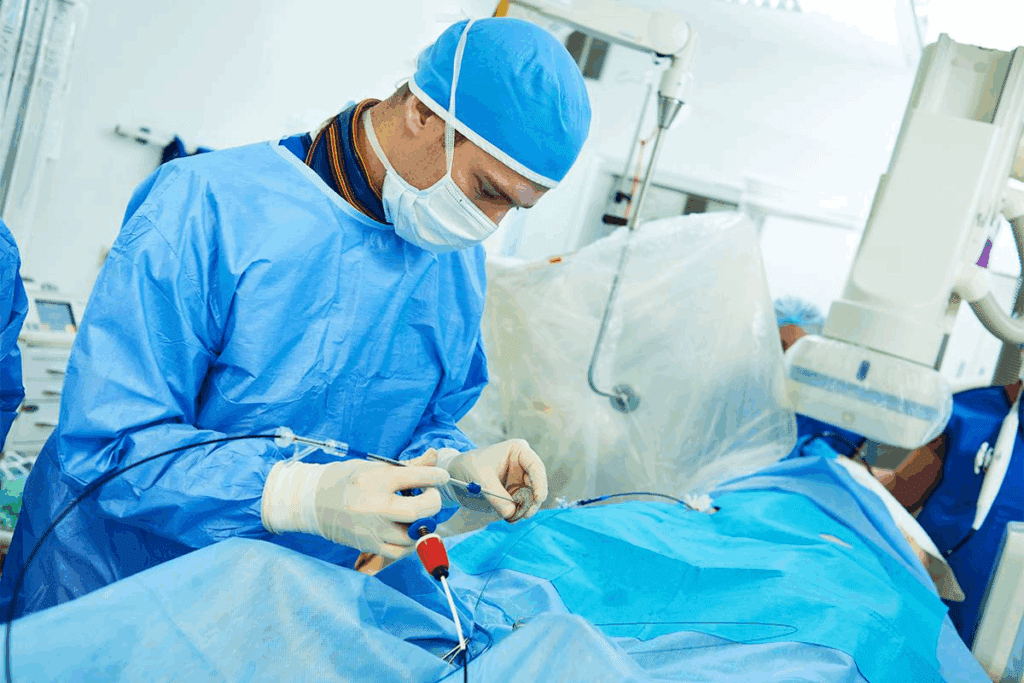
Learning about a coronary stent procedure is important for heart health. At Liv Hospital, we think education is key. A coronary stent procedure video shows how a stent is put into a blocked artery. This helps blood flow normally again and relieves symptoms.
We follow international standards and use proven methods to care for our patients. Watching a coronary stent procedure video helps patients understand the procedure and shows how it can treat coronary artery disease.
Key Takeaways
- Coronary stent procedures are minimally invasive and help restore blood flow to the heart.
- Stents are flexible tubes placed in arteries to increase blood flow.
- Watching a coronary stent procedure video can educate patients on the process.
- Liv Hospital follows international standards for coronary stent procedures.
- Understanding the procedure can help alleviate patient concerns.
Understanding Coronary Artery Disease and the Need for Stents
Coronary arteries carry oxygen and nutrients to the heart. When they get blocked, it’s a serious problem. Coronary artery disease happens when these arteries narrow or get blocked by plaque.
What Causes Coronary Artery Blockages
Blockages in coronary arteries are mainly due to plaque buildup. This plaque is made of fat, cholesterol, and other substances. It sticks to the artery walls, narrowing or blocking them, and cuts down blood flow to the heart.
Key factors contributing to plaque buildup include:
- High levels of LDL cholesterol
- Smoking
- Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Family history of heart disease
Symptoms That May Indicate Blocked Arteries
Blocked arteries can cause a drop in blood flow to the heart. This leads to symptoms like:
- Chest pain (angina)
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Pain or discomfort in the arms or legs
Medical experts say early treatment of coronary artery disease is key. It can greatly improve outcomes and lower the risk of serious problems.
“The goal of treating coronary artery disease is to relieve symptoms, slow disease progression, and prevent complications such as heart attacks.”
When Stent Placement Becomes Necessary
Stents are used when blockages are severe and cause symptoms. Or when there’s a high risk of heart attack. A stent is a small, mesh-like device placed in the artery to open it up and improve blood flow.
| Condition | Treatment Approach |
| Mild blockage without symptoms | Medication and lifestyle changes |
| Significant blockage with symptoms | Angioplasty with stent placement |
Whether to use a stent depends on many factors. These include the patient’s health, the blockage’s severity, and more.
