Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) is when the coronary arteries get narrowed or blocked. This happens because of fatty deposits called plaque. It’s a big reason for deaths all over the world.
Understand chd disease, its key signs, and if coronary heart disease is curable.
It’s important to know about CHD, its signs, and if it can be cured. At Liv Hospital, we focus on our patients. We use international standards and new ideas to give top-notch healthcare.
CHD is a big health problem worldwide. Knowing about it is the first step to managing it. We’ll look into the medical terms and what doctors think about curing CHD.
Key Takeaways
- Coronary Heart Disease is a leading cause of death globally.
- CHD occurs due to the narrowing or blockage of coronary arteries.
- Understanding CHD’s main signs is key for early detection.
- Liv Hospital offers advanced medical care for CHD patients.
- Knowing the medical term for CHD can help in seeking the right care.
What Is CHD Disease: Definition and Medical Terminology
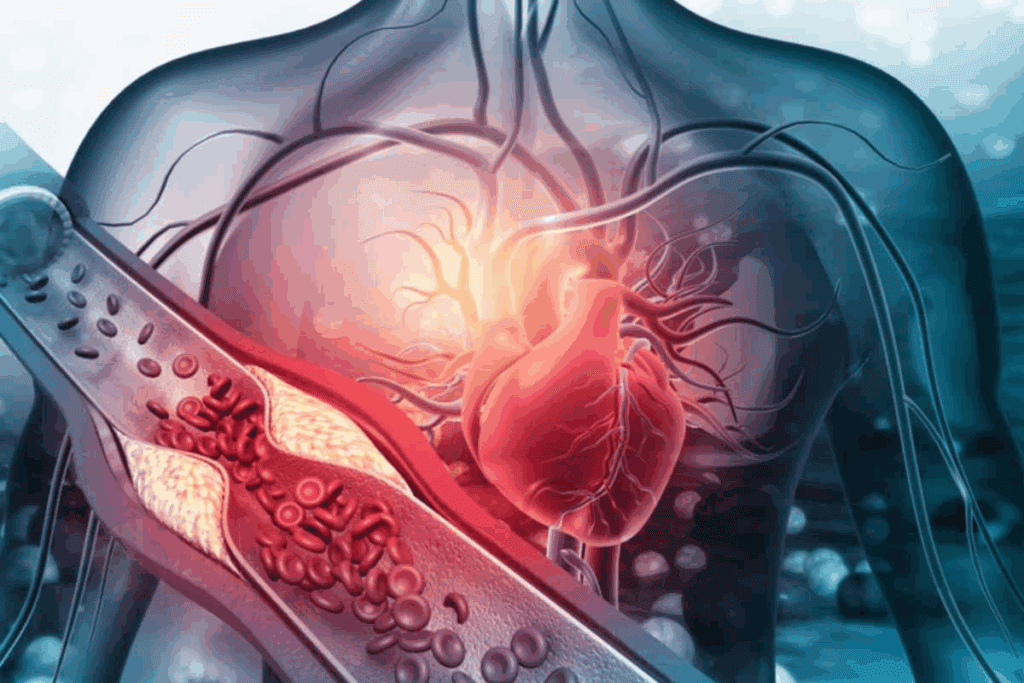
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) affects the heart by narrowing or blocking coronary arteries. These arteries carry blood to the heart muscle. This can cause symptoms and serious health issues.
What Does CHD Stand For in Medical Terms
CHD stands for Coronary Heart Disease in medical terms. It’s also known as Coronary Artery Disease (CAD). CHD means the coronary arteries are narrowed or blocked, reducing blood flow to the heart.
Coronary Heart Disease vs. Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary Heart Disease and Coronary Artery Disease are often confused. CAD refers to the narrowing or blockage of coronary arteries. CHD is the condition caused by this blockage, affecting the heart muscle’s blood flow.
How CHD Affects Heart Function
CHD reduces blood flow to the heart muscle. The heart needs oxygen and nutrients, which come through the coronary arteries. When these arteries are blocked, the heart muscle can suffer, leading to symptoms like chest pain and shortness of breath.
In severe cases, CHD can cause a heart attack. This happens when blood flow to the heart is blocked, damaging or killing heart muscle.
The Pathophysiology of Coronary Heart Disease
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) is caused by a mix of factors, mainly atherosclerosis. To grasp how CHD advances, we must explore its underlying mechanisms.
Atherosclerosis: The Primary Cause
Atherosclerosis is when plaque builds up in artery walls, making them hard and narrow. This is key to CHD’s development. We’ll look at how atherosclerosis impacts coronary arteries and its effects.
