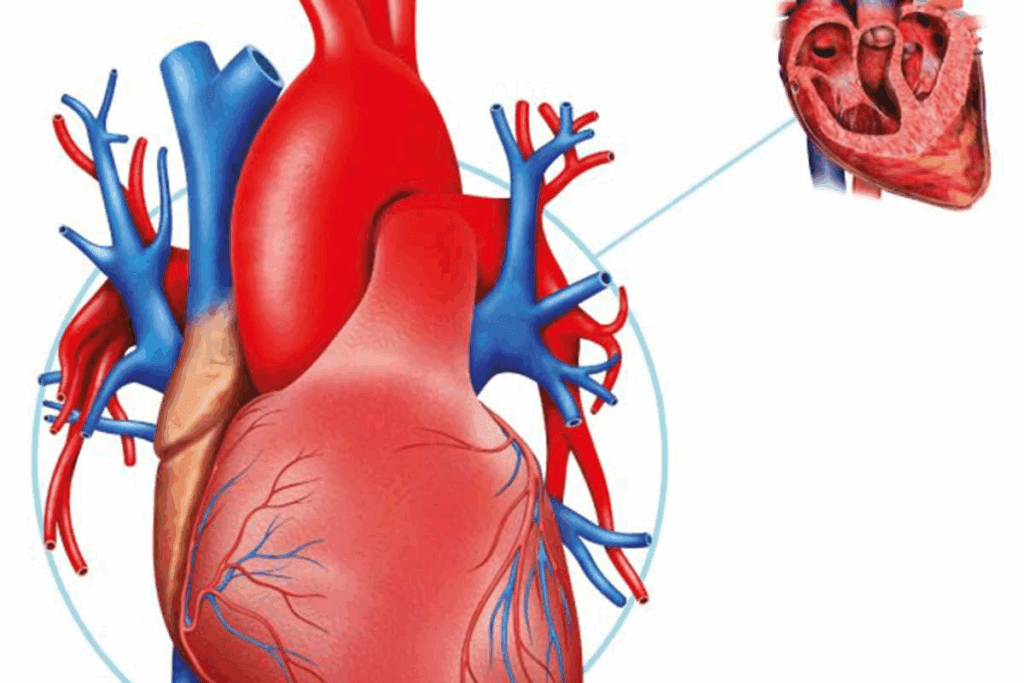
Learning about the heart’s anatomy is key for medical students and doctors. A labelled heart diagram helps show the heart’s main parts. This includes the atria, ventricles, big valves, and blood vessels.
At Liv Hospital, we know how important clear labels are in teaching medicine. The heart is a muscle that acts as the body’s pump. It takes in blood without oxygen and sends it to the lungs for oxygen. Then, it pumps oxygen-rich blood to the body’s arteries.
Using a labelled heart diagram makes it easier to understand the heart’s structure. It helps see how the heart works with the body’s blood system.
Key Takeaways
- Accurate labelling is key to understanding the heart’s anatomy.
- A labelled heart diagram makes it easier to see the heart’s main parts.
- Clear labels help us understand the heart’s role in the body’s blood system.
- Liv Hospital offers trusted care and education worldwide.
- Knowing the heart’s anatomy is vital for medical students and doctors.
