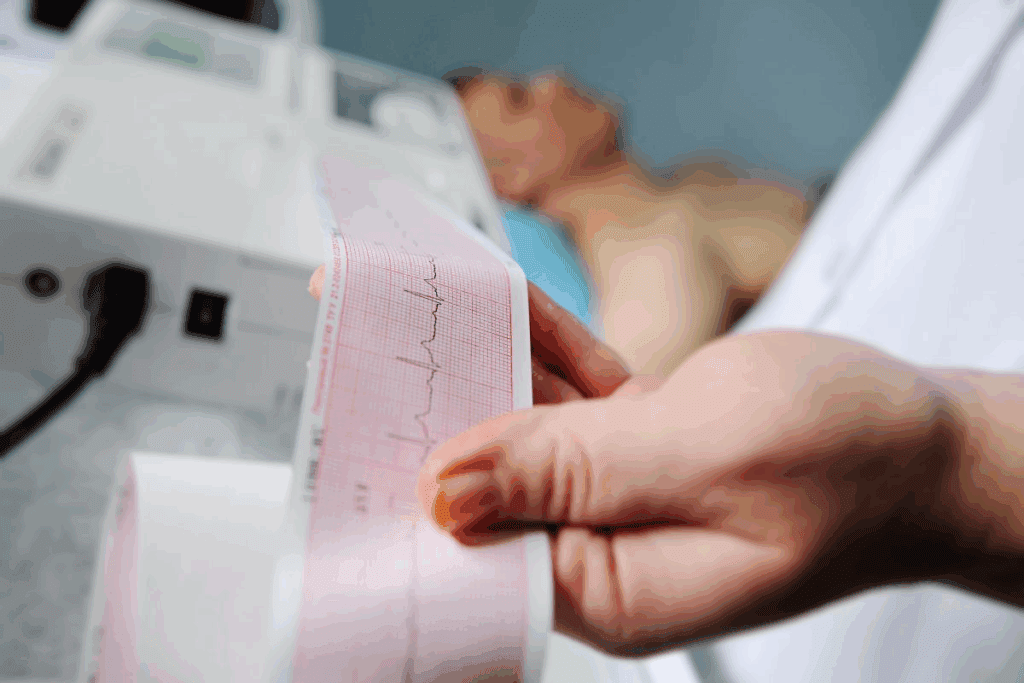
At Liv Hospital, we know how hard it is to diagnose atrial fibrillation (AF). This arrhythmia affects over 33 million people worldwide. It causes irregular and fast heartbeats, leading to serious problems like stroke and heart failure.Learn the 7 key features of atrial fibrillation EKG and how to identify AFib strip patterns accurately.
The main sign of AF on an EKG is an irregularly irregular rhythm. There are no P waves, and the atrium acts strangely. This makes fibrillatory waveforms. Knowing how to read these patterns is key for doctors to treat AF right.
Key Takeaways
- Atrial fibrillation is a common arrhythmia with big health risks.
- EKG is a key tool for spotting atrial fibrillation.
- Irregular rhythm and missing P waves are key EKG signs.
- Getting the diagnosis right is vital for good treatment.
- Liv Hospital’s cardiac care team offers detailed treatment plans.
The Clinical Significance of Atrial Fibrillation
Understanding atrial fibrillation (AF) is key to managing patients well. AF is a common heart rhythm disorder that affects millions. It causes a lot of health problems, deaths, and costs a lot for healthcare.
Prevalence and Lifetime Risk Factors
AF is the most common heart rhythm disorder. It gets more common with age. Studies show that about 1 in 4 people will get AF at some point in their lives.
Many things can increase your risk of getting AF. These include high blood pressure, heart failure, and heart disease. Lifestyle choices like being overweight, smoking, and drinking too much alcohol also raise your risk.
Pathophysiology of Atrial Electrical Chaos
AF happens because of changes in the heart’s electrical system. This leads to an irregular heartbeat. The atrial fibrillation ECG shows no clear P waves and has fibrillatory waves instead.
Many things can cause AF, like high blood pressure and heart valve problems. These changes can happen over time due to various reasons.
Impact on Patient Morbidity and Mortality
AF can lead to serious health issues. It increases the risk of stroke and heart failure. The irregular heartbeat can also weaken the heart over time.
Early diagnosis and treatment of AF are very important. Accurate afib ECG characteristics help doctors identify at-risk patients. This guides the right treatment for each person.
It’s also important to tell AF apart from other heart rhythm disorders, like afib vs afib with RVR ECG. This helps doctors tailor treatment plans to each patient’s needs.
Fundamentals of EKG Interpretation for Cardiac Arrhythmias
Understanding EKGs is key to spotting and treating heart rhythm problems. Doctors need to grasp the basics of EKG reading.