What Do Heart Stents Look Like? Visual Guide
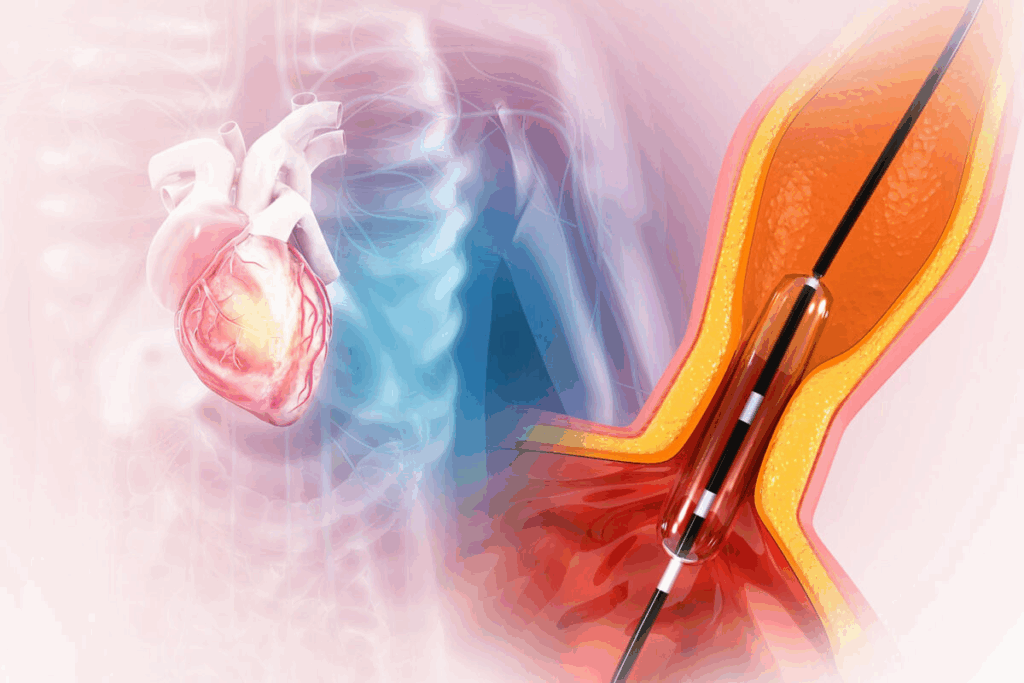
A heart stent is a tiny wire mesh tube used to keep an artery open. It’s small enough to go through a catheter and expands to keep the artery open. This improves blood flow to the heart.
The Mesh-Like Structure of Modern Stents
Modern heart stents are made of metal and have a mesh-like structure. They can be compressed for insertion and then expand once in place. This design also helps the artery heal around it.
Size and Dimensions: How Big Is a Heart Stent?
Heart stents come in different sizes but are generally small. They are about 2 to 4 millimeters in diameter and 8 to 38 millimeters long. To compare, they are roughly the size of a small paper clip or even smaller.
Real Heart Stent Images and Their Appearance
Real images of heart stents show their detailed mesh design. When expanded, they look like a cylindrical mesh tube in the artery. Pictures of stents in the heart show them expanded, keeping the artery open for normal blood flow.
| Stent Characteristic | Typical Measurement |
| Diameter | 2-4 mm |
| Length | 8-38 mm |
| Material | Metal (often stainless steel or cobalt-chromium) |
Types of Coronary Stents Available Today
There are many types of coronary stents, each with its own benefits. The right stent depends on the patient’s health, the blockage’s severity, and the doctor’s advice.
Bare Metal Stents: Structure and Use Cases
Bare metal stents are made from metals like stainless steel. They are simple in design and help keep the artery open. These stents are best for patients with a low risk of the artery narrowing again.
Drug-Eluting Stents: Medication Delivery System
Drug-eluting stents have a special coating that releases medicine. This medicine helps prevent the artery from narrowing. These stents are commonly used for patients at higher risk of artery narrowing.
Bioabsorbable Stents: The Newest Innovation
Bioabsorbable stents are made to dissolve in the body over time. They offer temporary support and then disappear, aiming to reduce long-term issues. Research is ongoing to learn more about their benefits and challenges.
| Stent Type | Characteristics | Use Cases |
| Bare Metal Stents | Simple metal design | Lower risk of restenosis |
| Drug-Eluting Stents | Medication coating | Higher risk of restenosis |
| Bioabsorbable Stents | Absorbable material | Potential for reduced long-term complications |
As shown in the table, each stent type has unique features for different patient needs. Choosing the right stent is a key decision based on individual factors.
The Coronary Stent Procedure Video: What to Expect
The coronary stent procedure is a minimally invasive method to open blocked arteries. It’s also known as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or angioplasty. This treatment is common for coronary artery disease.
