Learn what an epidural caudal steroid injection is. Our ultimate guide explains this powerful procedure and how it differs from other epidurals.
A caudal epidural steroid injection is a precise procedure. It delivers anti-inflammatory medication into the epidural space. This is done through the sacral hiatus, targeting the lower spine.
This method is different from other epidural injections. It has a specific anatomical approach. This makes it an effective treatment for various spinal conditions.
By injecting steroids directly into the epidural space near the lower spine, it provides relief from chronic pain.
The caudal approach is great for pain in the lower back and legs. It’s a trusted choice for patients with different spinal issues.
Key Takeaways
- A caudal epidural steroid injection delivers medication directly into the epidural space near the lower spine.
- This procedure differs from other epidural injections due to its specific anatomical location.
- It is an effective treatment for various spinal conditions, providing relief from chronic pain.
- The caudal approach is beneficial for addressing lower back and leg pain.
- It is a trusted choice for patients with diverse spinal issues.
Understanding Caudal Epidural Steroid Injections
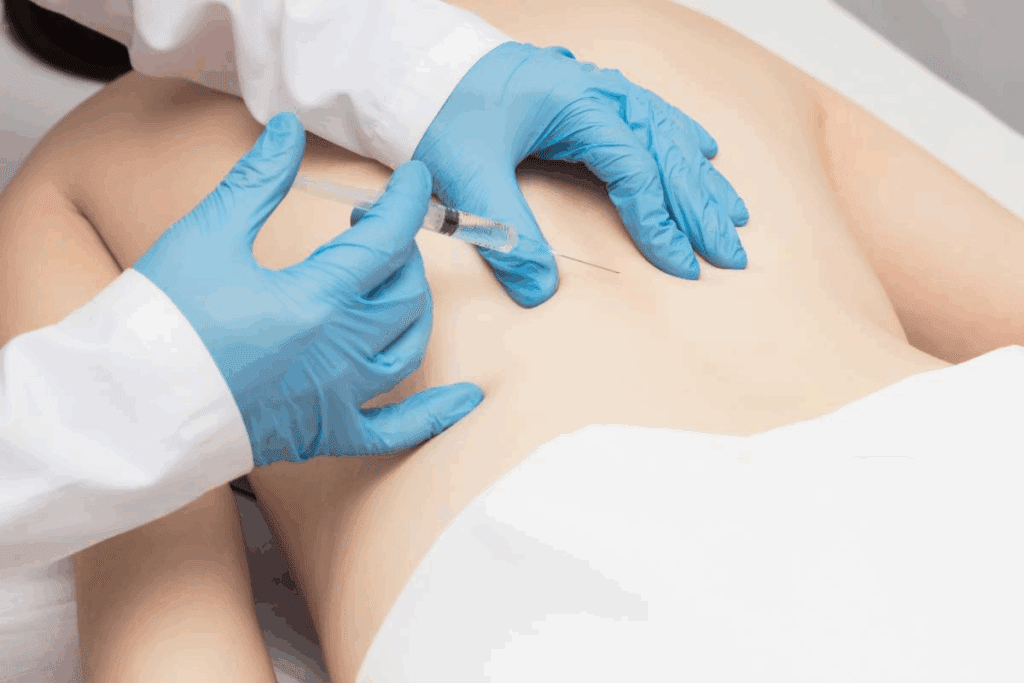
It’s important to know about caudal epidural steroid injections for doctors and patients. These injections help manage many spinal problems.
Definition and Basic Concept
A caudal epidural steroid injection puts corticosteroids into the epidural space. This is done through the sacral hiatus at the spine’s bottom. It aims to cut down inflammation and pain in the lower back and legs.
The caudal approach is great because it skips the lumbar spine. This might lower the chance of problems.
Historical Development of the Procedure
Epidural injections started in the early 1900s. But the caudal method became more popular over time. It’s simpler and safer.
First used for anesthesia, it’s now used for pain relief. Adding corticosteroids made it even better, helping patients with inflammation for longer.
The caudal epidural steroid injections have improved a lot. New imaging and needle techniques make it more precise and effective.
