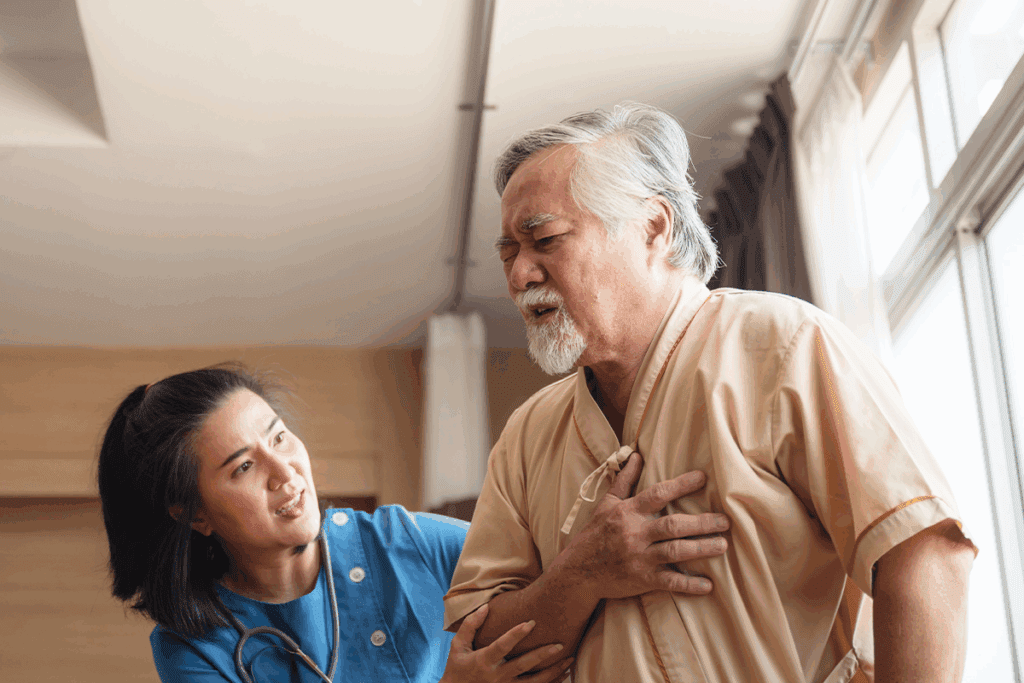
Distinguishing between heartburn and a heart attack can be tough. Both can cause chest pain, making it hard to tell them apart. At Liv Hospital, we know how vital it is to get the right diagnosis and care fast.
Dr. Juan Carlos Rozo, a cardiologist at Houston Methodist, says, “If you’re ever in doubt, it’s better to seek emergency care immediately.” We stress the need to know the differences between these two conditions. This knowledge is key to getting the right treatment.
Key Takeaways
- Heartburn and heart attack can have similar symptoms, making diagnosis critical.
- Chest pain is a common symptom of both conditions.
- Accurate diagnosis is essential for timely and effective care.
- Seeking emergency care is recommended if you’re unsure about your symptoms.
- Understanding the differences between heartburn and heart attack can save lives.
Understanding Chest Discomfort: Common Causes

It’s important to know why you might feel chest discomfort. This symptom can mean different things, from mild to serious. Every year, over 6.5 million people in the U.S. go to the emergency room for chest pain.Discover how to tell if it’s gerd or heart attack by understanding their symptoms.
The Alarming Nature of Chest Pain
Chest pain can be very worrying. It might mean something serious, like a heart attack. But it can also be from less serious issues, like heartburn or indigestion.
The type of chest pain you feel can tell you a lot. It might be sharp, dull, or burning. Knowing this can help figure out what’s wrong.
Most Common Conditions Causing Chest Discomfort
There are many reasons for chest discomfort, including:
- Heartburn and Acid Reflux: A burning feeling in your chest, often after eating.
- Heart Attack: A serious emergency with chest pain or discomfort, and other symptoms like shortness of breath.
- Angina: Chest pain or discomfort from reduced blood flow to the heart.
- Pulmonary Embolism: A blockage in a pulmonary artery, causing sudden and severe chest pain.
