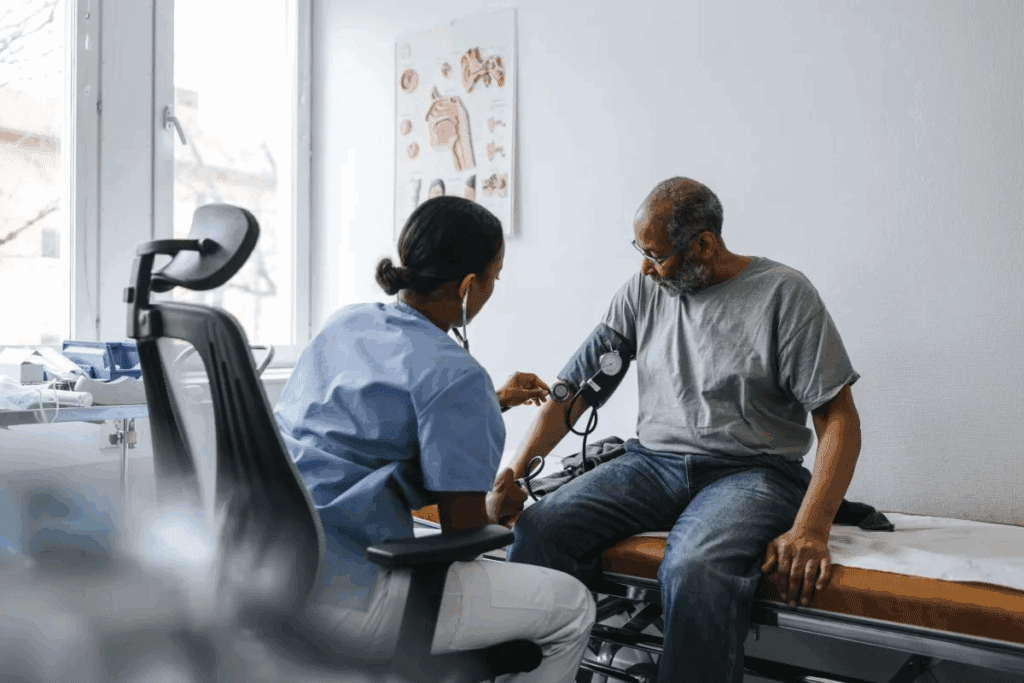
At Liv Hospital, we know how vital it is to stay informed about heart health. Beta blockers are key medications for heart conditions. They are often prescribed to help manage these issues.Learn what does a beta blocker do, how it works in your body, and the key benefits and side effects to know.
These drugs block adrenaline’s impact on the heart. This action lowers heart rate and blood pressure. Knowing how beta blockers work helps you make better choices for your treatment.
We aim to give you all the details about beta blockers. This includes their uses, effects, and safety aspects. Our goal is to help you understand these essential medications better.
Key Takeaways
- Beta blockers are used to manage hypertension, angina, arrhythmias, and heart failure.
- They work by blocking the effects of adrenaline on the heart.
- Beta blockers can reduce heart rate and blood pressure.
- Understanding the uses and effects of beta blockers is key for making informed decisions.
- Beta blockers are widely used in treating heart conditions.
1. The Fundamentals of Beta Blockers
Beta blockers are key in treating heart diseases and related issues. They help manage heart problems by blocking stress hormones like adrenaline. This makes the heart work less hard.
What Are Beta Blockers?
Beta blockers are drugs that help the heart by making it beat slower and with less force. This action lowers blood pressure and improves blood flow. It helps manage symptoms of heart conditions.
Common Types and Brands
There are many types of beta blockers, each with its own use. Some common ones include acebutolol (Sectral), atenolol (Tenormin), and metoprolol (Lopressor, Toprol XL). These are chosen based on what the patient needs.
Why Doctors Prescribe Them
Doctors use beta blockers for many reasons. They help with high blood pressure, irregular heartbeat, and survival after a heart attack. They also prevent migraine headaches and manage anxiety and performance anxiety.
