Artery Anatomy: Key Facts About How Arteries Work
At the heart of our circulatory system are arteries. These blood vessels carry oxygen-rich blood to our organs and tissues. Knowing how they work is key to understanding our circulatory health.
We will look into five important facts about artery anatomy. At Liv Hospital, we focus on giving each patient the care they need. Our team works hard to provide top-notch treatment and support.
Arteries are vital for our health. They help keep our cardiovascular system in good shape. In this article, we’ll dive into how arteries work, their role, and why they’re so important for our health.
Key Takeaways
- The circulatory system relies on arteries to transport oxygen-rich blood throughout the body.
- Arteries play a critical role in keeping us healthy and well.
- Understanding artery anatomy is essential for appreciating circulatory health.
- The structure and function of arteries are vital for delivering oxygen to organs and tissues.
- Maintaining healthy arteries is critical for preventing cardiovascular disease.
The Vital Role of Arteries in Blood Circulation
Arteries are key for blood flow, built to handle the heart’s strong pressure. They are essential for our body’s health and function.
What Are Arteries and Their Primary Function
Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the body. They are strong to handle the heart’s pressure. Their main job is to deliver oxygen and nutrients to our tissues and organs.
How Arteries Differ from Veins and Capillaries
Arteries are different from veins and capillaries in structure and function. Veins carry blood back to the heart, but arteries handle high-pressure blood. Capillaries are tiny for exchanging oxygen, nutrients, and waste with tissues.
| Characteristics | Arteries | Veins | Capillaries |
| Direction of Blood Flow | Away from the heart | Towards the heart | Exchange with tissues |
| Blood Pressure | High pressure | Low pressure | Low pressure |
| Wall Thickness | Thick walls | Thin walls | Very thin walls |
| Function | Supply oxygen and nutrients | Return deoxygenated blood | Exchange of substances |
Key Fact 1: The Three-Layered Structure of Arteries
Arteries have a special three-layered wall that is key to our circulatory system. The walls are made of the tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica adventitia. Each layer has its own role in how arteries work.
Understanding the Tunica Intima, Media, and Adventitia
The tunica intima is the innermost layer, covered in a single layer of endothelial cells. It’s vital for keeping blood flowing and stopping blood clots. The tunica media, in the middle, is mostly smooth muscle cells and elastic fibers. It helps control blood pressure and flow.
The tunica adventitia is the outer layer, made of connective tissue. It supports and holds the artery in place.
The three-layered structure helps arteries handle the high pressures from the heart. The elastic properties of the tunica media let arteries stretch and recoil with each heartbeat. This ensures blood keeps flowing smoothly throughout the body.
Key Fact 2: Types and Classification of Arteries
Arteries come in different types based on their structure, location, and function. Knowing these classifications helps us understand their role in the circulatory system.
Elastic Arteries: Properties and Functions
Elastic arteries have lots of elastic fibers. This lets them stretch and bounce back with each heartbeat. This is key for keeping blood pressure steady and ensuring blood keeps flowing.
The aorta and its main branches are elastic arteries. They are vital for the circulatory system because they:
- Help smooth out blood flow between heartbeats
- Keep blood pressure steady during diastole
- Push blood through the arterial tree
Muscular Arteries
Muscular arteries have a lot of smooth muscle in their walls. This lets them control blood flow to certain parts of the body. They are mainly involved in sending blood to different organs and tissues.
The main features of muscular arteries are:
- A thicker tunica media with more smooth muscle cells
- The ability to constrict or dilate to control blood flow
- Regulation of blood pressure through vasoconstriction and vasodilation
By understanding the different types of arteries and their roles, we can see how complex and efficient the circulatory system is.
Key Fact 3: Major Arteries and Their Functions
We start by looking at the key role of major arteries in our body’s circulatory system. We focus on their structure and how they work. These arteries are essential for carrying oxygen-rich blood to all parts of our body.
The Aorta and Its Branches
The aorta is the biggest artery, starting from the left ventricle of the heart. It splits into branches that send blood to the head, neck, and limbs. The aortic arch is a big part of the aorta, branching off into important arteries like the brachiocephalic trunk and left common carotid artery.
These branches help spread oxygenated blood all over the body. They supply vital organs and tissues.
Other Essential Arteries
Other key arteries include the pulmonary artery, coronary arteries, and carotid arteries. The pulmonary artery takes deoxygenated blood to the lungs. The coronary arteries give blood to the heart muscle.