Anatomy of the Caudal Spine and Epidural Space
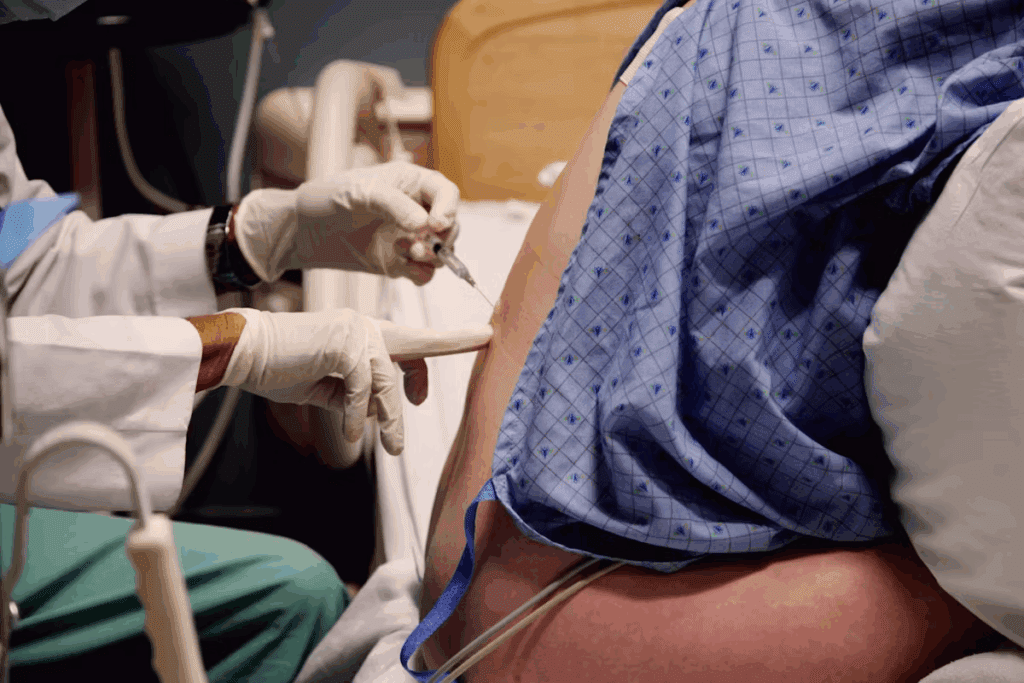
The anatomy of the caudal spine is key to understanding caudal epidural steroid injections. The caudal spine, or sacrum and coccyx, is at the base of the spine.
The Sacral Hiatus and Sacrococcygeal Ligament
The sacral hiatus is an opening at the sacrum’s lower end. It’s a key spot for caudal epidural injections. It’s surrounded by the sacral cornua and covered by the sacrococcygeal ligament.
The sacrococcygeal ligament connects the sacrum to the coccyx. It must be pierced for a caudal epidural injection to reach the epidural space.
The Epidural Space in the Lumbosacral Region
The epidural space is outside the dura mater, from the foramen magnum to the sacral hiatus. In the lumbosacral area, it’s important for epidural steroid injections. It lets corticosteroids get close to the affected nerves.
This space has fatty tissue, blood vessels, and nerve roots. The caudal injection location targets this space. It helps deliver medication to ease pain and inflammation in the lower back and legs.
Medical Conditions Treated with Epidural Caudal Steroid Injection
Many medical conditions can be treated with caudal epidural steroid injections. These injections help manage chronic pain from several spinal disorders.
Sciatica and Nerve Compression Syndromes
Sciatica causes pain that spreads along the sciatic nerve. It’s a common condition treated with these injections. Nerve compression syndromes also benefit from this treatment. The injection reduces inflammation around the nerves, easing pain.
Studies show caudal epidural steroid injections are effective for sciatica. By injecting steroids into the epidural space, they reduce inflammation and pain.
Herniated Discs and Degenerative Disc Disease
Caudal epidural steroid injections help with pain from herniated discs and degenerative disc disease. Herniated discs irritate nerves, while degenerative disc disease causes pain and stiffness.
- Reduces inflammation around the affected discs
- Relieves pressure on nerves
- Improves mobility and reduces pain
Spinal Stenosis and Other Indications
Spinal stenosis is another condition treated with these injections. It narrows the spinal canal, putting pressure on nerves and causing pain.
Other conditions treated include:
- Post-surgical pain
- Chronic low back pain
- Radiculopathy
Caudal epidural steroid injections target pain and inflammation. They offer a valuable treatment for those with these conditions. The procedure is great for those who haven’t seen results from other treatments or want to avoid surgery.
