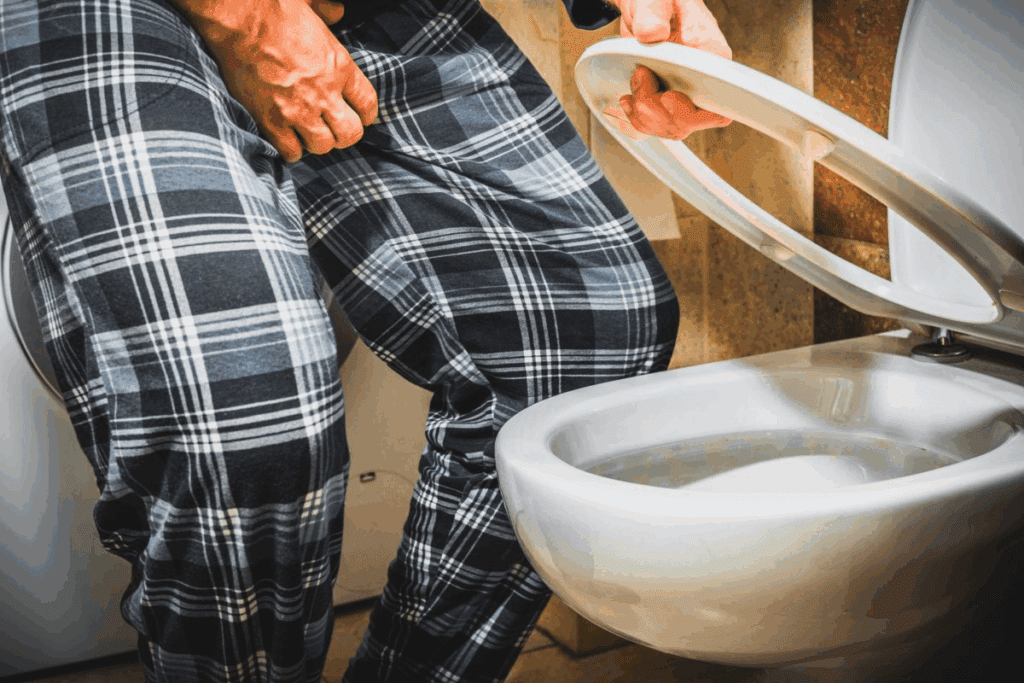
At Liv Hospital, we combine expert medical protocols with compassionate care to offer advanced treatments for bladder cancer. One such treatment is intravesical therapy. It involves introducing chemotherapy drugs directly into the bladder through a catheter.
Intravesical therapy is great for patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. It helps treat tumors that are hard to remove. By delivering medication directly to the bladder, this treatment targets cancer cells well while keeping side effects low.
We use intravesical instillation to give our patients the best care. We focus on their comfort and quality of life. This way, we offer top-notch healthcare with full support for international patients.
Learn how bladder chemo wash is used effectively for intravesical therapy in bladder cancer treatment.
Key Takeaways
- Intravesical therapy is a targeted treatment for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
- Chemotherapy drugs are introduced directly into the bladder through a catheter.
- This approach helps to minimize side effects while effectively targeting cancer cells.
- Liv Hospital provides complete care, focusing on patient comfort and quality outcomes.
- Intravesical instillation is a key part of our treatment protocol.
Understanding Intravesical Therapy for Bladder Cancer
Intravesical therapy is a treatment for bladder cancer. It involves putting medicine directly into the bladder through a catheter. This method works well for early-stage bladder cancers that only affect the bladder’s lining.
Definition and Basic Principles
Intravesical therapy uses a catheter to put medicine into the bladder. This way, the medicine can reach the cancer cells in the bladder lining. It avoids exposing the rest of the body to the drug.
The goal of intravesical therapy is to target cancer cells directly. This approach helps avoid side effects in other parts of the body. It makes the treatment more effective.
How Intravesical Therapy Targets Cancer Cells
Intravesical therapy delivers drugs right to the bladder tumor. The medicine stays in the bladder for a while before being flushed out. This method ensures the cancer cells get the treatment they need.
Benefits of Localized Treatment Approach
Intravesical therapy has many advantages. It has fewer side effects compared to other treatments. This is because the medicine only goes to the bladder. It doesn’t affect other parts of the body.
| Benefits | Description |
| Reduced Systemic Side Effects | Minimizes exposure of other body parts to the medication |
| Targeted Treatment | Delivers therapeutic agents directly to the cancer cells |
| Enhanced Efficacy | Maximizes the concentration of therapeutic agents at the tumor site |
The Bladder Chemo Wash Procedure Explained
Bladder chemo wash is a treatment that puts chemotherapy directly into the bladder to fight cancer cells. It’s a key part of treating bladder cancer with intravesical therapy.
