Every year, over 1.5 million Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans are done in the United States. They are key in finding and managing many health issues.
PET scans show how active the body’s cells are. This helps us spot problems and plan the best treatments. We do this by giving a tiny bit of radioactive material. This lets us see the body’s inside parts clearly.
PET scans are now a must-have in medical diagnosis. They give us deep insights into how the body works. This helps us give our patients care that’s just right for them.
Key Takeaways
- PET scans are a key tool in medical care.
- Positron Emission Tomography helps see how cells work.
- PET scans help find issues and plan treatments.
- They give us important views of the body’s inside.
- PET scans help make care more personal for patients.
Understanding PET Scan Technology
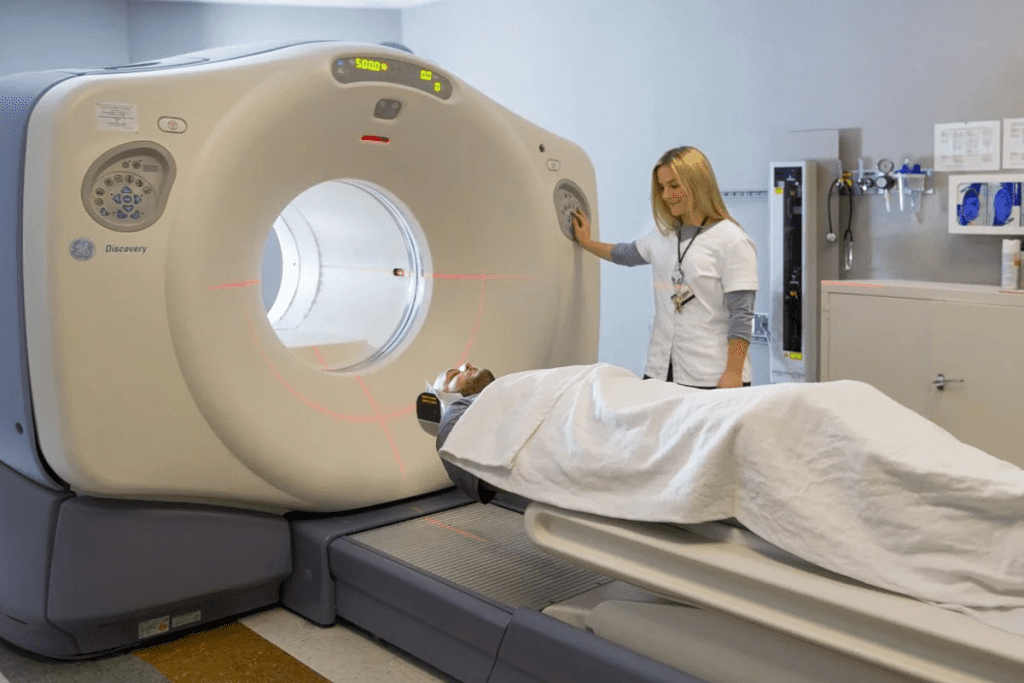
PET scan technology is key in today’s medical world. It gives doctors a peek into how our cells work. This tool helps them see and measure different body functions. It’s a big help in finding and treating many diseases.
The Science Behind Positron Emission Tomography
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) uses special particles to see inside the body. A radioactive tracer is injected, which goes to active areas. When it decays, it sends out gamma rays.
The PET scanner catches these rays. It uses them to make detailed pictures of what’s inside us. This helps doctors understand our body’s inner workings.
How PET Scanners Detect Metabolic Activity
PET scanners find metabolic activity by catching gamma rays. The most used tracer, Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG), goes to areas that use a lot of sugar. This includes growing cancer cells.
By seeing where FDG is, PET scans spot unusual activity. This helps doctors find diseases like cancer, brain problems, and heart issues.
PET scan technology is a big deal in medicine today. It shows how our body’s cells work. Knowing how PET scans work helps doctors take better care of us.
What Does a PET Scan Show?
