Effects
Nuclear stress tests are usually safe but can cause some side effects. You might feel dizzy, have chest pain, or react to the radioactive tracer. In rare cases, serious problems like a heart attack can happen.
Here are some common short-term side effects:
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Allergic reactions to the radioactive tracer
- Nausea or headache
- Fatigue or weakness
| Short-term Side Effect | Frequency | Severity |
| Dizziness | Common | Mild |
| Chest Pain | Uncommon | Moderate to Severe |
| Allergic Reactions | Rare | Moderate to Severe |
Long-term Concerns
One big worry about nuclear stress tests is radiation exposure. The test uses a radioactive tracer that can raise cancer risk over time. But, the amount of radiation is small.
To understand radiation exposure better, let’s compare it to natural background radiation:
| Radiation Source | Dose (mSv) |
| Nuclear Stress Test | 9-12 |
| Average Annual Background Radiation | 3 |
| Flight from New York to Los Angeles | 0.1 |
It’s key to weigh the benefits of nuclear stress tests against their risks. While there are dangers, the test’s findings are very helpful for heart health. Talk to your doctor about your specific risks and worries.
Radiation Exposure from Nuclear Stress Tests
It’s important for patients to know about radiation exposure from nuclear stress tests. These tests use small amounts of radioactive tracers to see how the heart works under stress.
Quantifying Radiation Doses
The dose from a nuclear stress test is measured in millisieverts (mSv) or millibecquerels (mBq). The dose can change based on the test protocol and the radiopharmaceutical used. On average, it’s between 9 to 12 mSv.
Here’s a table showing different doses from nuclear stress tests:
| Protocol | Average Effective Dose (mSv) |
| Standard nuclear stress test | 9-12 |
| Low-dose nuclear stress test | 4-6 |
| High-sensitivity nuclear stress test | 12-15 |
Comparing to Natural Background Radiation
Natural background radiation is always present in our environment. It’s measured in areas far from any radiation sources. The global average is about 2.4 mSv per year, but it can change based on where you are.
A nuclear stress test dose (9-12 mSv) is like 4 to 5 years of natural background radiation. This helps patients understand the amount of radiation they get from the test.
Is Radiation from Nuclear Stress Test Harmful?
The risk of harm from nuclear stress test radiation is debated. The linear no-threshold model says any radiation can cause cancer. But, the risk at these doses is thought to be low.
We need to think about the test’s benefits against the radiation risks. For many, knowing their heart health is worth it.
In conclusion, nuclear stress tests do involve radiation. But knowing the dose and comparing it to natural background radiation helps understand the risk. It’s key for patients to talk to their doctor about their specific situation and the test’s benefits.
Specific Dangers of Lexiscan and Chemical Stress Tests
Chemical stress tests, like those using Lexiscan, are important for diagnosing heart issues. Lexiscan, or regadenoson, helps patients who can’t exercise. But, it also has side effects and risks.
Lexiscan Stress Test Side Effects
Side effects from a Lexiscan stress test can vary. You might feel:
- Shortness of breath
- Headache
- Flushing
- Dizziness
- Nausea
Some people might have more serious reactions. This includes chest pain, severe headaches, or changes in heart rhythm. Always tell your doctor about any health issues or medicines you’re taking.
Pros and Cons of Chemical Stress Test
Chemical stress tests, like Lexiscan, have good and bad points. The good sides are:
- They help check for heart disease in those who can’t exercise
- They give important info on heart function under stress
- They’re often easier than exercise tests
The not-so-good sides are:
- They can have side effects from the stress agent
- They might not be as accurate as exercise tests
- Choosing the right patients is key to avoid risks
| Aspect | Pros | Cons |
| Patient Eligibility | Allows testing for patients unable to exercise | Requires careful patient selection |
| Diagnostic Value | Provides valuable information on heart function | May be less accurate than exercise stress tests |
| Patient Experience | Less physically demanding | Potential for side effects from stress agent |
Can a Nuclear Stress Test Cause a Heart Attack?
The chance of a heart attack from a nuclear stress test is very low. But, it’s not zero. The test is meant to check heart function under stress. It can rarely cause heart problems in people with heart disease or blockages.
A study in a Journal showed that serious heart problems, like heart attacks, happen in less than 1% of cases.
Thinking about a nuclear stress test can be scary, knowing the risks. But, for many, the benefits of finding and managing heart issues are worth it. It’s important to talk to your doctor about your risks and any worries you have.
Safety Protocols and Risk Mitigation
To keep patients safe, medical facilities have strict safety rules for nuclear stress tests. These rules help ensure patients are well taken care of during the test.
Medical Screening Before Testing
Before a nuclear stress test, patients must go through a detailed medical check. This includes looking at their health history, current health, and any medicines they take. Our main goal is to find any risks or things that could make the test unsafe.
The check-up might include a physical exam, ECG, and other tests if needed. This helps us understand each patient’s health better. It helps us lower the chance of bad reactions during the test.
Emergency Preparedness During Tests
Even with careful planning, emergencies can happen during nuclear stress tests. Medical facilities have emergency plans and tools ready. Our team is trained to act fast and right in emergencies, making sure patients get help right away if they need it.