What Exactly Is a Bladder Chemo Wash
A bladder chemo wash uses a catheter to put chemotherapy medicine into the bladder. This method lets the medicine reach the bladder lining, where cancer cells are found. The solution stays in the bladder for 1 to 2 hours to work on the cancer cells before being flushed out.
How the Medication Reaches Cancer Cells
The medicine in the bladder chemo wash targets and kills cancer cells on the bladder lining. After being put in, the solution touches the bladder’s inside, hitting the cancer cells right where they are. This way, the treatment works better because it’s exactly where it’s needed.
“Intravesical chemotherapy has been shown to be effective in treating bladder cancer by directly targeting the cancer cells within the bladder.”
Medical Expert, Oncologist
Duration and Frequency of Treatment Sessions
Chemotherapy treatment usually happens at a cancer day clinic. How often and for how long you’ll have treatment varies. Usually, you’ll have sessions once a week for a few weeks, then less often for maintenance.
| Treatment Phase | Frequency | Duration |
| Induction Phase | Once a week | 6 weeks |
| Maintenance Phase | Once a month | 6-12 months |
Knowing about the bladder chemo wash procedure and what to expect can ease worries. It helps patients get ready for their treatment journey.
Types of Medications Used in Intravesical Therapy
Intravesical therapy is a treatment that puts medications directly into the bladder. It fights bladder cancer by targeting cancer cells. This method helps avoid side effects that happen when drugs are taken by mouth.
Chemotherapeutic Agents
Chemotherapeutic agents are key in treating bladder cancer with intravesical therapy. Mitomycin C and Epirubicin are two main drugs used. They kill cancer cells or stop them from growing.
- Mitomycin C: This is a top choice for intravesical chemotherapy. It stops DNA from making copies, which stops cells from dividing.
- Epirubicin: This drug also stops cells from dividing by getting in the way of DNA. This leads to cell death.
Gemcitabine Bladder Instillation
Gemcitabine is another drug used in intravesical therapy. It’s a special kind of medicine that stops DNA from making copies. This leads to cell death. It’s good for treating bladder cancer when other treatments don’t work.
Comparing Effectiveness of Different Agents
How well different agents work in intravesical therapy depends on several things. These include the cancer’s stage and grade, and the patient’s health. Research has looked at how well mitomycin C, epirubicin, and gemcitabine work.
| Agent | Mechanism of Action | Common Side Effects |
| Mitomycin C | Cross-links DNA strands | Bladder irritation, hematuria |
| Epirubicin | Intercalates DNA strands | Bladder irritation, frequency |
| Gemcitabine | Inhibits DNA synthesis | Minimal systemic side effects |
Knowing about the different medications in intravesical therapy helps doctors make better treatment plans. This way, they can help patients with bladder cancer get the best results.
BCG Instillation: The Immunotherapy Approach
BCG instillation is a common treatment for early-stage bladder cancer. It uses a vaccine made from a germ related to tuberculosis. This method is key in treating non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
How BCG Works Against Bladder Cancer
BCG boosts the body’s immune system to fight bladder cancer cells. It’s put into the bladder through a catheter. This approach mainly affects the bladder, reducing side effects.
The BCG bacteria stick to the bladder wall, triggering an immune response. This response attacks the bacteria and cancer cells. Over time, it can clear out cancer cells, lowering the chance of it coming back.
BCG Treatment Protocol and Schedule
The BCG treatment starts with an induction phase and then maintenance therapy. In the induction phase, BCG is given once a week for six weeks. After that, there’s a maintenance schedule that may last one to three years.
The exact schedule depends on how well the patient responds. Regular check-ups and exams are key to track the treatment’s success and make any needed changes.
Differences Between BCG and Chemotherapy Instillation
BCG and chemotherapy instillations treat bladder cancer but in different ways. Chemotherapy directly kills cancer cells. BCG, on the other hand, boosts the immune system to fight cancer.
| Treatment Aspect | BCG Instillation | Chemotherapy Instillation |
| Mechanism of Action | Stimulates immune response | Directly kills cancer cells |
| Treatment Duration | Induction phase plus maintenance | Typically shorter duration |
| Side Effects | Can include bladder irritation, flu-like symptoms | May cause local irritation, systemic side effects depending on the drug |
It’s important to know the differences between BCG and chemotherapy. Our healthcare team helps patients choose the best treatment for their needs.
Preparing for Your Intravesical Treatment
Getting ready for your intravesical treatment is key to its success. This treatment targets bladder cancer directly. It’s important to prepare well to get the best results.
Pre-Treatment Instructions
Stop drinking fluids a few hours before treatment. This helps the medicine work better in your bladder.
Also, have blood tests before starting treatment. These tests check if it’s safe for you to begin.
Dietary and Fluid Recommendations
Eating well and drinking water are important during treatment. But, drink less before your treatment.
Talk to your doctor about any diet concerns. They can give advice based on your health.