A PET scan is more than just an image. It’s a detailed map of cellular activity in the body. It shows both normal and abnormal metabolism. This makes PET scans very useful for diagnosing and managing many medical conditions.
Cellular Metabolism Visualization
PET scans show how cells work by using a special tracer called fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG). This tracer builds up in areas where cells are very active. So, we can see how different tissues and organs are working at a cellular level.
The amount of tracer taken up is measured by the Standardized Uptake Value (SUV). Higher SUV values mean more metabolic activity. This is often seen in diseases like cancer.
Differentiating Between Normal and Abnormal Tissue Activity
PET scans are great at telling normal from abnormal tissue activity. Normal tissues have a certain metabolic level. But, tissues with diseases, like cancer, show much more activity.
Physiological Uptake vs. Pathological Findings
It’s important to know the difference between normal and abnormal activity on a PET scan. Normal activity is seen in tissues like the brain and heart. But, abnormal activity is linked to diseases.
| Characteristics | Physiological Uptake | Pathological Findings |
| Metabolic Activity Level | Normal, expected levels | Abnormally high or low levels |
| Distribution | Symmetric, uniform | Asymmetric, focal |
| Clinical Context | Correlates with normal function | Associated with disease or dysfunction |
Knowing the difference between normal and abnormal activity on a PET scan is key. It helps doctors make the right decisions for patient care and treatment.
Common Applications of PET Scans
PET scans are key in modern medicine, used in many areas. They help us understand how the body works and what’s wrong with it. This leads to better diagnoses and treatment plans.
Oncology Applications
In oncology, PET scans are vital for finding and checking cancer. They show how active tumors are and if they’re cancerous. For example, F-FDG PET/CT is used for many cancers like lymphoma and lung cancer.
They’re great for spotting cancer coming back and seeing how treatments work. This info helps doctors change plans to help patients more.
| Cancer Type | PET Scan Application | Benefits |
| Lymphoma | Staging and response assessment | Accurate staging, guides treatment decisions |
| Lung Cancer | Diagnosis, staging, and recurrence detection | Improved diagnostic accuracy, aids in treatment planning |
| Melanoma | Staging and detecting metastasis | Enhances detection of distant metastases, informs treatment choices |
Neurological Applications
In neurology, PET scans help with diagnosing and managing diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. They show how the brain works and help tell diseases apart. This helps us understand how severe a condition is.
F-FDG PET scans can spot where the brain isn’t working right in Alzheimer’s. This helps catch it early and start treatment sooner.
Cardiac Applications
In cardiology, PET scans check how well the heart works. They find out if parts of the heart can work again. This helps decide if surgery is needed and how well it might work.
PET scans are great for checking heart health in people with heart disease. They show how bad the damage is and where it is.
Using PET scans in different areas of medicine helps us care for patients better. It leads to better health outcomes.
PET Scans for Cancer Detection and Staging
PET scans have changed how we diagnose cancer. They give us key info on tumor activity and spread. We use them to see how active tumors are, which helps us understand how far cancer has spread.
How Cancer Appears on PET Scans
Cancer cells use more energy than normal cells, making them show up on PET scans. The tracer used in PET scans builds up more in cancer cells. This makes tumors look like “hot spots” on the scan. It helps us find tumors and see how they’re doing under treatment.
- High metabolic activity: Cancer cells use more glucose, making them visible on PET scans.
- Tumor detection: PET scans can spot tumors that other tests can’t see.
- Monitoring treatment response: We can see how well a tumor is responding to treatment by looking at metabolic activity changes.
Detecting Metastasis and Recurrence
PET scans are key in finding where cancer has spread or come back. This info is vital for planning treatment.
- Identifying metastatic sites: PET scans help find where cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
- Detecting recurrence: PET scans can spot cancer coming back sooner than other tests.
- Guiding treatment decisions: The details from PET scans help us choose the best treatment options.
PET Scan Accuracy in Cancer Diagnosis
PET scans are usually very accurate in cancer diagnosis. But, accuracy can depend on the cancer type and the tracer used. We take these into account when looking at PET scan results to make sure we’re diagnosing and staging correctly.