Understanding beta blockers helps patients see their importance in treatment. It’s important to follow the treatment plan and talk to doctors about any issues or side effects.
2. What Does a Beta Blocker Do to Your Heart and Body?
Beta blockers are key in keeping the heart healthy. They change how our heart and body react to stress. These drugs counteract the effects of adrenaline, a hormone that raises heart rate and blood pressure.
Blocking Adrenaline’s Effects
Adrenaline is a hormone our body makes when we’re stressed. It gets ready for ‘fight or flight’ by speeding up the heart and raising blood pressure. Beta blockers block the effects of adrenaline on the heart, making it work less hard.
By stopping adrenaline’s action, beta blockers help to:
- Reduce the heart rate
- Lower blood pressure
- Decrease the heart’s oxygen demand
Impact on Heart Rate and Blood Pressure
Beta blockers have a big impact on heart rate and blood pressure. By reducing the heart rate, they give the heart more time to fill with blood. This makes the heart work better. Lowering blood pressure also reduces strain on the heart and arteries, which can prevent damage over time.
How Quickly Beta Blockers Work
Beta blockers can start working a few hours after the first dose. But, it may take a few weeks to see their full effect. How fast they work depends on the type of beta blocker and the condition being treated.
It’s important to keep taking beta blockers as your doctor tells you to. Even if you don’t feel them working right away, don’t stop. Stopping them suddenly can cause withdrawal symptoms or make your condition worse.
3. Primary Medical Uses for Beta Blockers
Beta blockers are key in treating heart diseases. They help manage different heart conditions. This makes them vital in cardiology today.
Managing Hypertension
Beta blockers help control high blood pressure. They slow the heart rate and reduce blood pressure. This lowers the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Treating Angina and Preventing Heart Attacks
Beta blockers also treat angina, a pain caused by heart blood flow issues. They reduce heart oxygen need, easing pain and improving exercise. They also prevent heart attacks in at-risk patients.
“Beta blockers have been shown to reduce mortality and morbidity in patients with heart failure and those at risk of heart attacks.”
Controlling Heart Failure Symptoms
At first, beta blockers seem to weaken the heart. But, they actually help heart function over time. They do this by reducing heart workload and stopping harmful changes.
Beta Blocker Usage for Arrhythmias
Beta blockers help with irregular heartbeats by slowing the heart. This is great for those with atrial fibrillation or other fast heart rhythms.
| Condition | Beta Blocker Effect | Clinical Benefit |
| Hypertension | Lowers blood pressure | Reduces risk of heart disease and stroke |
| Angina | Reduces myocardial oxygen demand | Alleviates chest pain and improves exercise tolerance |
| Heart Failure | Improves heart function long-term | Reduces hospitalization rates |
| Arrhythmias | Slows heart rate, regularizes rhythm | Improves symptoms and quality of life |
In conclusion, beta blockers are vital for treating heart diseases. They manage hypertension, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias. This makes them essential in cardiology.
4. Beyond Heart Health: Other Uses for Beta Blockers
Beta blockers are used for more than just heart health. They are effective in treating many other health issues. This shows their wide range of uses.
Anxiety and Performance Anxiety Management
Propranolol is often used to treat anxiety and performance anxiety. It helps control physical symptoms like tremors and rapid heartbeat. Medical Expert. Baldwin says beta blockers can reduce performance anxiety without affecting thinking skills.
Migraine Prevention
Beta blockers are a top choice for preventing migraines. They make migraines less frequent, severe, and shorter. Propranolol and metoprolol are commonly used. They work by stabilizing blood vessel changes.
Thyroid Disorder Treatment
In thyroid storm, a serious condition, beta blockers like propranolol help control symptoms. They manage rapid heart rate and tremors. They don’t change thyroid hormone levels but help with symptoms.