The carotid arteries are critical for the brain. The internal carotid artery feeds the brain’s outer layer. The external carotid artery supplies the face and neck.
| Artery | Function | Region Supplied |
| Aorta | Distributes oxygenated blood | Body |
| Pulmonary Artery | Carries deoxygenated blood | Lungs |
| Coronary Arteries | Supplies blood to the heart | Heart Muscle |
| Carotid Arteries | Supplies blood to the brain | Brain |
Comprehensive Artery Anatomy: Location and Distribution
Arteries are found all over the body. They are key in bringing oxygen and nutrients to different areas. The network of arteries is complex, with each type serving a specific area.
Arteries of the Head and Neck Region
The head and neck get their blood from the aortic arch’s branches, like the carotid arteries. These arteries are vital for the brain and other head and neck structures.
Thoracic and Abdominal Arterial Networks
The thoracic and abdominal areas get their blood from the aorta’s branches. The thoracic aorta supplies the chest, while the abdominal aorta goes to the abdominal organs.
Arterial Supply to the Extremities
The extremities get their blood from the aortic bifurcation’s branches. The subclavian arteries serve the upper limbs, and the femoral arteries do the same for the lower limbs. These arteries split into smaller ones, leading to capillary networks. These networks deliver oxygen and nutrients to the tissues.
Key Fact 4: Physiological Functions of the Artery Wall
The artery wall is key to keeping our heart healthy. It helps control blood pressure and makes sure tissues get oxygen and nutrients.
Blood Pressure Regulation
The artery wall can get narrower or wider. This is thanks to the smooth muscle cells in its middle layer. When these cells tighten, the artery narrows, raising blood pressure. When they relax, the artery widens, lowering blood pressure.
Nutrient Delivery
The artery wall also helps tissues get what they need. The endothelial cells on the inside help move nutrients and oxygen from the blood to the tissues.
The artery wall’s job is complex. It involves many cell types working together. Knowing how it works helps us understand heart health better.
The Unique Properties of Arteries Structure
Arteries are amazing because they can change to meet the body’s needs. They do this through special features that help blood flow well. This is key for keeping the body healthy.
Elasticity and Compliance Mechanisms
Arteries stretch and shrink with each heartbeat. This lets blood keep flowing smoothly. They have elastic fibers that make this possible.
Compliance is when arteries get bigger to handle blood flow. Together, these two features help manage blood pressure. This ensures blood keeps flowing without interruption.
Adaptability to Changing Physiological Demands
Arteries can adjust to different needs, like more blood flow during exercise. They do this by changing size and thickness. This helps meet the body’s oxygen and nutrient needs.
Knowing how arteries work is important for heart health. Their ability to change helps the body function well. But, problems can lead to heart diseases.
Common Artery-Related Disorders and Their Impact
Common Artery-Related Disorders and Their Impact
It’s key to know about artery-related disorders to keep our heart healthy. Arteries are vital for our health. Problems with them can lead to big issues.
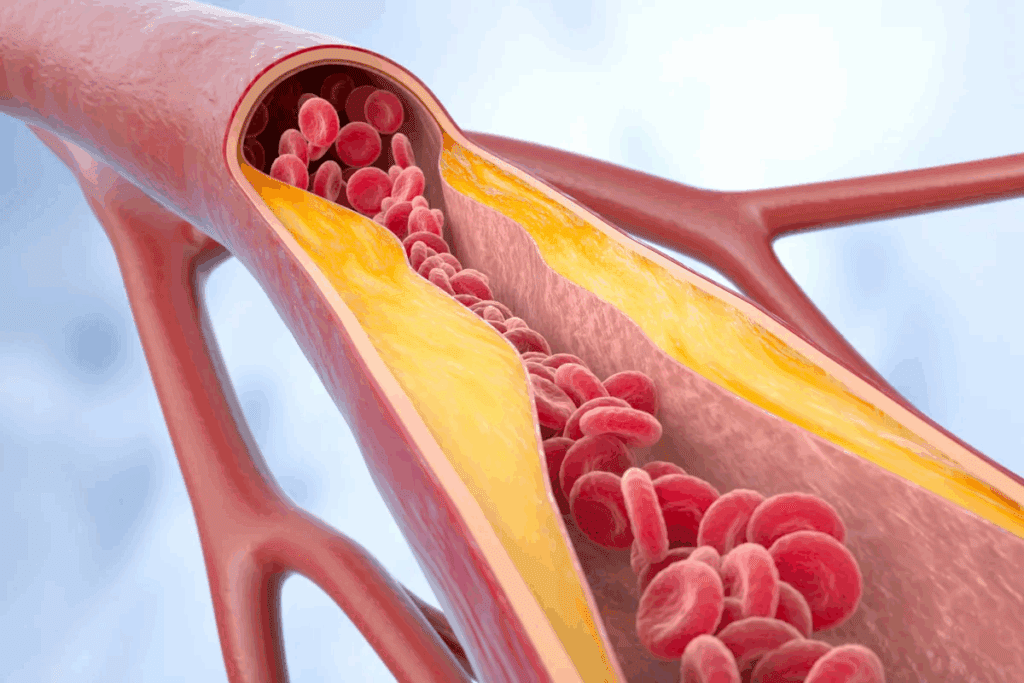
Atherosclerosis Development and Consequences
Atherosclerosis happens when plaque builds up in artery walls. This makes them hard and narrow. It can block blood flow, causing heart diseases.