The Value of Visual Learning in Cardiac Anatomy
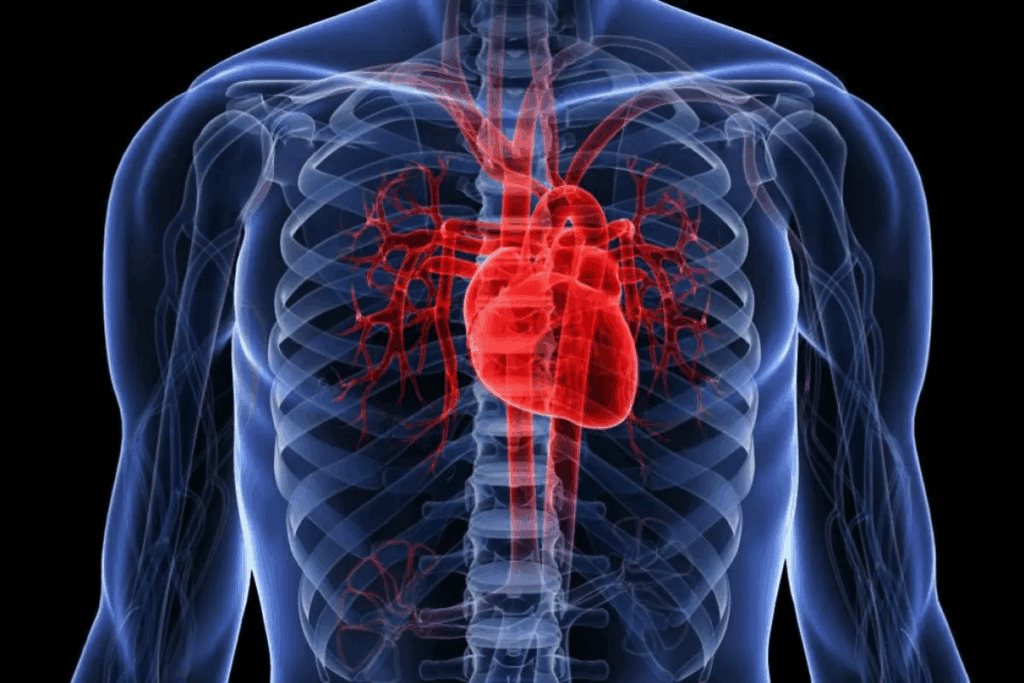
Visual learning has changed how we learn about the heart. It makes complex heart structures easier to understand. The heart, being very detailed, really benefits from pictures and diagrams.Learn the labelled heart diagram with key structures for easy anatomy understanding.
Visual aids help us remember complex heart information better. Pictures of the heart, with labels, are great. They show the heart’s parts clearly and simply.
How Visual Aids Enhance Retention of Heart Structures
Visual tools like heart diagrams are key. They help us organize complex heart info into easy-to-understand parts. This is very important for learning about the heart’s layout.
Visual aids help us understand by:
- Breaking down complex structures into simpler parts
- Showing how different heart parts relate to each other
- Offering a clear view of the heart’s anatomy
| Benefits of Visual Aids | Description |
| Simplification of Complex Structures | Visual aids make the heart’s complex anatomy easier to handle. |
| Enhanced Retention | Visual aids help us remember heart anatomy better by providing a clear framework. |
| Improved Understanding | Visuals help us grasp how heart structures are arranged. |
From Novice to Expert: Progression Through Visual Learning
Visual learning helps both beginners and experts. Using heart diagrams and other visuals, anyone can move from knowing little to being an expert in heart anatomy.
The journey includes:
- First, learning basic heart anatomy with visuals
- Then, getting to know more complex parts and how they connect
- Lastly, reinforcing what we know with more visual learning
By using visual learning, we can deeply understand the heart. This helps us better diagnose and treat heart problems.
The Fundamentals of Heart Anatomy and Function
The human heart is a complex organ. Knowing its basic anatomy and function is key to understanding heart health. By studying the heart’s structure and its role in the circulatory system, we learn about the life-sustaining mechanisms it supports.
Overview of the Heart’s Position and External Features
The heart sits in the thoracic cavity, between the lungs and behind the sternum. This spot helps it pump blood efficiently around the body. It’s covered by the pericardium, a protective sac, and connected to major vessels like the aorta and pulmonary arteries.
Knowing the heart’s outside helps us understand its inside and how it works. The pericardium, for example, not only guards the heart but also lets it move in the chest.
The Heart as a Pump: Basic Functional Anatomy
The heart is a pump that circulates blood. It has four chambers: the right and left atria, and the right and left ventricles. Blood moves from the atria to the ventricles, then into the body’s circulations.
The heart’s pumping is thanks to its muscular walls, mainly the thick myocardium layer. The heart muscle’s contraction and relaxation work together to pump blood efficiently, meeting the body’s needs.
The heart’s pumping efficiency is key to good circulation.
Relationship Between Structure and Circulatory Efficiency
The heart’s structure is closely tied to its pumping function. The thickness of the ventricular walls, the valves, and the muscle fibers all affect its efficiency. For example, the spiral fibers in the ventricles help pump blood well.
