The heart’s electrical system is a complex network that controls the heartbeat. It makes sure the heart’s chambers contract in sync. At the heart of this system is the sinoatrial node, or SA node, heart conduction pathway Can Low Iron Cause Heart Palpitations? 7 Key Ways It Leads to Related Symptomswhich acts as the heart’s natural pacemaker.
The electrical impulse from the SA node travels through a special conduction pathway. This pathway lets the heart pump blood efficiently all over the body. Knowing how this system works is key to understanding the heart’s function and how problems can cause arrhythmias or other heart issues.
At Liv Hospital, we focus on patient-centered care for our international patients. Our team of experts is here to make sure your heart’s electrical health is in good hands.
Key Takeaways
- The heart’s electrical system is governed by the sinoatrial node.
- The conduction pathway enables coordinated contraction of the heart chambers.
- Disruptions in the electrical impulse can lead to cardiac issues.
- Liv Hospital provides patient-centered care for international patients.
- Our team of experts is dedicated to ensuring optimal heart health.
The Remarkable Cardiac Electrical System
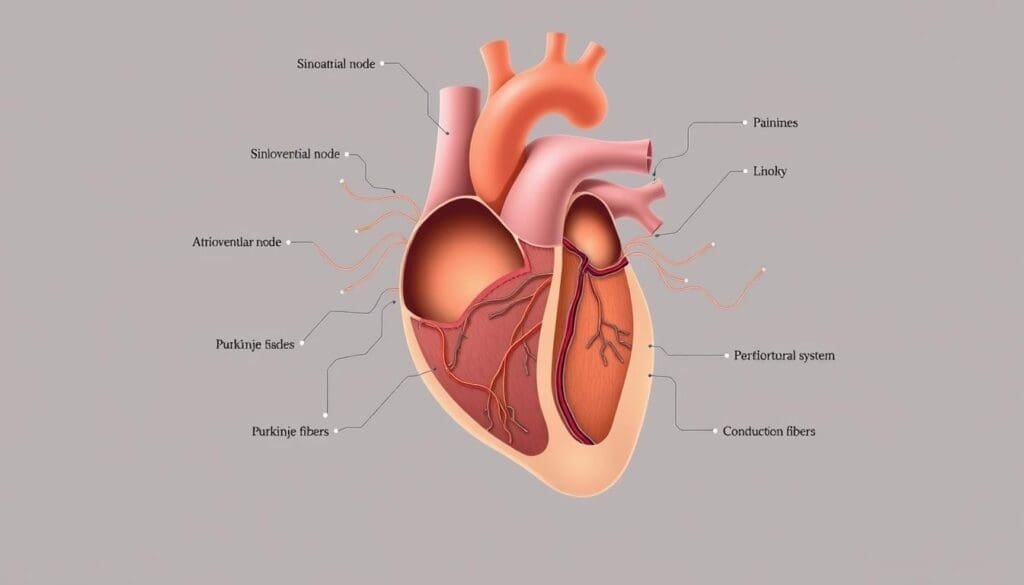
The cardiac electrical system is a complex network that controls the heartbeat. It turns electrical impulses into mechanical actions. These actions pump blood all over the body.
The Heart as an Electromechanical Organ
The heart works as an electromechanical organ. It needs a detailed electrical system to manage the heartbeat. This starts at the sinoatrial node in the right atrium, the heart’s natural pacemaker.
The sinoatrial node sends out regular electrical pulses. These pulses are between 60 to 100 times per minute. They move through the atrial tissue to the atrioventricular node (AV node). Then, they go to the ventricles via the Bundle of His and Purkinje fibers. This ensures the heart beats in sync.
The Importance of Coordinated Electrical Activity
Coordinated electrical activity is key for the heart to pump blood well. The heart’s electrical system makes sure the atria and ventricles contract together. A leading cardiologist notes:
“The heart’s electrical system is a finely tuned mechanism that relies on the precise coordination of electrical impulses to maintain a normal heart rhythm.”
This coordination helps the heart adjust to different situations. For example, it can speed up the heart rate during exercise or stress. This ensures the body gets what it needs.
| Component | Function |
| Sinoatrial Node | Generates electrical impulses |
| Atrioventricular Node | Delays impulse transmission to ventricles |
| Bundle of His | Transmits impulses to ventricles |
| Purkinje Fibers | Distributes impulses throughout ventricles |
Understanding the Heart Conduction Pathway and Its Components
The heart’s electrical conduction pathway is complex. It involves many specialized tissues. This system is key for coordinating the heartbeat, making sure the heart chambers contract together.