Atherosclerosis starts with lipid buildup, inflammation, and smooth muscle cell growth. These steps lead to plaque formation. Plaque can rupture, causing heart attacks.
Plaque Formation in Coronary Arteries
Plaque buildup in coronary arteries is vital in CHD’s path. These arteries supply blood to the heart. Any blockage can cause heart muscle damage. We’ll discuss plaque formation stages and its effects on arteries.
Plaque starts with endothelial dysfunction, then monocyte adhesion and lipid accumulation. Growing plaques can become unstable, leading to rupture and clotting. This often results in heart attacks.
Understanding CHD’s pathophysiology, focusing on atherosclerosis and plaque, is key. It helps in creating effective prevention and treatment plans. By knowing the complex factors in CHD, we can improve patient care.
Signs of Coronary Heart Disease: Recognizing the Symptoms
It’s important to know the signs of coronary heart disease early. This disease can show symptoms that are not always obvious.
Chest Pain (Angina): The Warning Signal
Chest pain, or angina, is a common symptom of CHD. It feels like discomfort in the chest or left side. It can also spread to the arm, neck, or jaw.
Recognizing angina is key. If you feel chest pain, see a doctor, even if it happens during stress or exercise.
Shortness of Breath and Fatigue
People with CHD may also feel short of breath and tired. These feelings can happen even when you’re not doing anything. They can get worse if not treated.
Fatigue makes you feel very tired. It’s because your heart is working too hard. If you’re always tired, you should get checked by a doctor.
Silent CHD: When Symptoms Are Absent
Some people with CHD don’t show any symptoms. This is called silent CHD. They might not know they have it until they have a heart attack.
Heart Attack: A Critical Manifestation of CHD
A heart attack is a serious sign of CHD. It happens when a coronary artery blocks completely. This damages the heart muscle.
Acting quickly during a heart attack is very important. If you think you’re having one, call for emergency help right away.
Risk Factors for Developing CHD Disease
CHD risk factors fall into two groups: modifiable and non-modifiable. Knowing these factors is key to preventing and managing coronary heart disease.
Modifiable Risk Factors
Modifiable risk factors are things we can change. They include lifestyle choices and medical treatments. The main modifiable risk factors for CHD are:
- High Blood Pressure: High blood pressure can harm the coronary arteries, making them more likely to block.
- High Cholesterol: High levels of LDL cholesterol can cause plaque in arteries, raising CHD risk.
- Diabetes: Diabetes increases CHD risk due to its link with high blood pressure, cholesterol, and inflammation.
- Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessel linings, making them more likely to block.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese raises CHD risk due to links with high blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes.
- Lack of Exercise: A sedentary lifestyle increases CHD risk by leading to obesity, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol.
By tackling these modifiable risk factors, we can lower our CHD risk.
Non-Modifiable Risk Factors
Non-modifiable risk factors are things we can’t change. These include:
- Family History: A family history of CHD, even at a young age, raises your risk.
- Age: CHD risk grows with age, with men over 45 and women over 55 at higher risk.
- Gender: Men face higher CHD risk than women, but women’s risk increases after menopause.
While we can’t change non-modifiable risk factors, knowing them helps us focus on modifiable ones.
Diagnosing Coronary Heart Disease: Tests and Procedures for Diagnosing CHD and Determining the Severity of the Disease,urocoronary heart disease curable, can coronary heart disease be cured, chd medical abbreviation
Diagnosing coronary heart disease is a detailed process. It starts with initial checks, then moves to non-invasive tests, and sometimes to invasive procedures. Accurate diagnosis is key to finding the right treatment and managing the disease well.
First, doctors take a detailed medical history and do a physical exam. Healthcare professionals look for risk factors like high blood pressure and high cholesterol. They also check for symptoms like chest pain and shortness of breath.
Non-invasive tests are very important in diagnosing CHD. These include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): This test records the heart’s electrical activity. It helps spot patterns that might suggest CHD.
- Stress Test: This test checks how well the heart works when stressed. It’s done through exercise or medicine.
- Echocardiogram: It uses sound waves to create heart images. This lets doctors check the heart’s structure and function.
Sometimes, doctors need to use invasive tests to see how bad CHD is. These include:
- Coronary Angiography: A dye is injected into the coronary arteries to see if there are blockages or narrowing.