The heart’s valves are also vital. They ensure blood flows only one way, preventing backflow and keeping circulation efficient. This shows how the heart’s structure and function are linked, highlighting the need to understand heart anatomy for good circulation.
By looking into the heart’s basic anatomy and function, we can see how it works. We learn how its structure supports its role in the circulatory system.
The 10 Essential Labels on a Labelled Heart Diagram
Understanding the heart’s anatomy is key for doctors and students. A labelled heart diagram is a vital tool for this. It helps people grasp the heart’s structure and how it works.
Chambers: Right Atrium and Right Ventricle
The heart has four chambers, with the right atrium and ventricle being very important. The right atrium gets deoxygenated blood from the body. This blood then goes to the right ventricle.
The right ventricle then pumps this blood to the lungs. There, it picks up oxygen.
| Chamber | Function |
| Right Atrium | Receives deoxygenated blood from the body |
| Right Ventricle | Pumps blood to the lungs for oxygenation |
Chambers: Left Atrium and Left Ventricle
The left atrium gets oxygen-rich blood from the lungs. This blood then goes to the left ventricle. The left ventricle sends this blood all over the body.
The left ventricle’s muscle is thicker. This shows it works harder than the right ventricle.
“The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body, supplying oxygen and nutrients to tissues and removing carbon dioxide and other wastes.”
The American Heart Association
Valves: Tricuspid, Mitral, Pulmonary, and Aortic
The heart has four valves to keep blood flowing the right way. The tricuspid valve is between the right atrium and ventricle. The mitral valve is between the left atrium and ventricle.
The pulmonary valve and aortic valve are at the ventricles’ connections to the pulmonary artery and aorta, respectively.
- Tricuspid Valve: Between right atrium and right ventricle
- Mitral Valve: Between left atrium and left ventricle
- Pulmonary Valve: Between right ventricle and pulmonary artery
- Aortic Valve: Between left ventricle and aorta
Major Vessels: Aorta and Pulmonary Artery
The aorta is the biggest artery. It starts from the left ventricle and carries oxygen-rich blood to the body. The pulmonary artery takes deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs.
Knowing these major vessels is key to understanding the heart’s role in the circulatory system.
Looking at a labelled heart diagram helps people understand the heart’s anatomy better. This knowledge is vital for medical professionals and students to master cardiac anatomy.
Step-by-Step Process for Heart Structure Labeling
Learning to label the heart’s parts is key in cardiac anatomy. We’ll show you how, starting with the four chambers. This will help you get good at heart structure labeling.
Starting with the Four Chambers: A Systematic Approach
To start label the heart anatomy right, know the four chambers. These are the right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle. Understanding these first is important because they are the heart’s core.
Start with the right atrium, then the right ventricle, left atrium, and lastly the left ventricle. This order helps you see how blood moves through the heart. Accurate labeling of these chambers is key to understanding blood flow.
Common Errors in Heart Anatomy Labeling and How to Avoid Them
A common mistake in heart anatomy labeling is mixing up pulmonary veins with pulmonary arteries. Remember, pulmonary veins carry oxygen-rich blood to the left atrium. Pulmonary arteries carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
Another mistake is getting the chambers mixed up. To avoid this, look at each chamber’s unique features. For example, the right ventricle has a thicker wall than the right atrium. This is because it pumps blood to the lungs. Paying attention to these details will help you improve your labelling heart skills.
By using this systematic method and knowing common mistakes, you can better understand cardiac anatomy. This will also help you label the heart’s structures more accurately.
Different Perspectives in Labelled Heart Diagrams
Different views in labelled heart diagrams help us understand the heart better. By looking at the heart from different angles, we learn more about its structure and how it works.
Anterior vs. Posterior Views: Key Differences
The front and back views of the heart show us different things. The front view shows the heart’s outer parts, like the ventricles and atria. The back view shows the heart’s back, with its connections to major vessels.
Knowing the differences between these views is key to understanding the heart. A labelled heart diagram with both views helps us see the heart from all sides.
| View | Key Features |
| Anterior | Ventricles, Atria, Outer Surface |
| Posterior | Atrial Connections, Major Vessels |
Cross-Sectional Heart Diagrams: What They Reveal
Cross-sectional heart diagrams give us a special look inside the heart. They show how the chambers, valves, and vessels are connected.