Normal Cardiac Conduction Patterns
The heart’s natural rhythm starts with the SA node, its pacemaker. The signal moves through the AV node and the bundle of His. It ends in the ventricular muscle. Knowing this path helps spot rhythm issues, like ecg afib.
The EKG shows this process. A P wave means the atria are depolarizing. Then, a QRS complex shows the ventricles depolarizing. Lastly, a T wave indicates the ventricles are repolarizing.
Standard EKG Lead Placement and Views
Getting EKG leads right is important for accurate readings. The 12-lead EKG gives a full view of the heart’s electrical activity. Leads are placed on the chest and limbs to capture the heart’s function.
- Limb leads (I, II, III, aVR, aVL, aVF) provide a frontal plane view.
- Precordial leads (V1-V6) offer a horizontal plane perspective.
This method helps find rhythm problems and other heart issues, like those seen in afib rhythm strip analysis.
Systematic Approach to Rhythm Analysis
There’s a specific way to read EKGs for rhythm problems. This includes:
- Looking at the rhythm and rate.
- Checking P wave shape and timing with QRS complexes.
- Examining QRS width and shape.
- Looking at intervals (PR, QT) for oddities.
By using this method, doctors can spot atrial fibrillation and other rhythm issues on atrial fibrillation telemetry strip recordings.
7 Diagnostic Features of Atrial Fibrillation EKG
Understanding atrial fibrillation on an EKG is key for correct diagnosis and treatment. Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a common heart rhythm problem. It shows specific patterns on an EKG that doctors need to spot for proper care.
AF’s EKG signs include an irregular rhythm, no P waves, and fibrillatory waves. These signs help doctors tell AF apart from other heart rhythm issues. They guide how to manage the condition.
Feature 1: Irregularly Irregular Rhythm
The irregularly irregular rhythm is a key sign of atrial fibrillation. It’s different from other heart rhythm problems. This irregular rhythm comes from the chaotic electrical activity in the atria.
Doctors look for this irregular rhythm in an afib strip. The lack of a regular pattern in the R-R intervals is a big clue.
Feature 2: Absent P Waves
In atrial fibrillation, there are no P waves. P waves show the electrical activity of the atria. In AF, this activity is chaotic, replacing P waves with fibrillatory waves.
The absence of P waves on an EKG is important. It shows there’s no coordinated electrical activity in the atria. This is key in telling AF apart from other fast heart rhythms.
Feature 3: Fibrillatory Waves (f-waves)
Fibrillatory waves (f-waves) are a sign of atrial fibrillation on an EKG. These waves show the chaotic electrical activity in the atria. The size of f-waves can vary, showing how active the atria is.
Looking at the afib waveform helps doctors understand the atria’s activity. This can help decide on treatment.
Feature 4: Variable R-R Intervals
The variability in R-R intervals comes from the irregular heart rhythm in AF. This irregular rhythm is a key part of AF’s EKG pattern.
On an atrial fibrillation rhythm strip, the R-R intervals vary a lot. This variation makes the heart rhythm even more unpredictable.
These four features—irregular rhythm, no P waves, fibrillatory waves, and variable R-R intervals—make up a strong EKG profile for AF. Spotting these signs is vital for accurate diagnosis and treatment of AF.
As we keep looking at EKG signs of atrial fibrillation, it’s important to think about how they affect treatment choices and patient results. The next features will help us understand AF better and how to manage it.
Analyzing Atrial Fibrillation Strips: A Systematic Approach
When we look at atrial fibrillation (AF) strips, we need a clear plan. We’ll show you how to check AFib cardiac strips step by step. This includes spotting different patterns and following important rules for recording.
Step-by-Step Assessment of Afib Cardiac Strips
To really understand an AF rhythm strip, we follow a set of steps:
- Check if the R-R intervals are regular
- See if there are any P waves
- Look for fibrillatory waves (f-waves)
- Count the ventricular rate
This careful check helps us figure out if atrial fibrillation is present and what it looks like on an ECG strip.
Coarse vs. Fine Afib Waveform Patterns
Atrial fibrillation can be either coarse or fine, depending on the size of the fibrillatory waves:
- Coarse AF: Waves are big and easy to spot
- Fine AF: Waves are small and harder to see
Knowing these patterns is key for making the right diagnosis and treatment plan.
Documentation Standards for Afib Rhythm Strips
It’s very important to document AFib rhythm strips correctly for patient care. We should note:
- The ventricular rate
- If there are fibrillatory waves and what they look like
- Any unusual patterns or changes
By sticking to these standards, we make sure everyone involved in the patient’s care can understand the information. This helps in managing the patient’s care better.
Atrial Fibrillation Telemetry Strip Interpretation
Telemetry monitoring is key in spotting atrial fibrillation, mainly in those with occasional symptoms. It lets doctors catch when AF starts and stops. This is critical for correct diagnosis and treatment.