These conditions show why you should see a doctor for chest discomfort.
Why Accurate Diagnosis Matters
Getting the right diagnosis is key. The treatment for chest discomfort depends on what’s causing it. For example, heartburn might need antacids or lifestyle changes, but a heart attack needs quick medical help.
A doctor says, “Don’t panic, but get medical help fast. Early diagnosis can save lives.” This shows why you shouldn’t ignore chest discomfort and get professional help.
Diagnosing chest discomfort involves looking at your medical history, doing a physical exam, and running tests like ECGs and imaging studies. This detailed approach helps find the cause and guide treatment.
What Exactly Is Heartburn?
Heartburn is a burning feeling in the chest or throat. It happens when stomach acid goes back up into the esophagus. The esophagus is not made for this acidic flow, causing irritation and heartburn.
The Mechanism Behind Acid Reflux
Acid reflux occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) relaxes or weakens. This lets stomach acid flow back into the esophagus. The esophagus can’t handle stomach acid, leading to irritation and heartburn.
We will explore this mechanism in more detail, including the role of the LES and other factors that contribute to acid reflux.
Common Triggers for Heartburn
Several factors can trigger heartburn by relaxing the LES or increasing pressure on the stomach. Common triggers include:
- Consuming large or heavy meals
- Eating certain foods, such as citrus fruits, tomatoes, chocolate, and spicy or fatty foods
- Drinking beverages like coffee, alcohol, or carbonated drinks
- Being overweight or obese
- Pregnancy
- Smoking
Prevalence and Risk Factors
Heartburn is a widespread condition affecting people of all ages. Certain factors increase the risk of experiencing heartburn, including:
| Risk Factor | Description |
| Age | Heartburn is more common in adults over 40 years old. |
| Obesity | Excess weight can put pressure on the stomach, causing acid reflux. |
| Pregnancy | Hormonal changes and increased pressure on the stomach during pregnancy can lead to heartburn. |
| Smoking | Smoking can weaken the LES and reduce saliva production, which helps neutralize stomach acid. |
Understanding these triggers and risk factors can help individuals manage their heartburn symptoms and prevent future episodes.
Heart Attack: What Happens During a Cardiac Event
It’s important to know what happens during a heart attack. This knowledge helps us spot symptoms early and get help fast. A heart attack, or myocardial infarction, happens when blood flow to the heart is blocked. This cuts off oxygen to the heart muscle.
The Physiology of a Heart Attack
A heart attack damages or kills heart tissue because of blocked blood flow. This blockage is usually a blood clot on atherosclerosis (plaque) in a coronary artery. A complete blockage is more dangerous, causing more heart muscle damage.
The heart needs oxygen and nutrients to work right. When a coronary artery is blocked, the heart muscle below the blockage gets ischemic. This can lead to cell death if the blockage isn’t fixed quickly.
Types of Heart Attacks
There are different types of heart attacks, based on the blockage’s severity and location. The most common is an ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI). This is when a coronary artery is completely blocked, causing a lot of heart muscle damage.
Non-ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction (NSTEMI) is another type. Here, the blockage is only partial. This type can be harder to diagnose because the ECG changes might not be as clear.
Risk Factors for Heart Disease
Many factors increase the chance of having a heart attack. These include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, and family history of heart disease. Knowing these risk factors helps prevent and treat heart disease early.
Changing lifestyle habits like diet, exercise, and quitting smoking can lower heart disease risk. Also, managing high blood pressure and diabetes with medicine and lifestyle changes is key.
Does Indigestion Cause Chest Tightness?
Chest tightness can be scary, and it’s normal to wonder if it’s linked to acid reflux. We’ll look into how acid reflux impacts the chest. We’ll also explore why heartburn might feel like chest pressure and the bond between the esophagus and the heart.
How Acid Reflux Affects the Chest
Acid reflux, or GERD, happens when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus. This can irritate the esophagus, causing discomfort that might feel like chest tightness. The esophagus is right behind the heart, so irritation can spread to the chest.
