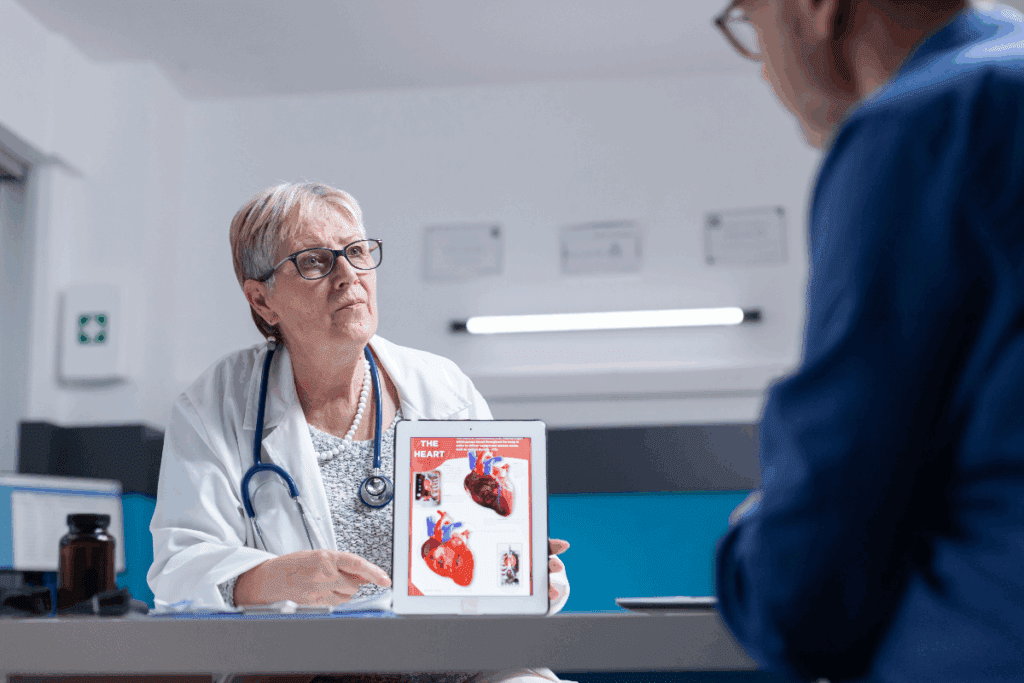
Chronic anxiety can harm our heart health a lot. It can make high blood pressure and high cholesterol worse. Studies show that our mental health affects our body. Depression and anxiety disorders can also happen after heart problems like heart failure and stroke.
It’s important to know how anxiety affects our heart. At Liv Hospital, we focus on top-notch healthcare for everyone. We use the latest medical methods to help you understand the connection between anxiety and heart health.
Key Takeaways
- Chronic anxiety can increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Mental health has physiological effects on the body.
- Understanding the link between anxiety and heart health is important.
- Liv Hospital provides support for international patients.
- Advanced medical protocols help manage and prevent heart problems.
The Connection Between Anxiety and Cardiovascular Health

It’s important to know how anxiety affects heart health. Anxiety disorders are a big mental health issue, hitting over 40 million adults in the U.S. People with anxiety are more likely to get heart disease.
Understanding Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders include generalized anxiety, panic disorder, and social anxiety. These conditions make people worry too much, affecting their daily lives. Anxiety can also cause physical symptoms like a fast heartbeat, sweating, and shaking.
Because anxiety disorders are common, we need to treat both mental and heart health. People with anxiety might smoke or not exercise, which can harm their heart.
The Prevalence of Anxiety and Heart Disease
Research shows anxiety and heart disease are linked. People with anxiety are at a 35-62% higher risk of heart attacks and strokes.
| Condition | Risk of Major Cardiovascular Events |
| Without Anxiety | Baseline Risk |
| With Anxiety | 35-62% Increased Risk |
Anxiety can really affect heart health, changing heart rate, blood pressure, and blood vessel function.
Knowing how anxiety impacts heart health helps doctors find better ways to help. They can work to lower the risk of heart disease in people with anxiety.
Can Anxiety Cause a Heart Attack? What Research Shows
Research shows a strong link between anxiety and heart health. This raises questions about whether anxiety can directly cause a heart attack. It’s clear that anxiety disorders can deeply affect our heart health.
