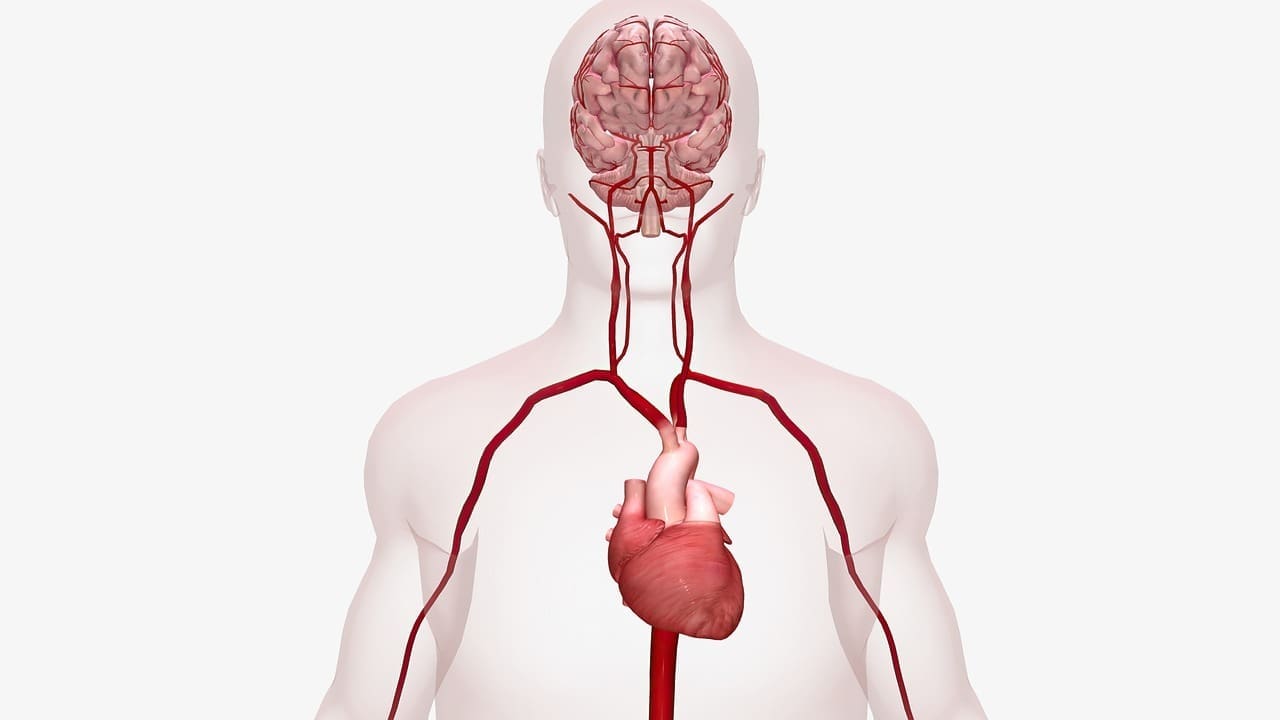
At Liv Hospital, we know how vital brain health is. Atherosclerosis cerebri, or cerebral atherosclerosis, happens when arteries to the brain get narrowed or blocked. This is due to plaque buildup. It can cause less blood to reach the brain, raising the chance of stroke and brain function decline.
We know spotting and managing cerebrovascular atherosclerosis early is key to avoiding big problems. By learning about its causes, signs, how it’s diagnosed, and treatment, we can improve brain health together.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding atherosclerosis cerebri is key to maintaining brain health.
- Cerebral atherosclerosis can lead to reduced blood flow to the brain.
- Early detection is critical in preventing stroke and cognitive decline.
- Managing cerebrovascular atherosclerosis requires a complete approach.
- Liv Hospital is dedicated to giving top-notch care for brain atherosclerosis patients.