Being ready for emergencies means having the right medicines and tools. This helps us deal with problems like allergic reactions or heart issues. Being prepared helps lower the risks of nuclear stress tests.
Post-Test Precautions
After the test, patients are watched closely to make sure they’re okay. We give clear instructions on what to do after the test, including any follow-up visits or precautions to take at home.
By following these safety steps and being proactive about risks, we make sure nuclear stress tests are safe and work well. Our dedication to keeping patients safe never wavers. We always update our safety rules to match the latest medical advice and best practices.
Understanding Nuclear Stress Test Results
It’s important for patients and doctors to understand nuclear stress test results. This test shows how well the heart works under stress. It helps find and manage heart disease. We’ll explain how to read these results, the difference between normal and abnormal, and how age affects them.
Normal vs. Abnormal Results
Nuclear stress test results can be normal or abnormal. Normal results mean the heart gets enough blood flow when stressed, with no big blockages. Abnormal results show less blood flow, which might mean blockages or heart disease.
Nuclear Stress Test Results by Age
Age plays a big role in reading nuclear stress test results. Older people might have different results due to age-related changes. These changes can affect how the heart works. We take these into account to make sure the diagnosis is right.
Blockage Nuclear Stress Test Images
Nuclear stress test images can show blockages in the heart’s arteries. These images help find areas where blood flow is low. Blockage nuclear stress test images help doctors see how bad the blockages are and where they are. This helps decide the next steps in treatment.
| Result Category | Description | Implications |
| Normal | Adequate blood flow under stress, no significant blockages | Low risk of coronary artery disease |
| Abnormal | Reduced blood flow under stress, possible blockages | May show heart disease, need more tests or treatment |
Accuracy and Limitations of Nuclear Stress Tests
Nuclear stress tests are a key tool in diagnosing heart issues. But, their results can be affected by many things. Knowing these can help us understand what the tests mean.
How Accurate is a Nuclear Stress Test?
Nuclear stress tests are usually very accurate. But, they’re not 100% right. Research shows they can spot coronary artery disease in 80% to 90% of cases. Yet, they might miss it in 20% to 30% of cases, leading to false positives.
False Positive and False Negative Results
False positives happen when a test says you have heart disease when you don’t. This can cause extra tests and worry. False negatives, on the other hand, might miss real heart disease. These errors can come from many places, like how the test is done or who looks at the results.
False positives can be due to things like breast tissue in women or diaphragm issues in both men and women. False negatives might happen if you have single-vessel disease or don’t get your heart rate up enough during the test.
Factors Affecting Test Accuracy
Many things can change how accurate nuclear stress tests are. These include:
- Patient factors: obesity, breast tissue, diaphragm position
- Technical factors: equipment quality, imaging protocol
- Interpreter factors: experience, variability in interpretation
Knowing these can help doctors make better choices for their patients.
Alternatives to Nuclear Stress Tests
Nuclear stress tests are common, but there are other ways to check heart health. These options are good for those worried about radiation or have certain health issues. They’re also great for people who can’t have nuclear tests.
Exercise Stress Tests Without Nuclear Imaging
Exercise stress tests, or treadmill tests, are a good choice. Patients walk on a treadmill or bike while their heart is checked. This test shows how well the heart works under stress and can spot heart disease.
Benefits of Exercise Stress Tests:
- No radiation exposure
- Cost-effective compared to nuclear stress tests
- Provides immediate results
- Helps assess overall cardiovascular fitness
Echocardiogram Stress Tests
An echocardiogram stress test uses ultrasound and stress to check the heart. It shows how well the heart pumps and spots problems. This test is non-invasive and doesn’t use radiation.
“Echocardiogram stress tests offer a non-invasive and radiation-free alternative for evaluating heart function under stress.”
Cardiac MRI and CT Angiography
Cardiac MRI and CT angiography give detailed views of the heart and blood vessels. Cardiac MRI checks heart function and finds scars without radiation. CT angiography uses X-rays to see the coronary arteries and find blockages.
Key advantages of Cardiac MRI and CT Angiography:
- High-resolution images of the heart and coronary arteries
- Ability to detect a wide range of heart conditions
- Useful for patients who cannot undergo traditional stress tests
A cardiologist, says,
“Cardiac MRI and CT angiography have revolutionized the way we diagnose and manage heart disease, providing detailed insights that were previously unavailable.”
In conclusion, there are many alternatives to nuclear stress tests. Each has its own benefits and uses. Knowing these options helps patients and doctors choose the best test for each person’s needs.
Special Considerations for Different Populations
Nuclear stress tests are not the same for everyone. Different groups need special care. This ensures the tests are safe and work well.
Nuclear Stress Tests for Elderly Patients
Elderly patients often have complex health histories. This makes the test more challenging. We must check their health before the test.
Important things to consider for elderly patients include:
- They might find it hard to exercise during the test
- They could have more health problems like kidney disease or diabetes
- They might need a different amount of the radioactive tracer
| Consideration | Implication for Elderly Patients |
| Physical Exertion | May require pharmacological stress instead of exercise |
| Comorbidities | Need for careful medical history assessment |
| Tracer Dosage | Potential need for dosage adjustment |
Gender Differences in Cardiac Testing
Studies show men and women have different heart disease symptoms. We must understand these differences when looking at test results.
