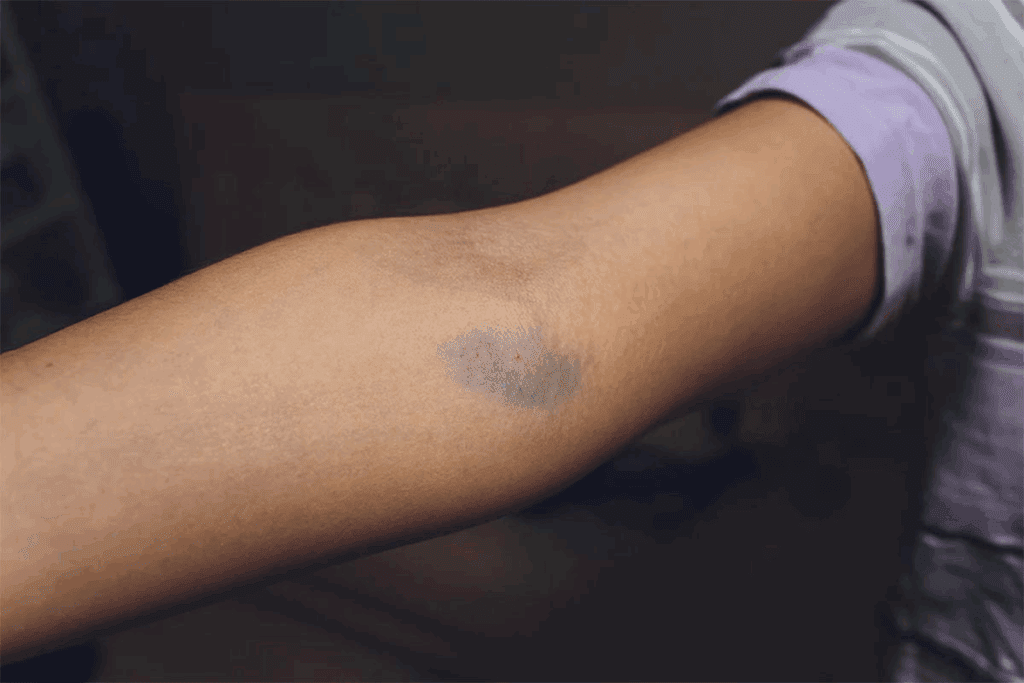
A blood clot in the arm is a serious issue called upper extremity deep vein thrombosis (UEDVT). It’s important to spot the signs early because it can cause serious problems, like pulmonary embolism. Get the essential guide on treatment for blood clot in arm. Learn the critical steps, symptoms to watch for, and the common causes.
Look out for cramping pain, swelling, and skin that looks bruised and feels warm. At Liv Hospital, we focus on keeping you safe and trusting us. We use the latest tools and follow international standards for personalized and ethical care.
Knowing the causes and treatment options is key to getting better. We make sure each patient gets care that fits their needs.
Key Takeaways
- Upper extremity deep vein thrombosis (UEDVT) is a serious condition requiring immediate medical attention.
- Symptoms include cramping pain, swelling, and bruised skin that is warm to the touch.
- Early recognition of signs is key to avoiding serious complications.
- Liv Hospital uses advanced diagnostic tools and follows international standards.
- Personalized and ethical care is our top priority at Liv Hospital.
Understanding Arm Blood Clots (UEDVT)
When a blood clot forms in the deep veins of the arm, it’s called upper extremity deep vein thrombosis (UEDVT). This condition can have serious health effects. We’ll explore what it is, how common it is, and its risks compared to leg blood clots.
What Is Upper Extremity Deep Vein Thrombosis?
UEDVT is a blood clot in the deep veins of the arm. It’s different from superficial vein thrombosis, which is in veins closer to the skin. If not treated, UEDVT can lead to serious problems, like pulmonary embolism.
How Common Are Arm Blood Clots?
Arm blood clots, or UEDVT, are less common than leg DVT. Yet, they make up a big part of all DVT cases. Medical News Today says 5 to 10% of DVT cases are in the arms. This number is going up because of more central venous catheters and better diagnosis.
Differences Between Arm and Leg Blood Clots
Arm and leg blood clots are both deep vein thrombosis, but they differ. Leg DVT is more common because of gravity and pressure. Arm DVT is linked to central venous catheters, hard arm work, or thoracic outlet syndrome. Knowing these differences helps in diagnosing and treating them correctly.
