Chronic low back and cervical pain can really hurt your quality of life. Epidural Steroid Injections (ESIs) are a helpful treatment for this pain. Interlaminar epidural steroid injections put medicine right into the spinal canal. This helps reduce inflammation and eases pain. Master the interlaminar ESI. Our ultimate guide explains the step-by-step procedure for lumbar and cervical epidural injections.
At Liv Hospital, we put our patients first. We make sure spine care is safe and effective. Our skilled doctors help patients understand the LESI procedure. They explain each step and answer any questions.
Patients need to know about the procedure and its benefits. We’ll guide you through it. We’ll talk about how it helps with conditions like herniated discs and nerve root irritation.
Key Takeaways
- Epidural Steroid Injections are used to relieve pain in the spine.
- The LESI procedure involves delivering medication into the spinal canal.
- Liv Hospital follows a patient-centered approach for spine care.
- The treatment is used for managing chronic low back and cervical pain.
- Understanding the procedure is key for patients considering this treatment.
Understanding Interlaminar ESI and Its Applications
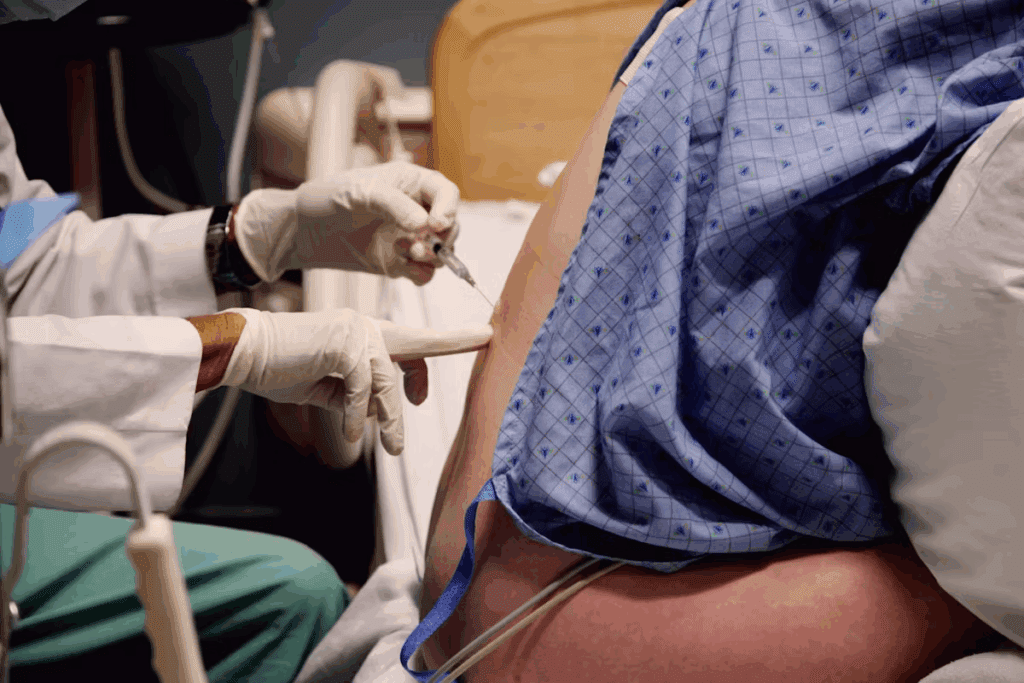
Healthcare professionals need to understand interlaminar ESI to treat spinal disorders well. Interlaminar epidural steroid injections (ESI) are key in pain management. They help with many spinal issues.
Definition and Mechanism of Action
Interlaminar ESI injects corticosteroids around the spinal cord. It aims to cut down inflammation and ease spine pain. The interlaminar approach uses a needle between two vertebrae’s laminae.
This method delivers steroids directly to the epidural space. It offers a lot of pain relief for spinal problems.
The steroids in interlaminar ESI fight inflammation. They calm the immune system and lessen nerve root inflammation. This reduces pain and discomfort.
Anatomical Considerations of the Interlaminar Space
The interlaminar space is key for this procedure. It’s the area between two vertebrae laminae. Knowing this area’s anatomy is vital for safe needle placement.
Spotting the interlaminar space correctly is essential for ESI success. It needs a deep understanding of spinal anatomy and imaging tools like fluoroscopy.
Differences Between ILESI and Other Injection Approaches
Interlaminar ESI is different from other epidural injections. The choice depends on the condition, patient anatomy, and the doctor’s choice.