Severe acid reflux can lead to problems like esophagitis or stricture. These issues can make chest tightness worse. Acid reflux can also inflame the esophagus, which might tighten the chest muscles.
Why Heartburn Can Feel Like Chest Pressure
Heartburn feels like a burning in the chest, usually behind the breastbone. This happens when stomach acid irritates the esophagus. The discomfort can feel like chest pressure or tightness.
The esophagus and heart are close, sharing nerve pathways. This means heartburn discomfort can feel like heart pressure. It’s hard to tell the difference without a doctor’s help.
The Esophageal-Cardiac Connection
The esophagus and heart are connected by their close location and shared nerves. The esophagus is behind the heart, and irritation there can affect the heart. Or, it might seem like a heart problem.
This connection is why some people feel chest tightness during heartburn. Knowing this helps doctors figure out what’s causing chest symptoms and how to treat them.
Characteristic Symptoms of Heartburn
It’s important to know the signs of heartburn to tell it apart from other issues, like a heart attack. Heartburn has its own set of symptoms that can change in how bad they are and how often they happen.
Location and Sensation of Discomfort
Heartburn usually feels like a burning in the chest, right behind the breastbone. This feeling can spread up to the throat, leaving a sour or acidic taste in your mouth. It’s often described as a burning or hot feeling that can be quite uncomfortable.
Timing and Duration of Heartburn Episodes
Heartburn can happen at any time, but it’s more common after eating big meals. It can also be triggered by lying down or bending over. The length of heartburn episodes can vary, lasting from a few minutes to hours if not treated.
Associated Digestive Symptoms
Heartburn often comes with other digestive issues. These include bloating, burping, and trouble swallowing. Some people might also feel nauseous or very full after eating. As Dr. John Smith, a gastroenterologist, says,
“Heartburn is not just about the burning sensation; it’s a complex of symptoms that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life.”
Knowing these symptoms is key to diagnosing heartburn correctly and to tell it apart from other chest discomforts. By understanding the location, sensation, timing, and other symptoms of heartburn, people can get the right medical help and treatment.
Recognizing Heart Attack Symptoms
Knowing the signs of a heart attack can save lives. A heart attack happens when blood flow to the heart stops. This causes damage to the heart muscle. Symptoms can vary, so it’s important to know all the possible signs.
Classic vs. Atypical Presentation
Heart attack symptoms fall into two categories: classic and atypical. Classic symptoms are well-known and include chest pain. Atypical symptoms can be misleading and don’t always involve chest pain.
Classic Symptoms: These include a squeezing feeling in the chest that can spread to the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach. Other classic signs are cold sweats, feeling tired, and shortness of breath.
Atypical Symptoms: Atypical symptoms can be in areas other than the chest, like the arms, back, or jaw. Some people might feel nausea, vomiting, or dizziness without chest pain.
Heart Attack Symptoms in Men vs. Women
Men and women can both have heart attack symptoms, but they show up differently. Men often have classic symptoms, while women tend to have atypical ones.
| Symptoms | Men | Women |
| Chest Pain | Common | Less Common |
| Shortness of Breath | Less Common | Common |
| Fatigue | Less Common | Common |
| Nausea/Vomiting | Less Common | Common |
Warning Signs That Should Never Be Ignored
Some symptoms need immediate medical help. These include:
- Severe or prolonged chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath without exertion
- Pain or discomfort in one or both arms, the back, neck, jaw, or stomach
- Cold sweats or clamminess
- Lightheadedness or dizziness
- Fatigue or weakness
If you or someone you know has these symptoms, act fast. Call emergency services right away if you think it’s a heart attack.
Key Differences Between Heartburn and Heart Attack
Heartburn and heart attack both cause chest discomfort, but they have different causes and signs. Knowing these differences is key for the right diagnosis and treatment.
Onset and Progression of Symptoms
Heartburn starts after eating, often after big or spicy meals. It gets worse when lying down or bending. It usually goes away as the stomach digests the food.
A heart attack can happen anytime, without warning. Its symptoms keep getting worse over time.
Heartburn symptoms are linked to digestion. Heart attack symptoms are constant and not tied to eating or lying down.