- Cardiac Catheterization: A catheter is put into a blood vessel and guided to the heart. It measures pressures, takes blood samples, or does angiography.
| Diagnostic Test/Procedure | Purpose | Key Findings |
| Electrocardiogram (ECG) | Records heart’s electrical activity | Identifies patterns suggesting CHD |
| Stress Test | Assesses heart function under stress | Reveals ischemia or arrhythmias |
| Echocardiogram | Images the heart’s structure and function | Assesses heart valve function and wall motion |
| Coronary Angiography | Visualizes coronary artery blockages | Identifies narrowing or blockages |
| Cardiac Catheterization | Measures heart pressures and takes blood samples | Provides detailed information on heart function |
By using these tests, doctors can accurately diagnose CHD and figure out how severe it is. This helps them create a good treatment plan. Early and accurate diagnosis is key to managing CHD and improving patient outcomes.
Is Coronary Heart Disease Curable? Current Medical Perspective
To understand if coronary heart disease is curable, we need to look at what doctors say. Coronary heart disease, or CHD, is when the heart’s main blood vessels get damaged. It’s a big reason for sickness and death around the world.
CHD happens when plaque builds up in the arteries, making them narrow or blocked. The question is, can we reverse or manage this process?
“Cure” vs. “Management” in Chronic Cardiovascular Conditions
For chronic diseases like CHD, the idea of a “cure” is tricky. Unlike quick illnesses, chronic ones need ongoing care.
Management means controlling symptoms, slowing the disease, and avoiding serious problems. For CHD, this might include changing your lifestyle, taking medicine, or surgery.
- Lifestyle changes: diet, exercise, smoking cessation
- Medications: statins, beta-blockers, antiplatelet agents
- Surgical procedures: angioplasty, coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)
Reversibility of Atherosclerosis: What Research Shows
Research shows atherosclerosis can slow down, stop, or even reverse with the right lifestyle and medicine.
Studies show big changes in lifestyle, like eating well, exercising, and quitting smoking, can help shrink atherosclerotic plaques.
Long-Term Prognosis for CHD Patients
The future for CHD patients depends on many things, like how bad the disease is, how well they respond to treatment, and if they stick to healthy habits.
With good care, many CHD patients can live full lives. But, it’s key for them to stay in touch with their doctors and keep up with treatment plans.
- Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers
- Adherence to prescribed medications
- Ongoing lifestyle modifications
In summary, while CHD isn’t curable in the usual sense, it can be managed well. By knowing the disease, its risks, and treatment options, patients can live better lives.
Treatment Options for Managing Coronary Artery Disease
Managing coronary artery disease requires different treatments. We will look at various options, from medicines to surgery and new treatments.
Medication-Based Treatments
Medicines are key in treating coronary artery disease. They help reduce symptoms, slow disease growth, and prevent serious problems. Common medicines include:
- Antiplatelet agents to prevent blood clots
- Statins to lower cholesterol levels
- Beta-blockers to reduce heart rate and blood pressure
- ACE inhibitors to relax blood vessels and lower blood pressure
| Medication Class | Primary Use | Examples |
| Antiplatelet Agents | Prevent blood clots | Aspirin, Clopidogrel |
| Statins | Lower cholesterol | Atorvastatin, Simvastatin |
| Beta-blockers | Reduce heart rate and blood pressure | Metoprolol, Atenolol |
Surgical Interventions and Procedures
For some, surgery is needed to improve heart blood flow. Common surgeries include:
- Angioplasty with or without stenting to open narrowed arteries
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) to bypass blocked arteries
These surgeries are suggested when medicines alone can’t manage symptoms or when blockages are severe.
Emerging Therapies and Research Directions
New research into coronary artery disease is promising. Emerging treatments include:
- Gene therapy to address genetic factors contributing to CAD
- Stem cell therapy to repair damaged heart tissue
- Novel anticoagulants with potentially fewer side effects
These new treatments offer hope for better treatments in the future.
Lifestyle Modifications to Control CHD
Managing coronary heart disease (CHD) needs a mix of changes in lifestyle. By making healthier choices, people can control their condition better. This can reduce symptoms and improve their life quality.
Heart-Healthy Diet Recommendations
Eating right is key for CHD management. Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Cut down on saturated fats, trans fats, sodium, and sugars.
The Mediterranean diet is good for the heart. It includes whole grains, fruits, veggies, and healthy fats like olive oil. Lowering sodium is also important to avoid high blood pressure, a big risk for CHD.
| Dietary Component | Recommended Intake | Benefits |
| Fruits and Vegetables | 5 servings a day | Rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants |
| Whole Grains | At least half of total grain intake | High in fiber, vitamins, and minerals |
| Lean Proteins | Variety of sources, including poultry, fish, and legumes | Lower in saturated fats, high in protein |
Exercise and Physical Activity Guidelines
Exercise is vital for managing CHD. Aim for 150 minutes of moderate exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise, each week. Also, do muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days a week.