We will look at the main parts of this pathway. We’ll see how they work together to keep the heart rhythm normal.
Specialized Tissues in the Cardiac Conduction System
The cardiac conduction system has special heart muscle cells in the myocardium. These cells send out electrical impulses that control the heartbeat. The system is supported by fibrous tissue.
“The cardiac conduction system is a vital network that ensures the heart beats in a coordinated manner,” it’s vital for heart function.
The SA node in the right atrium is the heart’s natural pacemaker. It starts the electrical impulse. The impulse then goes to the atrioventricular (AV) node, where it’s delayed.
This delay is key for ventricular filling. It makes sure the ventricles are full of blood before they contract.
The Sequential Flow of Electrical Signals
The flow of electrical signals through the heart is well-coordinated. The SA node starts the impulse, which travels through the atria, causing them to contract. Then, it reaches the AV node, where it’s briefly delayed.
This delay lets the ventricles fill with blood. It’s important for efficient cardiac output. The impulse then goes through the Bundle of His, bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers, making the ventricles contract.
Understanding how electrical signals flow is key for diagnosing and treating heart problems. By knowing how impulses are generated and conducted, doctors can spot and treat heart rhythm issues.
Fact 1: The Sinoatrial (SA) Node – Where It All Begins
The sinoatrial (SA) node is at the heart of our heart’s rhythm. It’s a small but key part that acts as the heart’s natural pacemaker. This node starts the electrical impulses that control our heartbeat.
Structure and Location of the Sinus Node
The SA node is about 15 millimeters long and 4 mm wide. It’s found in the upper right part of the heart’s right atrium. This spot lets it start the electrical impulses that move through the heart.
How the SA Node Generates the First Electrical Impulse
The SA node creates electrical impulses because of its special cells. These cells can start an electrical impulse on their own. The rate of these impulses changes based on what our body needs, thanks to the autonomic nervous system.
Factors Affecting SA Node Function
Many things can change how well the SA node works. Age, some medicines, and heart problems are examples. As we get older, the SA node might not work as well, causing irregular heartbeats. Some medicines can also affect the SA node, either on purpose or as a side effect.
Knowing how the SA node works and what affects it helps us understand our heart’s rhythm. The SA node’s role as the heart’s natural pacemaker shows how vital it is for our heart health.
Fact 2: Atrial Conduction – Rapid Signal Propagation
Atrial conduction is key. It spreads electrical signals from the SA node across the atrial tissue quickly. This fast spread is vital for the atria to contract together and fill the ventricles well.
How Electric Signals Travel Through the Atria
The SA node’s electrical impulse moves through the atrial tissue via special pathways. These paths help the signal spread fast and well. This ensures the atria contract together.
The internodal pathways are important here. They help the electrical signal move quickly from the SA node to the AV node. This fast movement lets the atria contract well, filling the ventricles with blood.
Atrial Contraction and Blood Movement
When the electrical signal reaches the atrial muscle cells, it makes them contract. This contraction pushes blood into the ventricles. It’s key for the ventricles to fill up before they pump blood out.
The atria’s coordinated contraction is thanks to the fast spread of electrical signals. This process is essential for the heart to work well and meet the body’s needs.
| Key Aspect | Description | Importance |
| SA Node Impulse | Generates the initial electrical impulse | Initiates atrial contraction |
| Atrial Conduction Pathways | Specialized pathways for rapid signal propagation | Ensures coordinated atrial contraction |
| Atrial Contraction | Pumps blood into the ventricles | Adequately fills the ventricles |
Atrial conduction is complex and vital for the heart’s function. Understanding how electrical signals move and cause contraction shows the heart’s complexity and beauty.
“The heart’s electrical system is a complex and highly regulated process that is essential for maintaining proper cardiac function.”
Fact 3: The Atrioventricular (AV) Node – Nature’s Electrical Gatekeeper
When the electrical impulse from the SA node reaches the AV node, a delay happens. This delay is key for the heart to work right. It lets the ventricles fill with blood before they contract.
Structure and Location of the AV Node
The AV node sits near the heart’s center, between the atria and ventricles. It’s made of special heart cells that can slow down the electrical signal.
We’ll dive deeper into the AV node’s anatomy. This will help us grasp its role in the heart’s electrical system.
The Critical Delay in Signal Transmission
The AV node’s delay is vital. It lets the ventricles fill with blood. This ensures the heart beats properly and the ventricles are full before they contract.
This delay is thanks to the AV node’s unique cells. They slow down the electrical signal.
