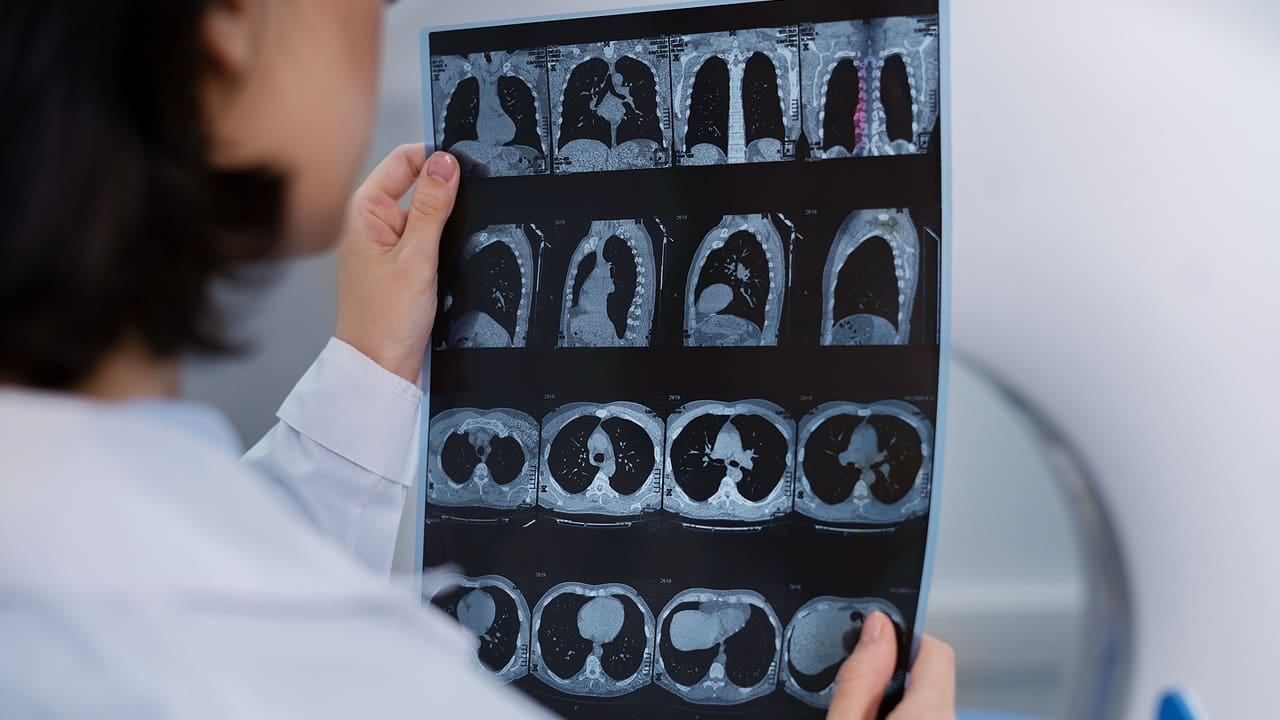
CT imaging has made it easier to spot aortic atherosclerosis early. This raises big questions about the seriousness of aortic changes in the belly and their impact on heart health.
At Liv Hospital, we focus on giving you reliable, patient-focused checks. Studies show that atherosclerosis is a big risk for heart diseases.
We’ll talk about what it means to have atherosclerotic plaques in the aorta. And how it affects your heart health overall.
Key Takeaways
- Early detection of aortic atherosclerosis is possible with advanced CT imaging.
- Atherosclerosis is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases.
- Comprehensive cardiovascular care is key for those with atherosclerotic aorta.
- Liv Hospital offers patient-centered checks with the latest medical methods.
- Knowing the impact of aortic atherosclerosis is essential for heart health.
Understanding Aortic Atherosclerosis and Its Significance
Aortic atherosclerosis is a major cardiovascular disease that we need to understand. It’s when plaque builds up in the aorta, the biggest artery. If not treated, it can cause serious health problems.
Definition and Pathophysiology of Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is when lipids, inflammatory cells, and fibrous elements build up in big arteries. It starts with damage to the artery’s inner layer. Then, lipids and inflammatory cells get in, causing plaque to form.
The process of atherosclerosis is complex, involving many cells and molecules. It’s not just about plaque buildup. It’s a dynamic process with inflammation, calcification, and changes in the artery wall.
“Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects the arterial wall, leading to plaque buildup and potentially severe cardiovascular events.”