By using PET scans with other diagnostic tools, we can get even more accurate results. This helps us make better treatment plans. Using PET scans in cancer diagnosis and staging has greatly improved patient care.
PET Scan vs. CT Scan: Key Differences
It’s important to know the differences between PET scans and CT scans. Both are used for medical imaging, but they have different uses and benefits.
Functional vs. Anatomical Imaging
PET scans show how the body’s parts work. They use a special tracer to light up active areas, which can mean different things like cancer. CT scans, on the other hand, give detailed pictures of the body’s inside, like organs and bones.
Radiation Exposure Comparison
Both scans use radiation, but in different ways. PET scans use a tracer that sends out positrons. CT scans use X-rays. The amount of radiation from a PET scan can change based on the tracer and the test. CT scans’ radiation depends on the scanner and what’s being looked at.
When Each Scan Type is Preferred
Choosing between a PET scan and a CT scan depends on what you’re looking for. PET scans are best for checking how active certain areas are, like in cancer. CT scans are better for seeing detailed pictures of injuries or structural issues.
| Characteristics | PET Scan | CT Scan |
| Imaging Type | Functional | Anatomical |
| Primary Use | Cancer diagnosis, neurological disorders | Trauma, structural abnormalities |
| Radiation Type | Positron emission | X-rays |
Knowing these differences helps patients and doctors choose the right test for each situation.
The PET-CT Combination: Enhanced Diagnostic Power
PET and CT scans together, known as PET-CT, have changed how we diagnose diseases. This mix of scans gives a clearer picture of what’s going on inside the body. It helps doctors make more accurate diagnoses and care for patients better.
Benefits of Hybrid Imaging
Using PET-CT scans has many advantages. It boosts diagnostic confidence and accurate disease staging. By merging PET’s functional data with CT’s detailed images, doctors can see the full picture of a patient’s health.
Clinical Applications of PET-CT
PET-CT is key in oncology for cancer staging, tracking treatment, and spotting disease return. It’s also useful in neurological and cardiac fields. It aids in diagnosing and managing conditions like Alzheimer’s and heart disease.
Improved Diagnostic Accuracy
PET-CT scans combine functional and anatomical data. This combo helps doctors make better decisions. It leads to better patient care and more effective treatments.
In summary, PET-CT is a big leap in medical imaging. It brings together the strengths of PET and CT scans. This results in better diagnosis and care for patients.
Preparing for a PET Scan
Getting ready for a PET scan involves several steps. These steps help make the process smooth and successful. We know that having a PET scan can feel daunting. But being well-prepared can really help.
Dietary Restrictions and Fasting Requirements
Following dietary restrictions and fasting guidelines is key. Usually, patients fast for 4-6 hours before the scan. But, this can change based on what your healthcare provider or the imaging center tells you. It’s also good to avoid sugary foods and drinks for 24 hours before.
Always follow the specific dietary instructions given to you. They are made just for you and the type of PET scan you’re having.
Medication Considerations
Telling your healthcare provider about all your medications is important. Some medications might need to be adjusted or stopped before the scan. Your healthcare provider will help you figure out how to manage your medications before your PET scan.
What to Wear and Bring
On the day of your PET scan, wear comfortable, loose clothes without metal parts. You might need to change into a hospital gown. It’s a good idea to bring your medical records, insurance info, and a list of your medications too.
By following these tips, you can help make sure your PET scan goes well. If you have any questions or worries, don’t hesitate to ask your healthcare provider or the imaging center for help.
The PET Scan Procedure: What to Expect
PET scans are a diagnostic tool that gives insights into the body’s metabolic processes. What can patients expect during the scan? We’ll explain the PET scan procedure, the key steps, and how to make the experience smooth.
Radiotracer Administration
The first step is the administration of a radiotracer. This is done through an intravenous (IV) line in your arm. The radiotracer, usually FDG (fluorodeoxyglucose), is a small amount of radioactive glucose. It accumulates in areas of high metabolic activity.
We use this tracer to visualize the metabolic processes in your body.