The Caudal Injection Location: Anatomical Considerations
To place caudal epidural steroid injections correctly, knowing the sacral anatomy is key. The sacral canal is a vital spot for this procedure. It’s where the injection starts.
The Sacral Canal Entry Point
The sacral canal goes from the spinal canal to the sacrum. It ends at the sacral hiatus. This opening is covered by the sacrococcygeal ligament. To get to the epidural space, the needle goes through the sacral hiatus. Fluoroscopic guidance helps place the needle right.
Anatomical Variations and Challenges
There can be challenges with caudal epidural steroid injections. The size and shape of the sacral hiatus and the sacrococcygeal ligament can vary. This makes it harder to reach the epidural space. For example, a smaller sacral hiatus needs more precise needle placement.
Also, anatomical variations like sacral fusion or past surgeries can make things harder. Before starting, imaging studies help find these issues and plan the best way to do the injection.
Types of Epidural Injections: A Comparative Overview
For those with spinal disorders, knowing about epidural injections is key. These injections are a common treatment for many spinal issues. The method used can greatly affect the results.
Interlaminar Epidural Injections
Interlaminar epidural injections put medication into the epidural space through the interlaminar space. This is usually done in the lower back. It’s good for treating central spinal stenosis and disc herniations. This method spreads the steroids widely, covering many nerve roots.
Transforaminal Epidural Injections
Transforaminal injections target specific nerve roots by going through the neural foramen. This method is great for treating radicular pain from specific nerve root issues. It’s seen as more precise and can help diagnose and treat at the same time.
Caudal Injection vs Epidural: Key Differences
Caudal epidural steroid injections go through the sacral hiatus. This makes them different from interlaminar and transforaminal injections. The main difference is the entry point and how the medication spreads. Caudal injections are less likely to cause dural puncture and are good for lower sacral nerve issues.
Choosing between interlaminar, transforaminal, and caudal injections depends on the condition, the patient’s body, and the doctor’s choice.
In summary, while all three types of epidural injections help with spinal pain, they differ in how they’re done, what they treat, and their effects. Understanding these differences helps doctors make better choices and improve care for patients.
The Caudal Epidural Steroid Injection Procedure
The caudal epidural steroid injection process has several important steps. These steps are key to making sure the treatment is safe and works well. A top pain management expert says, “Caudal epidural steroid injections are a great option for those with chronic lower back pain and radiculopathy.”
Patient Preparation and Positioning
First, the patient lies face down on a table with X-ray technology. The skin at the sacral area is cleaned with an antiseptic. Then, local anesthesia is given to reduce pain. Getting the patient in the right position is very important for the procedure’s success.
Needle Placement and Technique
A needle is inserted through the sacral hiatus under X-ray guidance. Contrast media is used to check the needle’s position. Getting the needle in the right spot is key to effectively deliver the medication.
Medication Delivery and Post-Procedure Care
After the needle is in place, a mix of steroid and local anesthetic is injected. Patients are watched for a bit before they go home. Instructions for aftercare are given to help with recovery.
A study shows, “Caudal epidural steroid injections are safe and effective for many with lower back pain.” By following the procedure and caring for patients properly, doctors can get the best results.
Imaging Guidance for Caudal ESI Procedures
Imaging guidance is key for the success and safety of caudal epidural steroid injections (ESI). The complex nature of the caudal anatomy requires advanced imaging. This ensures the steroid medication is placed correctly.
Fluoroscopic Guidance Techniques
Fluoroscopy is a common method for guiding caudal ESI procedures. It uses a fluoroscope to show real-time X-ray images. This helps the practitioner place the needle accurately in the caudal space.
Fluoroscopic guidance makes the injection more precise. It lowers the chance of mistakes like injecting into a blood vessel or puncturing the dura.
To confirm the needle’s position, contrast media is used. After the needle is in place, the steroid is injected. The spread of the medication is then checked under fluoroscopy.
Ultrasound Guidance Applications
Ultrasound is another important imaging tool for caudal ESI. It has benefits like no radiation and clear views of soft tissues in real-time. Ultrasound is great for patients where fluoroscopy isn’t an option.
Ultrasound lets practitioners see the needle, the surrounding tissues, and the medication spread. This live feedback helps them make any necessary adjustments. It ensures the medication is delivered accurately.