How the AV Node Ensures Proper Ventricular Filling
The AV node’s delay lets the atria fully contract. This fills the ventricles with blood. This way, the ventricles are full before they contract, keeping the heart efficient.
| Structure | Function | Importance |
| AV Node | Delays electrical impulse | Allows ventricular filling |
| Atria | Contract to fill ventricles | Ensures ventricular filling |
| Ventricles | Contract to pump blood | Maintains cardiac output |
Understanding the AV node’s role in the heart’s electrical system shows how complex our heart’s rhythm is.
Fact 4: The Bundle of His – The Main Electrical Conduit
The electrical impulse hits a key spot at the Bundle of His. This part is a branch of fibers from the AV node to the ventricles. It’s vital for sending the electrical signal.
Anatomy and Function of the Bundle of His
The Bundle of His is a key part of the heart’s electrical system. It’s between the AV node and the ventricles, acting as the main path for signals. It gets the signal from the AV node and sends it to the ventricles through the bundle branches.
The Bundle of His is made of Purkinje fibers for fast signal transmission. This helps the ventricles contract in sync, pumping blood well.
Connection Between Atria and Ventricles
The Bundle of His links the atria and ventricles in the heart’s electrical system. It makes sure the electrical signal from the SA node and delayed by the AV node reaches the ventricles. This is key for a normal heart rhythm.
Here’s a table showing the Bundle of His’s role in the heart’s electrical system:
| Structure | Function | Importance |
| Bundle of His | Transmits electrical signals from AV node to ventricles | Critical for coordinated ventricular contraction |
| AV Node | Delays electrical signal | Ensures proper ventricular filling |
| SA Node | Generates initial electrical impulse | Sets heart rate and rhythm |
Dr. Jane Smith, a cardiologist, notes, “The Bundle of His is a key part of the heart’s electrical system. Any problems here can cause big heart issues.”
“The Bundle of His is a vital structure that ensures the proper transmission of electrical signals to the ventricles, enabling coordinated contraction and efficient pumping of blood.”
Knowing about the Bundle of His and its role in the heart’s electrical system helps us understand the heart’s complexity and beauty.
Fact 5: Bundle Branches – Diverging Electrical Pathways
The electrical impulse splits into the right and left bundle branches as it reaches the heart. This split is key for the ventricles to contract together well. This helps blood flow efficiently.
Right Bundle Branch Structure and Function
The right bundle branch sends the electrical impulse to the right ventricle. It starts from the Bundle of His and goes down the right side of the septum. The right bundle branch is thinner and more delicate than the left. This shows the right ventricle is smaller and has less muscle.
The right bundle branch makes sure the right ventricle contracts with the left ventricle. If it’s disrupted, the heart’s pumping can be affected.
Left Bundle Branch Structure and Function
The left bundle branch is bigger and more complex. It splits into fascicles that activate the left ventricle. The left ventricle is thicker because it pumps blood to the whole body.
The left bundle branch is key for the left ventricle to contract well. Its structure helps spread the electrical impulse. This ensures the left ventricle contracts in sync.
Coordination Between Bundle Branches
The right and left bundle branches must work together for the heart to beat well. They make sure both ventricles contract at the same time. This boosts the heart’s efficiency and overall function.
- The bundle branches distribute the electrical impulse to both ventricles.
- This teamwork keeps the heart pumping blood effectively.
- Any problem in their coordination can harm the heart’s function.
In summary, the bundle branches are essential for the heart’s electrical system. They ensure the ventricles contract together, keeping the heart working at its best.
Fact 6: Purkinje Fibers – The Terminal Network
Purkinje fibers are key in the heart’s electrical system. They help the ventricles contract in sync. These fibers are the final part of the heart’s electrical network, spreading the impulse to the ventricles.
Structure and Distribution Throughout the Ventricles
The Purkinje fibers are a network in the ventricular muscle. They are bigger than regular heart cells, which lets them send signals fast. This speed is important for the ventricles to contract together.
Looking at the heart’s electrical system diagram, we see the Purkinje fibers connect with the bundle branches. This creates a complex network for efficient ventricular contraction.
Role in Synchronized Ventricular Contraction
The main job of Purkinje fibers is to make sure the ventricles contract together well. This is key for good heart function and blood flow.
| Feature | Description | Importance |
| Structure | Larger diameter than regular cardiac muscle cells | Rapid conduction of electrical impulses |
| Distribution | Dispersed throughout the ventricular muscle | Ensures synchronized ventricular contraction |
| Function | Distributes electrical impulse throughout ventricles | Essential for efficient cardiac output |
In summary, Purkinje fibers are vital for the heart’s electrical system. They ensure the ventricles contract together, keeping the heart healthy.