Continuous Monitoring Advantages
Telemetry strips have big benefits in managing atrial fibrillation. They help find AF episodes early. This lets doctors act fast, which can lower the chance of serious problems.
- Real-time monitoring lets doctors react quickly to heart rhythm changes.
- It also helps gather long-term data on AF patterns and how often they happen.
- It keeps patients safer by watching their heart all the time.
A study in a top cardiology journal found that constant monitoring in AF patients greatly improves results. It lets doctors act early.
“Telemetry monitoring is now a must-have for managing atrial fibrillation. It gives vital insights into AF episodes.”
Recognizing Afib Onset and Termination
Spotting when AF starts and stops on telemetry strips is key. Look for an irregular rhythm and no P waves.
| Feature | Description |
| Irregularly Irregular Rhythm | This shows AF, meaning the atria aren’t working together. |
| Absent P Waves | P waves are missing in AF, replaced by chaotic waves. |
| Fibrillatory Waves | These waves show the atria’s chaotic electrical activity. |
Common Artifacts and Misinterpretations on Telemetry
Telemetry monitoring has its challenges. Artifacts and misreads can lead to wrong diagnoses if not fixed.
Common artifacts include:
- Motion artifacts
- Electrical interference
- Poor electrode placement
Healthcare pros need to know about these issues. They must double-check their findings to ensure accurate telemetry strip readings.
Differentiating Atrial Fibrillation from Similar Arrhythmias
It’s important to tell atrial fibrillation apart from other heart rhythm problems. AF can have symptoms that look like other arrhythmias, making it hard to diagnose. We use special ECG signs to tell AF from other conditions.
Atrial Flutter vs. Atrial Fibrillation ECG Findings
Atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation are both fast heart rhythms. But they show different patterns on an ECG. Atrial flutter has a regular “sawtooth” pattern in leads II, III, and aVF. AF, on the other hand, has an irregular rhythm and no P waves.
The heart rate in atrial flutter is usually fast, between 250-350 bpm. It also has a consistent block, often 2:1 or 3:1.
Key differences on ECG:
- Regular vs. irregular ventricular response
- Presence of flutter waves vs. fibrillatory waves
- Constant vs. variable AV block
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia vs. Afib
Multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT) can look like AF. MAT has at least three different P-wave shapes and a fast heart rate. On an ECG, MAT shows P waves with different shapes, PR intervals that change, and a heart rate of 100-150 bpm.
ECG distinction: MAT and AF both have irregular rhythms. But MAT has visible P waves with different shapes, while AF has no P waves and fibrillatory waves.
Irregular Supraventricular Rhythms
Other irregular heart rhythms, like atrial tachycardia with variable block, can look like AF on an ECG. Looking closely at P-wave shape and PR intervals helps tell them apart.
“The key to accurate diagnosis lies in meticulous ECG analysis and understanding the nuances of various arrhythmias.” – Expert in Cardiac Electrophysiology
Atrial Fibrillation with Aberrant Conduction
AF with aberrant conduction can make diagnosis tricky. It has an irregular heart rhythm and abnormal QRS complexes. But, looking for fibrillatory waves and an irregular rhythm helps diagnose it.
Diagnostic tips:
- Look for fibrillatory waves in the baseline
- Identify irregular R-R intervals
- Check for varying QRS morphologies due to aberrancy
By carefully looking at these ECG signs, we can tell AF from other heart rhythm problems. This helps us choose the right treatment.
Afib vs. Afib with RVR: ECG Characteristics and Clinical Implications
It’s important to know the difference between atrial fibrillation (AFib) and AFib with rapid ventricular response (RVR). AFib has an irregular rhythm and no clear P waves on an ECG. When RVR is added, it affects the patient’s heart function a lot.
Defining Rapid Ventricular Response in Atrial Fibrillation
Rapid ventricular response in AFib means the heart beats over 100 times per minute. This happens because the atria send fast, irregular signals to the AV node. This results in a fast and irregular heart rhythm.
Identifying Afib with RVR on EKG Strips
To spot AFib with RVR on EKGs, look for an irregular rhythm and a heart rate over 100 bpm. The ECG will show:
- No P waves
- Fibrillatory waves (f-waves) causing a chaotic baseline
- Variable R-R intervals due to the irregular ventricular response
- A ventricular rate exceeding 100 bpm
Hemodynamic Consequences and Management Priorities
AFib with RVR can harm the heart, leading to low blood flow, low blood pressure, and even heart failure. The main goals are to slow the heart rate and manage symptoms.