Statistical Evidence on Anxiety and Heart Attack Risk
Many studies have looked into the connection between anxiety and heart attacks. A detailed review of these studies shows that people with anxiety disorders face a higher risk of heart problems.
A study in a top medical journal found that those with anxiety disorders are at a higher risk of heart disease and death from cardiovascular issues.
The 35-62% Increased Risk Factor
Research shows anxiety can raise the risk of a heart attack by 35% to 62%. This wide range shows how complex the relationship between anxiety and heart health is. It’s influenced by how severe the anxiety is, individual health, and lifestyle.
| Study | Increased Risk Factor | Population Studied |
| Journal of Cardiology | 35% | General Population |
| American Journal of Cardiology | 62% | Patients with Pre-existing Heart Conditions |
These findings highlight the importance of considering anxiety when checking heart health. Understanding this link helps us manage and reduce the risks of anxiety-related heart attacks.
The Physiological Mechanisms Behind Anxiety’s Impact on Heart Health
Anxiety sets off a chain of reactions in our body that can harm our heart. When we feel anxious, our body’s stress response kicks in. This leads to changes that can hurt our heart health.
The Fight-or-Flight Response
The fight-or-flight response is how our body reacts to threats. It gets us ready to face or run from danger. Stress hormones like adrenaline and cortisol make our heart beat faster and our blood vessels narrow.
This makes our blood pressure go up, and our heart works harder. But, if we’re always anxious, our heart can get tired.
Chronic Stress Hormones and Their Effects
Stress hormones, like cortisol, are key in how anxiety affects our heart. High levels of cortisol over time can change our heart and blood system. This can lead to high blood pressure and heart problems.
These hormones can also mess with other hormones in our body. This can make anxiety worse and create a cycle of problems.
Inflammation and Cardiovascular Damage
Anxiety can cause inflammation, which is bad for our heart. Chronic inflammation can damage the inside of blood vessels. This makes them more likely to get clogged and increases the risk of heart attacks.
The connection between anxiety, inflammation, and heart damage shows why we need to manage anxiety to keep our heart healthy.By understanding these mechanisms, we can see why treating both anxiety and heart health is important.
What Anxiety Does to Your Heart: Immediate Effects
Anxiety doesn’t just mess with our minds; it also affects our hearts right away. When we feel anxious, our body’s “fight-or-flight” response kicks in. This leads to changes that can harm our heart health.
Rapid Heartbeat and Palpitations
One common effect of anxiety on the heart is a fast heartbeat, or tachycardia. This happens because anxiety releases stress hormones like adrenaline. These hormones make the heart beat quicker. Sometimes, this can cause palpitations, where the heartbeat becomes irregular or strong. These symptoms can be scary and might feel like a heart attack.
Blood Pressure Spikes
Anxiety can also make blood pressure jump up right away. When we’re anxious, our blood vessels get smaller, and our heart beats faster. This is a big worry for people with high blood pressure or heart disease. High blood pressure can harm the heart over time.
Arrhythmias and Chest Pain
Anxiety can also cause irregular heartbeats, or arrhythmias. Some people might feel chest pain or discomfort because of anxiety. This can be mistaken for heart problems. It’s key to tell the difference between anxiety symptoms and serious heart issues. If you have chest pain or severe arrhythmias, get help right away.
Knowing how anxiety affects the heart can help us manage symptoms better. By recognizing these signs, we can take steps to protect our heart health.
Long-Term Heart Problems Caused by Anxiety
Anxiety can harm our heart health over time. It can lead to serious heart issues. These include atherosclerosis, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and problems with blood vessel function.
Acceleration of Atherosclerosis
Anxiety can make atherosclerosis worse. This is when plaque builds up in arteries. It can narrow and harden arteries, raising heart disease risk. Stress from anxiety boosts inflammation, helping plaque grow.
Development of Hypertension
Chronic anxiety can cause high blood pressure. Anxiety triggers our “fight-or-flight” response, raising blood pressure. Recurring high blood pressure can become a lasting problem, increasing heart disease and stroke risk.
Increased Cholesterol Levels
Anxiety can also raise cholesterol levels. Stress hormones can change our cholesterol levels. People with anxiety often have more “bad” cholesterol.