The Nature and Mechanism of Atherosclerosis Cerebri
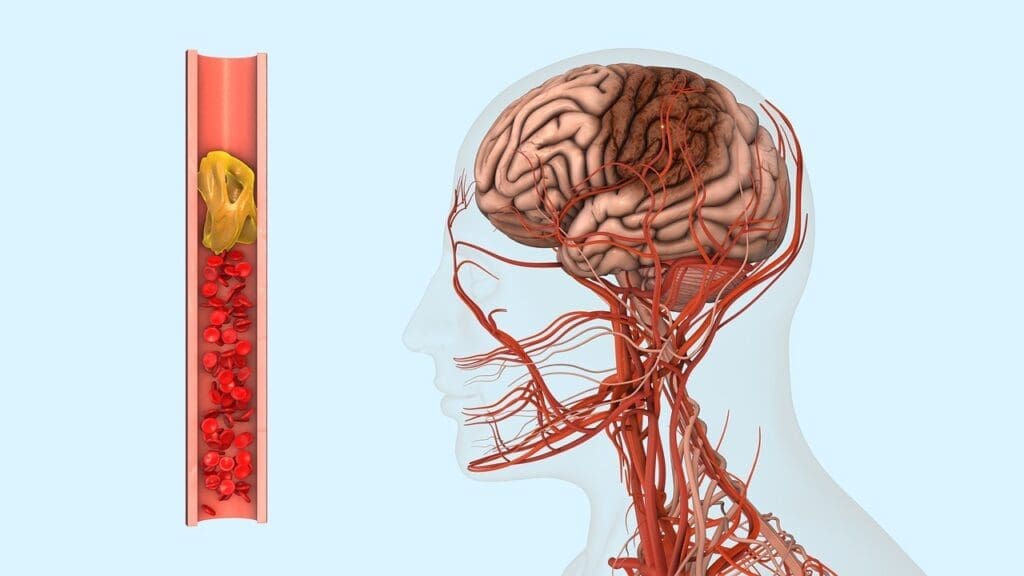
It’s important to understand atherosclerosis cerebri to find good treatments. We’ll explore what it is and how it forms in the brain’s arteries. We’ll also see how it’s different from other vascular diseases.
Definition and Medical Terminology
Atherosclerosis cerebri, or cerebral atherosclerosis, is when the brain’s arteries get narrow or hard. This happens because of plaque buildup. It’s a type of cerebrovascular atherosclerosis disease that affects the brain’s blood supply.
The terms around this condition are complex. They include atherosclerosis cerebrovascular disease and cerebral arteriosclerosis. These terms help doctors understand and treat the disease.
The Process of Plaque Formation in Cerebral Arteries
Plaque formation in the brain’s arteries starts with an injury to the artery lining. This injury can be caused by high blood pressure, smoking, or high cholesterol. Then, lipids, inflammatory cells, and smooth muscle cells build up, forming plaques.
As plaques grow, they can narrow the artery. This reduces blood flow to the brain. Symptoms like transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) or ischemic strokes can occur if the plaque blocks the artery.
Differences Between Cerebral Atherosclerosis and Other Vascular Conditions
Cerebral atherosclerosis is different from other vascular diseases like peripheral artery disease or coronary artery disease. They share some risk factors, but the main difference is where they occur. Cerebral atherosclerosis affects the brain’s arteries, making it unique.
Knowing these differences helps in creating specific treatments. While some treatments may be similar, cerebral atherosclerosis needs its own approach.
Cerebrovascular Anatomy and Blood Flow Dynamics
It’s key to know about cerebrovascular anatomy to grasp how atherosclerosis affects the brain. The brain’s blood supply comes from a complex network of arteries. This network is vital for our brain’s health and function.
Recent studies found that atherosclerosis in brain arteries might cause 10-15 percent of ischemic strokes worldwide. This shows why understanding brain artery anatomy and atherosclerosis is so important.
Key Brain Arteries Vulnerable to Atherosclerosis
The brain has several arteries that are more likely to get affected by atherosclerosis. These include the internal carotid arteries, vertebral arteries, and the circle of Willis. Atherosclerosis in these arteries can greatly reduce blood flow to important brain areas.
The internal carotid arteries supply blood to the front part of the brain. The vertebral arteries help with the back part. The circle of Willis at the brain’s base is key for spreading blood across the brain.
How Narrowed Arteries Impact Cerebral Circulation
Atherosclerosis can narrow arteries, affecting brain blood flow. This can cause brain tissue to not get enough blood. It might lead to temporary or permanent brain damage.
Narrowed arteries can cause many problems, like brain function decline and stroke risk increase. Knowing how this works helps in finding better treatments for atherosclerosis in the brain.