Other Approved and Off-Label Uses
Beta blockers are also used for other conditions. They treat essential tremors and glaucoma. Here’s a table of some off-label uses:
| Condition | Beta Blocker Used | Effectiveness |
| Anxiety/Performance Anxiety | Propranolol | High |
| Migraine Prevention | Propranolol, Metoprolol | High |
| Thyroid Storm | Propranolol | High |
| Essential Tremors | Propranolol | Moderate to High |
Beta blockers are used in many ways, not just for heart health. Their wide range of uses makes them very important in medicine.
5. Beta Blockers and Heart Palpitations: What You Should Know
Beta blockers have a complex role in heart palpitations. They can both cause and treat these irregular heartbeats. This is important for managing heart conditions.
Can Beta Blockers Cause Palpitations?
Even though beta blockers help with irregular heartbeats, they can sometimes make palpitations worse. This might happen when the body gets used to the medication or when it interacts with other health issues.
Beta Blockers for Heart Palpitations: Effectiveness
Despite the risk of causing palpitations, beta blockers are often effective in treating them. They work by slowing down the heart rate and reducing the strength of heartbeats. This can help ease palpitations, even those caused by stress or anxiety.
Propranolol and Palpitations: A Specific Case
Propranolol, a non-selective beta blocker, is commonly used for palpitations. It’s good for managing palpitations linked to performance or social anxiety. But, it’s important to use it carefully to avoid side effects.
In summary, beta blockers have a complex relationship with heart palpitations. They are, though, a valuable treatment option. Knowing how different beta blockers, like propranolol, work can help doctors find the best treatment for each patient.
6. Safety Concerns: Are Beta Blockers Bad for You?
Beta blockers are used a lot, but knowing their side effects is key for safety. They are mostly safe when taken right, but they can cause different effects. These can range from mild to serious.
Common Side Effects to Expect
Most people do okay with beta blockers, but some might feel certain side effects. These can include:
- Fatigue or feeling tired
- Cold hands or feet
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Slow heart rate
These side effects are usually mild and may get better as your body gets used to the medicine.
Rare but Serious Adverse Effects
Even though rare, some serious side effects can happen. These might include:
- Shortness of breath
- Worsening of heart failure symptoms
- Depression
- Sleep disturbances
If you have any severe or lasting side effects, tell your doctor right away.
Who Should Avoid Taking Beta Blockers
Some people should not take beta blockers or should be very careful. This includes:
| Condition | Reason |
| Asthma or severe lung disease | Beta blockers can trigger bronchospasm |
| Severe heart failure | Can worsen heart failure if not stabilized |
| Certain heart conditions (e.g., bradycardia, heart block) | Can exacerbate underlying heart issues |
Can Beta Blockers Cause Heart Failure?
Beta blockers are used to treat heart failure, but they need to be used carefully. They can sometimes make heart failure symptoms worse at first. But, when used right, they can help the heart work better over time.
In summary, beta blockers are usually safe and work well, but knowing their side effects and who should avoid them is important. Always talk to your doctor to understand the benefits and risks.
7. Long-Term Effects: Do Beta Blockers Shorten Your Life?
It’s important to know how beta blockers affect us over time. These medicines help manage heart conditions. Their long-term health impact is a big worry.
Research on Mortality and Beta Blockers
Many studies have looked into beta blockers and life span. They show that beta blockers don’t shorten life. Instead, they can help people live longer in some cases.
A major study found that beta blockers greatly cut down death rates in heart failure patients.
Key findings from research on beta blockers and mortality include:
- Reduced risk of death in heart failure patients
- Improved survival post-myocardial infarction
- Effective management of hypertension, reducing cardiovascular risk
Beta Blockers and Improved Survival in Heart Failure
Beta blockers help heart failure patients live longer. They make the heart work less hard and pump better. This is very important because heart failure is serious.
The way beta blockers help heart failure patients involves:
- Reducing sympathetic nervous system activity
- Lowering heart rate and blood pressure
- Improving cardiac function over time
Balancing Benefits and Risks
Beta blockers have big benefits but also some risks. Side effects can include tiredness, dizziness, and shortness of breath. But for many, the good they do is worth the risks.
We need to work with doctors to watch how beta blockers affect us. This way, we can get the most benefits while avoiding the downsides.