“Women are more likely than men to have false-positive stress tests, which can lead to unnecessary further testing and anxiety.”
Source: American Heart Association
To handle these differences, we look at:
- How symptoms and risks vary between genders
- Test sensitivity and specificity differences
- The need for gender-specific test protocols
Patients with Kidney Disease
Patients with kidney disease need special care with nuclear stress tests. Some tests use contrast agents that can harm their kidneys.
For patients with kidney disease, we:
- Look at the test’s risks and benefits
- Think about other ways to diagnose when possible
- Watch their kidney function before and after the test
By considering these special needs, we make sure nuclear stress tests are safe and effective for all patients.
Insurance Coverage and Cost Factors
Insurance coverage is key when it comes to the cost of nuclear stress tests. Knowing the financial side of this test helps patients make smart choices about their health.
Nuclear Stress Test Price Range
The cost of a nuclear stress test can change a lot. It depends on where you get the test, whether it’s at a hospital or outpatient center, and your insurance. On average, it can cost between $1,000 and $3,000 or more.
- Facility fees
- Physician fees for interpretation
- Cost of the radioactive tracer
- Additional testing or procedures
It’s important for patients to talk to their healthcare provider and insurance company. They can give a better idea of what the test will cost.
Insurance Requirements and Approvals
Insurance needs for nuclear stress tests can differ. Usually, you need a referral from a doctor and might need pre-approval for the test.
Key factors influencing insurance approvals include:
- Medical necessity as determined by a healthcare provider
- Pre-authorization requirements
- Network participation of the testing facility and healthcare providers
Patients should work with their healthcare team and insurance provider. This ensures they get the coverage they need for their nuclear stress test.
Frequency Guidelines for Nuclear Stress Testing
We look at how often nuclear stress tests should be done. This ensures patients get the right care without too much risk.
How Often Should You Have a Heart Stress Test?
The need for nuclear stress tests varies. It depends on the patient’s risk, symptoms, and past test results. Those at high risk of heart disease or showing heart symptoms might need tests more often. But, those at lower risk might not need them as frequently.
For people with stable heart disease, tests are usually done every 2-3 years. But, this can change based on the doctor’s judgment and the patient’s health status.
Risk-Based Testing Schedules
Testing schedules are based on a patient’s risk factors. These include age, family heart disease history, diabetes, and high blood pressure. Those with more risk factors might need tests more often.
- Low-risk patients might only need testing every 5 years or more.
- Moderate-risk patients may require testing every 2-3 years.
- High-risk patients or those with significant symptoms may need testing annually or as clinically indicated.
Guidelines for Repeat Testing
Rules for repeating nuclear stress tests aim to balance monitoring needs with risks. Decisions to repeat tests should be based on symptom changes, new findings, or the need to check treatment success.
By sticking to these guidelines, doctors can manage heart health well. This reduces unnecessary radiation and risk.
Conclusion: Balancing Benefits and Risks of Nuclear Stress Tests
Nuclear stress tests are a key tool for checking heart health. They provide detailed images of the heart’s function and blood flow. This helps doctors diagnose and manage heart disease.
But, these tests also have risks like radiation exposure and side effects. It’s important to think about these risks and benefits when deciding on this test.
Knowing about nuclear stress tests helps patients make smart health choices. We help international patients understand these complex medical decisions. We offer support and guidance every step of the way.
Choosing to have a nuclear stress test should be a decision made with a healthcare provider. They can help weigh the benefits against the risks. They can also suggest other tests to consider.
FAQ
What is a nuclear stress test?
A nuclear stress test is a test that uses a tiny bit of radioactive material. It shows how the heart works when it’s stressed, like during exercise or with medicine.
What does a nuclear stress test show?
This test can show where blood flow is low, scar tissue, and blockages in the heart’s arteries.
Why would a doctor order a nuclear stress test?
Doctors order this test to find heart disease, check heart attack risk, or see if treatments are working.
What are the risks associated with nuclear stress tests?
Risks include short-term side effects like dizziness and nausea. There’s also concern about long-term radiation effects.
Is radiation from a nuclear stress test harmful?
The test’s radiation is usually low. But, it can be a concern for young people or those needing many tests.
Can a nuclear stress test cause a heart attack?
It’s rare, but yes, it could happen, mainly in those with heart problems or not checked well before the test.
What are the alternatives to nuclear stress tests?
Options include exercise tests, echocardiograms, cardiac MRI, and CT angiography.
How often should you have a nuclear stress test?
It depends on your health and risk factors. High-risk patients might need tests every few years.
What is the price range for a nuclear stress test?
Prices vary a lot. They depend on where you are, the facility, and your insurance. Costs can be hundreds or thousands of dollars.
Are nuclear stress tests safe for elderly patients?
They can be safe for older patients if they’re checked and monitored well. But, there are special considerations.
How accurate are nuclear stress tests?
They’re very accurate for finding heart disease and risk. But, accuracy can depend on how well the test is done and interpreted.