Setting: Inside the Catheterization Laboratory
The procedure takes place in a catheterization laboratory. This room has X-ray imaging equipment. It helps cardiologists see the coronary arteries and place the stent accurately.
Duration: From 30 Minutes to 2 Hours
The time needed for a coronary stent procedure varies. It can be from 30 minutes to 2 hours. The complexity of the blockage and the number of stents used affect the time.
Key Moments Captured in Procedure Videos
Procedure videos show important moments. These include the catheter insertion, balloon inflation to expand the stent, and the final angiogram. This confirms the stent is in place correctly.
| Procedure Step | Description | Key Moments Captured |
| Catheter Insertion | Accessing the arterial system through a small incision | Guiding the catheter to the blocked artery |
| Balloon Inflation | Expanding the stent to open the blocked artery | Visualizing stent expansion via X-ray |
| Final Angiogram | Confirming successful stent placement and blood flow | Verifying the stent is fully expanded and functional |
Watching a coronary stent procedure video can help patients understand the process. It shows the steps and what to expect. This visual guide can ease concerns and prepare individuals for the procedure.
How Stents Are Inserted: The Balloon Angioplasty Method
Coronary stent placement uses balloon angioplasty, a procedure that opens up the heart’s blood flow. It involves several steps that our medical team will explain to you.
Accessing the Arterial System
The first step is to get into the arterial system. Our doctors use a thin, flexible tube called a catheter in the groin or arm. This tube is a path for the tools needed for the stent.
After the catheter is in, it’s guided to the heart with X-ray imaging. This lets our team see where the catheter is and make sure it’s in the right spot.
Navigating to the Blockage Site Using X-ray Guidance
Next, the catheter is moved to the blockage. Our doctors use X-ray to find the narrowed artery. A contrast agent might be used to make the blood vessels and blockage more visible.
Balloon Inflation and Stent Expansion Process
When the catheter reaches the blockage, a balloon is inflated. This expands the stent against the artery walls. This opens the artery, improving blood flow. The stent stays in place even after the balloon is gone.
Confirming Proper Placement
After the stent is expanded, we check if it’s in the right spot with angiography. This uses X-ray images with a contrast agent. Once it’s confirmed, the catheter is taken out, ending the procedure.
The stent stays in the artery, helping the vessel walls and keeping the artery open. This is a long-term fix that improves blood flow to the heart.
Patient Preparation and Experience During Stent Placement
Understanding the steps to stent placement is key. Knowing what to expect can ease your worries. It prepares you for the procedure.
Pre-Procedure Testing and Evaluation
We start with tests to check your health and artery condition. These include blood work, electrocardiograms, and angiograms. This helps us plan your procedure.
Medication and Fasting Requirements
You’ll need to fast before the procedure and might adjust your meds. We’ll tell you which meds to keep or stop. It’s important to follow these instructions to stay safe.
Consciousness Level and What Patients Feel
During the procedure, you’ll be awake but relaxed. You might feel some pressure or discomfort. But, this is usually manageable. Our team is there to make sure you’re comfortable.
Communication with the Medical Team During the Procedure
Even though you’re sedated, you can talk to our team if needed. Let us know if you feel any pain or discomfort. This helps us take better care of you.
After the procedure, you’ll take blood thinners to prevent clots. We’ll give you clear instructions on how to care for yourself and manage your meds. This will help you recover smoothly.
Before and After: Heart Stent Procedure Results
Putting in a coronary stent is key to getting blood flowing right to the heart again. We’ll look at the quick and lasting effects of this step. It shows big improvements for those with heart artery disease.
Immediate Changes in Blood Flow
Right after a stent is put in, blood flow to the heart gets better fast. The stent widens the blocked artery, letting blood flow freely. This cuts down the risk of heart attacks by keeping the artery open.
Angiogram Comparisons: Before and After Images
Angiogram pictures show the artery before and after the stent. They clearly show the artery opening up after the procedure. This proves the stent’s success in improving blood flow.
How Stents Integrate with Artery Walls Over Time
As time goes by, the stent blends with the artery wall. This is key for its long-term success. Modern stents, with their mesh-like design, let new tissue grow around them. This makes the stent part of the artery lining, keeping it open for blood flow.
Understanding how stents work and their role in heart disease shows their life-saving value. The quick and lasting benefits make this treatment a great choice for many.
Recovery and Life After a Coronary Stent Procedure
Life after a coronary stent procedure needs some changes. But, with the right help, patients can adjust well. The recovery includes several important steps to get back to normal life smoothly.
Immediate Post-Procedure Care
Right after the procedure, patients stay in the hospital for a few hours. Medical staff watch for any immediate problems and make sure the patient is okay. You might feel sore or bruised where the catheter was inserted, but this usually goes away in a few days.