8. How Do Beta Blockers Work in Your Body?
Beta blockers interact with specific receptors in the heart. They block adrenaline’s effects on beta receptors, mainly in the heart.
The Science of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor Blocking
Beta-adrenergic receptors trigger the “fight or flight” response. This increases heart rate and blood pressure. Beta blockers reduce the heart’s workload and its oxygen demand by blocking these receptors.
Selective vs. Non-Selective Beta Blockers
There are two types of beta blockers: selective and non-selective. Selective blockers, like metoprolol, target heart beta-1 receptors. Non-selective blockers, such as propranolol, affect both heart and lung receptors.
Duration of Action and Effectiveness
The action time of beta blockers varies. Some, like atenolol, last longer and are taken once daily. Others may need to be taken more often.
How to Know If Beta Blockers Are Working
Healthcare providers check heart rate, blood pressure, and symptoms to see if beta blockers are working. A table below shows key signs of effectiveness:
| Indicator | Expected Change |
| Heart Rate | Decrease |
| Blood Pressure | Decrease |
| Symptoms (e.g., chest pain, palpitations) | Reduction or elimination |
Understanding beta blockers and their effects helps healthcare providers tailor treatment for heart conditions.
Conclusion: Making Informed Decisions About Beta Blockers
Understanding beta blockers is key for those thinking about or already on these meds. Knowing how they work and their safety helps patients make smart choices about their health.
Beta blockers are great for heart health. They help with high blood pressure, chest pain, and heart failure. They block adrenaline’s effects, which helps control heart rate and blood pressure.
When used right, beta blockers are safe. But, like all meds, they can have side effects. It’s important to know these and talk to your doctor about any worries.
Deciding on beta blockers means knowing their good and bad sides. This way, people can get the most out of their treatment and live better.
The success of beta blockers comes from knowing how they work for heart health. With this knowledge, people can team up with their doctors for the best results.
FAQ
What are beta blockers and how do they work?
Beta blockers are medicines that stop adrenaline from affecting the heart and body. They lower heart rate and blood pressure. They work by attaching to beta-adrenergic receptors, which slows down the heart and makes it pump less forcefully.
Can beta blockers cause heart palpitations?
Yes, beta blockers can sometimes cause heart palpitations. This is more likely when you first start taking them or when you change your dosage.
Are beta blockers safe to take long-term?
Beta blockers are usually safe for long-term use if you follow your doctor’s advice. It’s important to watch for side effects and adjust your treatment as needed.
Do beta blockers shorten your life?
Studies show that beta blockers can help people with certain heart conditions live longer. But, how they affect life expectancy varies based on the individual’s health and other factors.
Can beta blockers cause heart failure?
Actually, beta blockers are often used to treat heart failure. They can improve the heart’s function and reduce symptoms. But, they can make heart failure worse if not used correctly or if you have certain health issues.
What are the common side effects of beta blockers?
Common side effects include feeling tired, dizzy, and having cold hands and feet. You might also have trouble breathing. These side effects usually get better over time as your body gets used to the medication.
Why are beta blockers prescribed for anxiety?
Beta blockers can help with the physical symptoms of anxiety, like shaking and a fast heartbeat. They are useful for performance anxiety and other specific anxiety conditions.
How quickly do beta blockers take effect?
Beta blockers start working a few hours after you take them. It might take a few days to see their full effects.
Are there different types of beta blockers?
Yes, there are selective and non-selective beta blockers. Selective blockers target specific receptors, while non-selective blockers affect more receptors, having a wider impact on the body.
How do I know if beta blockers are working?
You can tell if beta blockers are working by checking your heart rate, blood pressure, and symptoms. Regular check-ups with your doctor are key to see if they’re effective and to adjust your treatment if needed.
References:
Beta-blocker therapy in cardiovascular disease: Mechanisms and benefits – Discusses how beta blockers reduce heart workload without weakening the heart.




































