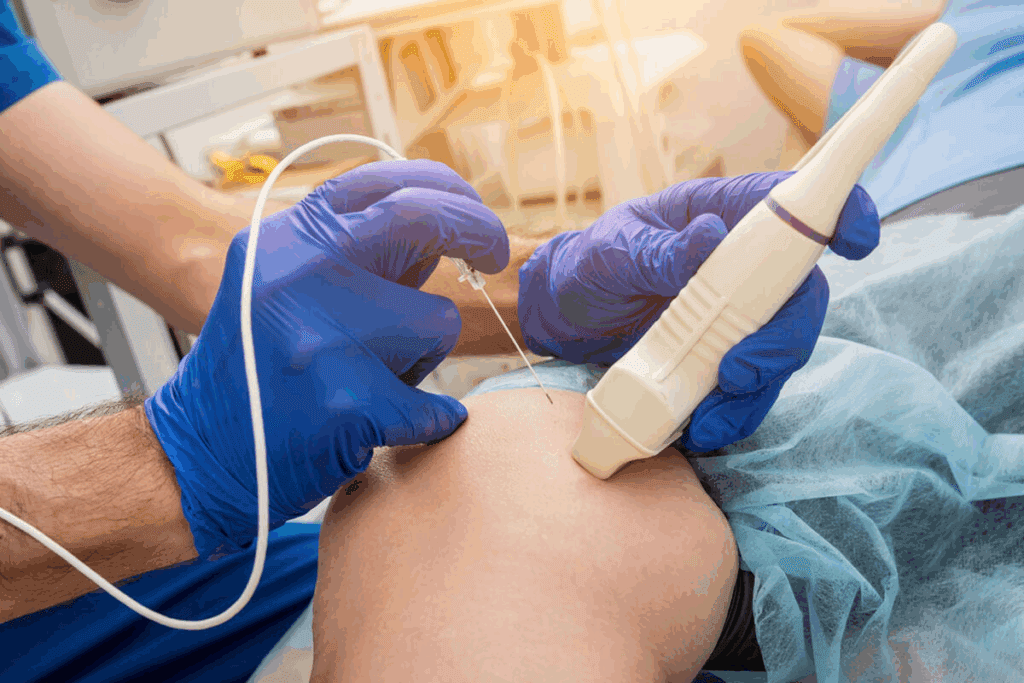
If you have an irregular heartbeat, knowing your treatment options is key. Cardiac ablation is a procedure that’s getting more attention, mainly when meds don’t work. At Liv Hospital, our experts use the latest methods to fix your heart rhythm. They focus on keeping you safe and comfortable.
Understand is cardiac ablation considered surgery, the procedure process, and what patients should know.
So, what is cardiac ablation? It’s a non-invasive way to treat heart rhythm problems. It makes small scars in the heart to stop bad electrical signals. It’s not like old-school ‘open-heart surgery.’ Our article will tell you more about heart ablation and if it’s considered surgery.
Key Takeaways
- Cardiac ablation is a minimally invasive procedure to treat irregular heart rhythms.
- It involves creating small scars in the heart tissue to block abnormal electrical signals.
- This technique is not considered traditional ‘open-heart surgery.’
- Liv Hospital specialists use advanced techniques to restore normal heart rhythms.
- Patient safety and comfort are prioritized during the procedure.
Understanding Cardiac Ablation: Procedure Overview
Cardiac ablation is a treatment for arrhythmias, which are irregular heartbeats. It targets the heart’s problem areas. This method is key for managing heart rhythm disorders that medicines can’t fix.
What Exactly is Cardiac Ablation?
Cardiac ablation, or heart ablation, uses catheters to send energy to the heart. This energy makes small scars in the heart. These scars block abnormal electrical signals that cause arrhythmias. Knowing what is cardiac ablation helps patients understand its benefits.
How Cardiac Ablation Works
The procedure starts with catheters guided through blood vessels to the heart. These catheters then send out energy to heat or cool the heart tissue. This creates lesions that stop the abnormal electrical pathways, fixing the heart rhythm.