The Scanning Process
After the radiotracer is administered, you’ll wait for about 60 minutes. During this time, you’ll be asked to remain as quiet and as motionless as possible. This ensures optimal uptake of the tracer.
Once the waiting period is over, you’ll be positioned on a scanning table. This table slides into the PET scanner. The scanning process itself takes between 30 to 60 minutes, during which you’ll need to remain as motionless as possible.
Duration and Comfort Considerations
The entire PET scan procedure, from preparation to the completion of the scan, can take several hours. The actual scanning time is generally between 30 to 60 minutes. To ensure your comfort, we recommend wearing loose, comfortable clothing and avoiding any metal objects.
It’s also a good idea to use the restroom before the scan. This minimizes discomfort during the procedure.
| Procedure Step | Duration | Comfort Tips |
| Radiotracer Administration | 5-10 minutes | Relax your arm, minimize movement |
| Waiting Period | About 60 minutes | Stay as quiet and relaxed as possible |
| Scanning Process | 30-60 minutes | Remain as motionless as possible, breathe normally |
Understanding PET Scan Images and Results
PET scan images can seem complex, but they’re easier to understand when broken down. These images show how active our body’s cells are. This is key for spotting and treating health issues.
How to Read PET Scan Images
PET scan images show up in shades of gray. Bright spots mean high activity, like inflammation or cancer. It’s important to look at these images with other health info to get a clear picture.
SUV Values and Their Meaning
The Standardized Uptake Value (SUV) shows how much a tracer is taken up by tissues. High SUV values might mean cancer. But, it’s just one clue in figuring out what’s going on.
| SUV Value Range | Interpretation |
| 0-2.5 | Typically considered normal |
| 2.5-4.0 | May indicate benign or malignant conditions |
| >4.0 | Often associated with malignant tissues |
Timeframe for Receiving Results
How long it takes to get PET scan results varies. It’s usually a few days to a week. Your doctor will talk about the results with you, explaining what they mean and what’s next.
Knowing about PET scan images and results helps us take charge of our health. By understanding how these images are read and what SUV values mean, we can better follow our health journey.
Radiation Exposure and Safety Concerns
It’s important to know about PET scan safety if you’re getting one. PET scans use small amounts of radioactive tracers. They help diagnose and monitor health conditions.
Radiation Levels in PET Scans
PET scans have low radiation levels. But, the amount can change based on the procedure and the radiotracer dose. Usually, the dose is between 4 to 7 millisieverts (mSv). This is similar to or a bit more than a CT scan of the same area.
How Long Are You Radioactive After a PET Scan?
The tracer in PET scans has a short half-life. It decays quickly, becoming less radioactive. Usually, it’s much less radioactive within a few hours. Drinking lots of water helps get rid of it faster.
Safety Precautions After the Procedure
To keep others safe, follow some guidelines after a PET scan. These include:
- Keeping a distance from others for a few hours
- Drinking plenty of water to get rid of the tracer
- Staying away from pregnant women and kids for at least 24 hours
By following these steps, you can reduce radiation exposure. This keeps you and those around you safe.
Side Effects and Risks of PET Scans
PET scans are a valuable tool for doctors, but they come with risks and side effects. It’s important to know that the benefits often outweigh the risks for many patients.
We will look at common side effects, allergic reactions to radiotracers, and long-term risks. This will give you a full picture.
Common Side Effects
Most people who get a PET scan don’t have many side effects. But some might feel:
- Mild discomfort or pain at the injection site
- Nausea or dizziness
- Headache
These effects usually go away quickly. But in rare cases, more serious reactions can happen. We’ll talk about those next.
Allergic Reactions to Radiotracers
Allergic reactions to PET scan radiotracers are rare but serious. Symptoms include:
- Hives or itching
- Swelling of the face, lips, or throat
- Difficulty breathing
If you have these symptoms, get medical help right away. Always tell your doctor about any allergies before a PET scan.