How Atherosclerosis Affects the Aorta
Atherosclerosis in the aorta changes the artery’s structure and function. The plaque makes the aorta stiff and less flexible. This affects its ability to handle pressure changes during the heart’s cycle.
| Effect on Aorta | Consequence |
|---|---|
| Plaque Buildup | Reduced Compliance |
| Increased Stiffness | Altered Blood Pressure Regulation |
| Potential for Embolism | Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Events |
Prevalence in the General Population
Research shows atherosclerosis is common in adults, often found by chance during imaging tests. It’s more common with age and in people with risk factors like high blood pressure, diabetes, and smoking.
Recent data shows aortic atherosclerosis affects a lot of adults worldwide. Knowing this helps us focus on prevention and early detection in public health efforts.
Aortic Atherosclerosis on CT Scan: Detection and Appearance

CT scans give a detailed look at the aorta. They help doctors spot atherosclerotic plaques. This is key for finding abdominal aortic atherosclerosis, where plaque builds up in the abdominal aorta.
Characteristics of Atherosclerotic Plaques on Imaging
On CT scans, atherosclerotic plaques show up based on their density, size, and where they are. These details help doctors understand how serious the plaque in abdominal aorta is. They also help figure out the risk of heart problems in the future.
- Density: Plaques can be calcified, non-calcified, or mixed.
- Size: Bigger plaques can narrow the aortic lumen more.
- Location: Plaques can be anywhere in the aorta, but some spots are more common.
Common Locations in the Aorta
Atherosclerosis can happen anywhere in the aorta. But, the abdominal aorta is more likely to be affected. This is because it’s bigger and has more branch vessels.
- The abdominal aorta, near where it splits into the common iliac arteries.
- The aortic arch, where blood goes to the head and upper limbs.
- The descending thoracic aorta, which can have widespread atherosclerosis.
Incidental Detection During Routine Imaging
Many cases of atherosclerosis on ct scan are found by accident. This shows how important it is to check the aorta during any CT scan of the abdomen or chest.
Knowing how atherosclerotic plaques look on CT scans helps doctors manage patients with abdominal aortic atherosclerosis better. This can lower the risk of heart problems.
Severity Classification of Atherosclerosis in the Abdominal Aorta
Doctors use severity levels to predict heart risks and plan treatments. The level of atherosclerosis in the abdominal aorta is key. It helps doctors manage patients better.
Mild Atherosclerosis of the Abdominal Aorta Without Aneurysm
Mild atherosclerosis means there’s a small amount of plaque. It doesn’t block blood flow much. But, it’s a sign to start making healthy lifestyle changes.
Key features of mild atherosclerosis include:
- Minimal plaque formation
- No significant luminal narrowing
- Absence of aneurysmal dilatation
Moderate Atherosclerosis of the Abdominal Aorta
Moderate atherosclerosis has more plaque, which can narrow the aorta. It’s a sign to watch closely and possibly take stronger steps to lower heart risks.
Characteristics of moderate atherosclerosis may include:
- Noticeable plaque accumulation
- Some degree of luminal stenosis
- Increased risk of cardiovascular events
Severe and Widespread Plaque in Abdominal Aorta
Severe plaque buildup in the abdominal aorta is a serious sign. It can cause big blockages or even stop blood flow. This is a high-risk situation that needs detailed care.
Features of severe atherosclerosis include:
- Extensive plaque buildup
- Significant luminal narrowing or occlusion
- High risk of cardiovascular morbidity
Knowing how severe atherosclerosis is in the abdominal aorta is key. It helps doctors make better plans for patients. This way, they can lower heart risks.
Scattered Atherosclerotic Involvement: Early Warning Signs
Atherosclerotic involvement in the aorta can be an early sign of vascular disease. Finding scattered atherosclerotic lesions in a CT scan is key. It shows how atherosclerosis might progress.
What Scattered Atherosclerotic Lesions Indicate
Scattered atherosclerotic lesions in the abdominal aorta mean atherosclerosis is starting. These lesions are not random. They show the vascular system is affected by atherosclerosis.
Studies show these lesions can signal widespread disease (Source: First web source). Their presence means risk factors like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or smoking are harming the blood vessels. So, finding these lesions is a call for doctors to check the patient’s heart risk.
Progression from Scattered to Diffuse Involvement
Lesions spreading from scattered to widespread is a serious sign. It can lead to heart problems. As atherosclerosis grows, lesions can get bigger and more complex.
This can cause serious issues like aneurysms or blocked arteries. Knowing this helps in preventing heart problems. Early detection lets doctors start treatments to slow the disease.