The cardiac ablation definition is about using energy to fix arrhythmias.
The Purpose of Heart Ablation
The main goal of heart ablation is to treat arrhythmias that medicines can’t fix. It makes targeted scars in the heart to stop irregular heartbeats. This can greatly improve life quality for those with certain arrhythmias, giving a lasting solution over medication.
Knowing the ablation cardiac definition and its use shows its importance for arrhythmia patients. By defining heart ablation and its benefits, we see its value in cardiology.
Is Cardiac Ablation Considered Surgery? Defining Medical Procedures
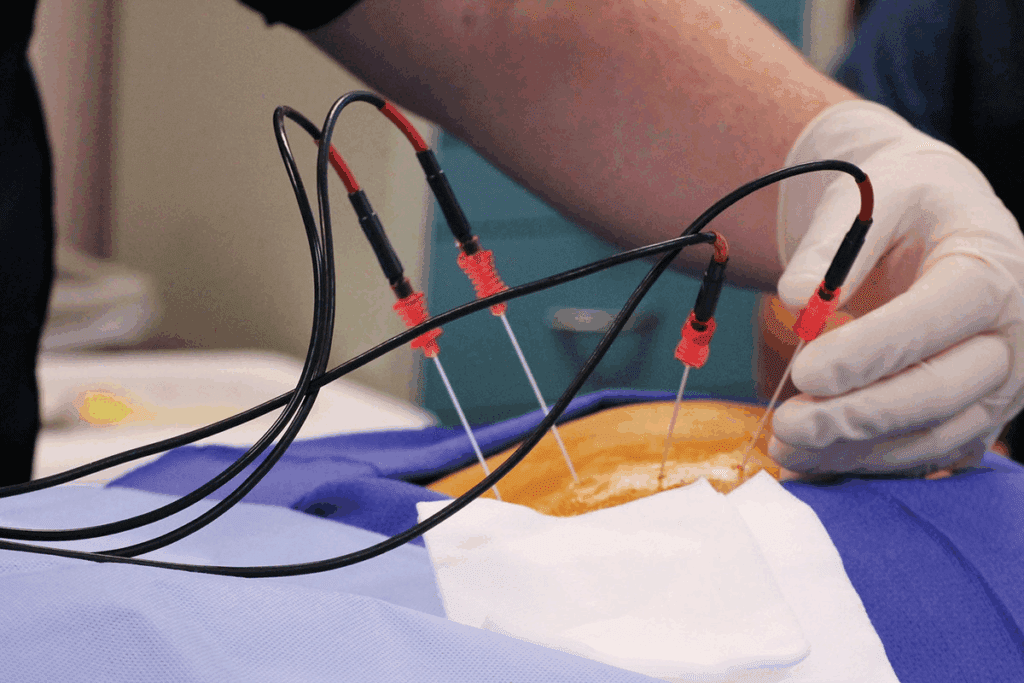
Cardiac ablation is a treatment for heart conditions like arrhythmias. It’s important to know if it’s surgery or not. This helps patients decide if it’s right for them.
Traditional Surgery vs. Minimally Invasive Procedures
Traditional surgery means big cuts to reach the heart. But, cardiac ablation uses small cuts. It uses catheters through veins in the leg to reach the heart.
Cardiac ablation is less invasive than open-heart surgery. It means less pain, quicker recovery, and fewer risks. This makes it different from traditional surgery.
Why Cardiac Ablation is Classified as a Procedure, Not Open Surgery
Cardiac ablation is not open surgery because it doesn’t open the chest. It uses percutaneous techniques to guide catheters through the skin to the heart. This reduces risks and recovery time.
It’s called a procedure because it’s minimally invasive. Advanced imaging guides the catheters. This method treats heart conditions with little disruption to the body.
Comparison with Other Cardiac Interventions
Cardiac ablation is different from other heart treatments. For example, CABG is major surgery with big cuts and long recovery. Cardiac ablation is less invasive for some heart issues.