Both fluoroscopy and ultrasound have their roles in caudal ESI. The choice depends on the patient’s anatomy, the practitioner’s preference, and the equipment available.
Benefits of the Epidural Caudal Steroid Injection Approach
The caudal epidural steroid injection method has many benefits. It is known for its effectiveness in pain relief and its low risk of complications. This makes it a preferred choice over other methods.
Safety Profile and Reduced Risk of Dural Puncture
This method is safe and has a low risk of dural puncture. The sacral hiatus is used to access the epidural space. This reduces the chance of dural puncture, which can cause headaches and nerve damage.
- Lower risk of dural puncture due to the caudal approach
- Reduced risk of nerve damage
- Fewer complications compared to more invasive epidural injections
Its safety makes it a good choice for those at risk of complications from other procedures.
Coverage of Sacral Nerves for Optimal Pain Control
The caudal epidural steroid injection also targets the sacral nerves well. This is key for managing pain in the lower back and legs. It helps in achieving optimal pain control for patients with chronic pain.
- Effective targeting of sacral nerves for pain relief
- Broad coverage area, ensuring complete pain management
- Potential for better results in complex pain cases
Caudal nerve blocks are great for this. They allow the steroid medication to reach the pain areas directly, improving treatment outcomes.
In summary, the caudal epidural steroid injection is safe and effective. It is a valuable treatment for chronic pain patients.
Potential Risks and Complications
It’s important to know the risks and complications of caudal epidural steroid injections. These injections are generally safe but can cause side effects and complications.
Common Side Effects
Common side effects include:
- Temporary pain or discomfort at the injection site
- Headaches due to leakage of cerebrospinal fluid
- Nausea and vomiting
- Facial flushing
- Increased blood sugar levels, which is a concern for diabetic patients
- Insomnia or disturbed sleep patterns
These side effects are usually mild and go away within a few days. Knowing about them helps manage expectations and care after the procedure.
Rare but Serious Complications
Though rare, serious complications can happen. These include:
- Infection at the injection site or within the epidural space
- Nerve damage or irritation leading to persistent pain or numbness
- Bleeding complications, which is a risk for those on anticoagulant therapy
- Allergic reactions to the steroid or local anesthetic used
- Accidental dural puncture leading to severe headache or other neurological symptoms
Healthcare providers must carefully evaluate patients before the procedure to minimize these risks.
Contraindications for Caudal Injections
Some conditions make caudal epidural steroid injections not suitable. These include:
- Active infection or sepsis
- Bleeding disorders or anticoagulation therapy
- Known allergy to steroids or local anesthetics
- Pregnancy, unless the benefits outweigh the risks
- Previous adverse reaction to epidural steroid injections
As one study noted, “Careful patient selection and thorough pre-procedure evaluation are key to minimizing risks and ensuring the safe administration of caudal epidural steroid injections.”
This highlights the need for a detailed assessment before treatment.
In conclusion, while caudal epidural steroid injections are useful in pain management, it’s vital to understand their risks and complications. Being aware of these factors helps mitigate risks and improve outcomes for both healthcare providers and patients.
Clinical Effectiveness of Caudal ESI
Understanding how well caudal epidural steroid injections work is key. They are being looked at for treating spinal problems and chronic pain.
Short-term Pain Relief Outcomes
Research shows caudal ESI helps with short-term pain relief. It’s used for sciatica and lumbar disc herniation. The injection puts steroids in the epidural space, which reduces inflammation and eases pain.
Clinical trials have shown many patients see better symptoms and function after the procedure.
Long-term Efficacy and Repeated Injections
How well caudal ESI works over time is being studied. Some patients get long-lasting pain relief, while others need more injections. Factors affecting long-term results include the condition, symptom severity, and how the patient reacts to the steroids.
Some patients need more than one injection. The timing and frequency depend on the patient’s needs and how they react to treatment.
Patient Selection for Optimal Results
Choosing the right patients is vital for caudal ESI success. Best candidates have specific spinal issues that steroids can help, like radiculopathy or lumbar spinal stenosis. A detailed check-up, including tests and a doctor’s assessment, helps find the right patients and predict treatment success.
- Patients with radiculopathy or lumbar spinal stenosis
- Individuals with significant pain and limited mobility
- Those who have not responded to conservative management
Special Considerations for Caudal Epidural Blocks
Healthcare providers must think about special patient factors when doing caudal epidural blocks. These factors can change how well and safely the procedure works.