Exercise helps manage weight, improves heart health, and reduces stress. Choose activities you enjoy and slowly increase their intensity and duration.
Stress Management Techniques
Chronic stress can harm CHD by raising blood pressure and heart rate. Use meditation, deep breathing, yoga, and tai chi to manage stress. Hobbies and time with loved ones can also help.
Smoking Cessation and Alcohol Moderation
Quitting smoking is essential for CHD management. Seek help through counseling, support groups, or nicotine replacement therapy to quit.
Also, drink alcohol in moderation. Limit it to one drink a day for women and two for men to lower heart disease risk.
By making these lifestyle changes, people with CHD can improve their health. It’s important to work with healthcare providers to create a plan that meets your needs and goals.
Living with Coronary Heart Disease: Long-Term Management
Living with CHD means having a long-term plan. This plan includes regular check-ups, rehab programs, and mental health support. It’s a team effort between patients and healthcare providers.
Regular Medical Follow-ups and Monitoring
Regular visits to the doctor are key for CHD management. These visits help doctors adjust treatments as needed. Continuous monitoring catches problems early, improving health outcomes.
Doctors may run tests like ECGs and blood work during these visits. Patient compliance with these tests is critical for managing CHD well.
Cardiac Rehabilitation Programs
Cardiac rehab is essential for CHD management. It helps patients recover from heart attacks and surgeries. Cardiac rehabilitation includes exercise, heart-healthy education, and stress management.
Studies show that rehab improves heart health and quality of life. Each program is customized to meet individual needs, ensuring a focused recovery.
Support Groups and Mental Health Resources
CHD can affect mental health, causing anxiety and depression. Support groups and mental health resources are vital. They offer a space to share experiences and learn from others.
Mental health services, like counseling, help patients deal with emotional challenges. This support improves overall well-being and condition management.
Conclusion: Advances in CHD Prevention and Treatment
Coronary heart disease (CHD) is a complex condition that needs a full approach. New medical tech and ongoing research are making CHD prevention and treatment better.
Understanding CHD’s causes, recognizing its signs, and knowing risk factors are key. A heart-healthy lifestyle, like eating right and staying active, can lower CHD risk a lot.
Today’s treatments, like medicines and surgeries, are showing great promise. New therapies and research are giving us hope for even better results.We must keep researching and finding new ways to prevent and treat CHD. This will help CHD patients live better lives. Advances in CHD treatment are leading to better patient outcomes. And preventing CHD is a big focus for healthcare experts all over the world.
FAQ
What does CHD stand for in medical terms?
CHD stands for Coronary Heart Disease. It’s when the coronary arteries get narrowed or blocked. This affects blood flow to the heart.
What is the difference between coronary heart disease and coronary artery disease?
CHD and CAD are often confused, but CAD is more specific. CAD is about the narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries. CHD is the heart’s response to this.
Is coronary heart disease curable?
CHD is not curable in the traditional sense. But, treatments and lifestyle changes can manage symptoms and slow the disease’s progress. This improves life quality.
What are the main signs of coronary heart disease?
Signs include chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, and fatigue. In severe cases, it can lead to a heart attack. Some people have silent CHD, where symptoms are not obvious.
Can coronary heart disease be cured?
The idea of curing CHD is complex. While treatments can reverse some aspects, managing and controlling the disease is often the main goal.
What are the risk factors for developing CHD?
Risk factors include lifestyle choices like diet, exercise, smoking, and stress. Non-modifiable factors include genetics, age, and family history.
How is coronary heart disease diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a medical history, physical exam, and tests like ECG and stress tests. Invasive procedures like coronary angiography are also used.
What lifestyle modifications can help control CHD?
To control CHD, eat heart-healthy, exercise regularly, manage stress, quit smoking, and drink alcohol in moderation. These steps help manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
What treatment options are available for managing CHD?
Treatments include medications for symptoms and risk factors. Surgical options like CABG and angioplasty are also available. New therapies aim to improve outcomes.
How can individuals live with coronary heart disease?
Living with CHD requires ongoing management. This includes regular doctor visits, cardiac rehab, and mental health support. These steps help maintain overall well-being.
References:
National Health Service (NHS). (2025). What Is CHD Disease What Are Its Main. Retrieved from https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/coronary-heart-disease/


