Unlike transforaminal injections, interlaminar ESI targets the epidural space broadly. It’s good for conditions affecting many nerve roots. It can be used in lumbar, cervical, and thoracic regions, making it flexible.
Indications and Patient Selection Criteria
Interlaminar ESI is a key treatment for some spinal disorders. It’s chosen based on a detailed look at the patient’s health, past medical issues, and what the treatment can offer.
Common Conditions Treated with Interlaminar Injections
These injections are often used for radicular and axial pain. This includes pain from disc problems, spinal stenosis, or after surgery. Radicular pain from herniated discs is a big reason for this treatment, as it can lessen inflammation and pain.
- Herniated discs
- Spinal stenosis
- Degenerative disc disease
- Post-surgical pain syndrome
Diagnostic vs. Therapeutic Applications
Interlaminar ESI has two main uses. It can help treat pain by reducing inflammation and can also help find the source of pain by blocking certain nerves.
Cervical epidural injections are used for neck pain or pain from disc problems. This makes interlaminar ESI a valuable tool in managing pain.
Contraindications and Precautions
While generally safe, there are some things to watch out for. These include bleeding disorders, active infections, and allergies to the medications used.
- Coagulopathy or bleeding disorders
- Active infection or sepsis
- Known allergy to corticosteroids or local anesthetics
- Pregnancy (relative contraindication, depending on the specific circumstances)
We look closely at each patient’s health and situation to lower risks and improve results.
Pre-Procedure Preparation and Planning
Getting ready for an interlaminar ESI is key to its success and safety. It involves several important steps. These steps help ensure the best results for patients.
Patient Education and Informed Consent
Teaching patients about the procedure is vital. We make sure they know the benefits, risks, and other options. We get their consent after discussing these points.
- The nature and purpose of the interlaminar ESI procedure
- Potential risks and complications, such as infection, bleeding, or nerve damage
- Expected outcomes and the possibility of variable responses to the treatment
- Alternative treatment options are available for their condition
This way, patients can make informed choices about their care.
Pre-Procedure Medication Management
Managing medications before an ILESI is important. We check the patient’s meds to see if any need to be changed or stopped. This includes:
- Anticoagulants: Patients are advised to stop anticoagulant medications for a specified period before the procedure to minimize the risk of bleeding.
- Diabetes Management: For diabetic patients, we provide guidance on managing blood sugar levels before and after the procedure.
- Other Medications: We assess the need for adjusting other medications that could interact with the procedure or affect patient safety.
Pre-procedural imaging review is also essential. It confirms the right spot for the injection and checks for any special needs.
Equipment and Medication Preparation
Getting everything ready is another big part of planning. This includes:
- Ensuring that all required sterile equipment is available and in good condition
- Preparing the correct dosage and type of steroid and local anesthetic
- Having emergency equipment and medications readily available in case of an adverse reaction
Fluoroscopic guidance helps make the injection more accurate. We check that the fluoroscopy works well and have the contrast ready.
By carefully preparing for the ILESI procedure, we can reduce risks and improve patient results.
Performing Lumbar Interlaminar ESI (LESI Procedure)
Doing a Lumbar Interlaminar ESI needs careful attention and a deep understanding of the spine. It’s a good treatment for those with lower back pain and other issues.
Patient Positioning and Site Preparation
Getting the patient in the right position is key for the LESI procedure. They lie on their stomach on a special table. A pillow helps bend their lower back.
- The skin is prepped and draped in a sterile manner.
- The area is anesthetized with a local anesthetic to minimize discomfort.
Fluoroscopic Guidance Techniques
Fluoroscopy helps place the needle accurately. The C-arm gives a clear view of the space between the vertebrae.
Key steps include:
- Adjusting the C-arm to optimize the view of the target area.
- Using a “tunnel vision” or “bullseye” view to align the needle with the fluoroscopic beam.
Needle Placement and Loss of Resistance Technique
The loss-of-resistance technique is vital for the LESI procedure. It confirms the needle is in the right space. A Tuohy needle is used for this.
- The needle is advanced slowly under fluoroscopic guidance.
- A syringe filled with saline or air is used to detect the loss of resistance as the needle enters the epidural space.
Contrast Injection and Medication Administration
After the needle is in place, contrast is injected to check the spread. Then, steroids and a local anesthetic are given.
Important considerations include:
- Confirming the correct placement of the needle with contrast before administering medication.
- Using the appropriate dose and type of steroid for the patient’s condition.