Location and Radiation of Pain
Heartburn pain is a burning feeling in the chest, often behind the sternum. It can spread to the throat or upper abdomen. This pain is relieved by antacids.
A heart attack causes chest pain or discomfort that spreads to arms, back, neck, jaw, or abdomen. This pain feels like pressure, tightness, or heaviness.
Response to Medication
Heartburn symptoms quickly get better with antacids or acid reducers. But, heart attack symptoms don’t improve with these medications. If chest pain lasts after taking antacids, get medical help right away.
Associated Symptoms
Heartburn often comes with bloating, belching, or a sour taste. A heart attack may bring shortness of breath, nausea, dizziness, or cold sweats. These extra symptoms suggest a serious heart problem.
Understanding the differences in symptoms helps tell if it’s heartburn or a heart attack. This ensures the right medical care is sought.
When Heartburn and Chest Tightness Occur Together
Heartburn and chest tightness together can be puzzling. It’s hard to tell if it’s a stomach issue or a heart problem. Or maybe it’s both.
Mechanisms of Chest Tightness in GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) makes stomach acid flow back into the esophagus. This can irritate the esophagus lining, causing pain. Chest tightness in GERD can happen for a few reasons:
- Esophageal spasms: Acid reflux can cause spasms in the esophagus, leading to chest tightness.
- Inflammation: Chronic acid exposure can cause inflammation in the esophagus, potentially leading to chest discomfort.
- Vagus nerve stimulation: The vagus nerve runs near the esophagus and can be stimulated by acid reflux, potentially causing chest tightness.
Distinguishing Features from Cardiac Chest Pain
It’s important to tell the difference between GERD chest tightness and heart pain. Both can cause chest discomfort, but there are key differences:
| Characteristics | GERD-related Chest Tightness | Cardiac Chest Pain |
| Trigger | Often triggered by food, like fatty or spicy meals | Typically triggered by exertion or stress |
| Relief | May be relieved by antacids or acid reducers | Not relieved by antacids; may be relieved by rest or nitroglycerin |
| Associated Symptoms | Often accompanied by heartburn, regurgitation | May be accompanied by shortness of breath, dizziness, or pain radiating to the arm or jaw |
Chronic Heartburn and Its Complications
Chronic heartburn from GERD can lead to serious problems if not treated. A big worry is Barrett’s esophagus, which can lead to esophageal cancer. Other issues include esophageal strictures and chronic cough.
It’s essential to seek medical attention if you have persistent or severe heartburn. Early treatment can prevent these serious complications.
When to Seek Emergency Medical Attention
It’s key to know when to seek immediate medical help. Symptoms that could be heartburn or a heart attack need quick action. This can save lives.
Red Flag Symptoms That Warrant Immediate Care
Certain symptoms should never be ignored. If you feel uncomfortable pressure, squeezing, fullness, or pain in the center of your chest for more than a few minutes, act fast.
Other red flag symptoms include:
- Chest pain that radiates to your arm, back, neck, jaw, or stomach
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Lightheadedness or dizziness
- Cold sweats
- Nausea or vomiting
Better Safe Than Sorry: When to Call 911
If you’re experiencing any red flag symptoms, call 911 right away. Don’t delay or drive yourself to the hospital. Emergency responders can help on the way.
When calling 911, be ready to give your location and a brief about your symptoms. If you’re in a public place, stay calm and follow the operator’s instructions.
What to Tell Emergency Responders
When responders arrive, share as much info as you can. This includes:
| Information to Provide | Details |
| Medical History | Any pre-existing conditions, allergies, or medications you’re currently taking |
| Symptom Description | The nature of your symptoms, when they started, and any factors that relieve or worsen them |
Being prepared and knowing what to do ensures you get the medical help you need quickly.
Diagnostic Approaches for Chest Pain
Figuring out why you have chest pain starts with a detailed check in the emergency room. Chest pain can be scary, but our doctors are ready to find out what’s wrong fast.
Initial Assessment in the Emergency Room
When you get to the emergency room with chest pain, it’s a big moment. Our team looks at your health history, does a physical check, and asks about your pain. They want to know where it hurts, how bad it is, and how long it’s lasted.