The buildup starts with lipids and inflammatory cells. Over time, it forms plaques. These can burst, causing heart attacks.High blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, and high cholesterol are big factors.
Aneurysms Formation and Associated Risks
An aneurysm is when an artery gets too big. It happens when the wall gets weak. This can be due to genetics, high blood pressure, or atherosclerosis.
The bigger the aneurysm, the higher the risk of it bursting. This is a big worry. Finding it early is very important.
Spotting an aneurysm early and treating it can save lives. Monitoring and surgery can help a lot. Knowing about these issues helps us keep our arteries healthy.
Recent Advances in Understanding Artery Anatomy
In recent years, we’ve made big strides in understanding artery anatomy. This has changed how we view cardiovascular health. It’s opened up new ways to diagnose and treat heart issues.
New Research on Arterial Function
Studies have greatly improved our grasp of how arteries work. We now know arteries do more than just carry blood. They also control blood pressure and flow through complex systems.
Key findings include:
- Researchers found new ways arteries adjust blood pressure and flow.
- They’ve learned more about how the endothelium keeps blood vessels healthy.
- They’ve discovered that stiff arteries can signal heart disease risk.
Technological Innovations in Arterial Imaging
New technologies have greatly helped us see artery anatomy better. These tools let us see artery structures in more detail and accurately.
Some notable advancements include:
- High-resolution ultrasound gives clear views of artery walls and blood flow.
- Advanced MRI lets us see artery anatomy without using contrast agents.
- Intravascular imaging shows what’s happening inside arteries.
Conclusion: The Importance of Maintaining Healthy Arteries
Keeping your arteries healthy is key to feeling good and having good blood flow. We’ve talked about how knowing about artery anatomy is important for your body’s health.
Living a balanced life helps a lot. Eating right, exercising, and not smoking are all good for your arteries. These actions can lower your risk of artery problems.
We stress how important it is to take care of your arteries. We urge you to act now to keep your arteries and circulatory system in top shape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary function of arteries in the circulatory system?
Arteries are key in sending oxygen-rich blood to the body. They make sure organs and tissues get the nutrients and oxygen they need.
How do arteries differ from veins and capillaries?
Arteries handle high pressure and spread blood around the body. Veins bring blood back to the heart. Capillaries help exchange nutrients and waste.
What are the three layers of an artery, and what are their functions?
An artery has three layers: the tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica adventitia. The tunica intima is the innermost layer. The tunica media has smooth muscle and elastic fibers. The tunica adventitia is the outermost layer, giving support and structure.
What is the role of the tunica media in arteries?
The tunica media controls blood pressure and flow. It does this by changing the artery’s diameter through muscle contraction and relaxation.
What are elastic arteries, and what are their properties?
Elastic arteries, like the aorta, have lots of elastic fibers. This lets them stretch and recoil with each heartbeat. It helps keep blood pressure and flow steady.
What are the major arteries in the body, and what are their functions?
Major arteries include the aorta, carotid arteries, and coronary arteries. They supply blood to important organs like the brain, heart, and other tissues.
How do arteries adapt to changing physiological demands?
Arteries can change their diameter and wall thickness. This is in response to changes in blood pressure and flow.
What are some common disorders that affect arteries?
Disorders like atherosclerosis, aneurysms, and peripheral artery disease can affect arteries. These can have big health consequences.
How do technological innovations improve our understanding of artery anatomy?
New imaging tech like ultrasound and MRI has helped us learn more about artery anatomy and function. This helps doctors diagnose and treat vascular diseases better.
Why is maintaining healthy arteries important for overall health?
Keeping arteries healthy is key for good blood flow and nutrient delivery. It helps prevent cardiovascular disease and other disorders.