Primary Causes and Risk Factors
Atherosclerosis cerebri is caused by many factors. Some can be changed, and others can’t. Knowing these factors helps prevent and manage the condition.
Modifiable Risk Factors
There are several risk factors for atherosclerosis cerebri that can be changed. These include:
- Hypertension: High blood pressure can damage blood vessel linings, making them prone to plaque.
- Hyperlipidemia: High cholesterol and triglycerides can lead to plaque formation.
- Diabetes Mellitus: Diabetes can harm blood vessels and nerves, raising atherosclerosis risk.
- Smoking: Smoking damages the heart and blood vessels, increasing atherosclerosis risk.
- Obesity and Physical Inactivity: Being overweight and inactive can lead to other risk factors like hypertension and diabetes.
Changing these risk factors through lifestyle and medical treatment can lower atherosclerosis cerebri risk.
Non-Modifiable Risk Factors
Some risk factors can’t be changed, but knowing them is important. These include:
- Age: Atherosclerosis risk increases with age, after 50.
- Family History: A family history of heart disease raises individual risk.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some genes can affect lipid metabolism, increasing atherosclerosis risk.
Age-Related Considerations for Patients Over 50
Age is a big risk factor for atherosclerosis cerebri. People over 50 face higher risks due to blood vessel changes. It’s key to manage modifiable risk factors in this age group.
| Risk Factor | Description | Impact on Atherosclerosis Cerebri |
|---|---|---|
| Hypertension | High blood pressure | Increases the risk of plaque formation and vessel damage |
| Hyperlipidemia | Elevated cholesterol and triglycerides | Contributes to the development of atherosclerotic plaques |
| Diabetes Mellitus | High blood sugar levels | Damages blood vessels and nerves, increasing risk |
Understanding and tackling both changeable and unchangeable risk factors helps prevent and manage atherosclerosis cerebri.
Clinical Manifestations of Atherosclerosis Cerebri
It’s important to know the signs of atherosclerosis cerebri to get help early. We’ll look at the first signs and symptoms that show the disease is getting worse. We’ll also talk about the urgent symptoms that need emergency care right away.
Early Warning Signs and Symptoms
Atherosclerosis cerebri can show itself in many ways. Transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) are a big warning sign. They cause temporary problems with blood flow, leading to numbness, weakness, or paralysis in the face, arm, or leg.
Other early signs include cognitive changes. This means trouble with memory, focus, or making decisions. Some people might see vision disturbances like blurry vision, double vision, or losing vision in one eye.
Acute Symptoms Requiring Emergency Care
When atherosclerosis cerebri gets worse, it can cause serious symptoms that need quick medical help. A severe headache that feels like a “thunderclap” is a big warning sign. It might mean a hemorrhagic stroke.
Other urgent symptoms include acute confusion, trouble speaking or understanding, and sudden weakness or paralysis. If you or someone you know has these symptoms, get help right away.
Knowing the signs of atherosclerosis cerebri is key to getting the right treatment fast. Spotting the early signs and urgent symptoms can help prevent serious problems.
Diagnostic Approaches and Assessment
Diagnosing atherosclerosis cerebri is a detailed process. It uses advanced imaging and clinical checks. We use various tools to see how much arteries are narrowed and how it affects the brain.
Non-Invasive Imaging Techniques
Non-invasive imaging is key in finding cerebral atherosclerosis. Carotid Ultrasound and Transcranial Doppler (TCD) check blood flow and find stenosis. Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) and Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) give clear images of the brain’s blood vessels. They help spot narrowing or blockages.
Laboratory Tests and Clinical Evaluations
Laboratory tests are vital for checking patients with suspected cerebral atherosclerosis. We test lipid profiles, blood glucose levels, and inflammatory markers. These tests show if atherosclerotic disease is present. Clinical checks, like neurological exams, show how the disease affects patients.
| Laboratory Test | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Lipid Profile | Assess cholesterol and triglyceride levels |
| Blood Glucose | Evaluate for diabetes mellitus |
| Inflammatory Markers | Assess for inflammation indicative of atherosclerosis |
Differential Diagnosis Considerations
When diagnosing atherosclerosis cerebri, we must think of other conditions that might look like it. We look at vasculitis, cardioembolic events, and other causes of cognitive decline. A detailed diagnostic process helps us rule out these and confirm cerebral atherosclerosis.