Endothelial Dysfunction
Anxiety can also harm blood vessel function. The inner lining of blood vessels, called the endothelium, is key to blood flow and pressure. When it’s not working right, it can cause heart problems.
| Long-term Heart Problems | Description | Potential Consequences |
| Acceleration of Atherosclerosis | Buildup of plaque in arteries due to chronic inflammation | Heart disease, heart attack |
| Development of Hypertension | High blood pressure due to frequent “fight-or-flight” responses | Heart disease, stroke |
| Increased Cholesterol Levels | Higher levels of LDL cholesterol due to stress hormones | Atherosclerosis, heart disease |
| Endothelial Dysfunction | Impaired blood vessel lining function | Atherosclerosis, hypertension |
It’s important to know how anxiety affects our hearts. By treating anxiety and making lifestyle changes, we can protect our heart health.
The Bidirectional Relationship: How Heart Disease Can Cause Anxiety
Heart disease and anxiety are closely linked. Heart disease can make anxiety worse. This means anxiety can lead to heart problems, and heart issues can also cause more anxiety.
Post-Heart Attack Anxiety
Having a heart attack or other heart issues can be very scary. It can lead to anxiety disorders. The fear of another heart attack or heart problems can be very distressing.
Post-heart attack anxiety can show up in many ways. People might worry a lot about their heart health. They might also be very scared to do physical activities or be too alert to any body sensations that might seem like heart problems.
Cardiovascular Anxiety Syndrome
Cardiovascular anxiety syndrome is when anxiety and heart disease symptoms feed into each other. People with heart disease might worry a lot about their condition. This worry can make their heart disease symptoms worse, creating a cycle.
This syndrome shows how important it is to deal with both the physical and mental sides of heart disease. By managing anxiety, people might see their heart disease symptoms get better. This can improve their life quality a lot.
The Vicious Cycle of Symptoms and Fear
Heart disease and anxiety can create a cycle that’s hard to break. Fear of heart problems can make anxiety worse. This can then make heart disease symptoms even more severe.
| Factors Contributing to the Cycle | Effects on Heart Disease | Effects on Anxiety |
| Fear of cardiac events | Increased heart rate and blood pressure | Heightened anxiety levels |
| Hypervigilance to bodily sensations | Misinterpretation of non-cardiac symptoms as cardiac | Increased worry and fear |
| Avoidance of physical activity | Reduced cardiovascular health | Reinforced fear of exertion |
It’s key to understand this cycle to find good treatments for both heart disease and anxiety. By stopping this cycle, people can get better heart health and feel less anxious.
Distinguishing Between Anxiety Symptoms and Heart Attack Symptoms
It’s important to know if you’re feeling anxious or having a heart attack. The signs of these two can look very similar. We’ll look at the common symptoms, when to get emergency help, and how doctors figure out what’s happening.
Common Overlapping Symptoms
Anxiety and heart attacks share symptoms like chest pain, rapid heartbeat, and shortness of breath. Anxiety can make you feel like something terrible is about to happen. Heart attacks can also cause this feeling. Knowing this helps doctors make the right call.
Here’s a table to show how symptoms can be similar:
| Symptom | Anxiety | Heart Attack |
| Chest Pain | Often sharp, localized | Typically pressure, radiates to arm or jaw |
| Rapid Heartbeat | Common, can be palpable | Can occur, often with other symptoms |
| Shortness of Breath | Frequent, can be severe | Common, often accompanied by chest pain |
When to Seek Emergency Care
If you’re feeling symptoms that could be anxiety or a heart attack, it’s best to get help right away. If you’re not sure, call for an ambulance or get someone to take you to the hospital.
Some signs that mean you should get help fast include:
- Severe chest pain or pressure that doesn’t go away with rest
- Shortness of breath without a clear reason
- Dizziness or fainting
- Severe headache or confusion
Diagnostic Approaches
Doctors use different tools to tell anxiety from a heart attack. These include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) to check the heart’s rhythm and look for problems
- Blood tests to see if there’s heart damage
- Imaging tests like echocardiograms or stress tests to see how well the heart is working
Getting the right diagnosis is key to the right treatment. If you’re feeling symptoms, don’t wait to see a doctor.
Managing Anxiety to Protect Your Heart Health
Managing anxiety is key to keeping your heart healthy and avoiding heart diseases. If anxiety is not handled, it can cause heart problems. So, it’s important to find good ways to manage it.