Post-Surgical Patients and Anatomical Alterations
Patients who have had spinal surgery face a special challenge with caudal epidural steroid injections. Changes in their body, like scar tissue or old hardware, can mess with how the medicine spreads. This can affect how well the treatment works.
Key considerations for post-surgical patients include:
- Looking at their past surgery records to know their body’s layout
- Using imaging tools like fluoroscopy or ultrasound to find their way
- Changing how much and how fast they inject the medicine
| Consideration | Description | Clinical Implication |
| Surgical History | Looking at past spinal surgeries | Helps predict what their body might look like |
| Imaging Guidance | Using tools like fluoroscopy or ultrasound | Makes it easier to get the medicine right |
| Injectate Adjustment | Changing how much and how fast to inject | Makes the medicine spread better and work better |
Pediatric and Geriatric Applications
Caudal epidural steroid injections are used for all ages, from kids to older adults. Each age group has its own special needs.
In kids, the treatment is often for conditions they’re born with or grow up with. Doctors carefully choose the right dose and method for the child’s size and age.
For older adults, the treatment is more complicated because they might have other health issues and take many medicines. It’s very important to check their overall health and how medicines might mix with the steroid.
By knowing these special needs, doctors can make caudal epidural blocks better for all kinds of patients. This makes the treatment safer and more effective.
Conclusion
Caudal epidural steroid injection is a helpful treatment for chronic pain. It involves injecting steroids into the epidural space through the sacral hiatus. This helps patients with sciatica, herniated discs, and spinal stenosis.
This method has many benefits. It has a lower risk of dural puncture and can target multiple nerve roots. Studies show it works well for both short-term and long-term pain relief.
Healthcare professionals need to know about the anatomy, procedure, and risks of caudal epidural steroid injections. This knowledge helps them choose the right patients for treatment. Proper technique is key for the best results.
In summary, caudal epidural steroid injection is a safe and effective treatment. It’s a valuable part of a complete pain management plan.
FAQ
What is a caudal epidural steroid injection?
This procedure involves injecting medication into the epidural space. It’s done through the sacral hiatus. It helps ease pain and inflammation in the lower back and legs.
How does a caudal epidural steroid injection differ from other epidural injections?
Unlike other epidural injections, caudal injections go through the sacral hiatus. Other injections might use different entry points.
What is the caudal injection location?
The caudal injection location is the sacral hiatus. It’s at the lower end of the sacrum. This spot allows access to the epidural space for injections.
What medical conditions are treated with epidural caudal steroid injections?
These injections help with sciatica, herniated discs, and more. They treat conditions that cause pain and inflammation in the lower back and legs.
What are the benefits of caudal epidural steroid injections?
They are a safe procedure with few risks. They offer effective pain relief. They also target sacral nerves for better pain control.
What are the possible risks and complications of caudal epidural steroid injections?
Side effects like pain at the injection site can happen. Serious issues like infection or nerve damage are rare but possible. Some patients, like those with bleeding disorders, should avoid it.
How is the caudal epidural steroid injection procedure performed?
First, the patient is prepared and positioned. Then, the needle is placed under imaging guidance. The medication is delivered next. After, the patient receives post-procedure care and monitoring.
What is the role of imaging guidance in caudal ESI procedures?
Imaging, like fluoroscopy or ultrasound, helps place the needle accurately. It ensures the medication is delivered correctly. This makes the procedure safer and more effective.
How effective are caudal epidural steroid injections in managing pain?
They can offer short-term pain relief. In some cases, they may also manage pain long-term. It depends on the condition and the patient’s response.
Are caudal epidural steroid injections suitable for all patients?
No, they’re not for everyone. Patients with certain conditions, like infections or bleeding disorders, should avoid them. Anatomical issues can also affect the procedure’s safety and success.
Can caudal epidural steroid injections be repeated?
Yes, they can be repeated. How often depends on the patient’s needs and response. Clinical guidelines also play a role in determining the frequency and number of injections.
References
Peng, J., et al. (2024). Systematic review and meta-analysis of current evidence in uterine artery embolization compared to myomectomy on symptomatic uterine fibroids. Scientific Reports, 14, Article 12345. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-69754-0


