Medication Adjustments Before Treatment
Tell your doctor about all your medicines. Some might need to be changed or stopped before treatment.
- List your medications, including dosages and frequencies.
- Discuss possible interactions with your treatment.
- Follow your doctor’s advice on medication changes.
What to Bring to Your Appointment
Bring things to make your treatment comfortable:
- Comfortable clothes.
- A book or something to relax with.
- Paperwork and insurance info.
- A list of your medicines and dosages.
Being well-prepared helps your treatment work better. It also makes you more comfortable.
Step-by-Step Guide to the Intravesical Procedure
The intravesical procedure is key in treating bladder cancer. Knowing what to expect can help a lot. We’ll walk you through from the first meeting to the time you need to stay in a certain position. This will help you feel more ready and confident.
Initial Consultation and Assessment
First, you’ll meet with your doctor to check your health and decide on treatment. This meeting is important to find out if you’re right for the procedure. It helps spot any risks or problems.
Your doctor will look at your medical history and talk about the treatment. They’ll also answer your questions. It’s important to tell them about any medicines you’re taking and any allergies you have.
The Catheterization Process
The next step is the catheterization process. A catheter is put through the urethra to get the treatment solution into the bladder. A trained healthcare professional does this.
Administration of the Treatment Solution
With the catheter in place, the treatment solution is given. This solution has chemotherapy that goes straight to the cancer cells in your bladder.
Retention Period and Patient Positioning
After the solution is in, you’ll need to keep it in your bladder for 1-2 hours. You’ll be told how to sit or stand to help the medicine spread evenly.
The table below shows how to position yourself during this time:
| Position | Duration | Purpose |
| Lying on back | 15 minutes | Allows medication to reach the bladder walls |
| Turning to the right side | 15 minutes | Ensures medication reaches the right bladder wall |
| Turning to the left side | 15 minutes | Ensures medication reaches the left bladder wall |
| Standing or walking | Remaining time | Helps distribute the medication throughout the bladder |
By following these tips, you can make sure the treatment works well and reduce side effects.
Managing Side Effects of Intravesical Therapy
Understanding and managing side effects of intravesical therapy can greatly improve patient outcomes. This therapy, including chemotherapy and BCG, is key for treating bladder cancer. Yet, these treatments can lead to side effects, ranging from mild to severe.
Common Side Effects of Chemotherapy Instillation
Chemotherapy instillation, like gemcitabine, can cause several side effects. These include bladder irritation, leading to discomfort or pain while urinating, and blood in the urine. These issues are usually manageable and may lessen once treatment ends.
| Side Effect | Frequency | Management Strategy |
| Bladder Irritation | Common | Hydration, pain management medication |
| Blood in Urine | Common | Monitoring, hydration |
| Urinary Tract Infection | Less Common | Antibiotics, medical attention if symptoms persist |
BCG Side Effects and Management
BCG (Bacillus Calmette-Guérin) is used to treat bladder cancer through immunotherapy. It’s usually well-tolerated but can cause side effects. These include flu-like symptoms, bladder irritation, and, less often, severe infections. Managing these side effects often involves medication and lifestyle changes.
Strategies for Minimizing Discomfort
To reduce discomfort from intravesical therapy, patients can take several steps:
- Stay hydrated to help flush out the bladder
- Use pain management medication as directed by a healthcare provider
- Monitor for signs of infection or severe side effects
Talking to your healthcare provider about any concerns or side effects is also beneficial. This can help adjust your treatment plan as needed.
When to Contact Your Healthcare Provider
While many side effects can be managed at home, there are times to contact your healthcare provider. Severe side effects, signs of infection, or persistent discomfort are reasons to seek medical attention. Quick communication with healthcare providers can prevent more serious complications.
Post-Treatment Care and Recovery
After your intravesical therapy, it’s important to take care of yourself. Dealing with bladder cancer and its treatment can be tough. We’re here to help you with the steps to care for yourself after treatment.
Immediate Post-Procedure Instructions
After the treatment, you’ll be watched for a bit before going home. Here’s what we suggest:
- Rest for the rest of the day
- Avoid hard activities
- Follow any instructions from your healthcare team
Hydration and Voiding Guidelines
Staying hydrated is key after treatment. Drinking lots of water, about 2-3 liters, helps clear your system. This can lower the risk of problems and aid in healing.
When you pee, you might feel some discomfort or burning. This is usually short-lived and should go away in a few days. If it doesn’t, call your healthcare provider.
Activity Restrictions After Treatment
To help you recover well, avoid certain activities for a while:
- Avoid heavy lifting and bending
- Don’t do strenuous exercise or have sex for a few days
- Make sure to rest often
Infection Prevention Measures
To lower the chance of infection, do the following:
- Keep good hygiene
- Watch your urine for signs of infection, like blood or odd smell
- Tell your healthcare provider if you notice any infection symptoms
By following these tips, you can help your recovery and avoid complications. If you have any worries or questions, don’t hesitate to contact your healthcare team. We’re here to support you every step of the way.