It’s vital to keep an eye on people with scattered lesions. Regular check-ups and the right care can prevent serious heart issues.
Health Implications of Abdominal Aortic Atherosclerosis
We look at the health effects of abdominal aortic atherosclerosis. This condition affects the aorta and has big impacts on heart health. It’s not just a local issue; it shows a bigger problem with atherosclerosis in the body.
Relationship to Coronary Artery Disease
Studies link abdominal aortic atherosclerosis to coronary artery disease. Atherosclerotic plaques in the aorta mean more likely plaques in the heart’s arteries. This is because atherosclerosis affects many blood vessels at once.
People with aortic atherosclerosis face a higher risk of heart disease. This shows why it’s key to check heart health in these patients.
Risk of Cerebrovascular Events
Abdominal aortic atherosclerosis also raises the risk of cerebrovascular events. This includes stroke and transient ischemic attacks. Atherosclerosis in the aorta can signal disease in the brain’s blood vessels, raising stroke risk.
This link shows why managing atherosclerosis risk is vital. It helps prevent heart and brain problems.
Predictive Value for Future Cardiovascular Events
The severity of abdominal aortic atherosclerosis predicts future cardiovascular events. Doctors can use this to understand a patient’s risk better. They can then plan the best care for each patient.
This shows why it’s important to check for aortic atherosclerosis. It’s part of a full check-up for heart health.
Comprehensive Assessment of Atherosclerosis Disease of the Abdominal Aorta
CT imaging is key in checking atherosclerosis disease of the abdominal aorta. It gives us detailed views of plaque and its characteristics. This is important for figuring out how severe the disease is and what treatment is best.
Role of CT Imaging in Diagnosis
CT imaging is essential for spotting atherosclerosis in the abdominal aorta. It shows us the aorta and its branches clearly. We can see the size, location, and type of atherosclerotic plaques with CT scans.
CT scans are great because they can spot both calcified and non-calcified plaques. This gives us a full picture of the atherosclerotic burden. Knowing this helps us understand the risk and decide on the best course of action.
Measuring Plaque Burden and Characteristics
Measuring plaque burden means looking at the volume and makeup of atherosclerotic plaques in the abdominal aorta. CT imaging lets us measure plaque volume and spot different plaque types like calcification and lipid-rich cores.
- Quantification of plaque volume
- Identification of plaque composition
- Assessment of plaque characteristics
These details are key to knowing how serious the atherosclerosis is and how it’s changing over time.
Comparison with Other Imaging Modalities
CT imaging is very useful, but other methods like ultrasound, MRI, and PET scans also have their place. Each has its own benefits and drawbacks.
| Imaging Modality | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| CT Imaging | High-resolution images, detects calcified and non-calcified plaques | Radiation exposure, contrast required |
| Ultrasound | Non-invasive, no radiation, cost-effective | Limited depth penetration, operator-dependent |
| MRI | High soft tissue contrast, no radiation | Expensive, limited availability, contraindications |
By looking at these options, we can pick the best imaging plan for each patient. This depends on their specific needs and situation.
Management Strategies Based on CT Findings
CT scans show how severe atherosclerosis is. This helps doctors create treatment plans that fit each person’s needs. They consider the size and type of plaques found.
Medical Management Options
Medical treatment is key for atherosclerosis. It includes medicines to lower risk factors.
- Statins: These drugs lower cholesterol and fight inflammation. They help keep plaques stable and lower heart risks.
- Antiplatelet Agents: Aspirin or P2Y12 inhibitors stop platelets from clumping. This lowers the chance of blood clots.
- Blood Pressure Management: Keeping blood pressure in check is vital. Doctors might use certain medicines to help.
A leading cardiology journal says statins greatly reduce heart risks in atherosclerosis patients.
“Statins are a cornerstone in the management of atherosclerosis, showing a clear benefit in lowering heart risk.”
Lifestyle Modifications
Changing your lifestyle is also important. These changes help lower risk factors and slow disease growth.
- Dietary Changes: Eating more fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean proteins helps control cholesterol and blood pressure.
- Physical Activity: Exercise boosts heart health, helps with weight, and reduces stress.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is key, as it’s a big risk factor for atherosclerosis.
Follow-up Protocols and Monitoring
Regular check-ups and tests are essential. They include CT scans to track the disease and see if treatments are working.
By keeping a close eye on patients and adjusting treatments, doctors can improve outcomes. This reduces the risk of atherosclerosis complications.
When Aortic Atherosclerosis Requires Intervention
When aortic atherosclerosis shows up on scans, it’s time to think about treatment. The severity and type of plaque matter a lot. They help decide the best course of action.