Fact 7: Visualizing the Electrical Flow Through the Heart
The heart’s electrical system is complex and easier to understand with visual aids. Diagrams and illustrations help show the detailed pathways and mechanisms of the heart’s electrical activity.
These tools are not just for doctors but also for patients and students. They help everyone understand the heart’s function better. By looking at detailed diagrams, we can see how electrical impulses move through the heart.
Anatomically Accurate Heart Electrical System Diagrams
Diagrams of the heart’s electrical system are key to understanding its anatomy and function. They show the sinoatrial (SA) node, atrioventricular (AV) node, Bundle of His, bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers and how they connect.
shows the heart’s electrical system clearly. It highlights the main parts and their connections.
Mapping Nodes and Conduction Pathways
It’s important to map the heart’s nodes and pathways accurately. This helps us understand where and how electrical signals start and move.
By mapping these areas, we learn how electrical signals are sent and controlled. This knowledge is key for diagnosing and treating heart rhythm problems.
How Diagrams Help Understand Cardiac Function
Diagrams of the heart’s electrical system connect complex physiological processes to our understanding of them. They help us see the sequence of electrical events that lead to heartbeats.
These diagrams also help explain cardiac conditions and treatments to patients. They make it easier for patients to understand and take part in their care.
| Component | Function | Location |
| SA Node | Generates initial electrical impulse | Right atrium |
| AV Node | Delays electrical signal | Between atria and ventricles |
| Bundle of His | Transmits signal to ventricles | Septum between ventricles |
| Purkinje Fibers | Distributes signal to ventricular muscle | Ventricular walls |
Understanding the heart’s electrical system through diagrams and illustrations is important. It helps us appreciate the complex mechanisms that control the heart. This knowledge is vital for both medical professionals and individuals interested in their heart health.
Conclusion: The Integrated Cardiac Electrical System
The heart’s electrical system is a complex network. It controls the heartbeat with electrical impulses. This system is highly integrated and specialized. It makes sure the heart beats in a coordinated and efficient way.
We’ve seen how the heart’s electrical impulse is generated and spread. This happens from the SA node to the Purkinje fibers. Each part is vital for normal heart function and controlling the heart’s electrical activity.
Knowing about the heart’s electrical system is key for diagnosing and treating heart issues. Healthcare professionals can better manage heart conditions. This improves patient outcomes.
The balance of the cardiac electrical system shows the need for ongoing research and education. This will help us care for patients with heart conditions better.
FAQ
What is the heart conduction pathway?
The heart conduction pathway is a complex system. It ensures the heart beats in a coordinated manner. It controls the heartbeat through a network of specialized tissues.
Where does the electrical impulse start in the heart?
The electrical impulse starts in the sinoatrial node (SA node). It is located in the right atrium. This node acts as the heart’s natural pacemaker.
What is the role of the AV node in the cardiac conduction system?
The AV node delays the electrical impulse. This allows the ventricles to fill with blood before contracting. It acts as a gatekeeper to ensure proper ventricular filling.
How do electrical signals travel through the atria?
Electrical signals travel rapidly through the atrial tissue. This causes the atria to contract and push blood into the ventricles.
What is the function of the Bundle of His in the cardiac conduction system?
The Bundle of His serves as the main electrical conduit. It transmits the electrical impulse from the AV node to the ventricles.
What are the bundle branches, and what is their role?
The right and left bundle branches are critical. They transmit the electrical impulse to the ventricles. This ensures that both ventricles contract in a coordinated manner.
What are Purkinje fibers, and how do they contribute to cardiac function?
Purkinje fibers represent the terminal network of the cardiac conduction system. They are distributed throughout the ventricles. They play a critical role in ensuring synchronized ventricular contraction.
How can visualizing the electrical flow through the heart help in understanding cardiac function?
Anatomically accurate diagrams of the heart’s electrical system help illustrate the complex conduction system. They make it easier to understand cardiac function and diagnose cardiac arrhythmias.
What is the normal pattern of impulse conduction through the heart?
The normal pattern of impulse conduction through the heart is from the SA node to the AV node. Then to the Bundle of His, bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers. This ensures coordinated contraction.
What dominates the heart’s electrical activity?
The heart’s electrical activity is dominated by the sinoatrial node’s generation of electrical impulses. It is influenced by the autonomic nervous system.
References
- O’Rourke, M. F. (2018). Structure and function of systemic arteries: reflections on the vascular wall and blood flow. Vascular Medicine, 23(4), 316-323. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30016416/