Evidence-Based Anxiety Treatments
There are proven ways to deal with anxiety, like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and medication. CBT helps change negative thoughts that cause anxiety. Medications like benzodiazepines and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) can also help.
It’s important to talk to a doctor to find the best treatment for you. Everyone is different, and what works for one person might not work for another.
Lifestyle Modifications for Both Conditions
Changing your lifestyle can help with both anxiety and heart health. Doing physical activity, like walking or yoga, can lower anxiety and boost heart health. Eating a balanced diet full of fruits, veggies, and whole grains is also good for you.
Stress-reducing activities like meditation and deep breathing can also help. Getting enough sleep and using relaxation techniques can help manage anxiety and protect your heart.
Medication Considerations
Medication can be helpful for anxiety, but it’s important to think about how it might affect your heart. Some anxiety meds can harm your heart, so talking to a doctor about the risks is vital.
By working with doctors and using a wide range of strategies, you can lower your risk of heart problems. This can also improve your life quality a lot.
Conclusion: Breaking the Anxiety-Heart Disease Cycle
It’s key to break the cycle of anxiety and heart disease for better health. Knowing how anxiety affects heart health helps people manage their anxiety. This can lead to better heart health.
Anxiety can harm the heart through stress and fight-or-flight responses. It’s vital to manage anxiety to protect the heart. There are proven ways to do this, like treatments, lifestyle changes, and medicines.
By focusing on both mental and heart health, we can stop the cycle of fear and symptoms. This approach helps reduce heart disease risk and improves life quality.
FAQ
What is the link between anxiety and heart health?
Anxiety can harm your heart health. It can raise your risk of heart disease and heart attacks. It can also cause inflammation and high blood pressure, damaging your heart over time.
Can anxiety cause a heart attack?
Anxiety itself doesn’t directly cause heart attacks. But, it can increase your risk. Studies show people with anxiety are more likely to have heart disease and heart attacks.
How does anxiety affect the heart?
Anxiety can immediately affect your heart. It can make your heart beat fast, cause palpitations, and raise your blood pressure. It can also lead to long-term heart problems like atherosclerosis and hypertension.
What are the symptoms of anxiety-related heart issues?
Symptoms include a fast heartbeat, palpitations, and chest pain. It’s important to know the difference between anxiety symptoms and heart attack symptoms, as they can be similar.
How can I manage anxiety to protect my heart health?
You can manage anxiety through treatments, lifestyle changes, and medication. Stress-reducing activities like meditation and yoga help. Regular exercise and a balanced diet are also key.
Can heart disease cause anxiety?
Yes, heart disease can cause anxiety. Having a heart attack or other heart issues can lead to anxiety. The fear of future events can create a cycle of symptoms and fear.
How can I distinguish between anxiety symptoms and heart attack symptoms?
If you’re experiencing symptoms that could be a heart attack, seek medical help. Tests like electrocardiograms and blood tests can help figure out what’s causing your symptoms.
What is the bidirectional relationship between heart disease and anxiety?
Heart disease and anxiety have a complex relationship. Heart disease can cause anxiety, and anxiety can increase the risk of heart disease. Getting care that addresses both mental and heart health is important.
Can anxiety lead to cardiovascular anxiety syndrome?
Yes, anxiety can lead to cardiovascular anxiety syndrome. This is a condition where you have excessive fear and anxiety about your heart health.
What lifestyle modifications can help manage anxiety and heart health?
Regular exercise, a balanced diet, stress-reducing activities, and enough sleep can help manage anxiety. They also reduce the risk of heart disease.
References
- Vaccarino, V., & colleagues (2020). The association of chronic anxiousness with cardiovascular disease: a cohort and meta‐analysis. Scientific Reports, Article 69427. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-69427-8
- Civieri, G., et al. (2023). Depression, anxiety and stress linked to poor heart health: How mental-health conditions accelerate cardiovascular risk. American Heart Association Newsroom. https://newsroom.heart.org/news/depression-anxiety-and-stress-linked-to-poor-heart-health-in-two-new-studies
- Ouakinin, S. R. (2016). Anxiety as a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 7, Article 25. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/psychiatry/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2016.00025/full


