Complications of Cerebrovascular Atherosclerosis Disease
It’s important to know the complications of cerebrovascular atherosclerosis. This disease increases the risk of serious health problems. These include transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) and long-term cognitive decline.
Cerebrovascular atherosclerosis can cause a lot of harm. “The presence of atherosclerotic plaques in cerebral arteries is a major risk factor for stroke and cognitive impairment,” says recent research.
Transient Ischemic Attacks (TIAs) as Warning Signs
TIAs, or “mini-strokes,” are warning signs of a bigger stroke. They happen when blood flow to the brain is temporarily blocked, usually by atherosclerotic plaques.
Recognizing TIA symptoms is key for quick medical help. Symptoms include sudden weakness or numbness, trouble speaking or understanding speech, and sudden vision changes.
Ischemic Stroke: Mechanisms and Outcomes
Ischemic stroke happens when a blood clot blocks a cerebral artery, often due to atherosclerosis. The stroke’s severity depends on where and how big the blockage is.
Outcomes can range from mild to severe disability or death. Prompt medical treatment is vital to reduce damage and improve chances of recovery.
Cognitive Decline and Vascular Dementia Progression
Cerebrovascular atherosclerosis is also linked to cognitive decline and vascular dementia. Reduced blood flow to the brain can cause progressive cognitive impairment.
Managing risk factors and living a healthy lifestyle are key to slowing cognitive decline. “Controlling hypertension, diabetes, and other cardiovascular risk factors is key to preserving cognitive function,” say clinical guidelines.
By understanding these complications and taking proactive steps, we can reduce the impact of cerebrovascular atherosclerosis disease on individuals and communities.
Current Treatment Strategies for Atherosclerosis Cerebri
Managing atherosclerosis cerebri requires a mix of treatments to protect brain health. As we learn more, new options are available to help patients.
We tailor treatments based on the latest research and each patient’s needs. We look at how severe the condition is, if symptoms are present, and the patient’s overall health.
Pharmacological Management
Medications are key in treating atherosclerosis cerebri. We use different drugs to manage risk factors and slow disease growth.
- Antiplatelet agents: These stop blood clots that can cause strokes.
- Statins: Statins lower cholesterol, reducing plaque and slowing disease.
- Antihypertensive medications: These control blood pressure, a major risk factor.
Surgical and Endovascular Interventions
Surgical and endovascular methods are also important. They help those with severe stenosis or high stroke risk.
Procedures like carotid endarterectomy and angioplasty with stenting improve blood flow. This reduces the risk of strokes.
Emerging Therapeutic Approaches
New research is exploring better treatments for atherosclerosis cerebri. This includes new drugs and advanced endovascular techniques.
| Therapeutic Approach | Description | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Novel Antiplatelet Agents | New medications with better safety and effectiveness than old ones. | Less risk of bleeding, better stroke prevention. |
| PCSK9 Inhibitors | Drugs that lower LDL cholesterol, potentially reducing plaque. | Better lipid control, possible plaque reduction. |
As we learn more, treatments for atherosclerosis cerebri will likely improve. This offers hope for those affected by this condition.
Prevention and Lifestyle Modifications
To prevent atherosclerosis cerebri, making dietary changes, staying active, and managing risk factors are key. A healthy lifestyle can greatly lower your risk of getting cerebrovascular atherosclerosis.
Evidence-Based Dietary Recommendations
Eating more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help manage atherosclerosis cerebri. It’s best to cut down on saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, like salmon and walnuts, are also good.
Studies show that a Mediterranean-style diet is great for heart health. It focuses on whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats, like olive oil.
| Dietary Component | Recommended Foods | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Fruits and Vegetables | Berries, Leafy Greens, Citrus Fruits | Rich in Antioxidants, Vitamins, and Minerals |
| Whole Grains | Oats, Quinoa, Brown Rice | High in Fiber, Helps Lower Cholesterol |
| Lean Proteins | Chicken, Fish, Legumes | Reduces Saturated Fat Intake |
Physical Activity Guidelines for Brain Health
Regular exercise is vital for brain health and preventing atherosclerosis cerebri. Aim for 150 minutes of moderate exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise weekly.