The Seriousness of Arm Thrombosis
Arm thrombosis, or UEDVT, is a serious issue that needs quick and proper treatment. A big risk is pulmonary embolism, when a clot piece goes to the lungs. Treatment usually starts with anticoagulants (blood thinners) to stop the clot from getting bigger and new ones from forming. If symptoms don’t get better or get worse, you should see a doctor.
Recognizing Blood Clot Symptoms in the Arm
It’s key to know the signs of arm blood clots for good care. Spotting these signs early can greatly help treatment and avoid problems.
Early Warning Signs
Early signs of a blood clot in the arm might be mild pain or swelling. The skin might also feel warm. Some people feel their arm is heavy or tired.
Being aware of these small signs is important. They can get worse fast. Medical News Today says symptoms can also include cramping pain and skin that looks red or blue.
Advanced Symptoms
As the problem gets worse, symptoms get more obvious. You might see more swelling, pain that gets worse with movement, and visible veins.
The skin might turn different colors, and the arm could feel heavy or sore. Watching these signs and getting help if they get worse is key.
Visual Appearance of Arm Blood Clots
Arm blood clots can look different. The skin might turn red, blue, or purple. Swelling can make the arm look bigger, and veins might show more.
In serious cases, the skin might look pale or feel cool. Spotting these signs is important because they mean a serious issue.
Symptoms That Require Immediate Attention
Some symptoms need quick medical help. These include severe pain, sudden swelling, and trouble moving the arm. If you see these signs, get help right away.
The American Heart Association says, “If you have symptoms of a blood clot, call 911 or your local emergency number.” Quick action is vital to save lives and prevent serious damage.
“If you have symptoms of a blood clot, call 911 or your local emergency number.”
American Heart Association
| Symptom | Description | Severity |
| Pain or discomfort | Mild to severe pain | Moderate |
| Swelling | Arm swelling | Moderate to Severe |
| Skin discoloration | Red, blue, or purple hue | Moderate to Severe |
| Visible veins | Prominent veins | Mild to Moderate |
Common
Many things can cause blood clots in the arm. These include physical activities and genetic factors. Knowing what causes them is key to preventing and treating them.
Medical Procedures and Interventions
Medical procedures can lead to blood clots in the arm. Devices like catheters and pacemakers increase this risk. Surgery, too, can cause blood clots, mainly if it’s in the arm or shoulder.
Underlying Health Conditions
Some health issues raise the risk of blood clots in the arm. Cancer is one, because it makes the body more likely to clot. Infections and inflammatory conditions also play a part.
Physical Factors and Activities
Physical activities and factors can also cause blood clots. Repetitive arm movements, common in athletes, can lead to UEDVT. Arm injuries can also cause clots. Knowing these risks helps prevent them.
Genetic and Inherited Clotting Disorders
Genetic disorders can also cause blood clots. Conditions like Factor V Leiden and Antithrombin III deficiency increase clotting risk. Knowing your family’s health history can help manage this risk.
By understanding these causes, we can take steps to lower our risk. And we should seek medical help when needed.
When to Seek Medical Help for Arm Blood Clots
Knowing when to get medical help is key to treating arm blood clots. If you notice symptoms, it’s important to understand how serious they are. This will help you know when you need to act fast.
Emergency Warning Signs
Some symptoms mean you need to call for help right away. These include:
- Severe pain or swelling in the arm
- Skin that is cool to the touch or pale
- Shortness of breath or chest pain
- Rapid heartbeat
- Dizziness or fainting
If you or someone else has these symptoms, call emergency services immediately. As the
“Clot care is time-sensitive, much like stroke or heart attack care.”
What Information to Provide Your Doctor
When you see your doctor, be ready with important information. This can help with diagnosis and treatment. Discuss:
- The onset and duration of your symptoms
- Any recent medical procedures or hospitalizations
- Your family history of blood clots or clotting disorders
- Any medications you’re currently taking
Sharing this info can help your doctor figure out the cause of your clot. They can then plan the best treatment for you.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
Your doctor may order tests to confirm a blood clot and its severity. These include:
- Ultrasound to visualize the clot
- Blood tests to check for clotting disorders
- Venography, an imaging test that uses X-rays and contrast dye
These tests help your healthcare provider understand the clot’s extent. They can then plan the right treatment.
Preparing for Your Medical Appointment
Before your appointment, write down your symptoms, medical history, and any questions. This helps ensure you get the most from your visit. It also helps your doctor have all the info they need to care for you effectively.
Being informed and prepared lets you actively manage your condition. This can improve your outcomes.
Treatment for Blood Clot in Arm: Medical Approaches
Several treatments are available for blood clots in the arm. These include medicines and surgery. The right treatment depends on the clot’s size, the patient’s health, and any other health issues.