Indications for Further Evaluation
More tests are needed if the atherosclerosis is severe. Research shows that advanced cases need stronger treatments. This could include procedures to lower the risk of heart problems.
Recent studies found that big aortic plaques raise heart event risks. This means a detailed check-up and treatment plan are needed.
“The presence of extensive aortic plaque is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular events, suggesting the need for a detailed assessment and management plan.”
Treatment Options for Advanced Disease
For severe aortic atherosclerosis, several treatments are available. These depend on the disease’s details and the patient’s health.
- Medical treatments like statins and antiplatelet drugs to lower heart risks.
- Changes in lifestyle, like quitting smoking and eating better, to slow disease growth.
- In some cases, procedures like angioplasty or stenting might be considered.
Emerging Therapies and Research Directions
New treatments for aortic atherosclerosis are being researched. Several promising areas are being explored.
New therapies include new medicines and advanced procedures. For example, PCSK9 inhibitors are being studied to lower heart risks in severe cases.
Managing aortic atherosclerosis well means keeping up with the latest research and guidelines. This helps provide the best care for patients.
Conclusion: Understanding the Significance of Your CT Findings
It’s key to understand what a CT scan shows about aortic atherosclerosis. This knowledge helps manage heart disease risk. Doctors can spot and treat atherosclerosis early, lowering the chance of heart problems later.
CT scans show how bad atherosclerosis is in the abdominal aorta. This info helps doctors decide the best treatment. They look at the type and location of atherosclerotic plaques to plan care.
Knowing what a CT scan reveals about aortic atherosclerosis is very important. It helps patients get the right care and make lifestyle changes to lower heart disease risk. Proper diagnosis and treatment can greatly improve health outcomes.
Getting CT findings right is critical for finding people at high risk of heart issues. By understanding atherosclerosis on a CT scan, doctors can create specific treatment plans. This helps reduce the risk of heart problems.
What is aortic atherosclerosis on a CT scan?
Aortic atherosclerosis on a CT scan shows atherosclerotic plaques in the aorta. These plaques can be seen and studied with computed tomography imaging. It helps us understand how severe the atherosclerosis is, which is key to knowing the heart risk.
How serious is atherosclerosis of the abdominal aorta?
Atherosclerosis of the abdominal aorta is quite serious. It raises the risk of heart problems and strokes. We stress the need to manage this condition to lower these risks.
What does mild atherosclerosis of the abdominal aorta without aneurysm mean?
Mild atherosclerosis without aneurysm means early atherosclerotic changes in the aorta. These changes are not yet severe. We keep a close eye on these cases to prevent further issues and manage risk factors.
What is scattered atherosclerotic involvement?
Scattered atherosclerotic involvement means atherosclerotic lesions at different spots in the aorta. This pattern is a warning sign. It shows a higher risk of the disease spreading.
How is the severity of atherosclerosis in the abdominal aorta classified?
The severity of atherosclerosis is classified as mild, moderate, or severe. This depends on the plaques’ extent and characteristics. We use this classification to decide on treatment and predict heart risk.
What are the health implications of abdominal aortic atherosclerosis?
Abdominal aortic atherosclerosis poses serious health risks. It increases the chance of heart disease, strokes, and future heart problems. Managing this condition is vital to reduce these risks.
How is atherosclerosis disease of the abdominal aorta assessed comprehensively?
Assessing atherosclerosis disease involves CT imaging to detect and study plaques. It measures plaque burden and assesses heart risk. We compare CT findings with other imaging to ensure accurate diagnosis.
What management strategies are available for atherosclerosis based on CT findings?
Management strategies include medical options, lifestyle changes, and follow-up plans. We tailor our approach to each patient’s needs. Emphasizing ongoing monitoring and risk factor management is key.
When does aortic atherosclerosis require intervention?
Intervention may be needed for significant cardiovascular risk or advanced disease. We consider various treatments, including new therapies, to improve outcomes.
What is the role of CT imaging in diagnosing atherosclerosis?
CT imaging is vital for diagnosing atherosclerosis. It provides detailed images of the aorta and its branches. This helps us detect and study plaques. We rely on CT scans to guide treatment and monitor disease.
How does atherosclerosis in the abdominal aorta relate to coronary artery disease?
Atherosclerosis in the abdominal aorta is linked to coronary artery disease. Both share common risk factors and mechanisms. The presence of abdominal aortic atherosclerosis may indicate a higher risk of coronary artery disease.