Exercise boosts heart health and brain function. Brisk walking, cycling, and swimming are great for brain health.
Managing Cardiovascular Risk Factors
It’s important to manage risk factors like high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol. Lifestyle changes and, if needed, medication can help.
Don’t forget to tackle other risks like smoking and obesity. Quitting smoking and keeping a healthy weight can lower your risk of atherosclerosis cerebri. For more on related risks, check out this article on gum disease and stroke.
Epidemiology and Recent Research Findings
Understanding atherosclerosis cerebri is key to better prevention and treatment. Recent studies have given us important insights. They show us how common and widespread this condition is.
Global Prevalence and Statistical Data
Atherosclerosis in brain arteries is a big cause of ischemic strokes worldwide. It’s believed that cerebral atherosclerosis disease causes 10-15 percent of these strokes. This highlights the need for more research into atherosclerosis cerebral.
Studies around the world have found different rates of cerebral atherosclerosis. Age, ethnicity, and lifestyle play big roles. For example, the risk goes up a lot after 50 years old.
Advances in Understanding Cerebral Atherosclerosis
New medical imaging and diagnostic tools have helped us understand cerebral atherosclerosis disease better. MRI and CT angiography are now key for diagnosing and tracking atherosclerosis in brain arteries.
Research into atherosclerosis cerebral is also making progress. It’s looking into how inflammation, lipid metabolism, and genetics affect it. This could lead to new ways to treat it.
As we learn more about atherosclerosis cerebri, our ways of managing it will improve. Using new research in treatment will help patients with cerebral atherosclerosis a lot.
Conclusion: Living with Cerebral Atherosclerosis and Future Outlook
Atherosclerosis cerebri is a complex condition that affects the brain’s blood flow. It can lead to serious problems like stroke and vascular dementia. Early treatment is key to reducing these risks and improving life expectancy.
We’ve looked at the risk factors, how to diagnose, and treatment options for atherosclerosis cerebri. Understanding this condition helps us see why prevention and lifestyle changes are vital for brain health.
As research grows, we’ll see new treatments for cerebral atherosclerosis. For now, it’s important for people to work with their doctors to manage their condition. This can help prevent strokes and other serious issues.
By being proactive and informed, we can improve life for those with atherosclerosis cerebri. This approach can lead to better outcomes and a higher quality of life.
What is atherosclerosis cerebri?
Atherosclerosis cerebri, or cerebral atherosclerosis, is when the brain’s arteries get narrowed or blocked. This happens because of plaque buildup. It can lead to less blood flow, stroke, and brain function decline.
What are the primary risk factors for developing atherosclerosis cerebri?
Main risk factors include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, and diabetes. Non-modifiable factors like age and family history also play a role.
How does atherosclerosis cerebri affect cerebral circulation?
Plaque buildup narrows arteries, reducing blood flow to the brain. This can cause stroke and brain function decline.
What are the early warning signs of atherosclerosis cerebri?
Early signs include transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), memory issues, and trouble with speech or understanding.
How is atherosclerosis cerebri diagnosed?
Doctors use ultrasound and MRI for imaging. They also check risk factors through lab tests and assess brain function.
What are the treatment options for atherosclerosis cerebri?
Treatments include medicines to control risk factors, surgeries to improve blood flow, and new treatments being researched.
Can lifestyle modifications help manage atherosclerosis cerebri?
Yes, eating right, exercising regularly, and managing risk factors can help manage the condition and prevent it from getting worse.
What is the significance of transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) in atherosclerosis cerebri?
TIAs are warning signs of a high risk of stroke. They need immediate medical attention.
How does atherosclerosis cerebri impact cognitive function?
Reduced blood flow can cause brain function decline. It can even lead to vascular dementia.
What is the global prevalence of atherosclerosis cerebri?
It’s a big problem worldwide, causing a lot of illness and death, mostly in older adults.
Are there any emerging therapeutic approaches for atherosclerosis cerebri?
Yes, research is looking into new treatments. This includes advanced surgeries and medicines.
How can patients with atherosclerosis cerebri manage their condition effectively?
Effective management includes medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and regular check-ups. This helps prevent the disease from getting worse and manage symptoms.