Long-term Risk Considerations
The main long-term risk of PET scans is radiation exposure. While the risk is low, it’s something to think about, mainly for those needing many scans.
| Risk Factor | Description | Mitigation Strategy |
| Radiation Exposure | Potential long-term risk of radiation-induced harm | Careful planning of scan protocols, minimizing dose when possible |
| Allergic Reactions | Rare but potentially severe reactions to radiotracers | Pre-scan assessment for allergies, preparedness for emergency responses |
It’s key to understand the risks and benefits of PET scans. Talk to your doctor about any worries you have before getting a PET scan.
“The key to minimizing risks associated with PET scans lies in careful patient selection, proper scan protocol, and thorough patient education.”
” Expert Opinion
Advantages and Limitations of PET Scans
PET scans are a key tool in medical diagnostics. They show how the body works, helping doctors make better treatment plans. But, like any tool, they have their good and bad sides.
Clinical Benefits
PET scans have many clinical benefits. They can spot diseases early, even before symptoms show. This early catch can lead to better treatment results.
They also check if treatments are working. This lets doctors make changes to the treatment plan as needed.
- Early disease detection
- Assessment of treatment effectiveness
- Guiding treatment decisions
Diagnostic Accuracy
PET scans are very accurate in diagnosing. They show where the body’s metabolism is off, helping tell if something is cancer or not. This is key in fighting cancer, helping doctors know how far it has spread.
Diagnostic accuracy gets even better when PET scans are paired with CT scans. Together, they give a clearer view of what’s going on inside the body.
Conclusion
PET scans are key in modern medicine, giving us a peek into how our bodies work. They help us understand the body’s metabolic activity. This makes them a vital tool in healthcare.
In fields like oncology, neurology, and cardiology, PET scans are very helpful. They help doctors find and treat diseases better. When used with CT scans, they make diagnosis even more accurate.
PET scans are essential in advanced medical care. They give doctors the information they need to make better treatment plans. As medical technology gets better, PET scans will likely play an even bigger role in healthcare.
For patients looking for top-notch medical care, knowing about PET scans is important. It helps them make informed choices about their health.
FAQ
What is a PET scan?
A PET (Positron Emission Tomography) scan is a medical test. It uses a radioactive tracer to see how the body works. This helps doctors find and track health issues like cancer and heart problems.
How does a PET scan work?
A PET scan injects a tiny amount of radioactive tracer into the body. This tracer goes to active areas. The PET scanner then picks up these signals, making detailed images of the body’s inner workings.
What does a PET scan show?
A PET scan shows where the body is most active. It helps spot problems like cancer cells. It also tells normal from diseased tissue.
What is the difference between a PET scan and a CT scan?
A PET scan looks at how the body works, while a CT scan shows what’s inside. They’re often used together. This gives a full picture of what’s happening inside the body.
How long does a PET take?
A PET scan’s time varies. It depends on the scan type and area being checked. But, it usually takes 30-60 minutes.
Are there any side effects from a PET scan?
Side effects from PET scans are usually mild. You might feel a bit uncomfortable where the tracer was injected. Or, you might get tired. But serious side effects are rare.
How long are you radioactive after a PET scan?
After a PET scan, you’re usually not radioactive for long. Most people stop being radioactive a few hours later.
Can PET scans detect cancer?
Yes, PET scans are great for finding and checking cancer. They spot cancer cells by showing where the body is most active.
How accurate are PET scans in cancer diagnosis?
PET scans are very accurate for cancer detection. They work best when used with other tests like CT scans.
Is a PET scan painful?
No, PET scans are not painful. You might feel a bit uncomfortable when the tracer is injected. Or, when you’re lying down during the scan.
Can I eat before a PET scan?
Dietary rules for PET scans differ. Some scans need you to fast or follow a special diet. Your doctor will tell you what to do.
How do I prepare for a PET scan?
To get ready for a PET scan, follow your doctor’s instructions. This might mean not eating, fasting, or avoiding certain medicines. Wear comfy clothes and arrive early to fill out any paperwork.




