Anticoagulant Medications (Blood Thinners)
Anticoagulant medicines, or blood thinners, are often the first choice. They stop the clot from growing and prevent new ones. They don’t dissolve clots but help the body break them down slowly.
Common Anticoagulants:
- Warfarin
- Rivaroxaban
- Apixaban
- Dabigatran
Thrombolytic Therapy (Clot-Busting Drugs)
For serious cases or when the limb is at risk, thrombolytic therapy might be used. This treatment uses drugs to quickly dissolve the clot. It’s for emergencies or when blood thinners don’t work.
Mechanical Thrombectomy Procedures
Mechanical thrombectomy removes the clot from the blood vessel. It uses different methods, like catheter-directed thrombectomy. It’s used for big clots or severe symptoms.
Angioplasty and Stent Placement
After the clot is gone or dissolved, angioplasty and stent placement might be done. This opens up the blood vessel and keeps blood flowing well. It also stops future clots.
The table below shows the treatment options for blood clots in the arm:
| Treatment Option | Description | Used For |
| Anticoagulant Medications | Prevent clot growth and new clot formation | Initial treatment, prevention |
| Thrombolytic Therapy | Dissolve clots quickly | Severe cases, emergency situations |
| Mechanical Thrombectomy | Physically remove clots | Large clots, severe symptoms |
| Angioplasty and Stent Placement | Restore blood flow, prevent future clots | Underlying narrowing or blockage |
At-Home Management and Self-Care Steps
Managing arm blood clots at home is key to healing. By following these steps, you can help your body recover. This can also lower the chance of serious problems.
Using Compression Sleeves Correctly
Compression sleeves are a big help in managing arm blood clots. They apply gentle pressure to reduce swelling and improve blood flow. Here’s how to use them right:
- Choose a sleeve that fits comfortably, not too tight or too loose.
- Wear the sleeve as directed by your healthcare provider, typically during the day.
- Remove the sleeve at night unless your doctor says not to.
- Watch for any signs of skin irritation or pressure damage.
Proper Arm Elevation Techniques
Elevating your arm is also very important. It helps reduce swelling and eases pain. Here’s how to do it right:
- Place your arm above your heart.
- Use pillows or a wedge to support your arm while elevating it.
- Avoid bending your arm in ways that could block blood flow.
- Elevate your arm for 15-20 minutes, several times a day.
Pain Management Strategies
Managing pain is a big part of at-home care for arm blood clots. Here are some tips:
- Follow your healthcare provider’s advice on pain medication.
- Use cold or warm compresses as suggested to ease pain.
- Rest your arm and avoid hard activities.
- Keep an eye on your pain levels and tell your doctor if it changes a lot.
Activity Modifications During Recovery
Changing your daily activities is key during recovery. Here’s what to do:
- Avoid heavy lifting or bending.
- Take regular breaks to rest your arm.
- Adjust your workspace to lessen strain on your arm.
- Slowly go back to normal activities as your doctor advises.
By following these steps, you can improve your recovery from arm blood clots. This can also help prevent serious issues.
Living with and Managing Arm Blood Clots
After finding out you have an arm blood clot, it’s key to manage it well. “Living with blood clots means knowing how to handle them,” says Medical Expert, a top vascular specialist.
Adjusting Daily Activities
Changing your daily routine is important to avoid more problems. Stay active by moving around often and don’t overdo it. It’s important to find a balance between rest and activity to help you get better.
Managing Medication Side Effects
Dealing with medication side effects is also a big deal. Blood thinners help stop new clots but can cause bleeding. Watch for bleeding signs and tell your doctor right away.
“The key to managing arm blood clots lies in a combination of medical treatment and lifestyle adjustments,” notes the Medical organization.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Arm blood clots can really affect your mood and mind. Feeling anxious or scared is normal. Getting help from doctors, family, and support groups can help you feel better.
When to Return to Normal Activities
Deciding when to go back to normal activities needs a doctor’s advice. They’ll guide you based on how you’re doing. Start slowly and with doctor’s approval to avoid problems.
Understanding your condition, making changes, and following doctor’s orders can help manage arm blood clots. This way, you can live a better life.
Preventing Recurrence of Arm Blood Clots
To prevent arm blood clots from coming back, we need to make lifestyle changes and possibly take medication for a long time. We’ll talk about how to lower the risk of getting clots again.
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Risk
Changing your lifestyle can greatly lower the chance of getting arm blood clots again. Here are some tips:
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce pressure on veins.