Treatment Schedules and Long-term Management
It’s important for patients with bladder cancer to know about treatment schedules and long-term management. The plan is made just for them, based on their cancer’s risk level.
Induction vs. Maintenance Therapy
Intravesical therapy has two parts: induction and maintenance. Induction therapy is the first step, given weekly for about 6 weeks. It tries to get rid of cancer cells in the bladder.
Maintenance therapy comes after induction. It helps stop cancer from coming back. How often and for how long depends on the patient’s risk level. For those at intermediate risk, it’s less often for a year. For high-risk, it can last up to 3 years.
| Risk Category | Induction Therapy Schedule | Maintenance Therapy Schedule |
| Intermediate-Risk | Weekly for 6 weeks | Less frequent over 1 year |
| High-Risk | Weekly for 6 weeks | Less frequent over up to 3 years |
Monitoring Treatment Response
It’s key to watch how well the treatment is working. Regular cystoscopies help check for cancer coming back.
“Regular follow-up is essential to ensure the treatment’s effectiveness and to make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.”
Expert Opinion
Follow-up Cystoscopy Schedule
The timing of follow-up cystoscopies changes based on the patient’s risk and how they’re doing. They’re done more often in the first few years and less after that.
Adjusting Treatment Based on Response
The treatment plan changes if the patient’s response isn’t good. If cancer comes back or doesn’t respond, other treatments might be tried.
We know intravesical therapy is tough, but we’re here to support our patients. By watching how they do and adjusting the plan, we aim to get the best results for them.
Conclusion: Optimizing Your Intravesical Therapy Experience
Intravesical therapy is a targeted way to manage bladder cancer. To get the most out of it, you need to know about the treatment options. This includes the types of medications and possible side effects.
Talking to your healthcare provider about your treatment is key. They can help choose the best option for you. Knowing the treatment duration and side effects to watch for is also important.
Working with your healthcare team and following their plan can improve your therapy’s success. This teamwork helps you understand and make decisions about your care. It’s all about getting the best results from your bladder cancer treatment.
FAQ
What is intravesical therapy for bladder cancer?
Intravesical therapy is a treatment for bladder cancer. It involves putting medication directly into the bladder through a catheter. This method targets cancer cells in the bladder lining without harming other parts of the body.
How does intravesical chemotherapy work?
Intravesical chemotherapy kills cancer cells in the bladder. Chemotherapy drugs like mitomycin C and epirubicin are used. This treatment aims to kill cancer cells in the bladder lining while reducing side effects elsewhere in the body.
What is a bladder chemo wash?
A bladder chemo wash is a procedure where chemotherapy is put into the bladder. It uses a catheter to deliver the medication. The treatment stays in the bladder for a while before being flushed out, helping to kill cancer cells.
What are the benefits of intravesical therapy?
Intravesical therapy has many benefits. It targets bladder cancer cells directly, reducing side effects compared to other treatments. It also helps keep the bladder working well. It’s most effective for early-stage bladder cancer.
What types of medications are used in intravesical therapy?
Intravesical therapy uses different medications. Chemotherapy drugs like mitomycin C, epirubicin, and gemcitabine are common. BCG (Bacillus Calmette-Guérin) is also used. It works as an immunotherapy to boost the immune system against cancer.
How is BCG instillation different from chemotherapy instillation?
BCG instillation boosts the immune system to fight cancer. Chemotherapy instillation directly kills cancer cells. BCG is often used for high-risk bladder cancer.
What should I expect during the intravesical procedure?
During the procedure, a catheter is used to put the treatment into the bladder. The treatment stays in the bladder for about an hour before being flushed out. You might be asked to change positions to make sure the treatment covers all areas of the bladder.
How can I manage side effects of intravesical therapy?
Side effects include bladder irritation and needing to urinate often. To feel better, drink lots of water and avoid things that irritate the bladder. If side effects get worse, talk to your doctor.
What are the post-treatment care instructions after intravesical therapy?
After treatment, drink plenty of water and follow your doctor’s instructions for urinating. You might need to rest and avoid certain activities. It’s also important to prevent infections and keep up with follow-up appointments.
How often will I need to undergo intravesical therapy?
How often you need treatment depends on your specific situation. Your doctor will decide based on the type of medication, the cancer’s stage and grade, and how you respond. You’ll get a treatment plan that might include different phases.
Can intravesical therapy be used for all stages of bladder cancer?
Intravesical therapy is mainly for early-stage bladder cancer. For more advanced stages, other treatments might be needed. Your doctor will choose the best treatment for you based on your condition.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2025). How to Use Bladder Chemo Wash for Effective.




