Key benefits of cross-sectional diagrams include:
- Detailed view of internal structures
- Enhanced understanding of spatial relationships
- Improved visualization of blood flow pathways
3D Models vs. 2D Diagrams: Advantages for Learning
Both 3D models and 2D diagrams have their own benefits for learning about the heart. 2D diagrams are clear and simple. But 3D models are more interactive and realistic.
3D models can enhance learning by:
- Allowing rotation and manipulation of the heart model
- Providing a more realistic representation of cardiac anatomy
- Facilitating a deeper understanding of complex structures
In conclusion, using different views in labelled heart diagrams helps us learn more about the heart. This includes looking at the heart from different angles, using cross-sectional diagrams, and exploring 3D models.
Tracing Blood Flow Through a Labelled Heart Diagram
To understand how the heart works, we need to see how blood moves through it. A labelled heart diagram helps us visualize this process. It’s key for learning about the heart’s structure and how it functions.
We’ll look at how blood moves through the heart. We’ll focus on the pulmonary and systemic circuits. Knowing these circuits helps us understand how the heart keeps blood flowing.
The Pulmonary Circuit: Right Heart Structures
The pulmonary circuit takes deoxygenated blood from the body to the lungs and back. It starts when blood comes back to the heart through the superior and inferior vena cava into the right atrium. Then, it goes through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle.
The right ventricle pushes blood through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery. This artery takes it to the lungs for oxygen.
The Systemic Circuit: Left Heart Structures
After getting oxygen in the lungs, blood goes back to the heart through the pulmonary veins into the left atrium. It then moves through the mitral valve into the left ventricle.
The left ventricle pumps it through the aortic valve into the aorta. The aorta splits into smaller arteries that spread oxygenated blood all over the body.
| Circuit | Structures Involved | Function |
| Pulmonary Circuit | Right Atrium, Tricuspid Valve, Right Ventricle, Pulmonary Valve, Pulmonary Artery | Transports deoxygenated blood to lungs |
| Systemic Circuit | Left Atrium, Mitral Valve, Left Ventricle, Aortic Valve, Aorta | Distributes oxygenated blood to body |
By following blood flow in a labelled heart diagram, we learn how the heart circulates blood. This is key for anyone studying the heart’s anatomy and function.
Digital Resources for Interactive Heart Diagram Labeling
Digital tools have changed how we learn about heart anatomy. Now, we have many digital resources for interactive learning. These tools make studying the heart more fun and effective.
Online Platforms for Self-Paced Learning
Online platforms offer interactive heart diagrams for self-paced learning. You can learn about cardiac anatomy at your own speed. These platforms have drag-and-drop exercises, quizzes, and games to help you remember.
Some top online platforms include:
- Anatomy education websites
- Medical learning portals
- Interactive anatomy atlases
These resources cover all of heart anatomy. You can explore the heart’s structure and function in detail.
Mobile Applications for Heart Anatomy Practice
Mobile apps let you learn about heart anatomy anywhere, anytime. They have interactive diagrams and labeling exercises. This makes learning convenient and fun.
Mobile apps offer many benefits:
- They are easy to carry and access
- They have interactive and engaging content
- They let you check your progress and learn more
| Feature | Online Platforms | Mobile Applications |
| Accessibility | Accessible via web browsers | Downloadable on mobile devices |
| Interactivity | Drag-and-drop labeling, quizzes | Interactive diagrams, flashcards |
| Flexibility | Self-paced learning | Learning on-the-go |
Using these digital tools can improve your heart anatomy knowledge. You’ll get better at labeling heart diagrams accurately.
Practical Exercises to Master Heart Anatomy Labels
Learning heart anatomy is more than just knowing facts. It’s about practicing with exercises like labeling diagrams. These activities help us understand the heart better and get better at spotting its parts.
To really get good at heart anatomy labels, start with blank diagram exercises. These exercises let you label heart diagrams on your own. It’s a great way to check and improve your knowledge.