Pacemaker implantation is also minimally invasive. But, cardiac ablation targets arrhythmias by destroying abnormal heart pathways. Knowing these differences helps choose the best treatment.
Types of Cardiac Ablation Techniques
Cardiac ablation procedures have grown into several types, giving hope to those with heart rhythm issues. These new methods have better results and more choices for those who didn’t do well with old treatments.
Radiofrequency Ablation
Radiofrequency ablation is a common method in cardiac ablation. It uses high-frequency electrical energy to make precise lesions in heart tissue. This stops abnormal electrical pathways. It’s great for treating atrial fibrillation and supraventricular tachycardia.
Cryoablation
Cryoablation, or cryotherapy, freezes and destroys bad heart tissue with extreme cold. It keeps healthy tissue safe, lowering complication risks. It’s good for treating some arrhythmias, like atrial fibrillation.
Laser Ablation
Laser ablation uses laser energy to make lesions in heart tissue. It targets abnormal electrical pathways precisely. Though not as common as radiofrequency, it’s an option for those not suited for other methods.
Other Emerging Techniques
New techniques like ultrasound ablation and hybrid methods are being researched. They aim to make cardiac ablation safer and more effective.
Knowing about the different cardiac ablation techniques helps patients and doctors choose the best treatment. Each method has its own benefits and uses, helping to improve heart rhythm disorder treatments.
Common Heart Conditions Treated with Cardiac Ablation
Cardiac ablation is a key treatment for many heart conditions. It fixes abnormal heart rhythms in a way that’s less invasive than surgery. This makes it a popular choice for managing arrhythmias.
Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is a common heart rhythm disorder. It causes fast and irregular heartbeats. Cardiac ablation for AFib creates lesions to stop abnormal signals.
We use advanced mapping to find and target these areas. The success rate varies, but many patients see big improvements in their symptoms and quality of life.
Atrial Flutter
Atrial flutter is another arrhythmia treated with cardiac ablation. It’s marked by a fast, regular heart rhythm. Ablation for atrial flutter creates a block in the heart tissue.
- Many patients find long-term relief from symptoms after atrial flutter ablation.
- Radiofrequency or cryoablation techniques are often used.
- It’s important to evaluate each case to see if ablation is the best option.
Supraventricular Tachycardia
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) causes rapid heartbeats from above the ventricles. Cardiac ablation for SVT is often very effective. We pinpoint the exact location of the abnormal pathway.
Radiofrequency energy is used to create scars in the heart tissue. This blocks the abnormal signals. The procedure is usually well-tolerated, and most patients can resume their activities quickly.
Ventricular Tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia (VT) is a serious arrhythmia from the ventricles. Cardiac ablation for VT is used when other treatments fail. We target the specific heart tissue areas causing the arrhythmia.
VT ablation is complex and requires advanced techniques. We work closely with patients to find the best treatment plan.
Knowing about the heart conditions treated with cardiac ablation helps patients make informed decisions. We’re dedicated to supporting and guiding our patients through treatment, aiming for the best outcomes.
Preparing for a Cardiac Ablation Procedure
Knowing what to expect and how to prepare for cardiac ablation can make you feel less anxious. It can also improve your results. We’ll walk you through the key steps to make sure your procedure goes smoothly.
Pre-Procedure Testing
Before your cardiac ablation, you’ll have several tests. These tests check your heart and overall health. You might have:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) to record your heart’s electrical activity
- Echocardiogram to look at your heart’s structure and function
- Blood tests to find any underlying conditions
- Stress test to see how your heart performs under stress
These tests help your cardiologist plan the best approach for your procedure.
Medication Adjustments
Your cardiologist might ask you to change your medications before the procedure. This could mean:
- Stopping blood thinners a few days before
- Changing the dosage of certain heart medications
- Telling your cardiologist about all medications and supplements you take
It’s important to follow these instructions carefully. This helps reduce risks during and after the procedure.
Day-of-Procedure Instructions
On the day of your procedure, you’ll get specific instructions. These might include:
- Fasting for a certain period before the procedure
- Avoiding certain personal care products
- Arranging for someone to drive you home after the procedure
Following these instructions is key to your safety and the success of the procedure.