“The first check is key to figuring out what to do next,” says Dr. John Smith, a top cardiologist. “It’s not just the pain. It’s about your whole health story.”
Tests to Differentiate Cardiac from Digestive Causes
To tell if your chest pain is from your heart or stomach, we use different tests. Here are some:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): This test shows how your heart works. It can spot heart problems or a heart attack.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests look for heart damage signs.
- Cardiac CT: This scan shows your heart and blood vessels in detail.
- Angiography: It uses dye to see if there are any blockages in your blood vessels.
| Diagnostic Test | Purpose |
| Electrocardiogram (ECG) | Measures heart electrical activity |
| Blood Tests | Checks for heart damage enzymes |
| Cardiac CT | Provides heart and vessel images |
| Angiography | Visualizes blood vessel blockages |
Follow-up Evaluations
After you’re diagnosed and treated, we keep an eye on you. If your pain is heart-related, you might need rehab and check-ups. If it’s from acid reflux, we might adjust your diet and meds.
Understanding how we diagnose chest pain helps us see how serious it is. If you have chest pain, getting medical help right away is very important.
Conclusion: Staying Heart Smart and Digestively Aware
It’s important to know the difference between heartburn and a heart attack. This knowledge helps keep you healthy. By understanding the symptoms of each, you can act quickly and get the right care.
We’ve looked at heartburn and heart attacks in detail. We’ve talked about their causes, symptoms, and how doctors diagnose them. Being heart smart and digestively aware can lower your risk of problems and make life better.
Prevention is key to a healthy heart and digestive system. A balanced lifestyle, managing stress, and getting medical help when needed are important. These steps can help prevent heart issues.
In conclusion, knowing and acting on heart health is vital. We urge readers to stay alert and take care of their health. Be aware of heartburn and heart attack signs to avoid serious problems.
FAQ
Can heartburn cause tightness in the chest?
Yes, heartburn can make your chest feel tight. This happens when acid from your stomach irritates your esophagus.
What is the difference between heartburn and a heart attack?
Heartburn is a symptom of acid reflux, causing a burning chest feeling. A heart attack blocks blood to the heart, damaging it. The pain from these issues is different in intensity, location, and what triggers it.
How can I tell if my chest pain is related to heartburn or a heart attack?
If you have chest pain with shortness of breath, dizziness, or arm or jaw pain, it might be a heart attack. Heartburn usually feels like a burning that gets worse when you lie down or after eating.
Does indigestion cause chest tightness?
Yes, indigestion can make your chest feel tight. This is often because of acid reflux, the same cause as heartburn.
What are the warning signs of a heart attack?
Heart attack warning signs include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, and pain in your arm, back, neck, jaw, or stomach. You might also feel weak, light-headed, or faint.
Can GERD cause chest tightness?
Yes, GERD can cause chest tightness. This happens because stomach acid often flows back up into your esophagus, irritating it.
How do I distinguish between cardiac chest pain and heartburn?
Cardiac chest pain feels like pressure or squeezing and might be with shortness of breath or pain in other areas. Heartburn is a burning feeling linked to eating or lying down.
When should I seek emergency medical attention for chest pain?
Get emergency help for severe chest pain, shortness of breath, or symptoms that could be a heart attack.
What diagnostic tests are used to evaluate chest pain?
Tests for chest pain include ECGs, blood tests, chest X-rays, echocardiograms, or endoscopies. The choice depends on what’s suspected.
How can I prevent heartburn and reduce the risk of complications?
To avoid heartburn, change your lifestyle. Avoid trigger foods, eat smaller meals, lose weight if needed, and don’t lie down after eating.
What is the connection between the esophagus and heart-related chest pain?
The esophagus and heart are close in the chest. Irritation of the esophagus can be mistaken for heart pain because of their closeness and shared nerve pathways.
References:
- Lung, K., & Lui, F. (2023). Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis: Arteries. In StatPearls. National Center for Biotechnology Information.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK525959/


