Blank Diagram Exercises: Fill-in Practice
Blank diagram exercises are key for learning heart anatomy. By labeling diagrams ourselves, we get to really engage with the material. This method is great because it makes us remember what we’ve learned.
- Start with the basic structures: Begin by labeling the four chambers of the heart: the right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle.
- Move on to the valves: Identify and label the tricuspid, mitral, pulmonary, and aortic valves, understanding their roles in blood flow.
- Include major vessels: Label the aorta and pulmonary arteries, recognizing their significance in the circulatory system.
To get the most out of blank diagram exercises, practice often. Start with simple diagrams and make them more complex as you get better.
Collaborative Learning Activities for Heart Anatomy
Learning together with others is another smart way to master heart anatomy labels. Working in groups lets us share knowledge and learn from each other’s strengths and weaknesses.
- Group labeling sessions: Organize study groups where participants take turns labeling diagrams, discussing any challenges or questions that arise.
- Create teaching materials: Work together to develop educational materials, such as labeled diagrams or flashcards, that can be used to teach others about heart anatomy.
- Participate in online forums: Engage with online communities or forums focused on cardiac anatomy, sharing insights and learning from others in the field.
By mixing blank diagram exercises with group learning, we can build a strong learning plan. This plan helps us understand and remember heart anatomy labels better.
Conclusion: From Diagram to Understanding – The Path to Cardiac Anatomy Mastery
Learning about cardiac anatomy is key in medical school. It helps doctors and nurses understand and treat heart problems well. Using labelled heart diagrams and other tools helps people learn about the heart’s parts.
By following the steps in this article, anyone can get better at understanding the heart. The labelled heart diagram is a big help. It shows the heart’s complex parts clearly, making it easier to learn.
We believe learning about the heart is very important. We suggest using interactive digital tools and doing hands-on exercises to learn more. This way, doctors and nurses can give the best care to their patients.
FAQ
What is the importance of a labelled heart diagram in understanding cardiac anatomy?
A labelled heart diagram is key for medical students and doctors. It helps them spot the heart’s parts like the atria, ventricles, and valves. This makes it easier to understand how the heart works and its role in the body.
How do visual aids improve retention of heart structures?
Visual aids, like labelled heart diagrams, help people learn about the heart. They make it easier to remember the heart’s parts. This helps in understanding the heart’s complex structures.
What are the basics of heart anatomy and function?
The heart’s basics include its position and how it pumps blood. It also covers the heart’s structure and how it circulates blood efficiently.
What are the 10 essential labels on a labelled heart diagram?
The 10 key labels on a labelled heart diagram are the chambers and valves. They also include the major vessels like the aorta and pulmonary artery.
How can I label the heart’s structures accurately?
To label the heart’s structures right, start with the chambers. Then, follow a step-by-step method. This helps avoid mistakes and deepens your knowledge of the heart.
What are the different perspectives used in labelled heart diagrams?
Labelled heart diagrams show the heart from different angles. You can see the anterior and posterior views, cross-sections, and 3D models. This gives a full view of the heart’s anatomy.
How can I trace blood flow through a labelled heart diagram?
To follow blood flow in a labelled heart diagram, look at the pulmonary and systemic circuits. This shows how blood moves through the heart and its role in the body.
What digital resources are available for interactive heart diagram labeling?
There are online platforms and apps for interactive heart diagram labeling. They offer self-paced learning and chances to practice and reinforce your knowledge of the heart.
What practical exercises can help me master heart anatomy labels?
Practical exercises like blank diagrams and group learning can help you get better at heart anatomy labels. They improve your grasp of the heart’s structure.
How can I improve my understanding of cardiac anatomy?
To get better at cardiac anatomy, use labelled heart diagrams and other learning tools. Practice labelling and take part in interactive learning activities.
References:
- StatPearls. (2023). Anatomy, Thorax, Heart Muscles. In NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK545195/
- TeachMeAnatomy (Fitzgerald, G.). (2024). The chambers of the heart – atria & ventricles. https://teachmeanatomy.info/thorax/organs/heart/atria-ventricles/
- SEER Training Modules. (n.d.). Structure of the Heart. https://training.seer.cancer.gov/anatomy/cardiovascular/heart/structure.html