Questions to Ask Your Cardiologist
Getting ready for your cardiac ablation means being informed. Ask your cardiologist:
- What are the possible risks and complications?
- How will you manage pain or discomfort during recovery?
- What are the expected outcomes, and how will success be measured?
Asking these questions helps you understand what to expect. It also lets you make informed decisions about your care.
| Preparation Step | Description | Importance |
| Pre-Procedure Testing | Includes ECG, echocardiogram, blood tests, and stress test | High |
| Medication Adjustments | Adjusting blood thinners and heart medications | High |
| Day-of-Procedure Instructions | Fasting, avoiding certain products, arranging transportation | High |
| Questions to Ask | Inquiring about risks, pain management, and expected outcomes | High |
What to Expect During a Cardiac Ablation
Having a cardiac ablation can feel scary, but knowing what to expect can help. We’ll walk you through the process. This will help you understand what happens during this treatment for heart rhythm disorders.
The Procedure Environment
A cardiac ablation happens in an electrophysiology (EP) lab. This lab has the latest imaging and monitoring tools. A team of experts, like cardiologists and nurses, work together to make sure everything goes smoothly.
Anesthesia Options
There are different anesthesia choices for cardiac ablation. These include conscious sedation and general anesthesia. The cardiologist decides based on the procedure’s complexity and the patient’s health. Conscious sedation keeps you awake but relaxed. General anesthesia makes you sleep through it.
Step-by-Step Procedure Process
The procedure starts with numbing the area where the catheters go. Then, small cuts are made in the groin to reach the blood vessels. Catheters are then guided to the heart to find and fix the arrhythmia.
The catheters use energy to make lesions on the heart tissue. This stops the abnormal electrical pathways that cause the arrhythmia.
Typical Duration and Monitoring
The procedure can last from 2 to 4 hours, sometimes longer for complex cases. The team watches your heart closely with advanced tools. After it’s done, you’ll go to a recovery area to wake up.
Recovery After Cardiac Ablation
Recovering from cardiac ablation involves several steps. These include immediate care after the procedure, a stay in the hospital, and recovery at home. Knowing each step is key to a successful healing process.
Immediate Post-Procedure Care
Right after the procedure, patients are watched closely in a recovery area. Our team checks their heart rate and blood pressure to make sure everything is okay. They also manage any pain or discomfort with medication.
Hospital Stay Duration
The time spent in the hospital varies. It depends on the patient and the type of ablation done. Most patients go home the same day or after a night. Our team gives personalized advice based on each patient’s situation.
At-Home Recovery Timeline
Recovery at home usually takes a few days to a week. During this time, patients should:
- Rest and avoid hard activities
- Take their medications as directed
- Watch the insertion site for infection signs
- Go to all scheduled follow-up appointments
Activity Restrictions and Return to Normal Life
There are certain activities to avoid during recovery. These include:
| Activity | Restriction Period |
| Heavy lifting | 1-2 weeks |
| Strenuous exercise | 1-2 weeks |
| Driving | 24-48 hours |
| Returning to work | 2-7 days |
Most people can get back to normal in a week or two. This depends on their health and job type. We offer tailored advice to help them ease back into their lives.
Risks, Complications, and Success Rates
It’s important to know the risks and complications of cardiac ablation before you decide to get it. This treatment is generally safe but comes with some risks.
Potential Short-Term Complications
Short-term issues can include bleeding, infection, and arrhythmias. Rarely, serious problems like cardiac tamponade or stroke might happen.
To lower these risks, follow your doctor’s instructions before and after the procedure. Also, don’t miss any follow-up appointments.
Possible Long-Term Side Effects
Long-term side effects are rare but can include arrhythmia coming back or new ones. Sometimes, the heart’s electrical system can get damaged.
Seeing a cardiologist regularly is key to catch and manage any long-term issues early.