Essential Medications Following Stent Placement
Patients take antiplatelet medications to stop clots from forming around the stent. Taking these medications as directed is key for the procedure’s success. Following the doctor’s advice on dosage and how long to take them is very important.
Activity Restrictions and Return to Normal Life
It usually takes a few days to a week to get back to work and physical activities. Try to avoid heavy lifting, bending, or hard activities during the first recovery period. Always check with your doctor for when it’s okay to start doing normal things again.
Long-Term Monitoring Requirements
Regular visits to a cardiologist are needed to check on the stent and heart health. You might need tests like stress tests or angiograms to make sure everything is working right and there are no new blockages.
Understanding the recovery process and following the recommended steps can greatly improve outcomes after a coronary stent procedure. Always talk to healthcare professionals for personalized advice and support during the recovery journey.
Potential Risks and Complications of Heart Stent Procedures
Heart stent procedures are usually safe. But, there are risks and complications to know about. It’s important to understand these to make good choices and take care of yourself after the procedure.
Common Minor Complications
Minor issues might include bruising or bleeding where the catheter was inserted. You could also have an allergic reaction to the dye used or temporary kidney problems. Most minor problems get better on their own or with a little treatment.
Serious Risks to Be Aware Of
More serious problems include blood clots in the stent, which can cause a heart attack. Another risk is restenosis, where the artery gets narrow again. Though rare, these serious issues can be deadly and need quick medical help.
Signs That Require Immediate Medical Attention
If you have chest pain, trouble breathing, severe bleeding, or signs of infection at the catheter site, get help right away. Knowing these signs can help a lot.
Success Rates and Safety Statistics
Heart stent procedures work well for most people, improving blood flow in over 90% of cases. Here are some important stats on the safety and success of coronary stent procedures.
| Procedure Outcome | Success Rate |
| Immediate Blood Flow Improvement | 95% |
| Restenosis Rate (within 1 year) | 5-10% |
| Major Complication Rate | <2% |
Knowing about the risks and complications helps patients take care of themselves better. This ensures the best results from their heart stent procedure.
Conclusion: The Life-Saving Impact of Coronary Stent Procedures
Coronary stent procedures have changed how we treat heart disease. They greatly improve patients’ lives. By watching a coronary stent procedure video, patients can learn what to expect.
Seeing a heart stent surgery video gives insights into the process. It shows how the stent is placed and its immediate effects on blood flow. This helps patients understand the benefits of stents.
Stents lower the risk of heart attacks and ease symptoms of heart disease. New stent technologies, like drug-eluting and bioabsorbable stents, offer more options for treatment.
We’ve highlighted the key points of coronary stent procedures. This shows their life-saving role and the need for ongoing medical progress in this area.
FAQ
What does a stent in the heart look like?
A heart stent is a small, mesh-like tube made of metal. It keeps arteries open, improving blood flow. Modern stents are made from materials like stainless steel or cobalt-chromium alloy.
How big is a stent in the heart?
Heart stents vary in size. They’re usually between 8mm to 38mm long. They expand to fit the artery’s diameter, which is between 2.5mm to 4.5mm.
What is a coronary stent procedure video?
A coronary stent procedure video shows the stent placement in a coronary artery. It covers the steps from accessing the artery to deploying the stent.
How are stents installed?
Stents are installed using balloon angioplasty. A catheter with a balloon and stent is guided to the blockage. The balloon is inflated to expand the stent, keeping the artery open.
What are the different types of coronary stents available?
There are several coronary stents, including bare metal, drug-eluting, and bioabsorbable stents. Each type has its own benefits and use cases, based on the patient’s condition.
What is the recovery process like after a coronary stent procedure?
After the procedure, patients are monitored for hours. They may need medications to prevent clotting and activity restrictions. Most can return to normal activities within a week.
What are the possible risks and complications of heart stent procedures?
Heart stent procedures are generally safe but can have complications. These include minor issues like bruising and serious risks like stent thrombosis. Patients should know the signs of serious complications.
How do stents integrate with artery walls over time?
After placement, the stent keeps the artery open. Over time, the artery wall grows around the stent, securing it. The type of stent affects how it integrates with the artery.
Can I see before and after images of heart stent procedures?
Yes, angiogram comparisons before and after stent placement show the procedure’s effectiveness. These images illustrate the improved blood flow through the artery after the stent is placed.
What should I expect during a coronary stent procedure?
During the procedure, you’ll be awake but sedated. The team will access your arterial system, navigate to the blockage, deploy the stent, and confirm its placement using X-ray imaging. The procedure takes between 30 minutes to 2 hours.
References
Bamias, A., et al. (2017). Current clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review. Cancer Treatment Reviews, 53, 107-116. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5469586/