- Regular exercise to improve circulation.
- Avoiding prolonged periods of immobility.
- Quitting smoking to improve overall vascular health.
Long-term Medication Considerations
For many, taking medication for a long time is key to preventing arm blood clots from coming back. This might include:
- Anticoagulant medications (blood thinners) to prevent new clots from forming.
- Antiplatelet drugs to prevent platelets from clumping together.
It’s important to stick to your medication plan and go to follow-up appointments. This helps your doctor see if the treatment is working and make changes if needed.
Regular Monitoring and Follow-up Care
Regular checks are important to catch any signs of a clot coming back early. This includes:
| Monitoring Activity | Frequency | Purpose |
| Blood tests | Regular intervals | To monitor blood clotting factors |
| Ultrasound | As recommended by doctor | To check for new clots or changes in existing clots |
| Follow-up appointments | Scheduled by healthcare provider | To assess overall condition and adjust treatment plan |
Recognizing Early Signs of Recurrence
Knowing the early signs of arm blood clot recurrence can help get quick medical help. Look out for:
- Swelling or pain in the arm.
- Warmth or redness in the affected area.
- Visible veins or discoloration.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s very important to see a doctor right away.
Conclusion
It’s important to know the signs, causes, and treatments for a blood clot in the arm. Deep vein thrombosis in the arm needs quick medical care to avoid serious problems.
We talked about different treatments like medicines, clot-busting therapy, and mechanical removal. If symptoms don’t go away or get worse, you should see a doctor right away.
The Medical organization says getting medical help fast is key to treating blood clots. Knowing the risks and taking steps to prevent them can help avoid blood clots in the arm.
Managing deep vein thrombosis means both medical treatment and making lifestyle changes. Understanding your treatment options and taking action can lower the chance of another clot. It also helps improve your health overall.
FAQ
What is upper extremity deep vein thrombosis (UEDVT)?
UEDVT is a blood clot in the deep veins of the arm. It can cause pain, swelling, and other issues if not treated quickly.
How common are arm blood clots compared to leg blood clots?
Arm blood clots are less common than leg ones. But, they are serious, mainly for people with certain health issues or after medical procedures.
What are the symptoms of a blood clot in the arm?
Symptoms include pain, swelling, warmth, redness, and tenderness. You might also see a visible cord or discoloration.
What are the causes and risk factors for developing arm blood clots?
Causes and risk factors include medical procedures, health conditions, physical factors, and genetics. Knowing these can help prevent and detect early.
When should I seek medical help for an arm blood clot?
Seek help right away for severe pain, arm movement issues, or signs of a pulmonary embolism like shortness of breath or chest pain.
How is a blood clot in the arm diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a physical exam, medical history, and tests like ultrasound, venography, or blood tests to confirm the clot.
What are the treatment options for arm blood clots?
Treatments include anticoagulant meds, thrombolytic therapy, mechanical thrombectomy, and angioplasty with stent. The choice depends on the clot’s severity and your health.
How can I manage arm blood clots at home?
Manage at home with compression sleeves, arm elevation, pain management, and activity modification. Always follow your doctor’s advice.
How can I prevent the recurrence of arm blood clots?
Prevent recurrence with lifestyle changes, long-term meds, regular checks, and knowing early signs. Your doctor can give personalized advice.
What are the possible complications of arm blood clots?
Complications include pulmonary embolism, post-thrombotic syndrome, and clot recurrence. Quick treatment and prevention can lower these risks.
Can arm blood clots be life-threatening?
Yes, they can be life-threatening if they travel to the lungs. Seek immediate medical help if you have symptoms of a pulmonary embolism.
How long does it take to recover from an arm blood clot?
Recovery time varies based on the clot’s severity, treatment, and health. Symptoms can improve in weeks, but full recovery may take longer.
References
- Mangiafico, M., Oberti, F., Giubilato, S., Luzzati, R., Squadrito, F., Bono, A., … & Di Stasi, S. (2024). Superficial venous thrombosis: A comprehensive review. Healthcare, 12(4), 500. https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9032/12/4/500
- StatPearls [Internet]. (2023). Superficial thrombophlebitis. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556017/
- Zhang, Y., Ding, J., Guo, H., Liang, J., & Li, Y. (2020). Associations of Fish and Omega-3 Fatty Acids Consumption With the Risk of Venous Thromboembolism: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Frontiers in Nutrition, 7, 614784. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/nutrition/articles/10.3389/fnut.2020.614784/full