Success Rates by Condition
The success of cardiac ablation depends on the condition. For SVT, success rates are often over 90%. But for atrial fibrillation, success rates are lower and might need more procedures.
| Condition | Success Rate | Repeat Procedure Rate |
| Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) | 90-95% | 5-10% |
| Atrial Flutter | 80-90% | 10-20% |
| Atrial Fibrillation | 60-80% | 20-40% |
Factors Affecting Outcomes
Many things can affect how well cardiac ablation works. These include the type of arrhythmia, your health, and any heart disease you might have.
Key factors affecting outcomes include:
- The specific arrhythmia being treated
- Patient’s age and overall health
- Presence of underlying heart disease
- Operator experience and technique
Knowing these factors and talking to your cardiologist can help you decide if cardiac ablation is right for you.
Conclusion: Making an Informed Decision About Cardiac Ablation
Cardiac ablation is a key treatment for many heart rhythm problems. It’s a less invasive option compared to traditional surgery. Knowing if cardiac ablation is considered surgery is important for patients to make the right choice.
Cardiac ablation, or heart ablation, uses energy to destroy bad heart pathways. This makes it different from traditional surgery. It’s done with small cuts and catheters, making it less invasive.
Thinking about cardiac ablation means looking at its good and bad sides. It can be very effective for some heart issues. But, it might have risks too. Patients should talk to their cardiologist to know the chances of success and possible dangers.
Understanding cardiac ablation, its benefits, and risks is key to making a choice. Being well-informed helps patients decide if cardiac ablation is right for them. This is the first step to managing their heart health effectively.
FAQ
What is cardiac ablation?
Cardiac ablation is a procedure to treat irregular heart rhythms. It creates small scars in the heart to block bad signals.
Is cardiac ablation considered a surgery?
No, it’s not traditional surgery. It uses catheters to treat the heart, not open-heart surgery.
What are the different types of cardiac ablation techniques?
There are radiofrequency, cryoablation, and laser ablation. Each has its own use and benefits. The choice depends on the patient’s needs.
What heart conditions are treated with cardiac ablation?
It treats conditions like atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia. It helps restore a normal rhythm and improves symptoms.
How do I prepare for a cardiac ablation procedure?
You’ll get tested beforehand and adjust your meds. Follow your doctor’s instructions and ask questions.
What can I expect during a cardiac ablation procedure?
You’ll be in a special room and get anesthesia. Catheters will be used to treat the heart. The procedure is closely monitored.
What is the recovery process like after cardiac ablation?
You’ll need rest and recovery. The hospital stay varies. Follow activity restrictions at home and can return to normal life in a few days.
What are the possible risks and complications of cardiac ablation?
Risks include bleeding or infection. There can also be long-term side effects. Success rates vary based on the condition and patient factors.
What is the success rate of cardiac ablation for different heart conditions?
Success rates differ by condition. For example, it’s often effective for supraventricular tachycardia but may need repeat procedures for atrial fibrillation.
How does cardiac ablation compare to other cardiac interventions?
It’s a unique treatment compared to meds or surgery. The choice depends on the patient’s condition and preferences.
What is the difference between cardiac ablation and heart oblation?
Cardiac ablation treats arrhythmias. “Heart oblation” is not a recognized term related to cardiac ablation or surgery.
Is cardiac ablation a painful procedure?
It’s not painful due to anesthesia or sedation. Patients are usually comfortable during the procedure.
Can I undergo cardiac ablation if I have other health conditions?
Suitability depends on the conditions and their severity. Discuss your medical history with your cardiologist to determine the best treatment.
References:
Government Health Resource. (2025). Is Cardiac Ablation Considered Surgery What You Need. Retrieved from https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/arrhythmia/prevention–treatment-of-arrhythmia/ablation-for-arrhythmias
- Natale, A., & others. (2024). Catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation: indications and future perspectives. European Heart Journal, 45(41), 4383-4398. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39322413/
- Nakahara, S., & colleagues. (2023). Catheter ablation of ventricular tachycardia associated with structural heart disease: efficacy and safety. ScienceDirect. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0914508722002404



