- Rate control: Using medications to slow the ventricular rate
- Rhythm control: Considering cardioversion or antiarrhythmic medications to restore sinus rhythm
- Assessing and managing symptoms and hemodynamic instability
| Management Strategy | Description | Clinical Goal |
| Rate Control | Using beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, or digoxin to slow ventricular rate | Reduce ventricular rate to |
| Rhythm Control | Using cardioversion or antiarrhythmic drugs to restore sinus rhythm | Restore normal sinus rhythm |
| Anticoagulation | Administering anticoagulants to prevent thromboembolic events | Reduce stroke risk |
Rate Control Assessment on Continuous Monitoring
Keeping an eye on the heart rate is key for managing AFib with RVR. It lets doctors adjust treatments as needed and catch any problems early.
Understanding AFib with RVR helps doctors improve patient care. They can tailor treatments to better outcomes.
Paroxysmal, Persistent, and Permanent AF ECG Findings
Atrial fibrillation (AF) comes in different forms, each with its own ECG signs. Knowing these signs is key for doctors to give the right care. We’ll look at the ECG signs of paroxysmal, persistent, and permanent AF. We’ll talk about their features, how to monitor them, and what happens after cardioversion.
Paroxysmal AF ECG Characteristics
Paroxysmal AF means AF comes and goes, lasting less than 48 hours. On an ECG, it shows irregularly irregular rhythms with different fibrillatory waves. You won’t see P waves, and the R-R intervals change a lot.
Monitoring Approaches for Intermittent Afib
For those with paroxysmal AF, continuous monitoring is used to catch episodes. This can be done with Holter monitors or implantable loop recorders. The aim is to find AF episodes and see how long they last.
Progression Patterns on Serial EKGs
Serial EKGs can show how AF changes from paroxysmal to persistent or permanent. We watch for changes in fibrillatory wave size, heart rate, and how long episodes last. This helps predict how the disease will progress and plan treatment.
Post-Cardioversion ECG Changes
After cardioversion, the ECG usually shows a return to normal rhythm. But, post-cardioversion ECG changes can happen, like temporary ST-segment changes or atrial stunning. It’s important to watch these changes to see if cardioversion worked and to decide what to do next.
Conclusion: Clinical Application of Atrial Fibrillation EKG Interpretation
Understanding atrial fibrillation on EKG is key for patient care. Knowing how to read afib ecg helps doctors diagnose and treat better. We’ve looked at the main signs and patterns of atrial fibrillation ekg, showing its importance in healthcare.
Doctors can make better choices for patients by knowing how to read atrial fibrillation ekg. They can spot the irregular rhythm and missing P waves. This helps them manage atrial fibrillation well.
Using what they learn from atrial fibrillation ekg, doctors can plan treatments and check how patients are doing. This approach helps improve patient care and results.
As we keep improving in heart care, knowing how to read atrial fibrillation ekg will stay important. Keeping up with new knowledge helps us give the best care to patients with atrial fibrillation.
FAQ
What is atrial fibrillation and how is it diagnosed using an EKG?
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a heart rhythm disorder. It’s diagnosed with an electrocardiogram (EKG). The EKG looks for signs like missing P waves and irregular heartbeats.
What are the 7 diagnostic features of atrial fibrillation on an EKG?
The 7 signs of AF on an EKG include an irregular rhythm and missing P waves. It also looks for fibrillatory waves and variable heartbeats. These features help tell AF apart from other heart issues.
How do you differentiate atrial fibrillation from other similar arrhythmias on an EKG?
To tell AF from other heart rhythm problems, we look at the EKG closely. We check for flutter waves in atrial flutter and multiple P wave shapes in multifocal atrial tachycardia.
What is the significance of rapid ventricular response (RVR) in atrial fibrillation?
AF with rapid ventricular response (RVR) is serious. It means the heart beats too fast, which can be dangerous. An EKG shows this by a heart rate over 100 beats per minute.
How do you interpret atrial fibrillation telemetry strips?
Reading AF telemetry strips means spotting when AF starts and stops. We also look at the wave patterns and watch out for mistakes in monitoring.
What are the ECG characteristics of paroxysmal, persistent, and permanent atrial fibrillation?
Paroxysmal AF has short episodes. Persistent AF lasts longer and needs treatment to fix. Permanent AF is a long-term condition. Each has its own ECG signs and monitoring needs.
How does atrial fibrillation affect patient morbidity and mortality?
AF can lead to serious problems like stroke and heart failure. It’s important to diagnose and manage AF well to reduce these risks.
What is the importance of accurate EKG interpretation in managing atrial fibrillation?
Getting AF diagnosis right is key. It helps us tell AF from other heart issues. It also guides how to treat AF, like controlling heart rate or rhythm.
References:
Atrial Fibrillation with Rapid Ventricular Response – EKG features, hemodynamic consequences, and management of AF with RVR.



