By following these steps and using fluoroscopy, the LESI procedure is done safely and effectively. It helps patients with lower back problems find relief.
Cervical Interlaminar Epidural Injection Technique
For those with cervical spine issues, interlaminar epidural injections are a targeted treatment. This method injects steroids into the epidural space around the cervical spine. It helps ease pain and inflammation.
Specific Anatomical Considerations for Cervical ESI
The cervical spine’s anatomy is unique, needing careful thought for injections. The ligamentum flavum is thinner in the cervical region, and the space is narrower than in the lumbar area. This means precise needle placement is key to avoiding problems.
Knowing the cervical spine’s anatomy is key to a successful procedure. The epidural space has fatty tissue, veins, and nerve roots. Accurate imaging is essential.
Patient Positioning for Cervical Procedures
Getting the patient’s position right is critical for cervical injections. They are placed in a prone position with their neck slightly flexed. This opens up the interlaminar space for better needle placement.
Fluoroscopic guidance is used to ensure the needle is in the right spot. The C7-T1 interspace is often chosen because of its larger space.
Needle Trajectory and Depth Control
Placing the needle for cervical injections needs careful planning. The needle is guided under fluoroscopy, using a loss-of-resistance technique to find the epidural space. Depth control is critical to avoid dural puncture or spinal cord injury.
A small-gauge needle and gentle advancement under fluoroscopy help in precise placement. Continuous imaging keeps the needle on track.
Medication Delivery and Safety Measures
After the needle is in place, a contrast agent is injected to check the spread. Then, steroids are given to reduce inflammation and pain.
Safety steps include monitoring for complications like nerve injury, infection, or allergic reactions. Patients are watched for any immediate side effects.
Thoracic Interlaminar ESI: Technical Considerations
Doing interlaminar ESI in the thoracic spine needs a deep understanding of its narrower space. The thoracic spine’s unique shape makes it different from the lumbar and cervical areas.
Unique Challenges of the Thoracic Interlaminar Approach
The thoracic interlaminar approach faces challenges due to its narrower space. Studies show the thoracic epidural space is smaller than the lumbar area, making it harder. The spine’s curve also affects where and how the needle goes.
There’s a risk of hurting the spinal cord because the needle is close. It’s very important to place the needle carefully to avoid problems.
Modified Techniques for Thoracic Procedures
To tackle the challenges of thoracic interlaminar ESI, new methods have been created. One method uses a paramedian approach to make needle placement more accurate and safer.
Using fluoroscopy is key for thoracic interlaminar ESI. It lets us see the needle’s path in real-time and check if it’s in the right spot. Injecting contrast under fluoroscopy confirms the needle is in the epidural space before steroids are given.
Safety Protocols Specific to Thoracic ESI
For thoracic interlaminar ESI, safety is a top priority. This includes choosing the right patients, doing a detailed check before starting, and being very careful with the needle. It’s important to watch for any complications like spinal cord injury, dural puncture, or bleeding in the epidural space.
We also follow strict sterile technique to lower the chance of infection. Teaching patients about the risks and benefits is a big part of keeping them safe.
Image-Guided Injection Techniques and Documentation
Fluoroscopic imaging is key in interlaminar epidural steroid injections. It makes the procedure safer and more effective. This technology helps us place needles accurately and deliver medication correctly.
Fluoroscopic Imaging Optimization
To get the most from fluoroscopic guidance, we need to tweak the imaging settings. We adjust the X-ray beam for clear views of the target area. Proper collimation and patient positioning are vital for quality images.
Using contrast agents is also important. They help us see where the needle is and where the medication goes. The right contrast agent and how we use it can make the procedure a success.
Contrast Pattern Interpretation
Understanding the contrast pattern is a key part of the procedure. We look at how the contrast spreads to make sure the medication goes where it should. A characteristic “pearl-like” or “railroad track” appearance on the screen means it’s in the right place.
| Contrast Pattern | Interpretation |
| Pearl-like or railroad track | Epidural space |
| Linear or streak-like | Subdural or intravascular injection |
| Diffuse or cloud-like | Soft tissue or incorrect placement |
Documentation Requirements
Keeping accurate records is vital for patient safety and procedure success. We document the procedure, including needle placement, medication, and any issues.
Good documentation helps with follow-up care and checks if the treatment worked. It’s important for ongoing care and legal reasons.
Post-Procedure Care and Complication Management
Good care after an interlaminar ESI is key for the best results and to avoid problems. The right care after the procedure can make a big difference in how well a patient recovers and how happy they are.
Immediate Post-Procedure Monitoring
Right after the epidural steroid injection, patients need to be watched closely. This watch includes looking for any signs of trouble, like nerve damage, dural puncture, or allergic reactions. Close observation helps catch any problems early.
Patient Instructions and Activity Guidelines
Patients need clear instructions on what to do after the procedure. This includes advice on activity levels, managing pain, and knowing when to worry. Telling patients to stay away from hard activities for a bit can help avoid problems. Also, giving them a number to call for any worries can make them feel safer and more satisfied.
Common Complications and Their Management
Even though it’s usually safe, interlaminar ESI can sometimes cause issues. Problems like pain at the injection site, headaches, and vasovagal reactions can happen. Effective management of these includes steps to prevent them and knowing how to treat them if they do happen. For example, using clean techniques can lower infection risks, and having emergency gear ready can help with severe reactions.
Rare but Serious Adverse Events
Though rare, serious problems like spinal cord injury, epidural hematoma, or severe allergic reactions can occur. It’s important for doctors to know about these risks and have plans in place. This means having emergency tools ready and knowing what to do in serious cases.
By knowing about possible problems and having a solid aftercare plan, doctors can make interlaminar ESI safer and more effective.
Conclusion: Clinical Outcomes and Best Practices
Interlaminar epidural steroid injection is a key treatment for chronic pain. It offers significant relief and boosts function and quality of life. At Haydel Spine Pain & Wellness, we’ve seen it help manage chronic pain effectively.
The lesi procedure, done with care and guidance, leads to good results. Knowing the anatomy, when to use it, and how to do it right helps doctors choose the right patients and do the procedure well.
For the best results, careful planning before the procedure, accurate needle placement, and watching patients closely after are key. Following these steps helps avoid problems and makes the treatment more effective. This way, patients get better faster.
FAQ
What is an interlaminar epidural steroid injection (ESI)?
An interlaminar epidural steroid injection is a small procedure. It treats chronic pain in the neck, back, and legs. Steroids are injected into the space around the spinal cord.
What conditions are treated with interlaminar ESI?
This treatment helps with herniated discs, spinal stenosis, and degenerative disc disease. It also treats nerve root irritation. These issues can cause long-term pain and discomfort.
How does interlaminar ESI differ from other epidural injection techniques?
Interlaminar ESI injects medication through the interlaminar space. Other methods, like transforaminal or caudal, have their own uses and benefits.
What are the benefits of using fluoroscopic guidance during interlaminar ESI?
Fluoroscopic guidance helps place the needle accurately. This reduces risks and ensures the medication reaches the right spot. It can make the procedure more effective.
What are the common complications associated with interlaminar ESI?
Common issues include pain or discomfort at the injection site, headaches, and dizziness. Rare but serious problems include infection, nerve damage, or allergic reactions.
How is post-procedure care managed after interlaminar ESI?
After the procedure, we watch for immediate problems. We give instructions on what activities to avoid and manage any side effects or complications.
Can interlaminar ESI be used for diagnostic purposes?
Yes, it can help find the source of pain. It also checks if epidural steroid injections work for chronic pain.
What is the role of contrast injection during interlaminar ESI?
Contrast injection confirms the needle is in the right place. It ensures the medication goes to the correct spot, improving the procedure’s success.
Are there any contraindications for interlaminar ESI?
Yes, it’s not for everyone. Conditions like bleeding disorders, active infections, or allergies to the medication are contraindications. Certain anatomical or medical issues also make it unsafe.
How is patient selection determined for interlaminar ESI?
We choose patients based on their medical history, physical exam, and imaging studies. This ensures the procedure is right for their condition.
References
- Manchikanti, L., Knezevic, N. N., Navani, A., Christo, P. J., Limerick, G., Calodney, A. K., Grider, J., Harned, M. E., Cintron, L., Gharibo, C. G., Shah, S., Nampiaparampil, D. E., Candido, K. D., Soin, A., Kaye, A. D., Sanapati, M. R., Atluri, S., Pasupuleti, R., Manchikanti, M. V., … Hirsch, J. A. (2021). Epidural interventions in the management of chronic spinal pain: American Society of Interventional Pain Physicians (ASIPP) comprehensive evidence-based guidelines. Pain Physician, *24*(S1), S27–S208. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8754496/




































